Apologia Biology 2nd Edition Module 7
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Genetics
The science that studies how characteristics get passed from parent to offspring.

Genetic Factors
The general guideline of traits determined by a person's DNA.

Environmental Factors
Those "nonbiological" factors that are involved in a person's surroundings such as the nature of the person's parents, the person's friends, and the person's behavioral choices

Spiritual Factors
The factors in a person's life that are determined by the quality of his or her relationship with God.

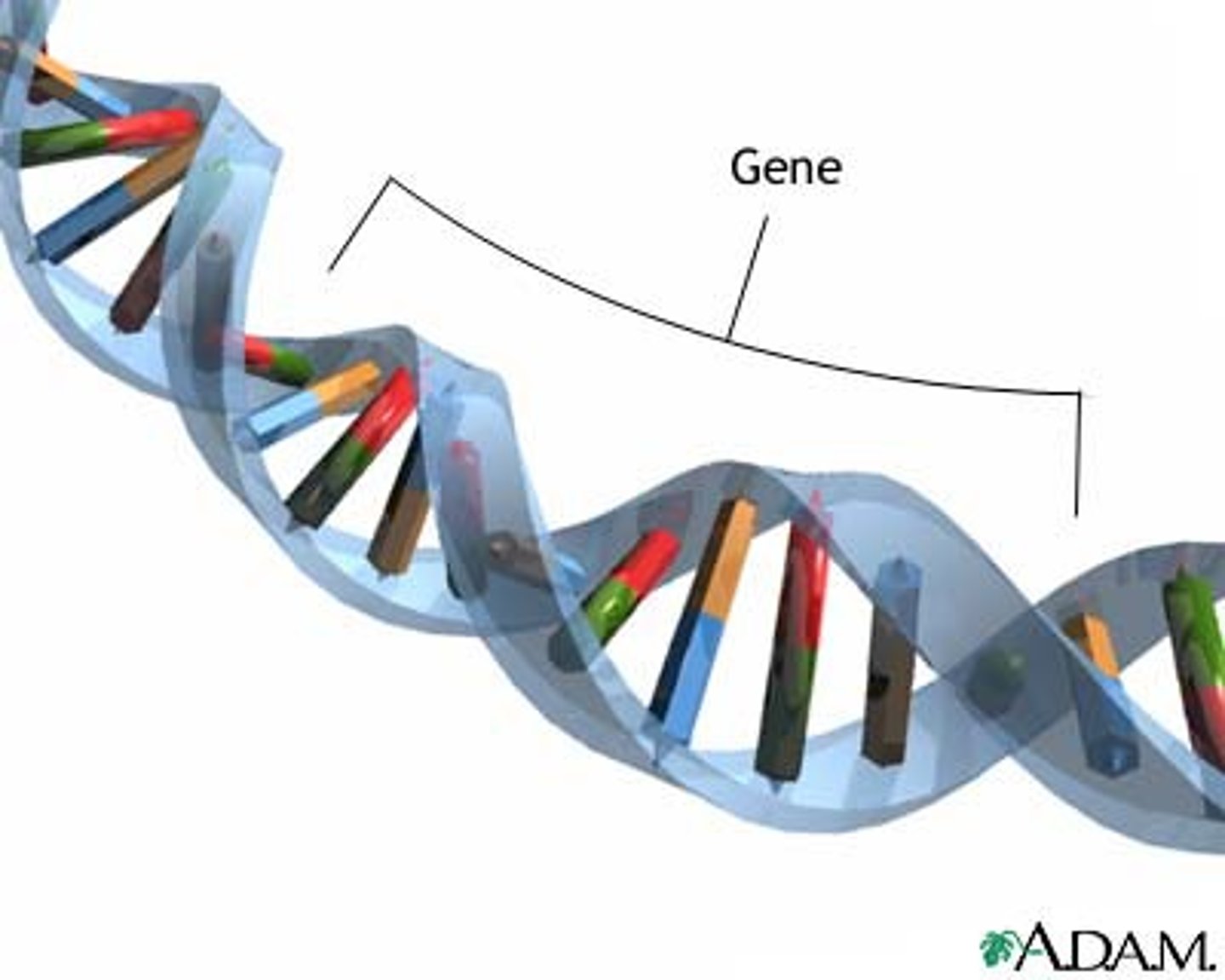
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for the production of a protein or a portion of a protein, thereby causing a trait.
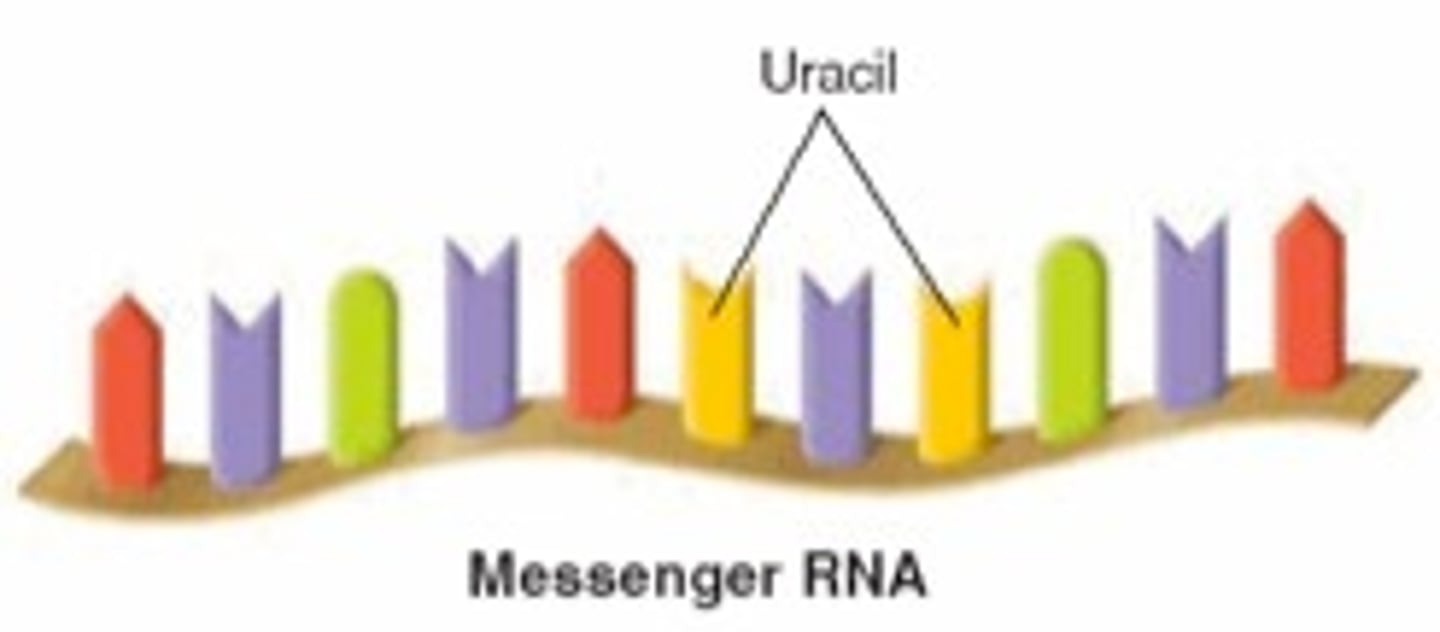
Messenger RNA
The RNA that performs transcription
Anticodon
A three-nucleotide base sequence on RNA

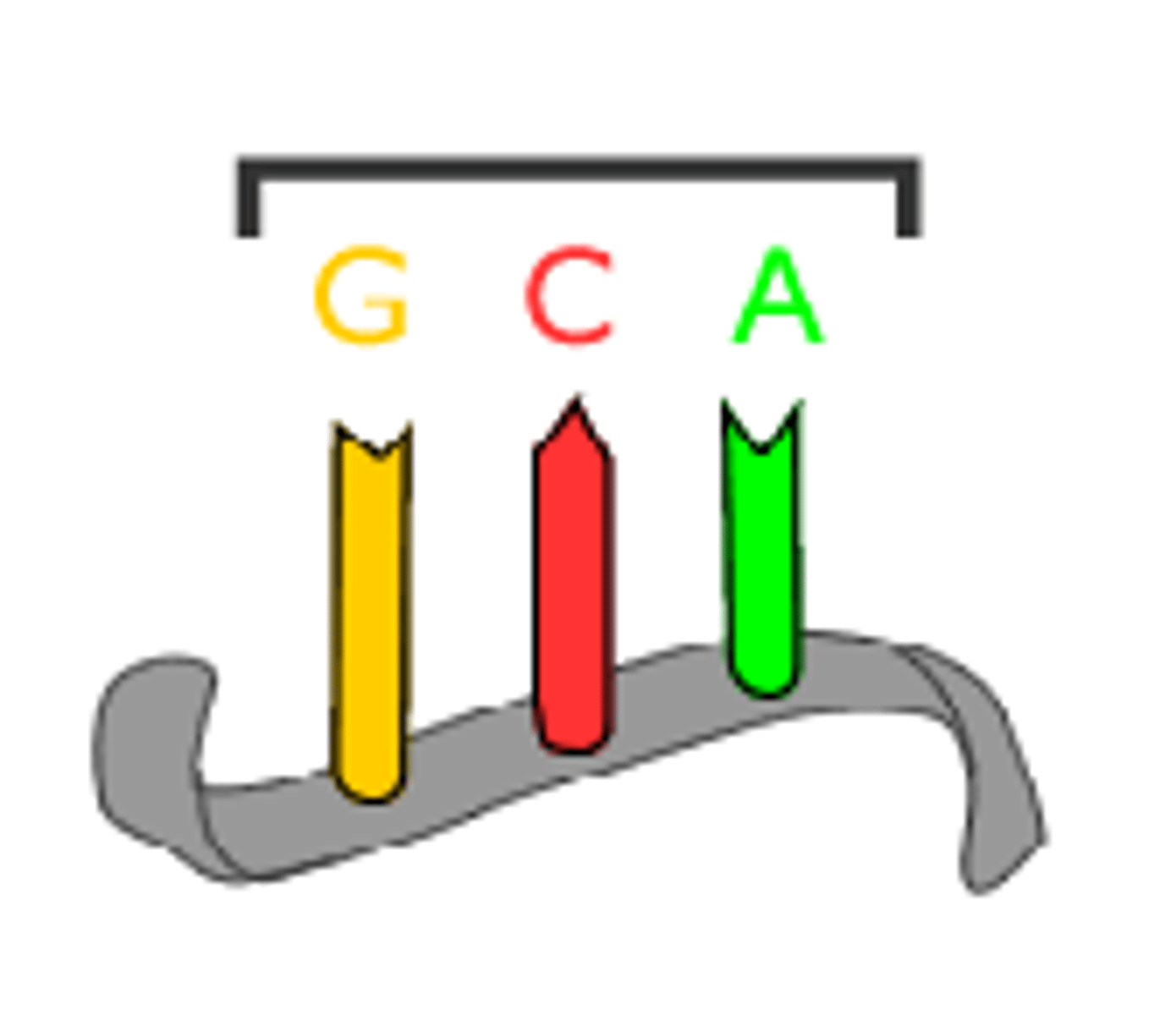
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotide bases on mRNA that refers to a specific amino acid
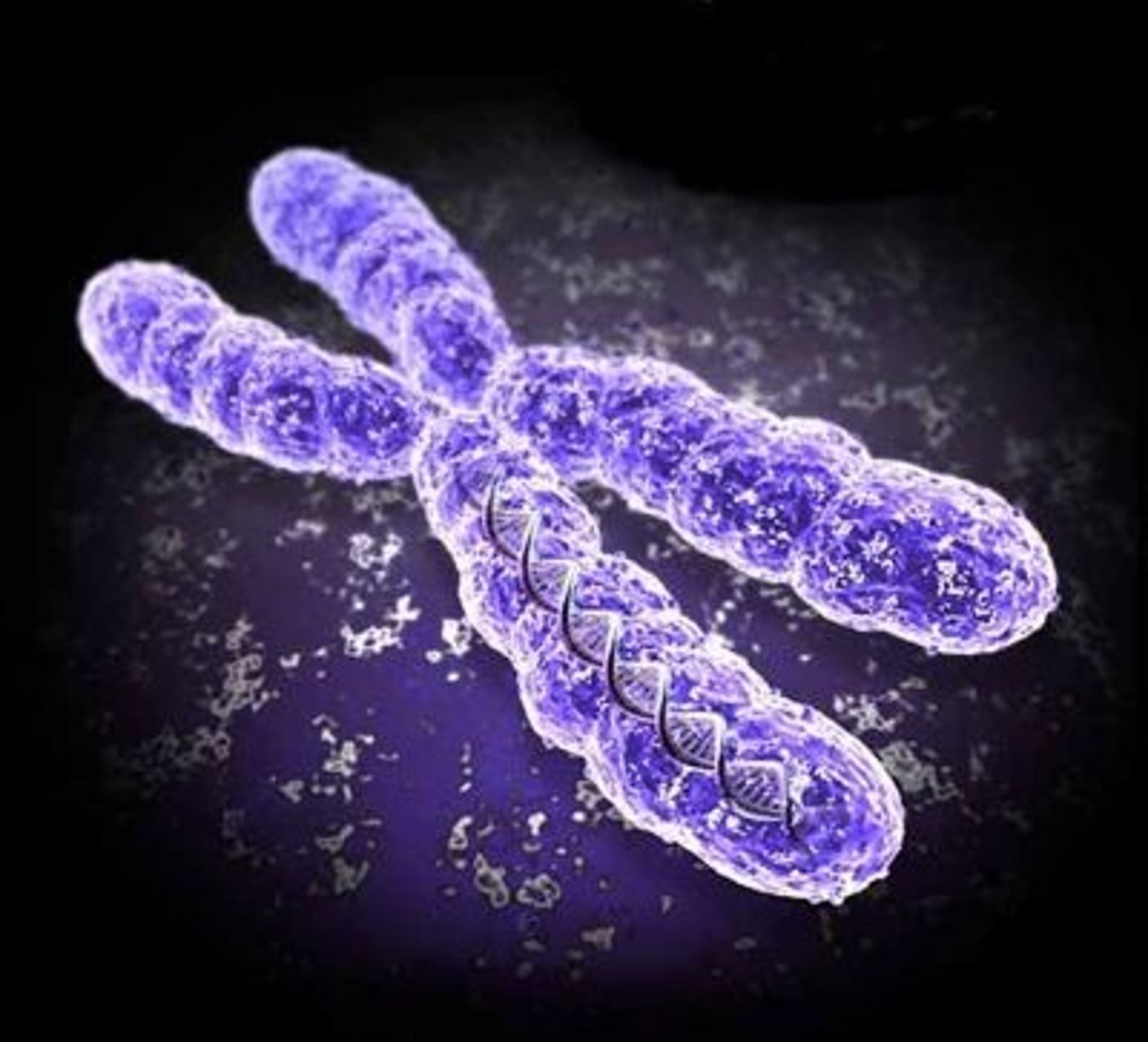
Chromosome
DNA coiled around and supported by proteins, found in the nucleus of a cell.
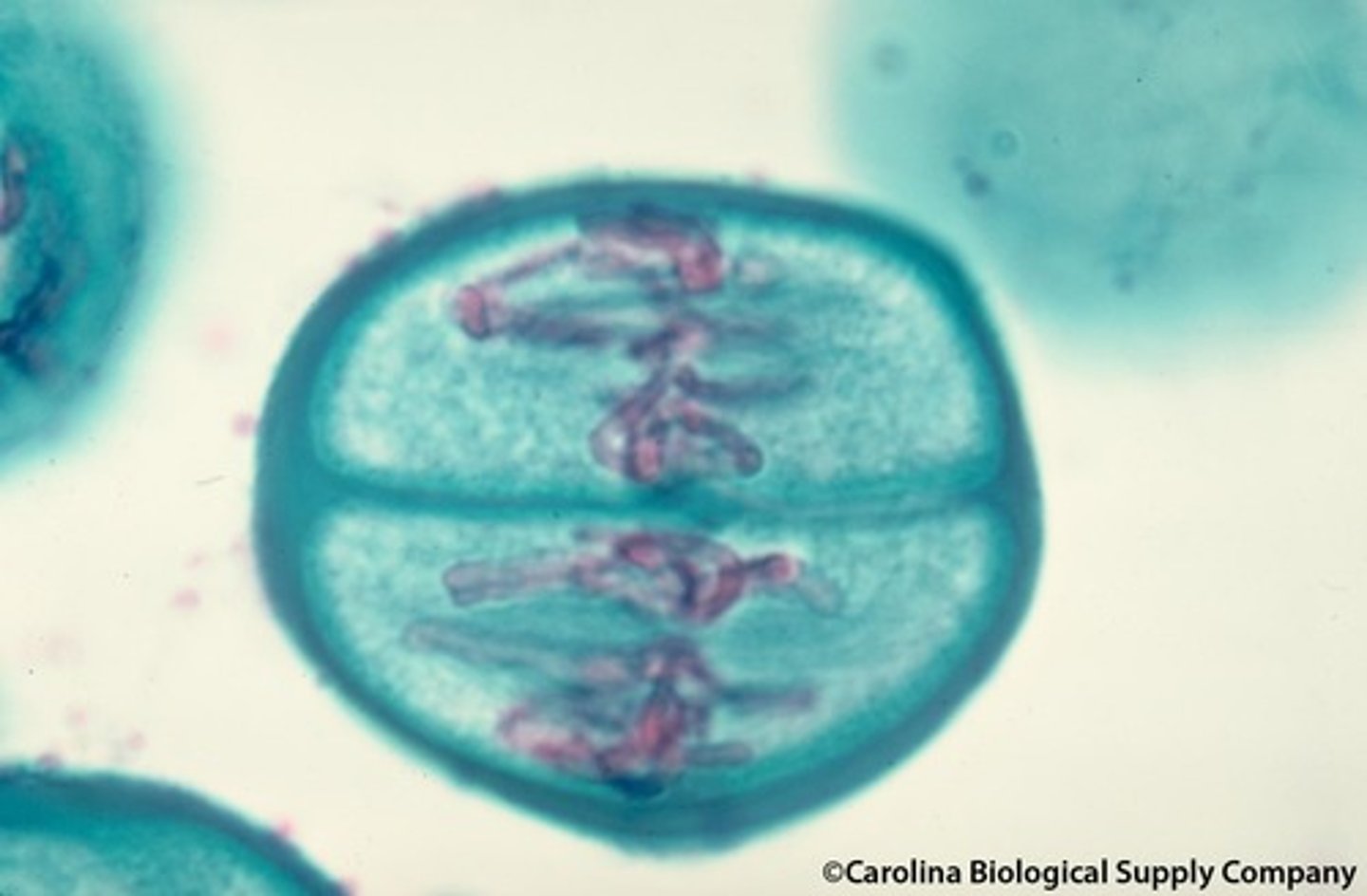
Mitosis
A process of asexual reproduction in eukaryotic cells.
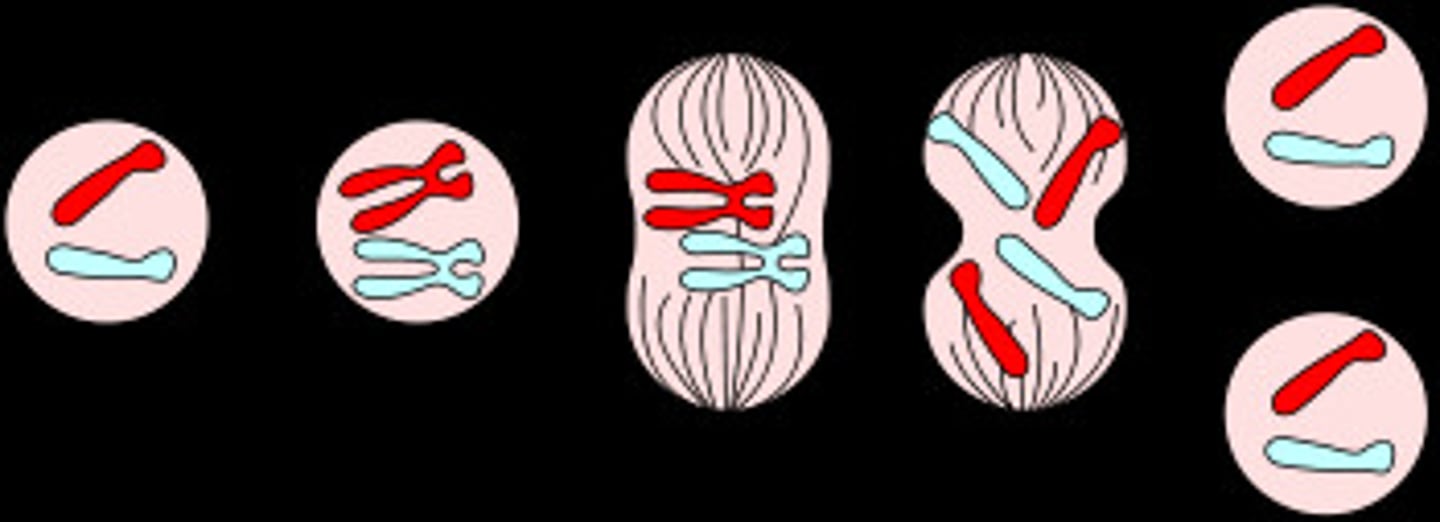
Interphase
The time interval between cellular reproduction

Mother Cell
A cell ready to begin reproduction, containing duplicated DNA and centrioles

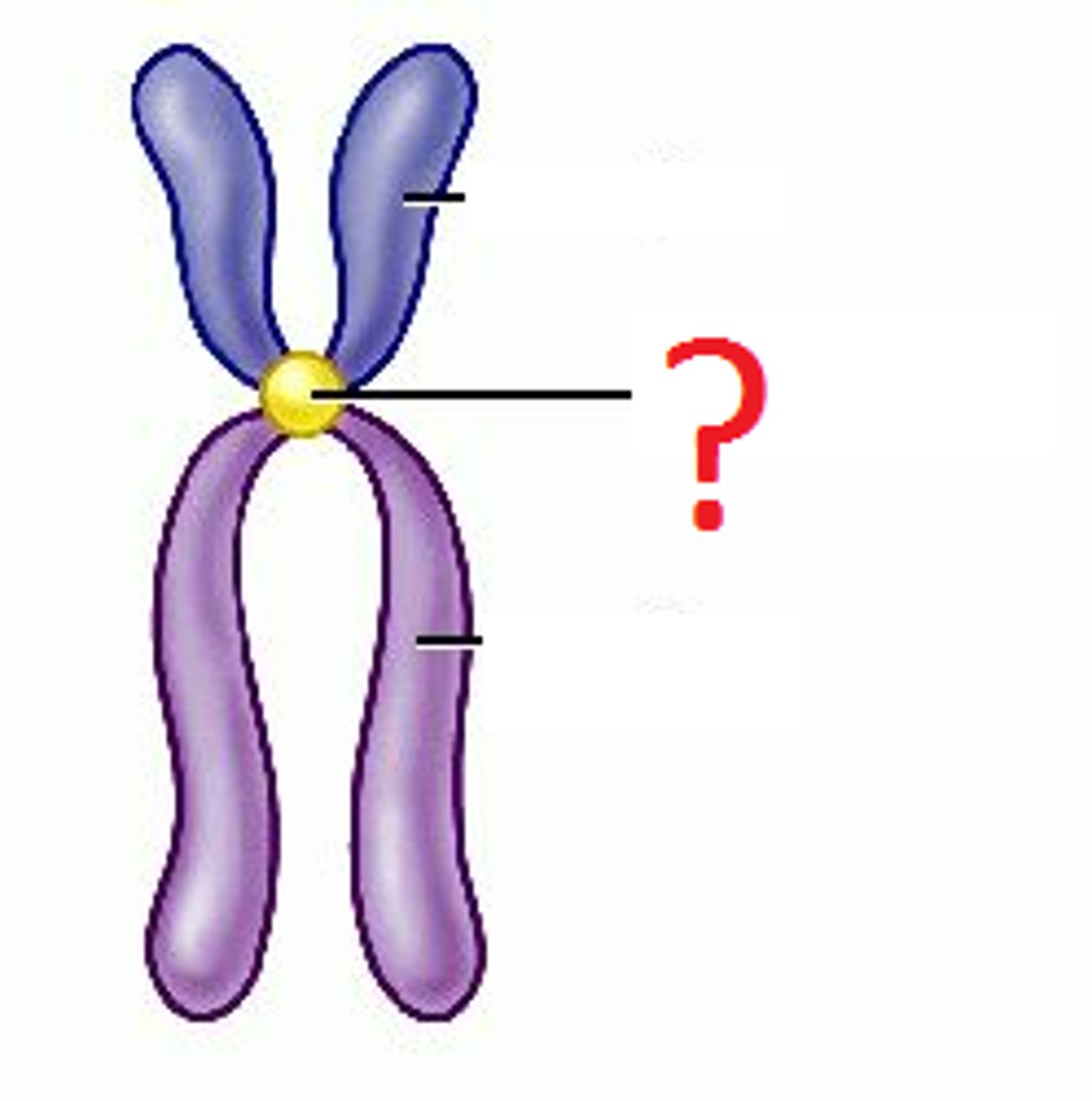
Centromere
The region that joins two sister chromatids
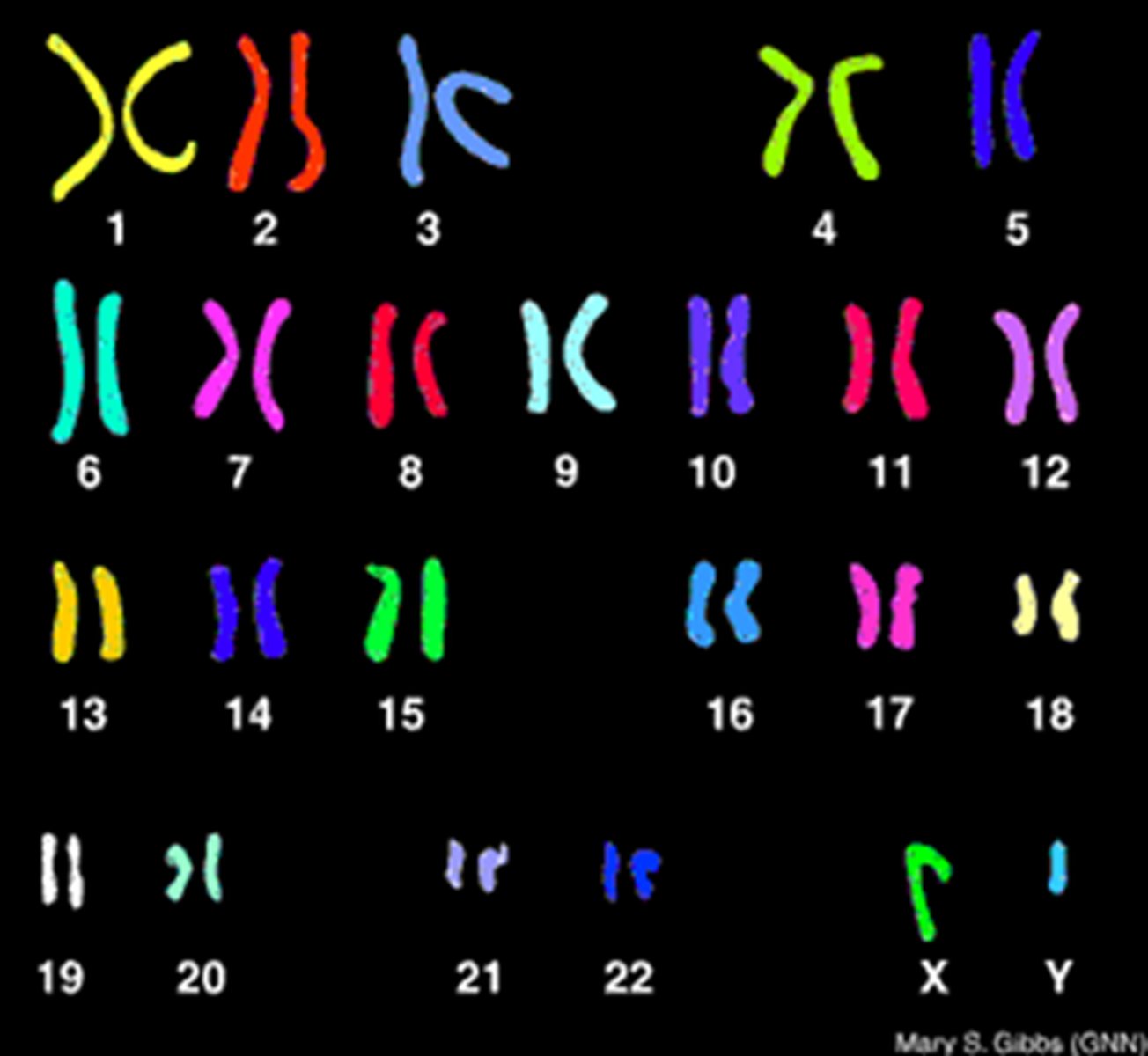
Karyotype
The figure produced when the chromosomes of a species during metaphase are arranged according to their homologous pairs.
Diploid cell
A cell with chromosomes that come in homologous pairs.
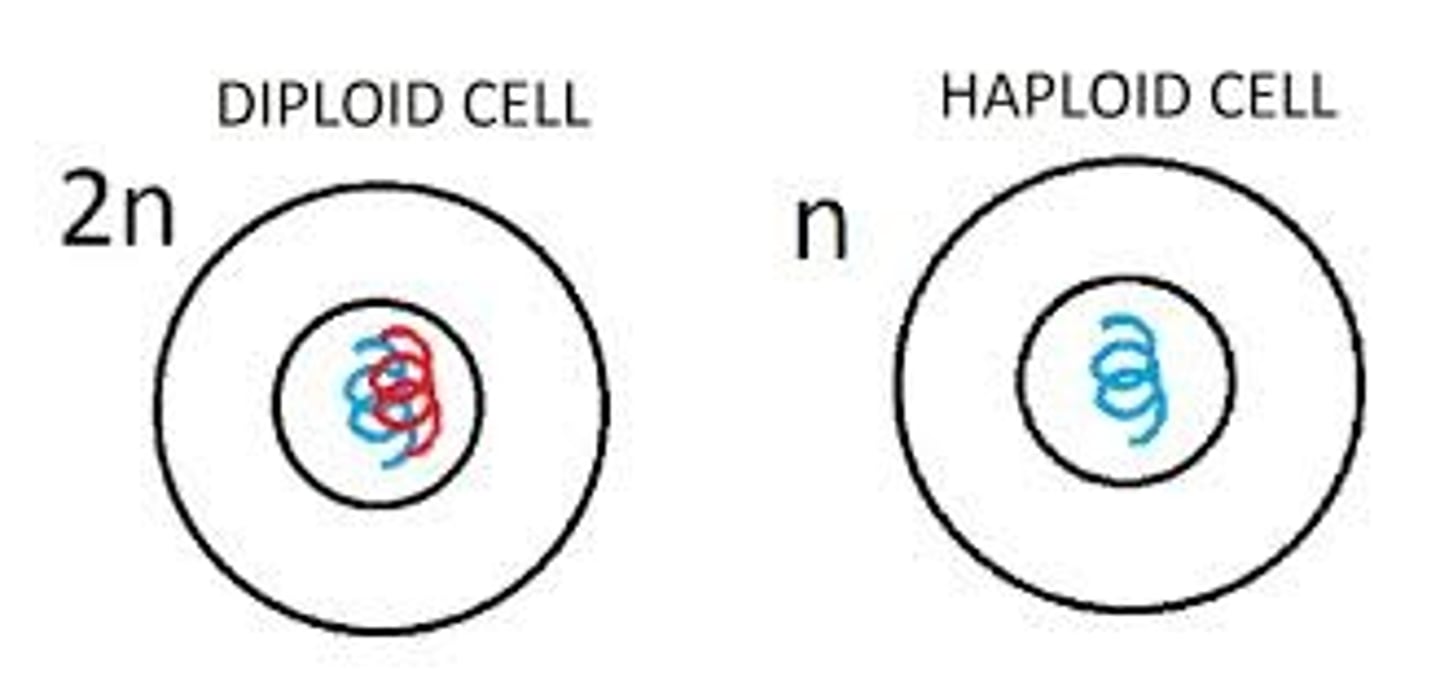
Haploid cell
A cell that has only one representative of each chromosome pair.
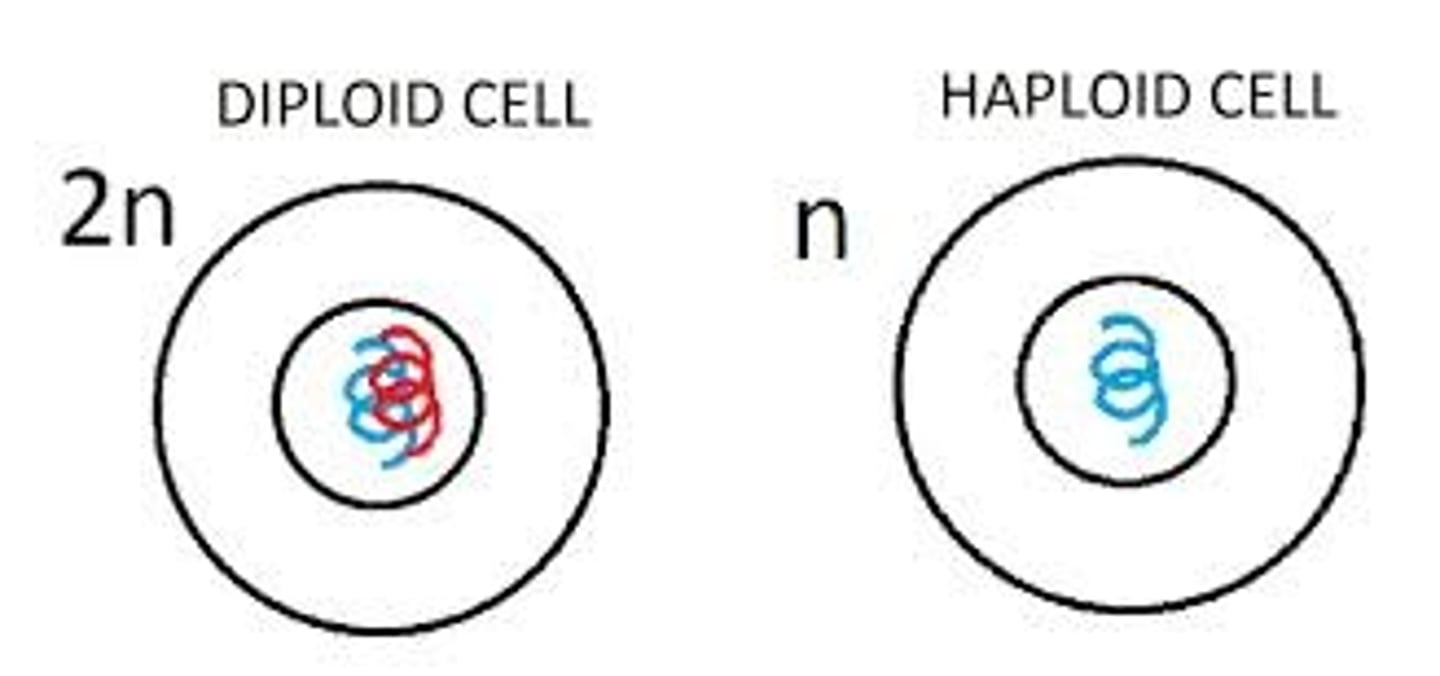
Diploid number (2n)
The total number of chromosomes in a diploid cell

Haploid number (n)
The number of homologous pairs in a diploid cell
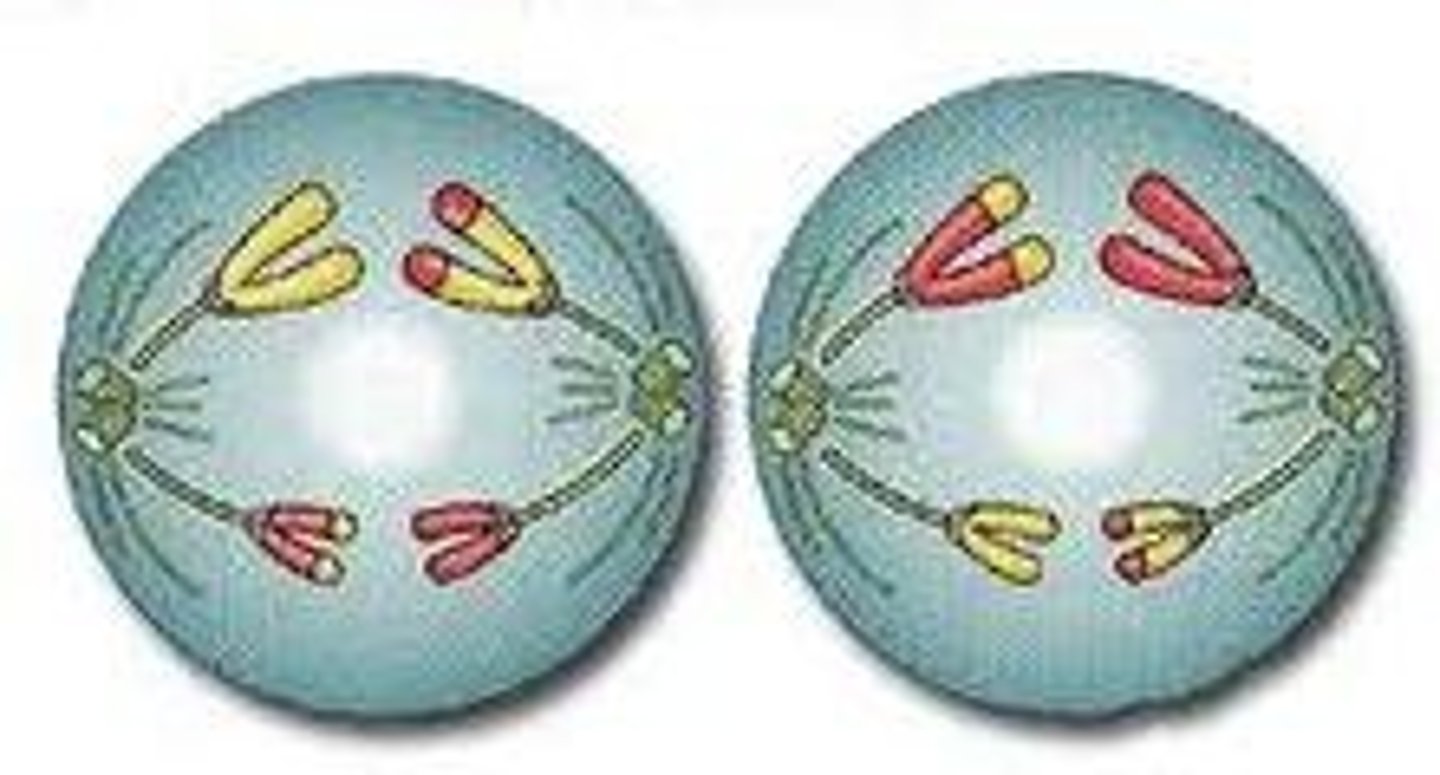
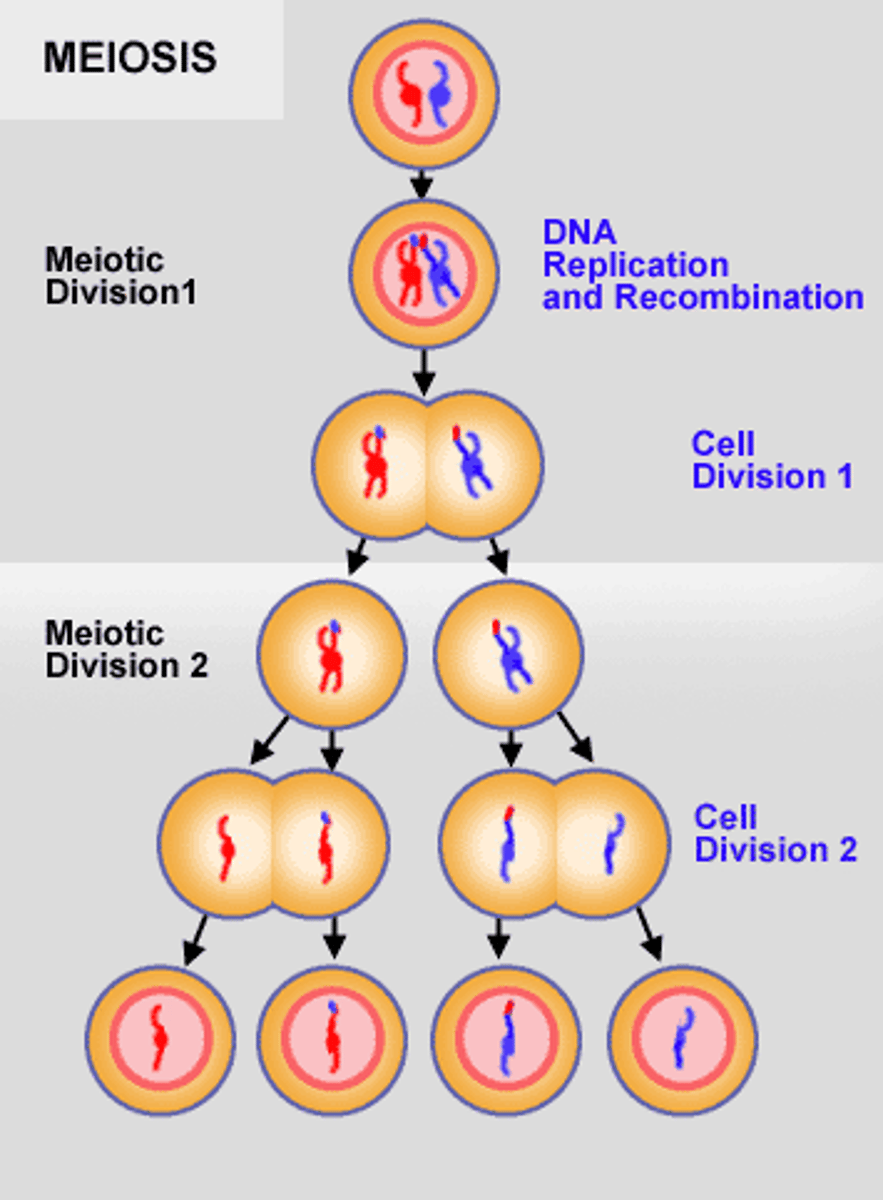
Meiosis
The process by which a diploid (2n) cell forms gametes (n).
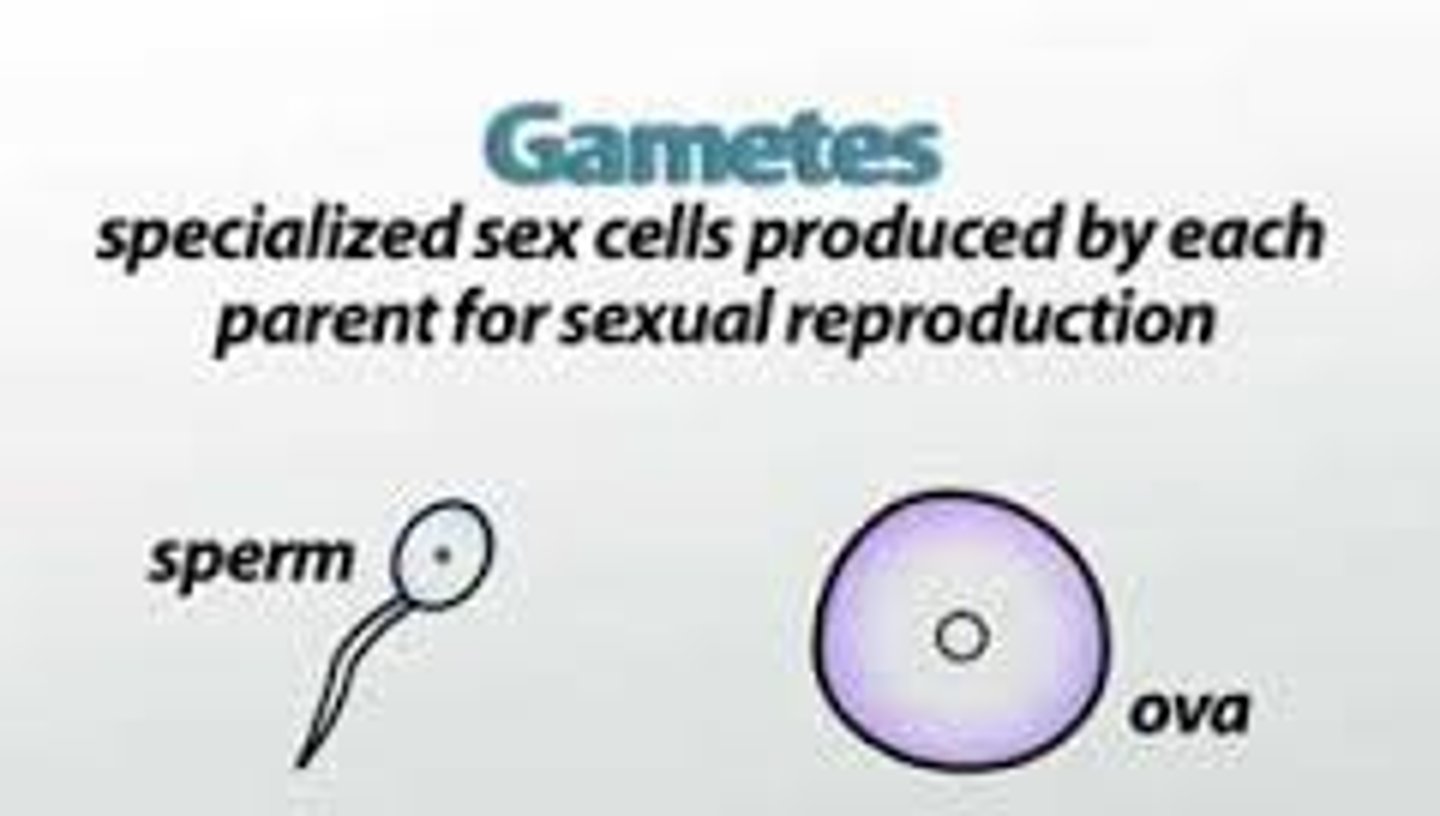
Gametes
Haploid cells (n) produced by diploid cells (2n) for the purpose of sexual reproduction
Virus
A non-cellular infectious agent that has two characteristics: 1) It has genetic material (RNA or DNA) inside a protective protein coat 2) It cannot reproduce on its own

Antibodies
Specialized pathogens that aid in destroying infectious agents
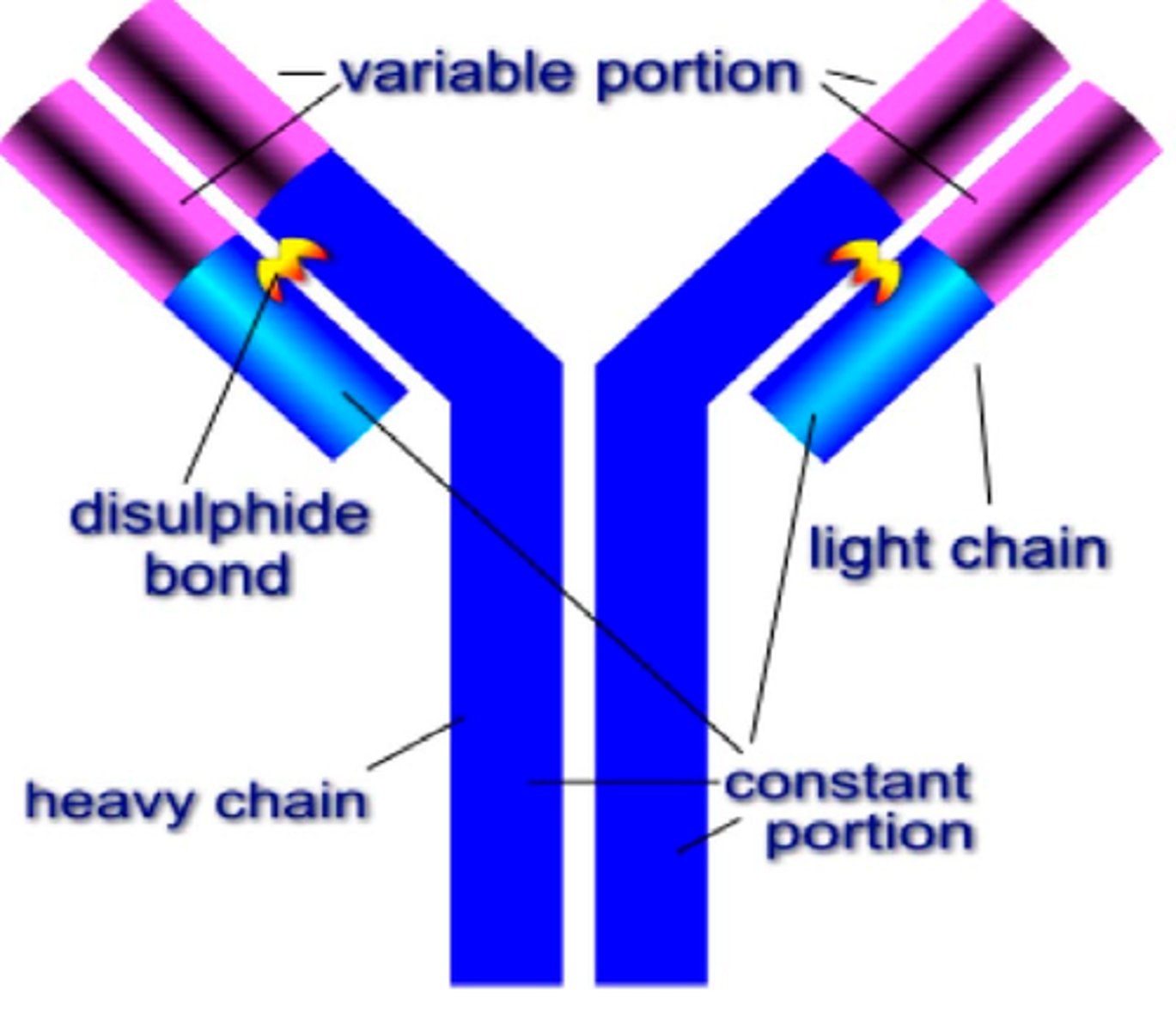
Vaccine
A weakened or inactive version of a pathogen that stimulates the body's production of antibodies which can help in destroying the pathogen
