GP- red blood cells
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
no, it is a condition
is anemia a disease?
it can be...
a reduction in the total RBC count
a reduction in the packed cell volume
a reduction in hemoglobin concentration
what is anemia?
oxygen carrying capacity and delivery to tissue
the order of consequences are as follows:
1. decrease in PVC, Hb, or RBCs
2. reduced ability to carry O2
3. hypoxia in organs and tissues
4. clinical signs of anemia
anemia causes a decrease in _________
work overload
what is the consequence of anemia on the cardiovascular system?
tachypnea, hypoxia
what is the consequence of anemia on the respiratory system?
hematuria, renal damage (only with hemolytic anemia)
what is the consequence of anemia on the urinary system?
jaundice, tissue hypoxia
what are the systemic consequence of anemia?
weakness
exercise intolerance
pale mucous membranes
tachycardia
what are the main clinical signs of anemia?
jaundice, hematuria, hemoglobinuria
hemolytic anemia will cause what clinical signs?
hemolytic anemia
if a patient is demonstrating these signs:
weakness, exercise intolerance, tachycardia, jaundice, hematuria, and hemolobinuria, what type of anemia can we guess it has?
regenerative
if there is a loss of blood (hemorrhage), is this anemia considered regenerative or non-regenerative?
regenerative
is hemolytic anemia considered regenerative or non regenerative?
non regenerative
is the lack of production of RBCs (bone marrow disease) considered regenerative or non regenerative?
bone marrow disease
what is the cause of a nonregenerative anemia?
primary- unknown cause
secondary- tumor, parasite, bacteria, nutritional, renal failure, inflammation, etc
what is the difference between a primary and a secondary bone marrow disease?
iron deficiency
copper deficiency
vitamin B12/folic acid deficiency
what are the types of nutritional bone marrow disease?
because kidneys produce erythropoietin, which is needed for RBC synthesis
why can chronic renal failure cause anemia?
regenerative
because this means that the body is able to compensate for the lost/destroyed RBCs by making more
in which- regenerative or nonregenerative anemia, do we see a high number of reticulocytes?
high; low
high reticulocytes because the body is regenerating the RBCs that are lost/destroyed
low hemoglobin because there are more reticulocytes, which take up more space in the blood than mature RBCs, but still carry the same amount of Hb
in regenerative anemia, we will have a _______ number of reticulocytes and a ______ % of hemoglobin. (high/low)
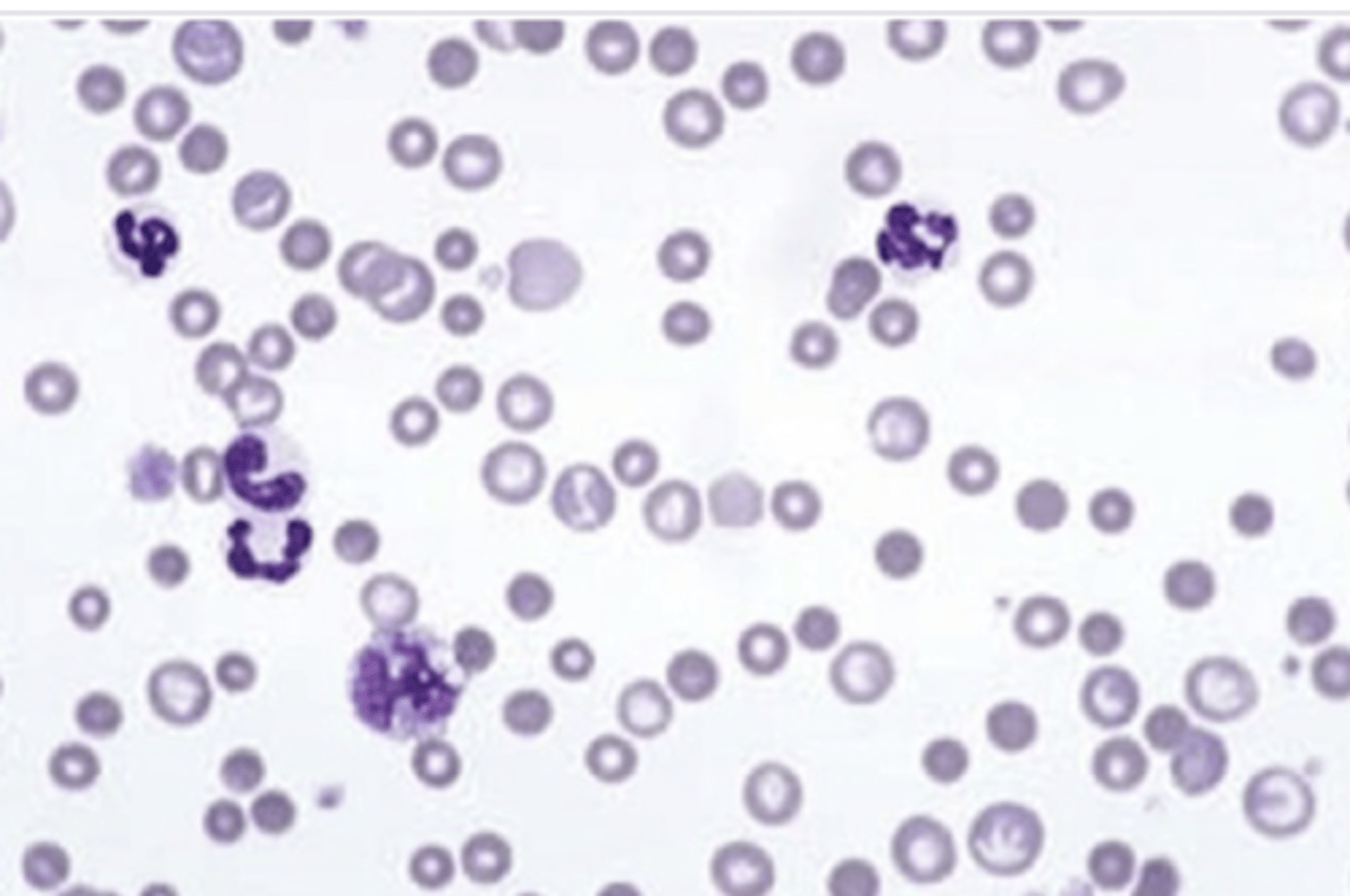
reticulocytes are larger, rounder, and have genetic material
how can we differentiate a mature RBC and a reticulocyte on a blood smear?
non regenerative
because all of the RBCs are mature
is this anemia regenerative or non regenerative? why?
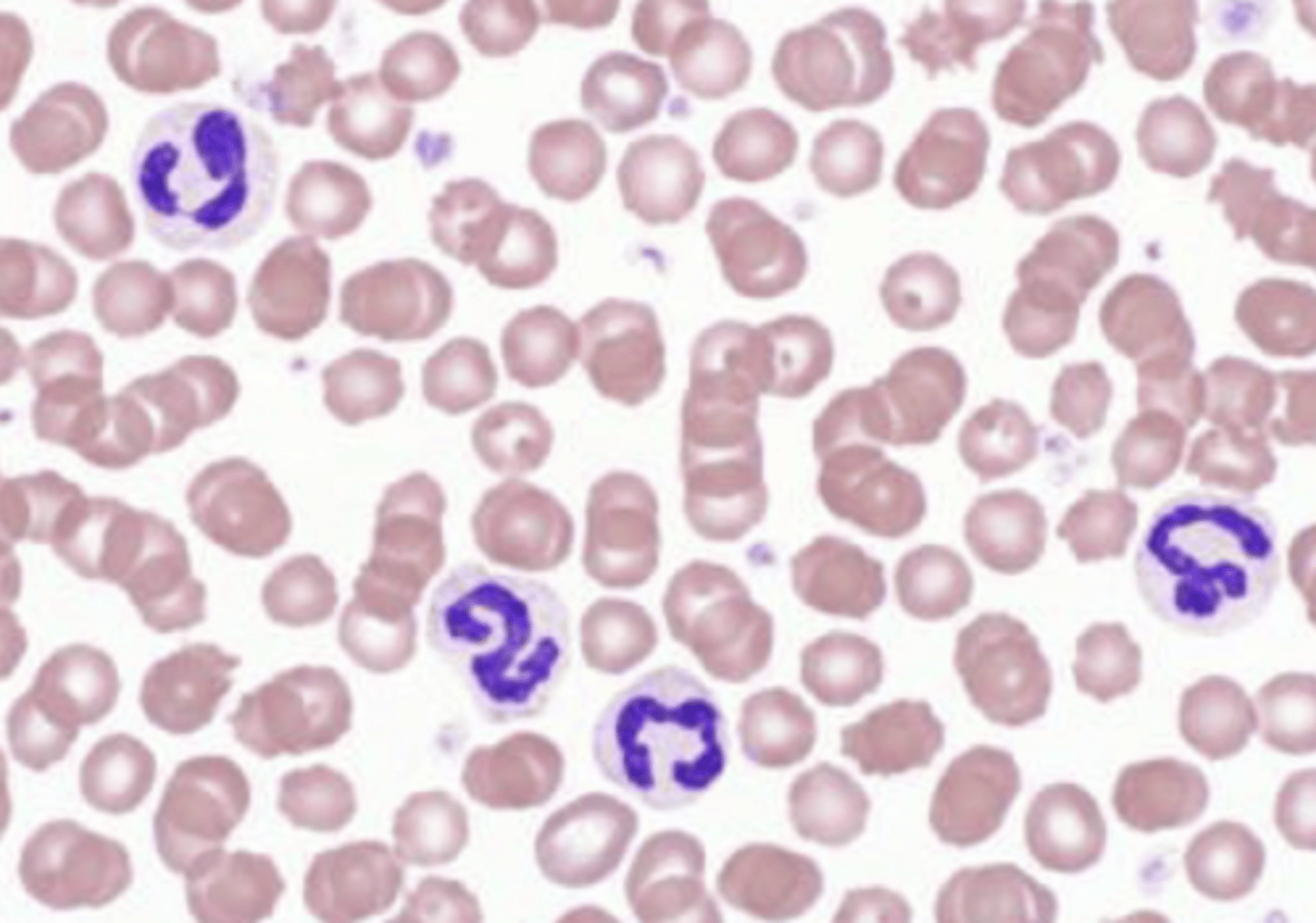
regenerative
because there are both mature RBCs and reticulocytes
is this anemia regenerative or non regenerative? why?
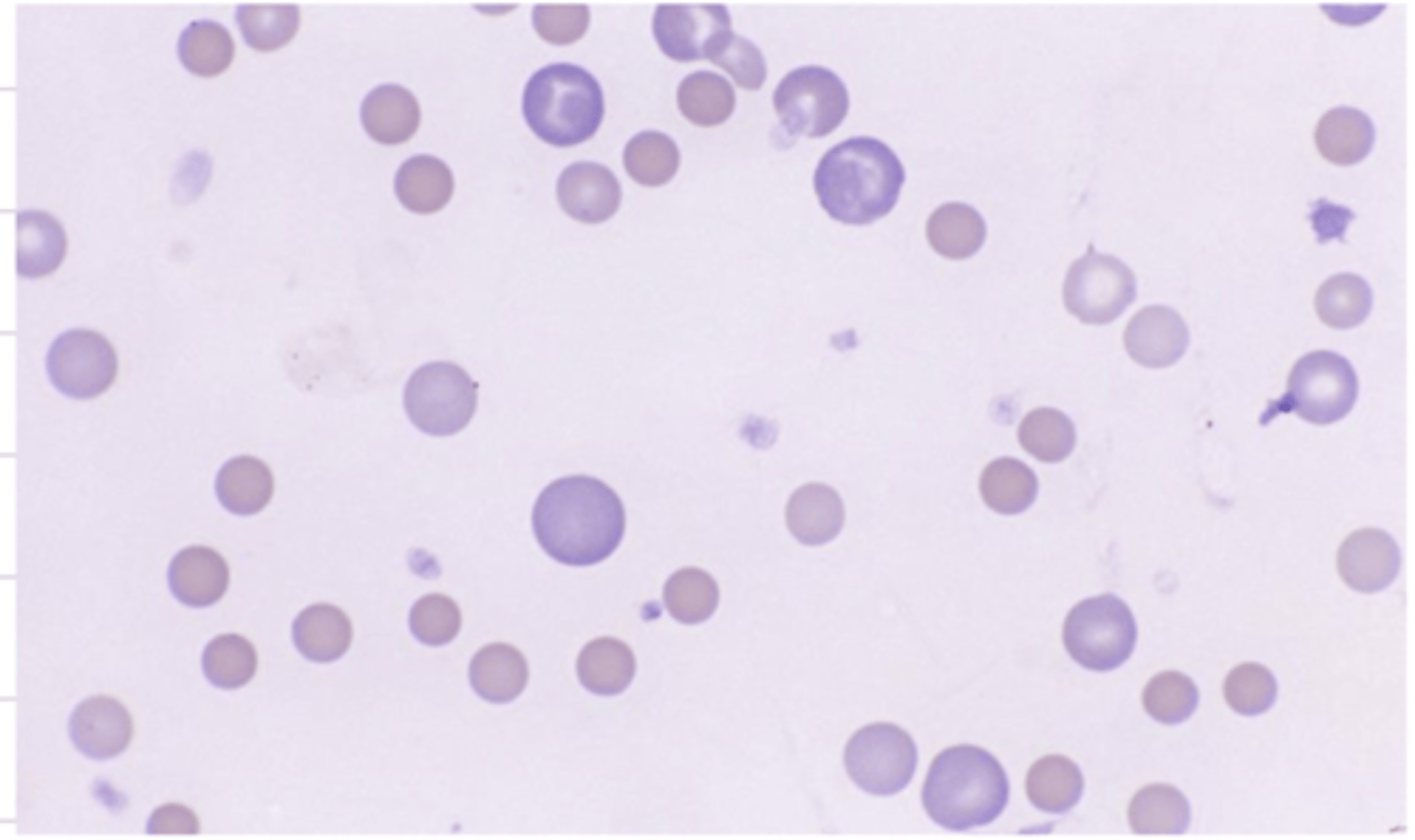
regenerative
we see reticulocytes with genetic material (stained basophilically)
is this anemia regenerative or non regenerative? why?
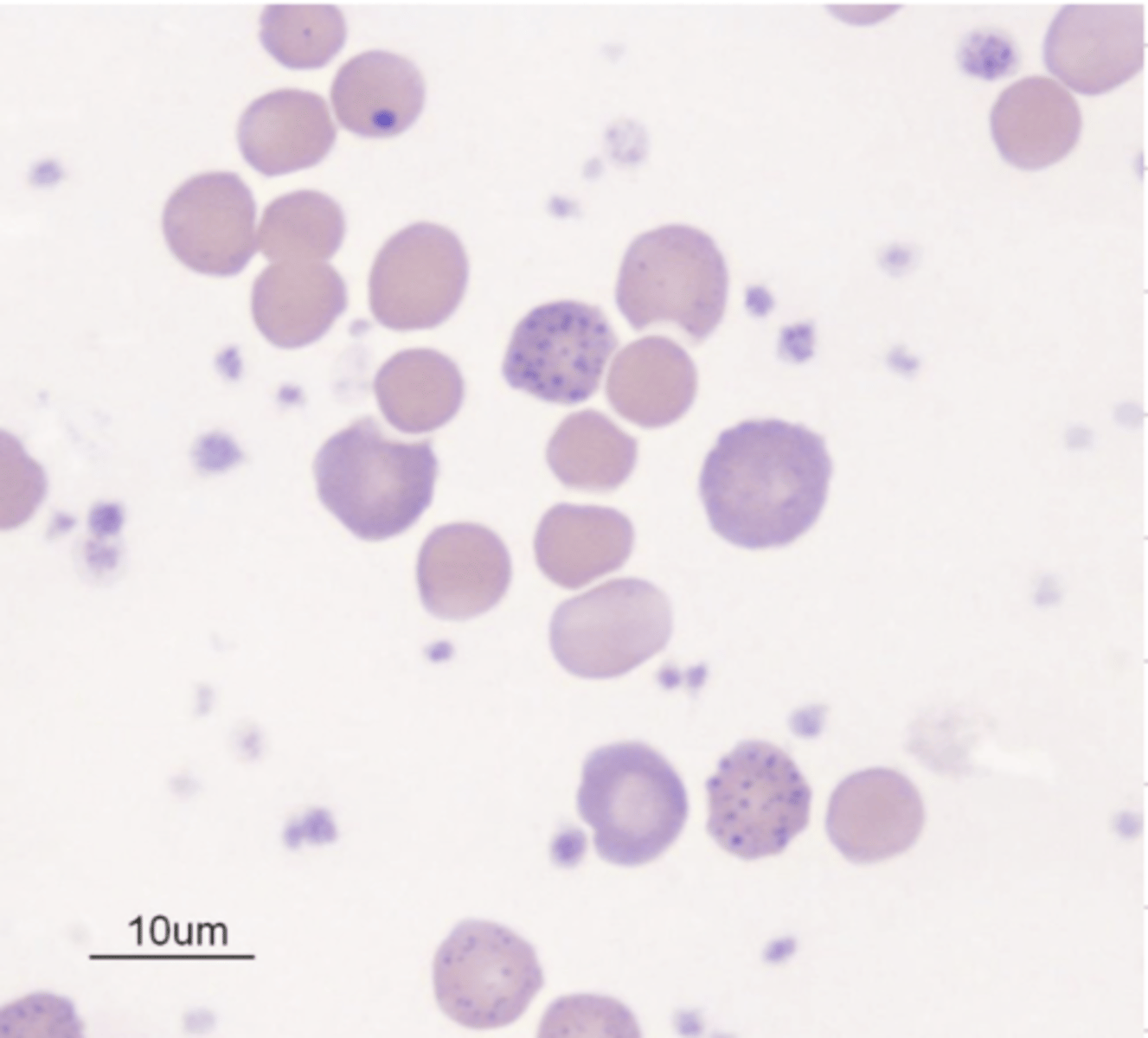
the % of volume taken up by RBCs in the blood
=hematocrit
what is a packed cell volume (PCV)?
the # of RBCs
what is RBC count?
100
Hb concentration is the amount of Hb in ________ml of blood
the Hb content and size of RBCs
in order to specify the TYPE of anemia
RBC indices give us information about...
mean corpuscular volume
the average volume of a RBC
what is MCV?
(Hct/RBC)x10
Hct- hematocrit
how do we calculate mean corpuscular volume?
regenerative
the mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is higher in what type of anemia?
FALSE- bone marrow disease causes non regenerative anemia, which will not have a higher than normal MCV. regenerative anemia has a high MCV because the patient has a higher number of reticulocytes
true or false- if in a blood analysis the MCV is high, we can guess that the anemia is due to a bone marrow disease
the average amount of hemoglobin per RBC
what does the Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) measure?
(Hb/RBC)x 10
how is the mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) calculated?
iron deficiency anemia
if the mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) is low, what type of anemia does this indicate?
the average concentration of Hb per unit volume of RBCs
what is mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)?
Regenerative
this is because in regen. anemia, the reticulocytes are larger, so there are less, but they can carry the same amount of Hb as the mature RBCs- if there are less, the total concentration of Hb will be lower
the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is lower in ________anemia
(Hb/Hct)x 100
Hb- hemoglobin
Hct- hematocrit
how is the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) calculated?
macrocytic
if there is a high MCV, we call this _______ anemia
normocytic
exceptions:
iron deficiency anemia- micro
vit B12 deficiency anemia- macro
is nonregenerative anemia normocytic, macrocytic, or microcytic?
iron deficiency anemia and copper deficiency anemia
what type of anemia is microcytic (low MCV)?
any regenerative anemias
vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
what type of anemia is macrocytic (high MCV)?
the RBCs are normal size
nonregenerative anemia
what does normocytic mean? what type of anemia does this describe?
they can carry the same
which can carry a greater amount of hemoglobin- mature RBCs or reticulocytes?
regenerative anemia
which type of anemia will we have a low MCHC?
the RBCs have less color
regenerative anemia and iron deficiency anemia
what does hypochromic anemia mean? what type of anemia does this correlate do?
the MCHC is normal
does nonregenerative anemia have a high or low MCHC?
true
(exception- iron deficiency anemia is hypochromic)
true or false- nonregenerative anemia is normochromic
high; low
regenerative anemia has a ________ MCV and a ______ MCHC
normal; normal
(except vit B12 deficiency, which is macrocytic and iron deficiency, which is hypochromic)
nonregenerative anemia has a ________ MCV and a ______ MCHC
regenerative
if a blood analysis shows a high MCV and a low MCHC, can we say it is regenerative or nonregenerative anemia?
nonregenerative:
normocytic- normal sized RBCs (no reticulocytes)
normochromic
nonregenerative or regenerative? why?
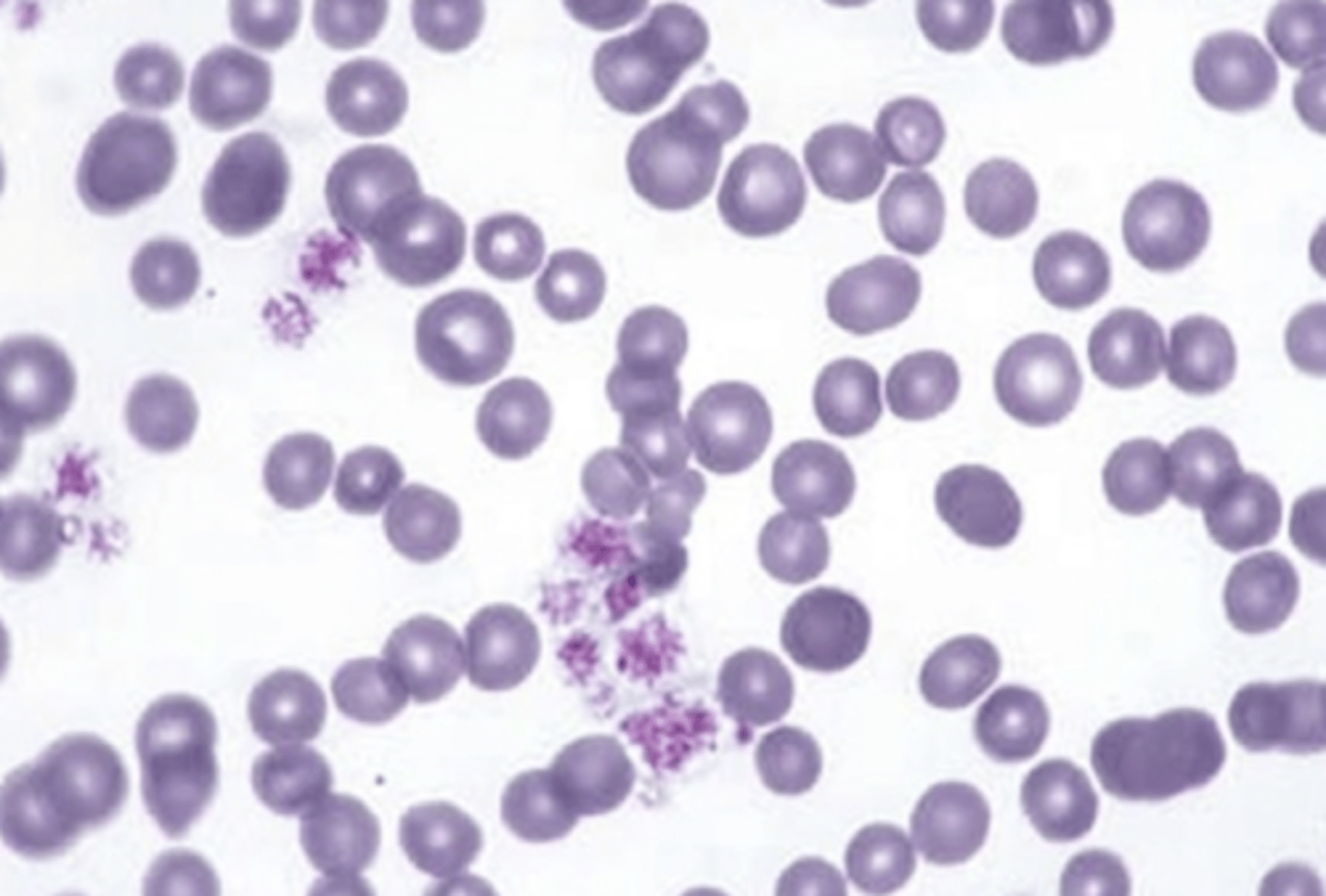
regenerative:
macrocytic- bigger cells (reticulocytes)
hypochromic- paler cells
nonregenerative or regenerative? why?
it measures how varied the RBC size is
what does Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) measure?
that the RBCs vary a lot in size
(high RDW)
what does anisocytosis mean?
anisocytosis
if we have a high RDW, we say that the anemia has a high....
(standard deviation of volume/MCV)x 100
how is the red blood cell distribution width (RDW) calculated?
regenerative
what type of anemia has a high anisocytosis?
low
because they have a normal RDW
does nonregenerative anemia have a high or low anisocytosis?
reticulocyte count
the most effective way to measure regeneration in dogs and cats is ______
because they do not have reticulocytes in peripheral blood
why can we not use reticulocyte count to measure regeneration in horses?
3-4 days
+ more days for the peak of the regenerative response
how long does it take after a hemorrhage/loss of blood for the number of reticulocytes to increase?
pre-regenerative anemia
the period in between the hemorrhagic event and the measurable increase of reticulocytes in blood is called....
3-4; several more days
it takes _______ until reticulocytosis is evident on the RBC count, and _____ until the regenerative response peaks
RBC size
color
shape
RBC distribution
RBC inclusions
blood smears provide us with information about...
more color-
reticulocytes have some RNA, which absorb dyes, so regen. anemia can have polychromasia
what is polychromasia?
hemolytic anemia
hemorrhagic anemia
what are the types of regenerative anemia?
a low RBC count because of blood loss
what is hemorrhagic anemia?
low
in hemorrhagic anemia, will we discover a high or low total protein content in the blood analysis?
trauma
digestive- ulcers, neoplasia, parasites
infections
clotting defects
what can be the causes of hemorrhagic anemia?
internal- there is a breakdown of RBCs without the loss of protein and iron; quick regeneration
external- loss of RBCs and proteins (hypoproteinemia); proteins are replaced quicker
what is the difference between internal and external hemorrhagic anemia?
external hemorrhage
hypoproteinemia is caused by...
15-20
with acute hemorrhagic anemia, clinical signs show up when blood loss is ________%
30-40%
with acute hemorrhagic anemia, what percentage of blood needs to be lost in order for it to be life-threatening?
spleen
in horses, 30% of RBCs are stored in the _____
-they do not have reticulocytes in their peripheral blood
-30% of RBCs are stored in the spleen, and sympathetic stimulation (stress, exercise, etc.) induces a false increase in hematocrit
what is important to know about the blood of horses?
horses
greyhounds
in what animals does sympathetic stimulation cause a release of more RBCs, which causes a false increase in hematocrit/PCV?
cats and pregnant animals
what animals have a physiological lower PCV/hematocrit?
hematocrit (PCV)
RBC count
Hb concentration
what 3 tests can give us the information we need to diagnose anemia?
first 24hrs: normal PCV/Hct
after 24hrs: low PCV/Hct, low protein
3 days after: high reticulocytes
7 days after: maximum # of reticulocytes
in a patient with acute hemorrhage, how do test values change over time?
adults- internal bleeding tumors, gastric ulceration
young- parasites, external wounds (rare)
what are the causes of a chronic hemorrhage?
acute
in which- acute or chronic hemorrhagic anemia, do clinical signs appear quicker?
NO
because the body has more time to compensate. for clinical signs to appear, the Hct must be lower than in acute blood loss.
are clinical signs quick to appear in chronic hemorrhagic anemia? why or why not?
chronic
chronic hemorrhage can cause depletion of iron, which will be iron deficiency anemia
in what type of hemorrhagic anemia can it become nonregenerative?
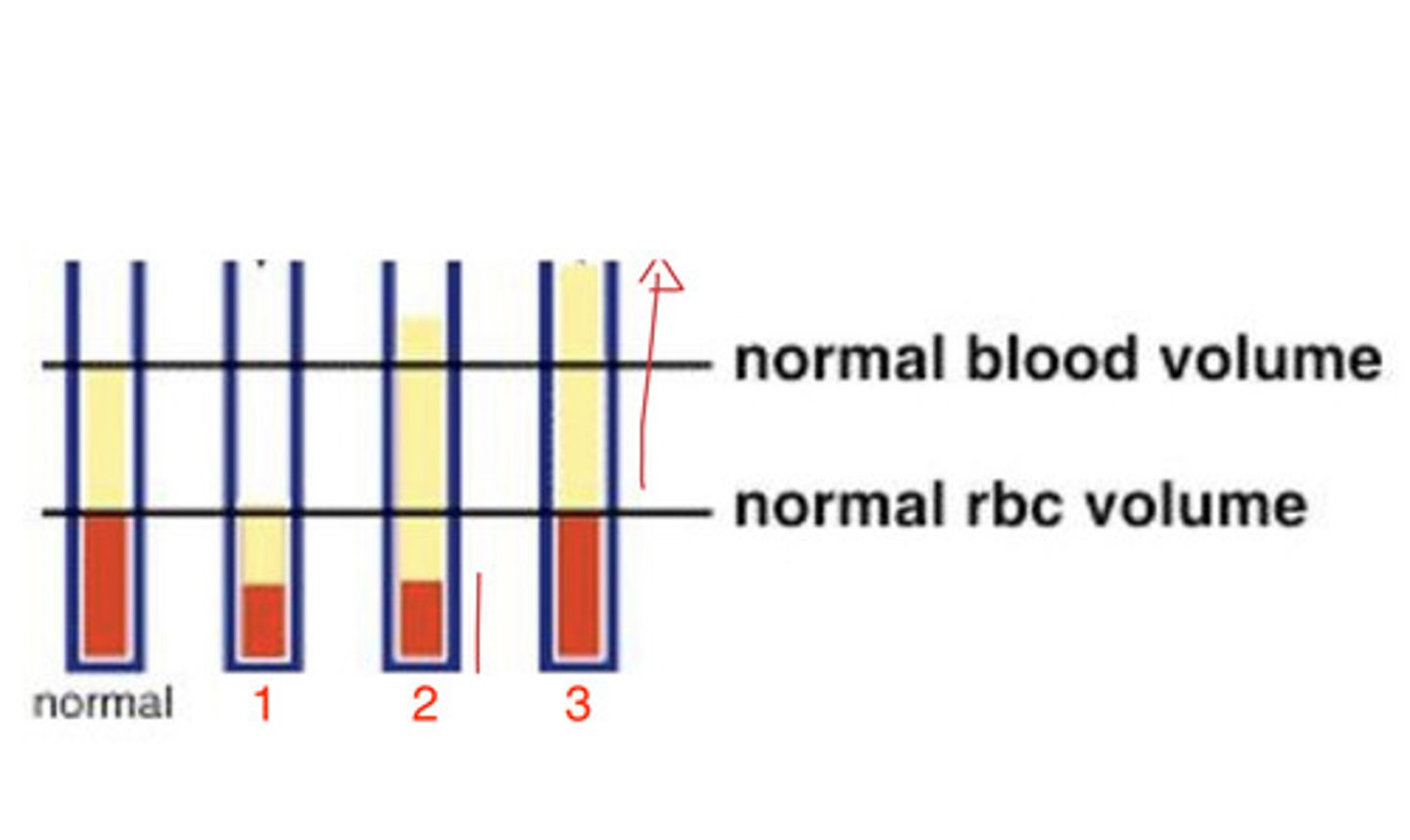
1
which shows acute hemorrhagic anemia?
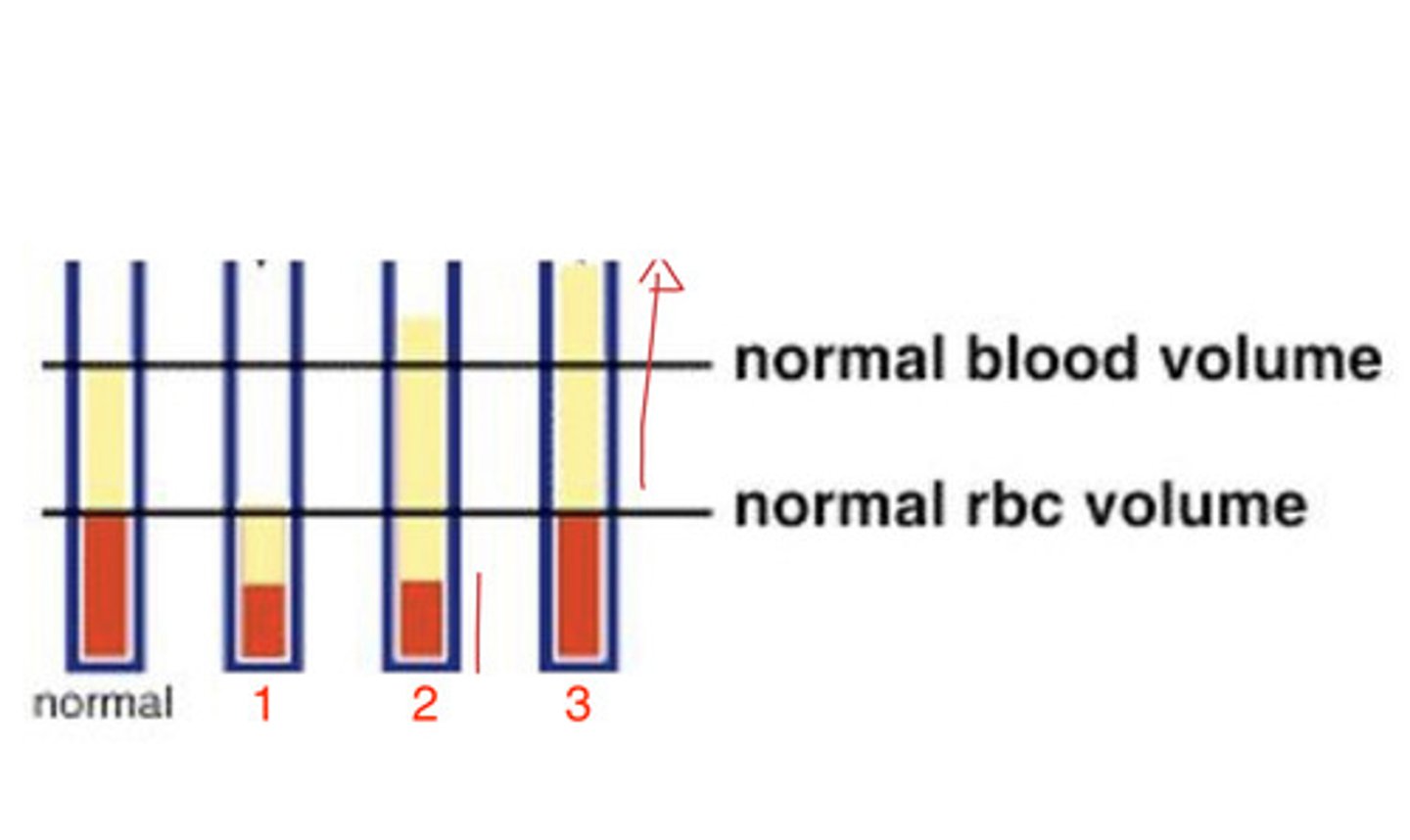
2
low blood, but high plasma bc the body is compensating
which shows chronic hemorrhagic anemia?
nonregenerative
is iron deficiency anemia regenerative or nonregenerative?
anemia due to premature destruction of RBCs
what is hemolytic anemia?
hemolytic
in which type of anemia- hemolytic or hemorrhagic, is the bone marrow regenerative response higher?
if the hemolysis is slow, hematopoiesis can compensate
why might a patient with hemolytic anemia show normal PCV, RBC count, and Hb?
intracorpuscular/intrinsic causes:
RBC inborn defects- congenital and hereditary disorders (rare)
extracorpuscular/extrinsic causes:
immune mediated hemolytic anemia (autoimmune disorder)
infectious (parasites)
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia- mechanical damage
oxidative stress
what are the possible causes of hemolytic anemia?
intravascular hemolytic anemia
if in the hematocrit, the plasma is darker than usual, what does this indicate?
intravascular- hemolysis occurs in the blood vessels; will produce hemoglobinuria
extravascular- hemolysis occurs in macrophages or spleen; will produce bilirubinuria
what is the difference between intravascular and extravascular hemolysis?
intravascular hemolytic anemia
if the animal has hemoglobinuria, we can suspect what type of anemia?
hemoglobinuria
splenomegaly
bilirubinuria
bulirubinemia (jaundice)
hepatomegaly
weakness, tachycardia, tachypnea, pale mucous membranes
what are the clinical signs that an animal with hemolytic anemia presents?
intravascular hemolytic anemia
bc dark red urine indicates hemoglobinuria
urine this color can indicate ______ anemia
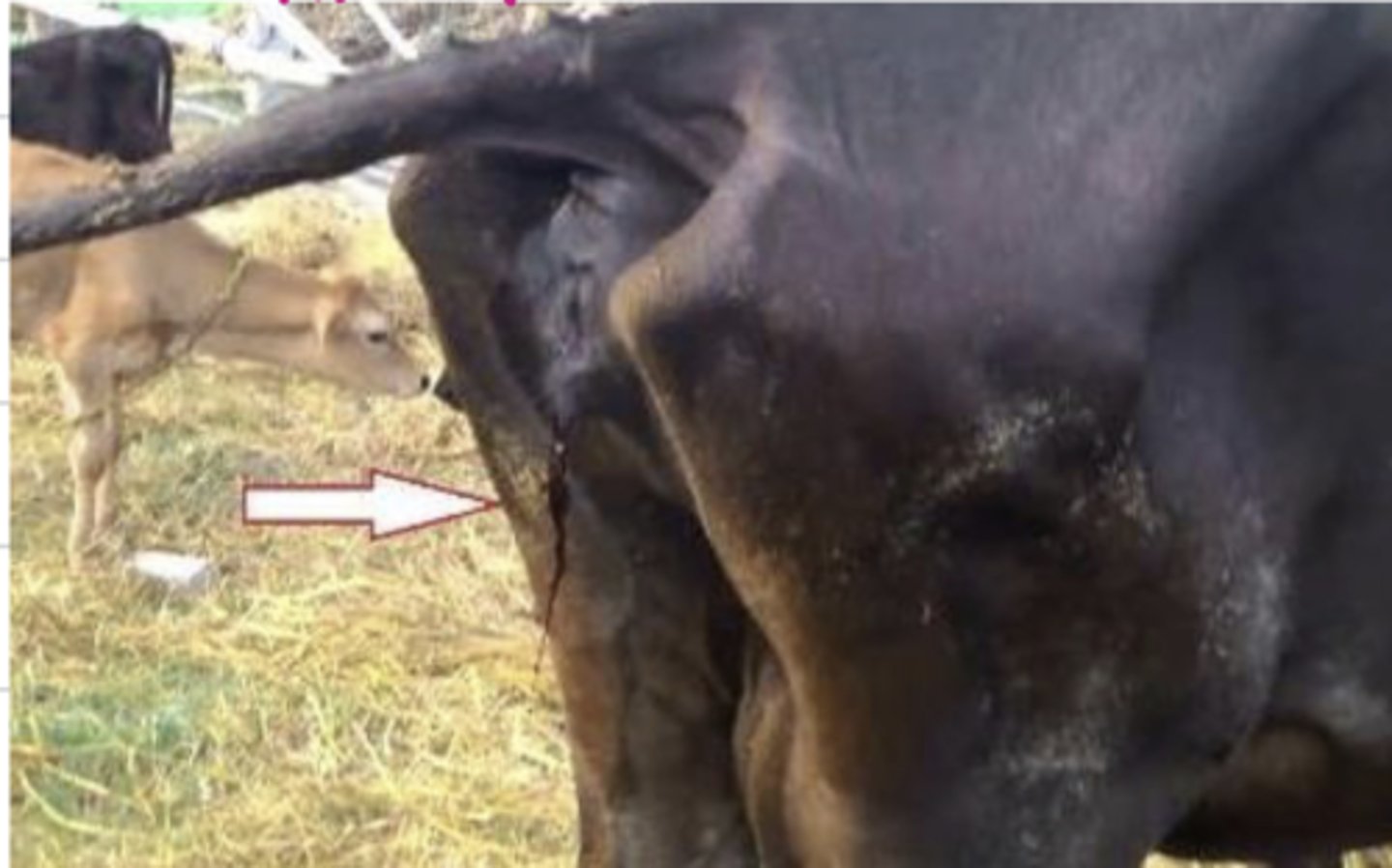
hemolytic anemia
because the destruction of RBCs releases their proteins into the blood
if we have an anemic animal with hyperproteinemia (high total protein in blood), what type of anemia can we guess it has?
extravascular hemolytic anemia
in a urinalysis, we find that an anemic patient has a high bilirubin content. what type of anemia can we diagnose it with?
hemolytic anemia
in what type of anemia is agglutination typical?
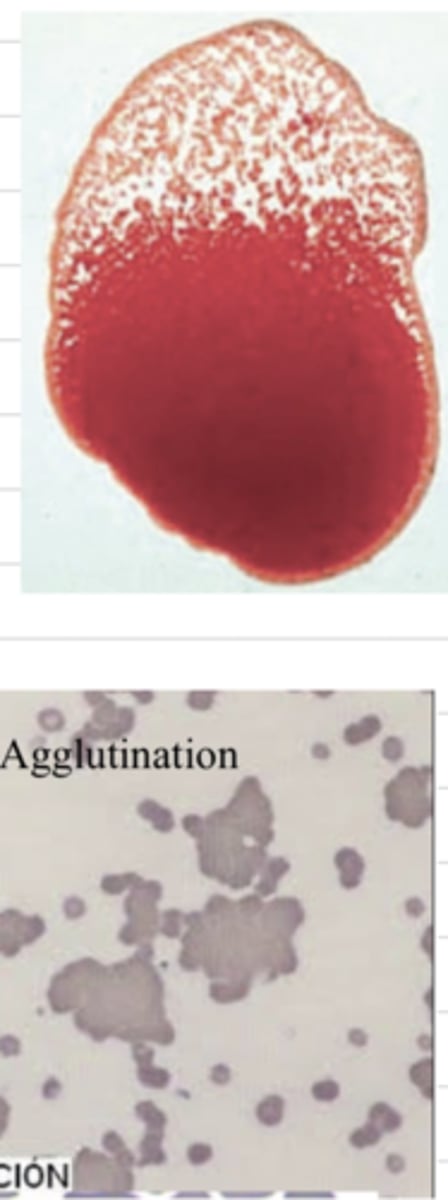
hemolytic anemia
in a hematocrit, we find a low PCV. in a blood smear from a sample of the same patient, we find agglutination, lots of reticulocytes, and spherocytes. what is the diagnosis?
agglutination
high reticulocytes
anisocytosis
abnormal shaped RBCs (spherocytes, fragments)
in a blood smear of a patient with hemolytic anemia, what will we see?