PLTW POE
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Which lever has an IMA <1
3rd class
Which lever has an IMA >1
2nd class
Which lever has an IMA that can be less than or greater than 1
1st class
What are the 6 simple machines?
Levers, screws, wedges, pulleys, inclined planes, and a wheel and axle
How do you find the IMA of a lever?
They’re all on the formula sheet :)
Which circuit flows in only one direction?
series
Where do you measure current?
Ammeter, put it into the circuit (hope R=0 here to not disturb current)
Where do you measure voltage?
Voltmeter, observer, (R=infinity), should be placed parallel to circuit, outside of it.
Where do you measure resistance?
Ohmmeter, on either side of a resistor or on the device to see how much it is resisting.
How do you find current and voltage in a series circuit?
Current stays the same, add up the voltages.
How do you find current and voltage in a parallel circuit?
Add up the currents, voltage stays the same.
Equation for power into a system?
IV(current*voltage)
Equation for power out of a system?
Work/time - J/s
Moment of inertia formula
bh³/12
Moment of inertia units
in^4
What letter symbolizes max deformation?
M
Moment =
force/distance from pinned connection
Moment vs moment of inertia
Moment of inertia is based on the cross sectional area of a beam (bh³/12) moment is based on force and distance from one fixed point (fD)
Moment
Basically torque, f*d, in Nm
Unit for beam deflection
in
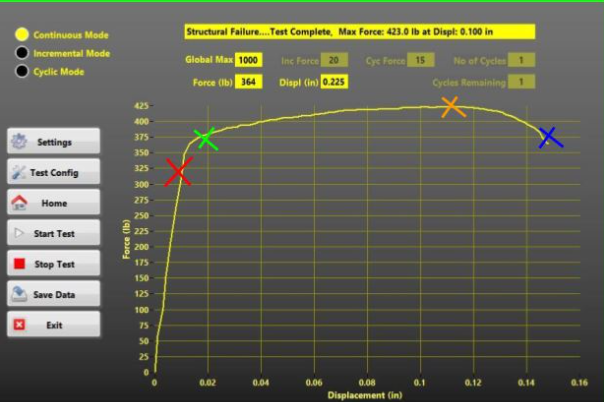
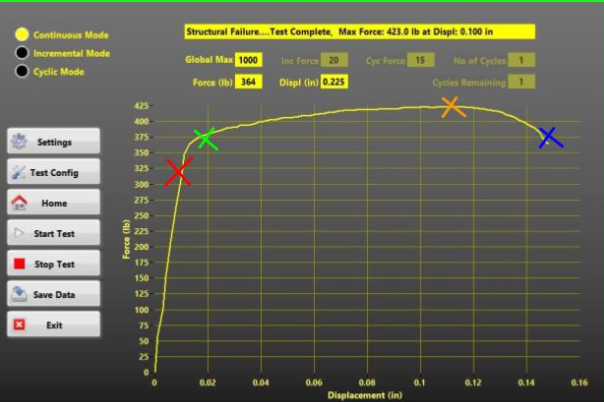
failure point, yield point, tensile strength, proportional limit
Blue, green, orange, red
Average kinetic energy of particles in an object
temperature
How to find heat
Q=mc(T1-T0) (q= heat energy, m=mass, c=specific heat)
The transfer of thermal energy by movement of fluid (liquid or gas) is called
convection
Which law of thermodynamics says "If two systems are separately found to be in thermal equilibrium with a third system, the first two systems are in thermal equilibrium with each other"
the zeroth law
Which direction is positive in RPM?
counter-clockwise
Alternative Energy |
Any source of energy other than fossil fuels that is used for constructive purposes. |
Ampere
The unit of electric current in the meter-kilogram-second system of units. Referred to as amp and symbolized as A.
Conduction
The transfer of heat within an object or between objects by molecular activity, without any net external motion.
Convection
Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass will rise and the cooler portions will sink.
Current
The net transfer of electric charge (electron movement along a path) per unit of time.
Electrical Energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
Electricity
The flow of electrical power or charge.
Electromagnetic Energy
Energy caused by the movement of light waves.
Electrolysis
The process separating the hydrogen-oxygen bond in water using an electrical current.
Energy
The ability to do work.
Entropy
The function of the state of a thermodynamic system whose change in any differential reversible process is equal to the heat absorbed by the system from its surroundings divided by the absolute temperature of the system.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The law that heat is a form of energy, and the total amount of energy of all kinds in an isolated system is constant; it is an application of the principle of conservation of energy. Also known as conservation of energy.
Fuel Cell Stack
Individual fuel cells that are combined in series
Heat
Energy in transit due to a temperature difference between the source from which the energy is coming and where it is going
Kelvin
The scientific unit in which absolute temperature is measured. Symbolized by K.
Line of best fit
A straight line that best represents all data points of a scatter plot. Regression line/trend line.
Ohm
The unit of resistance. Ω.
Ohm’s Law
States that the direct current flowing in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the circuit’s voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Radiation
The process by which energy is transmitted through a medium, including empty space, as electromagnetic waves
Renewable energy
A resource that can be replaced when needed
Resistance
The opposition a device offers to the flow of direct current
R-value
The measure of resistance to heat flow
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy flows from hot to cold unless something is done to stop it.
Temperature
A property of an object which determines the direction of heat flow when the object is placed in thermal contact with another object. Average kinetic energy of particles in an object.
Thermal equilibrium
Refers to the property of a thermodynamic system in which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings.
Thermodynamic system
A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity.
Thermodynamics
The study of the effects of work, heat, and energy on a system.
U-value
A measure of thermal transmittance through a material.
Volt
The unit of potential difference symbolized as V.
Voltage
The potential difference measured in volts. The amount of work to be done to move a charge from one point to another along an electric circuit.
Absolute Pressure
The total pressure exerted on a system, including atmospheric pressure.
Atmospheric Pressure
The pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere.
Check Valve
A valve that allows flow in one direction but prevents flow in the opposite direction.
Compressor
An air pump that compresses air into a receiver tank.
Crank
A part of an axle or shaft bent out at right angles, for converting reciprocal to circular motion and vice versa.
Cylinder
A device used to convert fluid power into mechanical power in the form of linear motion.
Directional-Control Valve
Used to control which path fluid takes in a circuit.
Double-Acting Cylinder
A cylinder that can act under pressure in both directions (extend and retract) to move a load.
Flow Velocity
The distance the fluid travels through a system in a given period of time.
Fluid Power
The use of a fluid (liquid or gas) to transmit power from one location to another.
Lubricator
A device used to spray an oil mist into the stream of a pneumatic system.
Piston
A sliding piece moved by or moving against fluid pressure which usually consists of a short cylindrical body fitting within a cylindrical chamber or vessel along which it moves back and forth.
Pressure Regulator
A type of pneumatic pressure control valve that controls the maximum pressure in a branch of a circuit.
Pressure Relief Valve
A type of pressure control valve that limits the maximum pressure in a hydraulic or pneumatic circuit.
Pump
A device used to create flow in a hydraulic system.
Receiver Tank
A device that holds the compressed air in a pneumatic system.
Reservoir
The tank that holds the fluid in a hydraulic system.
Single-Acting Cylinder
A cylinder that acts under pressure in one direction only and returns automatically when the pressure is released.
Solenoid
A switching device that uses the magnetic field generated by an electrical current for actuation.
Transmission Lines
Used to transport fluid in a circuit.
Valve
Any device that controls, either automatically or manually, the flow of a fluid.
Viscosity
A measure of a fluid’s thickness or resistance to flow.
Volume
The amount or quantity of something.
Moment of inertia
The mathematical property of a cross-section that gives important information about how that cross-sectional area is distributed about a centroidal axis. Changes based on plank vs joist. bh³/12
Modulus of Elasticity
Ratio of increment of stress to increment of strain, based on chemical makeup.
Centroid?
Add all areas, find all y-values, multiply, then do Ay/A. Same for x to find x-value for it
Trusses?
EFx=AB+ACx, EFy=Ay+ACsin(theta), EFy=By+BCsin(theta). If angles are the same and Ay and By are, AC and BC are too
Smallest thing a material can be broken down into while retaining its properties
Atom
Metals
Good conductors, 1-3 valence electrons
Nonmetals
Most are gases at room temp, solids brittle, dry, poor heat and electricity conductor
Metallic
pure metal
metal alloys
good conductors
strength and plasticity
Ceramic
Compound of metal+nonmetal
Good insulators
Strength at high temps and brittleness
Organic
are or were living at one point
carbon and hydrogen
genetically alterable
renewable, sustainable
Polymeric
mostly organic
low density
flexibility and elasticity
plastics/elastomers
Composite
made of more than one
layer- alternate layers binded together
particulate- discrete particles of one material surrounded by a matrix of others
Fiber-reinforced- Composed of contiunous or discontinuous fibers in a matrix of another
Thermoelectric
Electrical stimuli provoke thermo responses; thermo stimuli provoke electrical responses
Flow Shop
Larger quantities of products
Production line
Special purpose machines
Job Shop
Small quantities of products
Large variety of products
Products move through the shop to various machines
General-purpose machines
Linked-Cell Shop
Manufacturing and subassembly cells connected to final assembly
Lean production system
One piece flow system
Project Shop
Product being manufactured cannot be easily moved during production.
Production processes are brought to the product.
Examples:Bridges, ships, large airplanes, locomotives, large machinery
Continuous Process
Large plants
Utilized in the manufacture of liquids, oils, gases, and powders
Lean Manufacturing
100% “good” units flow from process to process
Integrated quality control (IQC)
All employees are inspectors
Rolling
Material passes through a series of rollers, reducing its thickness with each pass
Forging
Material is shaped by the controlled application of force (blacksmith)