GCSE Computer Science
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/265
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:37 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
1
New cards
Algorithm
A sequence of steps to be performed to solve a problem
2
New cards
Computer Program
An implementation of an algorithm
3
New cards
Data Structure
Specialized format for storing and organizing data
4
New cards
Procedure
A names section of code which performs a task and does not return a value
5
New cards
Function
A named section of code which performs a task and returns a value
6
New cards
Parameter
A special type of variable which can be passed through sub-routines
7
New cards
Scope
The reach of a variable/data structure
8
New cards
Computer System
A combination of software and hardware
9
New cards
Character
Single Value "a" or "9"
10
New cards
Integer
Whole Number
11
New cards
Boolean
True or False Value
12
New cards
ASCII
Character Set: Limited to 7 bits, only applicable in Latin based languages
13
New cards
Real
Integer or
Decimal Number
Decimal Number
14
New cards
Binary
Composed of 1's and 0's
15
New cards
Hexadecimal
Composed of Integers 0-9 and Strings A-F
16
New cards
Denary
Composed of Digits 0-9
17
New cards
Run-Time Error
Error that occurs while the program is running
18
New cards
Unicode
Alternative character set
19
New cards
Iteration
The process of repeating steps
20
New cards
Selection
A question is asked and from the response several paths can be taken
21
New cards
Sequence
The order in which instructions are performed
22
New cards
Logic Error
An error in the logic of the code which causes it to run incorrectly but not crash
23
New cards
Syntax Error
An error in the syntax of the code
Will cause the program to crash
Will cause the program to crash
24
New cards
Sample Rate
The frequency at which samples are taken
25
New cards
Requirements
When the team decides what the software needs to do, To think about what the user will want the program to do
26
New cards
Design
Working out the smaller details of the program by breaking it down into smaller chunks
27
New cards
Implementation
The program code is written
28
New cards
Testing
Testing the program under various conditions to make sure it is going to work
29
New cards
Evolution
Maintaining and updating the program
30
New cards
Lossy Compression
Removes some of the file's original data to reduce file size
31
New cards
Resolution
How tightly packed the pixels are
32
New cards
Bit Map Image
Images composed of lots of pixels
33
New cards
Vector Image
Image created in graphics packages and consist of shapes called objects
34
New cards
Lossless Compression
Various algorithms are used to find parts in the data that are repeated
35
New cards
Ring Topology
Fast data transfer but if one machine fails the whole network will fail.
36
New cards
Bus Topology
Easy and cheap to install but if the main cable fails the whole network will crash
37
New cards
Star Topology
Reliable and high-performing but expensive to install and if a hub/switch fails the devices will not have network connection
38
New cards
CPU
Brains of the computer. Mainly processes and uses data to perform taks
39
New cards
GPU
A chip/processor designed to boost the performance of games and graphics
40
New cards
RAM
Primary Storage device which allows data to be stored and retrieved on the machine
41
New cards
Volatile Memory
Memory which only maintains it's storage while the machine is active
42
New cards
Non-Volatile Memory
Memory which maintains it storage whether or not the machine is active
43
New cards
Logic Gate
A diagram which represents boolean logic
44
New cards
Virtual Memory
Memory that appears to be main storage although most if it is held in secondary storage
45
New cards
Cache
Memory that is easily accessed by the CPU and is very fast
46
New cards
Secondary Storage
Non-Volatile memory that is not directly accessible by the CPU
47
New cards
Optical
Data is recorded by making marks in a pattern that can be read back with the aid of light.
48
New cards
Magnetic
A mechanical device in which the media is inserted
49
New cards
Solid State
A grid of electrical cells which quickly send and receive data
50
New cards
NOT gate
A logic gate that takes in 1 input & outputs the opposite
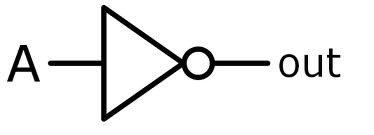
51
New cards
AND gate
A logic gate that takes in 2 inputs and only outputs True if both inputs are True
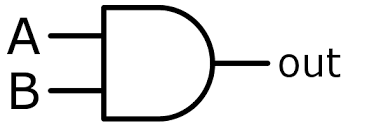
52
New cards
OR gate
A logic gate that takes in 2 inputs and outputs True if either inputs are True
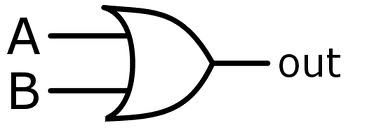
53
New cards
Truth table
A table which holds possible states on inputs and shows the corresponding final output of a logic diagram
54
New cards
Logic Diagram
A diagram combining multiple logic gates to show the inputs and final output of a system
55
New cards
Boolean Logic
Logic which can only produce a True or False outcome

56
New cards
Hardware
The physical elements of a computer system
57
New cards
Sotware
The logical programmed parts of a computer system that tells the hardware how to function
58
New cards
Embedded system
A system developed for a single, or set purpose. E.g. A washing machine, microwave, digital watch
59
New cards
General Purpose System
A computer system that can change its purpose by adding more software
60
New cards
ROM
Non Volatile. Small area of memory which holds the boot up program.
61
New cards
Device Driver
A program stored on the hard drive that tells the computer how to communicate with a hardware device such as a printer, mouse, or keyboard.
62
New cards
Defragger
System software which tidies up the physical locations of where data is saved on a storage device.
63
New cards
Scheduler
System software which establishes the order in which instructions are executed by the processor
64
New cards
GUI
A User Interface which incorporates the four elements of Windows, Icons, Menus, & Pointers

65
New cards
System Software
software responsible for the general operation of a computer system, including the operation of hardware, running application software, and file management

66
New cards
Application Software
computer software created to allow the user to perform a specific job or task. eg. Word, Excel, browsers, games

67
New cards
Autoupdate
A scheduled patch to software (usually system software) to ensure that it is completely up to date with the latest features.
68
New cards
Firewall
A security system consisting of a combination of hardware and software that limits the exposure of a computer or computer network to attack from crackers
69
New cards
Spyware
A computer program which is installed without permission, sometimes through a virus or sometimes as part of the installation of a program. It works by collecting information and sending it back to another source. The information collected could include the websites you have been visiting or what you have been downloading. This can be used for marketing purposes but also for fraud.

70
New cards
Antivirus
System software that is specifically designed to detect viruses and protect a computer and files from harm

71
New cards
Computer Virus
a software program capable of reproducing itself and usually capable of causing great harm to files or other programs on the same computer
72
New cards
Computer Worm
Self-replicating program designed to carry out some unauthorised activity on a victim's computer. This software can spread themselves from one computer to another without any assistance from victims.
73
New cards
Trojan
A piece of software that appears to be a legitimate application, utility, game, or screensaver that performs malicious activities surreptitiously
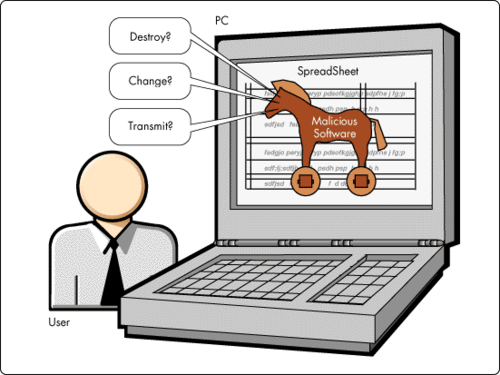
74
New cards
Phishing
An attack that sends an email or displays a Web announcement that falsely claims to be from a legitimate enterprise in an attempt to trick the user into surrendering private information
75
New cards
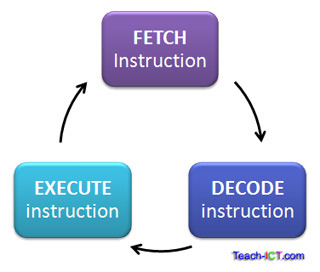
Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
This is the process that all Stored Program Computers follow in order to run instructions within the machine.
Instructions are stored within main memory as a combination of both instruction & data.
Instructions are stored within main memory as a combination of both instruction & data.
76
New cards
Microprocessor
Another name for the central processing unit that is generally made from a single integrated circuit.
Multi-core CPUs are made up of more than one microprocessor.
Multi-core CPUs are made up of more than one microprocessor.

77
New cards
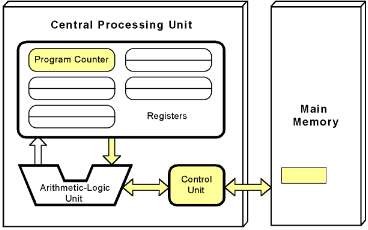
Control Unit
Component of a processor that directs and coordinates most of the operations in the computer.
78
New cards
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The circuits that do the math and logic operations inside the processor. The "gateway" all inputs and outputs pass through.
79
New cards
CPU Register
Internal memory in the CPU. These store information that the arithmetic and logic units need to carry out the current instruction.
80
New cards
Program Counter (PC)
A register inside the CPU which holds the address of the next instruction to process.
81
New cards
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
A register inside the CPU which holds the current instruction (not the data)
82
New cards
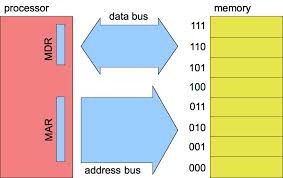
Memory Address Register (MAR)
A register inside the CPU which holds the address of the current instruction to process. This allows the actual instruction to be loaded.
83
New cards
Memory Data Register (MDR)
A register inside the CPU which holds the data of the current instruction to process.
84
New cards
Accumulator
A register inside the CPU which holds the running total or result of the current instruction.
85
New cards
Address Bus
A physical wire which transmits memory addresses between the CPU and the RAM
86
New cards
Data Bus
A physical wire which transmits data between the CPU and the RAM
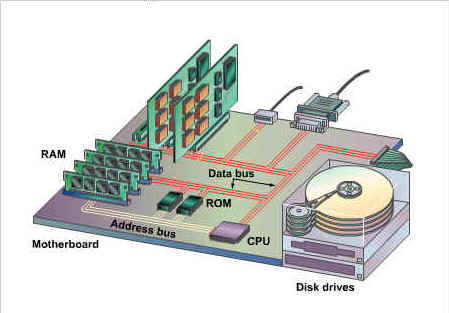
87
New cards
Binary Search
Takes the median of a sorted list, and if it is greater than the input, then the top half of the list is removed, and a new list is created until the correct match is found.
88
New cards
Efficiency of algorithms
Speed, Size, Storage
89
New cards
Bubble Sort
Easy to code, however with a longer list can be very inefficient
90
New cards
Name Five Data Types
Integer, Real, Boolean, String, Character
91
New cards
Definite Iteration
Repeating the process until a desired result with a finite number of iterations, that is calculable. Do Until - Loop
92
New cards
Indefinite Iteration
Repeating an iteration that is conditional, and may be repeated infinitely. While-End While
93
New cards
Nested Selection
A selection within a selection
94
New cards
=
Equal to
95
New cards
<>
not equal to
96
New cards
<
less than
97
New cards
>
greater than
98
New cards
Abstraction
Abstraction is the process of removing all unnecessary information from a set of instructions so that the aim of the instructions is not distracted from and so that the final product is as good as possible. The abstracted data is simpler and more relevant to the operation. Abstraction can speed up the program.
99
New cards
less than or equal to
100
New cards
>=
greater than or equal to