10 Ruminant Protozoa
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why are Eimeria spp. (coccidia) not zoonotic
Eimeria spp. are incredibly host, site, and cell specific
T/F: Eimeria spp. are likely to cause coccidiosis
F; many species are non or mildly pathogenic
CS associated with coccidiosis
Severe diarrhea ± blood, dehydration
Patient demographic for coccidiosis
Young, old, and stressed
Ruminant species that is more likely to die from coccidiosis
Goats
Why is “winter coccidiosis” a thing
Animals in closer contact to preserve warmth spread disease more easily
Coccidiosis syndrome more common in the NW US
“Nervous coccidiosis” causing neuro signs and occasionally death
Type of life cycle in Eimeria spp.
Direct LC
Where does Eimeria spp. set up shop
Various locations in the SI
Gross lesions associated with the more pathogenic species of Eimeria spp.
Nodules in the SI
How do DH get infected with Eimeria spp.
Ingestion of sporulated oocysts
How long does it take for an oocyst to undergo sporogony
24-48 hours in environment
How does Eimeria spp. (and any apicomplexan really) cause damage in the host
Asexual replication (schizogony/merogony) is incredibly damaging
Morphology of Eimeria spp. eggs
Small but variable egg with centrally located morula or spores (depending on development), may see a micropyle cap if you are lucky
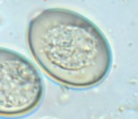
Eimeria spp. that are different than normal and are larger and brown
Eimeria macusaniensis (camelids)
Goal of Eimeria spp. treatment
Manage clinical disease
Management techniques to decrease incidence of coccidiosis
Reduce exposure to infective oocysts: clean feces, elevate feed
Prophylactic treatment
When should prophylactic coccidiostats be given
Just before or just after a period of increased stress
How do prophylactic coccidiostats allow for adaptive immunity
Knocks down the level of internal Eimeria spp. but doesn’t wipe out the entire population
Eimeria spp. treatment that is toxic to horses
Ionophores
Coccidiostats used in goats
Decoquinate, monensin
ELDU that may be warranted but cannot be used for market animals
Diclazuril or toltrazuril
CRYPTOSPORIDIUM