Chemistry Final Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/314
Last updated 11:34 PM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
315 Terms
1
New cards
AB →(heated) A + B
decomposition
2
New cards
combustion reaction
a substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat
3
New cards
how to tell if a chemical reaction is occuring (5 things)
1. evolution/formation of a gas
2. formation of a solid
3. release/absorption of heat
4. color change
5. change in pH
4
New cards
9
nona
5
New cards
10
deca
6
New cards
12
dodeca
7
New cards
what does the atomic number represent
the number of protons in an element
8
New cards
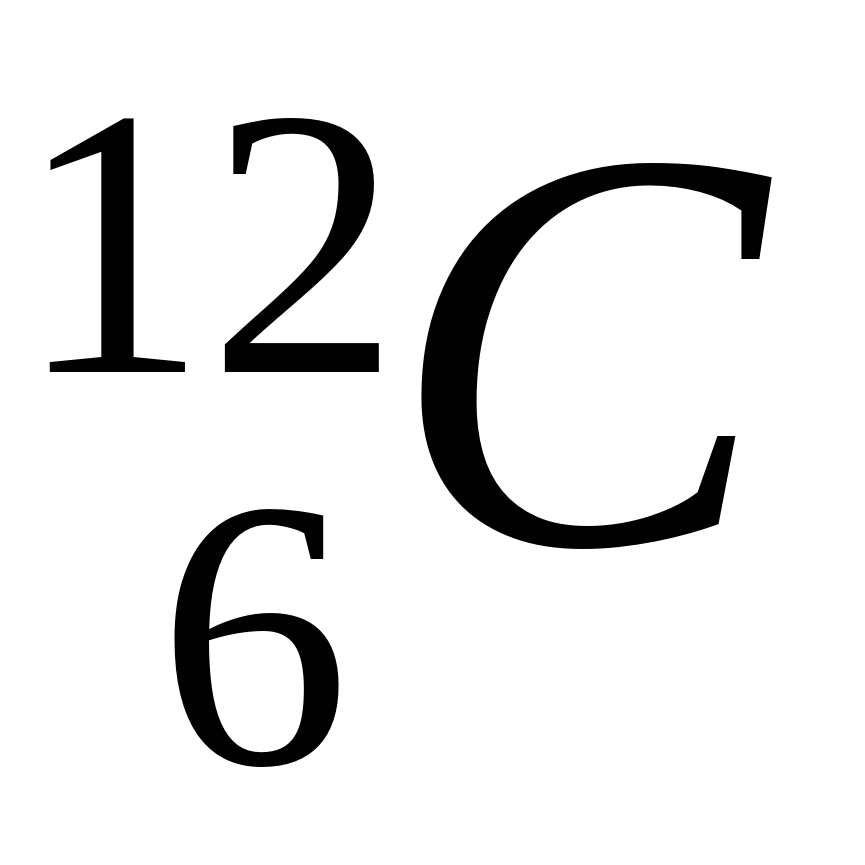
what is this called?
nuclear notation/isotope symbol
9
New cards
where is the atomic number located in the isotope symbol/nuclear notation?
the subscript
10
New cards
ex: carbon-12 ; what is this called?
hyphen notation
11
New cards
where is the mass number located in the isotope symbol/nuclear notation?
superscript
12
New cards
what does the mass number represent?
the number of protons and neutrons added together
13
New cards
how do you find the number of neutrons in an element?
mass number - atomic number
14
New cards
isotope
all isotopes of an element have the same number of electrons and protons (atomic number) but different number of neutrons resulting in different mass numbers
15
New cards
in isotopes, what two subatomic particles are the same?
protons and electrons
16
New cards
isotopic mass formula
total mass / # of atoms
17
New cards
percent abundance formula
\# of atoms / total # of atoms x 100
18
New cards
atomic mass formula
AWAM = (rel.abundance of isotope 1 x 100) + (rel.abundance of isotope 2 x 100) + (rel.abundance of isotope 3 x 100)
19
New cards
relative abundance formula
percent abundance / 100
20
New cards
the # of protons can be directly determined from what?
the atomic number (ex: Cu is atomic number 29, so it contains 29 protons in the nucleus)
21
New cards
if an atom is neutral, how can the # of electrons be determined?
same as the # of protons
22
New cards
what does it mean in terms of electrons and protons, when an atom has a positive charge?
there are less electrons, and more protons
23
New cards
each positive charge on an atom or ion represents what? ex: Mg²⁺
there is one less electron than proton (in Mg²⁺ there are 12 protons which means there would only be 10 electrons)
24
New cards
what does it mean in terms of electrons and protons, when an atom has a negative charge?
more electrons than protons
25
New cards
each negative charge on an atom or ion represents what? ex: O²⁻
there is one more electron than proton (in O²⁻, oxygen has 8 protons, but would have 10 electrons)
26
New cards
what are the two most common methods for communicating the # of subatomic particles in an atom?
hyphen notation and nuclear notation
27
New cards
chemical symbol def (ex: NaCl)
form of shorthand notation for naming an element
28
New cards
compound def
substances in which 2 or more elements are chemically combined
29
New cards
chemical formula def
combination of symbols which represent the composition of a compound
30
New cards
fragmentation def
the process of breaking apart a molecule
31
New cards
do like charged particles repel or attract
repel
32
New cards
do oppositely charged particles repel or attract
attract
33
New cards
neutral atom def
\# of protons and electrons are the same
34
New cards
what happens in detection?
ions collide w/ a metal plate. electrons are transferred from the metal to the ion, producing a current and thus a signal to a computer
35
New cards
what happens in deflection?
ions are attracted to the negative side of an electromagnetic field causing separation of the mixture based on mass and charge
36
New cards
what happens in ionization?
electrons are knocked off sample particles to form (mostly) +1 ions
37
New cards
what happens in acceleration?
Ions move through a series of charged plates to form a narrow beam of high speed particles with equal kinetic energy
38
New cards
SIG FIGS - are nonzero #s significant or not significant
significant
39
New cards
SIG FIGS - are 0s between two non zero #s significant or not significant
significant
40
New cards
SIG FIGS - are leading zeros or trailing zeros without a decimal significant or not significant
not significant
41
New cards
SIG FIGS - are zeros at the end of a # that also contains a decimal, significant or not
significant
42
New cards
SIG FIGS - are exact numbers or counting numbers significant or not
not significant
43
New cards
in SIG FIGS, the last digit is always…
estimated
44
New cards
SIG FIGS RULES FOR MATH OPERATIONS - if the digit following the last digit is greater than 5, then…
the last digit should be increased by 1
45
New cards
SIG FIGS RULES FOR MATH OPERATIONS - if the digit following the last digit is less than 5, then…
the last digit should stay the same
46
New cards
SIG FIGS RULES FOR MATH OPERATIONS - if the digit following the last digit is 5 but followed by nonzero digits, then…
the last digit should be increased by 1
47
New cards
SIG FIGS RULES FOR MATH OPERATIONS - if the digit following the last digit is 5 but not followed by nonzero digits and proceeded by an odd digit, then…
the last digit should be increased by 1
48
New cards
SIG FIGS RULES FOR MATH OPERATIONS - if the digit following the last digit is 5 but not followed by nonzero digits and proceeded by an even digit, then…
the last digit should stay the same
49
New cards
when adding or subtracting SIG FIGS, the answer must contain…
same # of digits to the right of the decimal point as there is in the starting measurement with the fewest # of digits to the right of the decimal point (ex: 5.44 + 2.6103 = 8.0503 → 8.05)
50
New cards
when multiplying or dividing SIG FIGS, the answer must contain…
the same # of SIG FIGS as there is in the starting measurement w/ the fewest # of SIG FIGS (ex: 12 x 6.41 = 76.92 → 77)
51
New cards
mass formula
density x volume
52
New cards
a measurement provides what kind of data
quantitative
53
New cards
accuracy indicates…
how close a measurement is to the accepted or true value
54
New cards
precision indicates…
how close together or how repeatable results are
55
New cards
ACCURATE measured values are ____ to the accepted value
close
56
New cards
PRECISE measured values are close to _____
one another but not necessarily close to the accepted value
57
New cards
% error formula
% error = l Experimental value - Accepted Value l / Accepted Value x 100
58
New cards
10⁹
Giga
59
New cards
10⁶
Mega
60
New cards
10³
kilo
61
New cards
10²
hecto
62
New cards
10¹
deca
63
New cards
10⁻¹
deci
64
New cards
10⁻²
centi
65
New cards
10⁻³
milli
66
New cards
10⁻⁶
micro
67
New cards
10⁻⁹
nano
68
New cards
mass of substance
molar mass
69
New cards
moles of substance
avagadro's number
70
New cards
avogadro’s number
6\.022 x 10²³ units
71
New cards
formula mass def
the mass of a SINGLE atom of an element, one unit of a compound, or molecule
72
New cards
formula mass units
amu
73
New cards
molar mass def
the mass of ONE MOLE of a substance (element, compound, or molecule)
74
New cards
molar mass units
g/mol (grams per mole)
75
New cards
mole def
a counting # representing 6.022 x 10²³ particles of anything (ions, atoms, molecules, etc.)
76
New cards
molecular formula def
a formula giving the # of atoms of each of the elements present in one molecule of a specific compound
77
New cards
empirical formula def
a chemical formula showing the simplest ratio of elements in a compound rather than the total # of atoms in a molecule
78
New cards
CONVERTING TO SCIENTIFIC NOTATION - when moving the decimal to the right…
the exponent is negative
79
New cards
CONVERTING TO SCIENTIFIC NOTATION - when moving the decimal to the left…
the exponent is positive
80
New cards
significant figures are measured ____ , plus one estimated digit
precisely
81
New cards
law of definite proportions states…
a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions, regardless of the amount of the sample, where it was found, or how it was prepared
82
New cards
hydrate def
a pure substance that contains water molecules embedded in its crystal structure
83
New cards
anhydrous
the solid that remains behind water molecules ; “without” water
84
New cards
electromagnetic radiation def
a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travles through space
85
New cards
electromagnetic radiation has two types of characteristics
wave-like and particle-like
86
New cards
wave length def
the distance between two corresponding points on adjacent waves
87
New cards
greek symbol for wavelength
λ - lambda
88
New cards
wavelength units of measurement
distance - m, cm, nm, etc.
89
New cards
frequency def
the # of waves cycles per unit of time
90
New cards
calculating wavelength and frequency equation
c = λv
91
New cards
greek symbol for frequency
v - nu
92
New cards
frequency units of measurement
waves/second
93
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum def
an arrangement of all forms of ER based on wavelength, frequency, and energy
94
New cards
photon
a particle of ER having 0 mass and is carrying a quantum of energy (specific amount)
95
New cards
containing a quantum of energy is defined as
the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom
96
New cards
types of ER
radio, radar, infrared, visible, UV, x-rays, gamma rays
97
New cards
types of ER (longest wavelength to shortest wavelength)
radio, radar, infrared, visible, UV, x-rays, gamma rays
98
New cards
types of ER (highest frequency to lowest frequency)
gamma rays, x-rays, UV, visible, infrared, radar, radio
99
New cards
calculating frequency of a wave
v = wave cycles/time
100
New cards
wavelength and frequency are (inversely proportional or proportional)
inversely proportional