RBC pathology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
polycthemia
thrombosis (high RBC)
male hemoglobin adn female
male: 13.8 - 17.2
Female: 12.1-15.1
hematocrit
Fraction or % of blood that is packed with RBCs
males; 40-52%
Female; 38-48%
hematopoiesis
production of new blood cells
stem cell in bone marrow called hemocytoblasts
growth factors stim differentiation into
RBC
WBC
platelets
Erythopoiesis
lose nucleus and the reticulocyte is released into blood
persist foe 24 hours, loss of cytoplasmic RNA, mature RBC
remains in circulation for 110-120 days before removed by macrophages in spleen
homeostatic control of RBC in blood
decreased blood oxygen (from low RBC) → kidney makes erytopoietin → stims RBC production to get to set point
fate of old damaged RBC
globin → amino acids
heme → iron recycle, converted into biliruibin (yellow pigment)
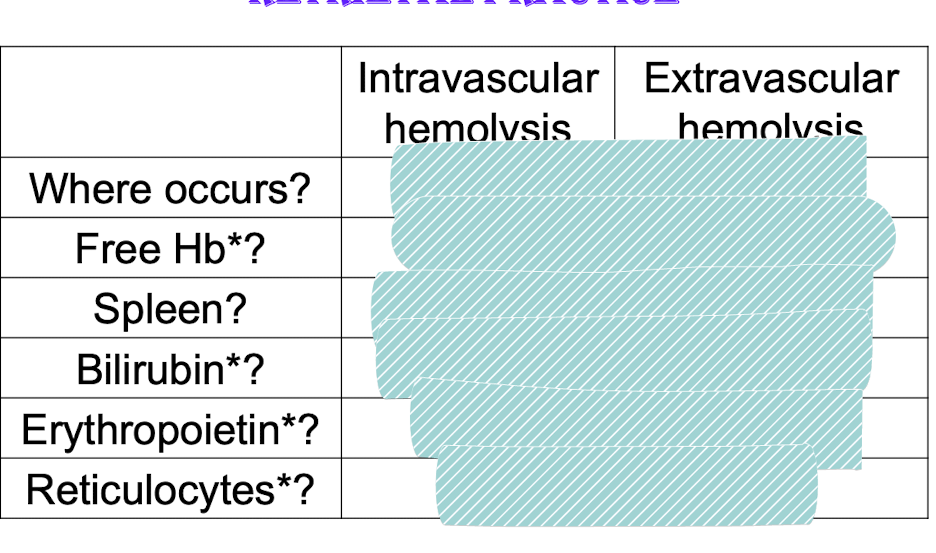
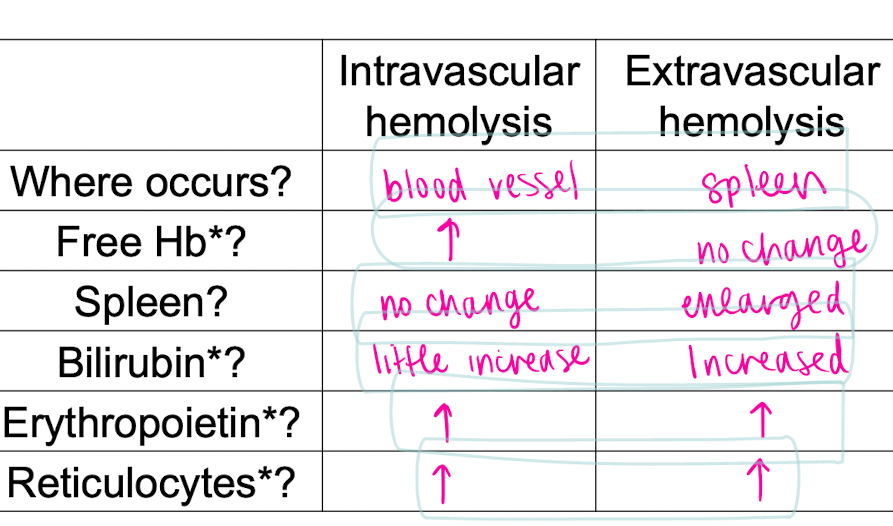
two main hemolysis (hemolytic anemia)_
Red cell membrane is damaged and cell bursts in blood vessels: intravascular hemolysis (hemoglobinemia, hemoglobinuria, loss of iron)
mechanical forces
toxins
Red cell defective and phagocytized by macrophages in spleen
Extravascular hemolysis consequences
too many cells trapped in spleen:
splenomegaly
hemolytic anemia
hyperbiliruibinemia
deposits in tissue → jaundice
to liver: high level in bile → gallstones
hereditary spherocytosis pathogensis
autosomal dominant
mutation in cytoskeletal proteins
Band 3
ankyrin
spectrin
the link between cytoskeleton and bilayer weakens
unsupported areas of lipid bilayer lost “blebs”
lose more membrane than cytosol
Decrease in surface to volumer ratio
trapped and destoryed in spleen
smaller
spherical
dont deform
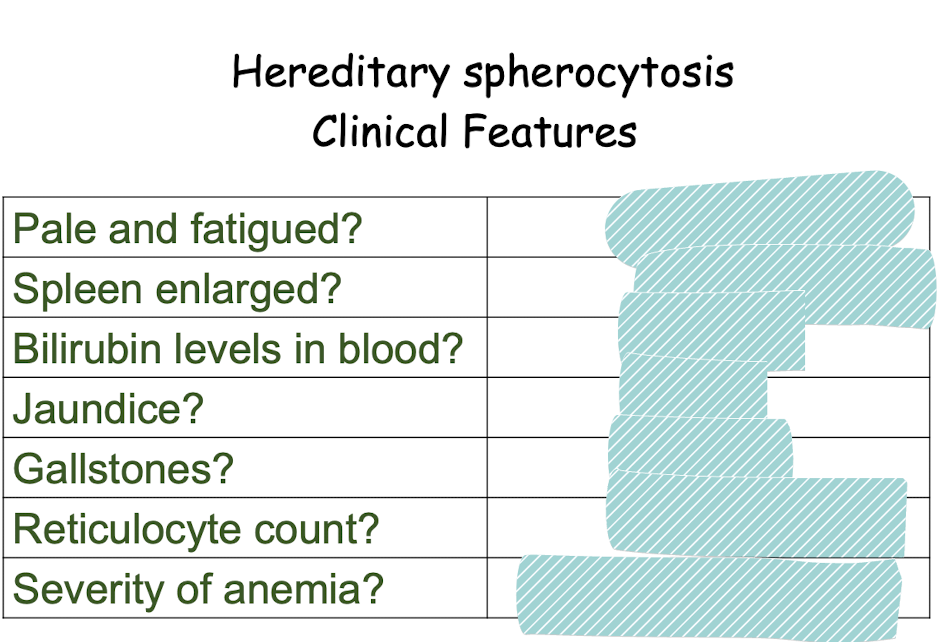
yes anemic
yes cna be huge
elevated
yes
yes
elevated
subclinical to severe
how can you tell if someone has hereditary spherocytosis
do a peripheral blood smear to look for spherocytes
no zone of central pallor
variation in size with many small RBC
hereditary spherocytosis treatment
splenectomy
+
reduce RBC destruction and correct anemia
-
risk of infection (immune organ)
pathogenesis of sickle cell anemia
point mutation in gene for B globin chain of hemoglobin
sickle:
2 mutated B globin,
2 alpha globin (hemoglobin S)
normal
2B globin
heme (fe)
hemoglobin A (HbA): 96
genetics of sickle cell anemia
homozygous: both mutated alleles
no HbA
mostly HbS
disease
hetero
60% HbA
40% HbS
inhereited in recessive pattern
reversible sickling
healthy: oxyhemoglobin S → biconcave
Deoxyhemoglobin S in RBC → HbS polymerizes → reversible sickling
factors affect sickling of RBC
oxygen tnesion
presence of other forms of hemoglobin (HbF (fetal) prevent polymerization: 5-6 months to switch from HbF to HbA
conc of HbS in RBC
dehydration promotes sickling
Sluggish blood flow
longer time in capillaries → more time to sickle in microvasculature
esp spleen and bone marrow, and with inflammation
Consequences of sickle
chronic hemolytic anemia (mod to severe) → both extra and intravascular → 20 day lifespan of RBC
Episdoic pain crises (vasoocclusive crisis) associated with ischemic tissue damage
spontaneosuly
precipitating stimulus →
slows down flow
increase conc of HbS
signs/sympt of sickle cell anemia
fatigue palllor
low hemoglobin levels
elevated erythropoitein levels
elevated reiculocytees
elevated bilirubin → jaundice and gallstones
how does thalassemia differ from sickel cell anemia
thess
Mutation that causes the amount of a globin or B globin chain to bre reduced or absent
minor to intermed to major
sickle
mutation in B globin causing HbS
Sc trait
Sc anemia
pathogeneis of anemia from B thalassemia
reduced synthesis of B globin
inadequate HbA formation
RBC less hemoglobin
Excess unpaired a globin in erythroid percurors causes hemoglobin to aggregate and precipitate → membrane damage
extravasvular hemolysis and apopotsis of precursors in bone marrow
b thalassemia peripheral blood smer
pale cells (hypochromic) small cells, microcystic?
general manifestations of b thalasassemia anemia
reduced hemoglobin → less O2
tonf of erythopoitein
hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, skeleton abornamliites
skeletal: marrow hyperplasia and expansion
frontal bossing
b thalassemia treatment options
bone marrow transplant
blood transfusion thruout life
req for surival
iron overload and failure and death: prevented by ion chelators (excrete via kidney)
B thalassemia minor vs major
minor:
target cells
mild microcytic
hypochromic anemia
asymptomatic
Anemias of diminished erythhropoiesis
inadequate nutrinets
iron
folic acid
vitamin B12
Bone marrow failure (aplastic anemia)
systemic inflammation (chronic disease)
bone marrow infiltration by tumor or inflammatory cells
peripheral blood smear of iron deficient anemia
hypochromatic, microcytic due to decreased hb production
main causes of iron deficiency
Chronic blood loss
GI tract
uterus
Increased requirement
pregnancy
inadequate iron intake
dietary insufficiency is not common in uS
general intestinal malabsorption
folate and vitamin B12 anemia causes ___? what is its pathogenesis
megaloblastic anemia
big cells
Erythroid progenitor
Lacks either folate or B12
Insufficent DNA synthesis and cel division
Unimpaired RNA and protein synthesis
macro-ovalocytes
megaloblastic anemia blood smear
hypersegmented nuclei
large hyperchromic cells
what causes glossitis: what is it?
nutritional deficiencies, such as folic acid, vitamin B12, iron deificency
inflammation and atrophy of lingual papillae
vitamin B12 deficiency consequncies
nerve demyelination in spinal cord
numbness. tingling, burning in hands and feet
loss of position sense
unsteady gait
megaloblastic anemia reversible, neurological problems irreversible
main causes of folic acid deficiecy
decreased diet intake
destoryed by cooking
stores only last few weeks
chronic alcoholism or liver diseae
folate stored in liver
increased req (preg)
MAlabsorption (celiac)
drug induced
vitamin B12 deficiency caues
Not diet unless vegetarian or vegan
meat, fish, eggs
malabsorption
loss of intrinisc factor
pernicious anemia (autoimmune to parietal cells)
loss of acid and pepsin to release vitamin B12
loss of IF: absorption