How Markets Work
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How do economic agents make rational decisions?
Consumers → maximise utility (amount of satisfication gained from consuming a good/service)
Firms → maximise profits
What is demand?
Quantity of goods/services that will be bought at a given price and time
How does a Demand Curve look like?
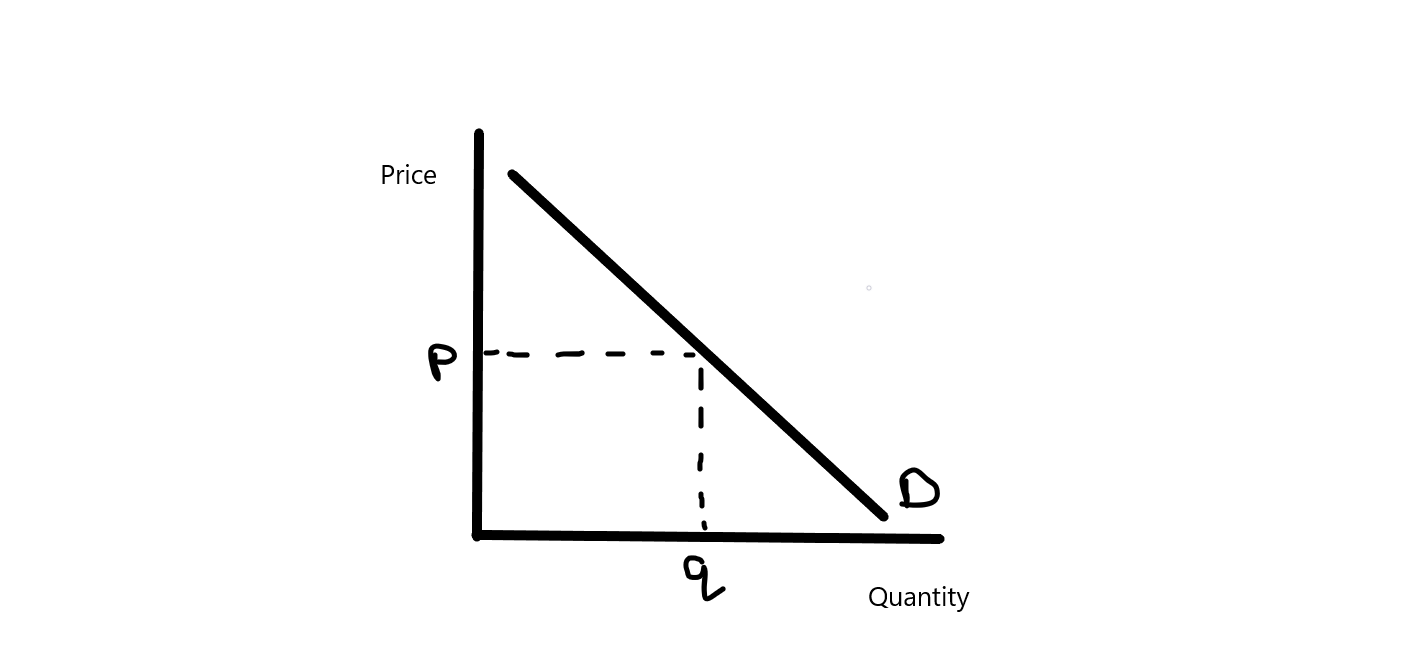
Why does the Demand curve go from the top left to the bottom right?
The law of diminishing utility - the utility gained fron consuming a unit will decrease as more units are consumed (e.g if more pizza eaten, less satisfication gained by a person)
What causes a movement along the demand curve?
Price changes → extension or contraction of demand
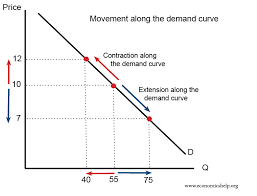
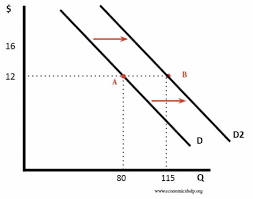
What five factors cause a shift in the demand curve?
Changes in:
Income
Price of other goods
Population
Preferences
Advertising
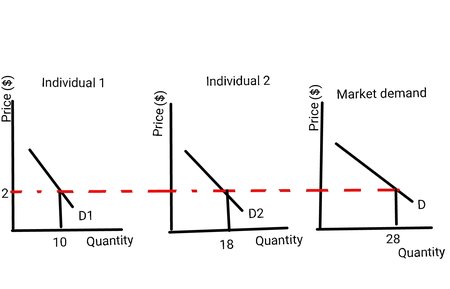
How to find the market demand curve from indivdual demand curves?
Add the firms’ demand curves together to get the market demand curve
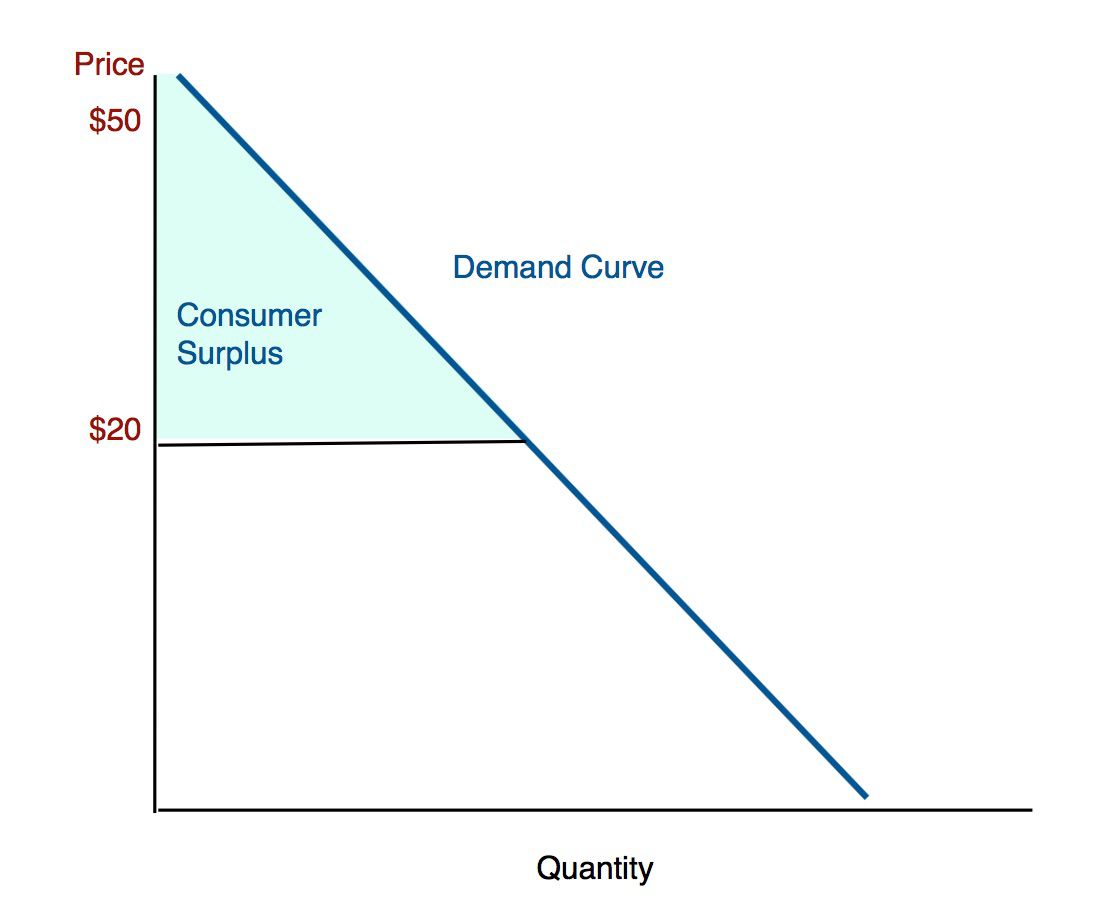
What is consumer surplus?
The difference between the price the consumers are willing to pay + the price they actually pay (for the consumers who got a good deal)
What is supply?
Quantity of goods that sellers are prepared to sell at a given price + time
How does a supply curve look like?
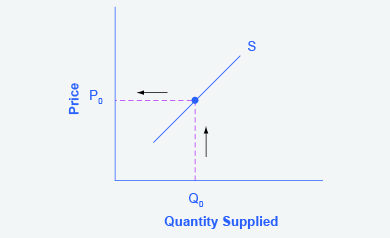
Why does the supply curve go from the bottom left to the top right?
If the price of a good increases, producer are likely to supply more to take advantage of higher prices
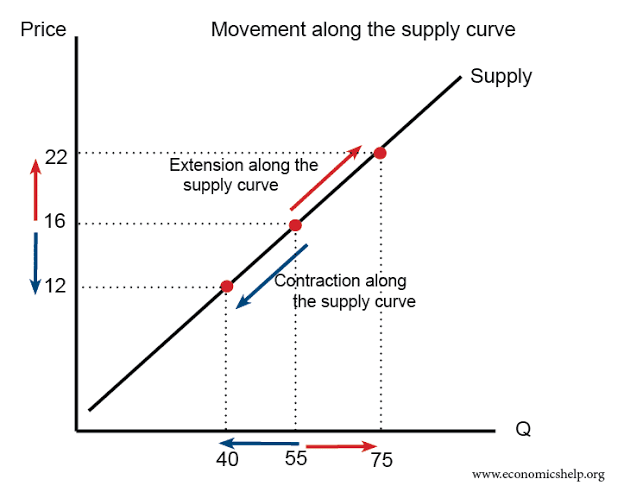
What causes a movement along the supply curve?
Price changes → extension or contraction of supply
What three factors cause a shift in the supply curve?
Changes in:
Cost of production
Tech
Indirect taxes + subsidies
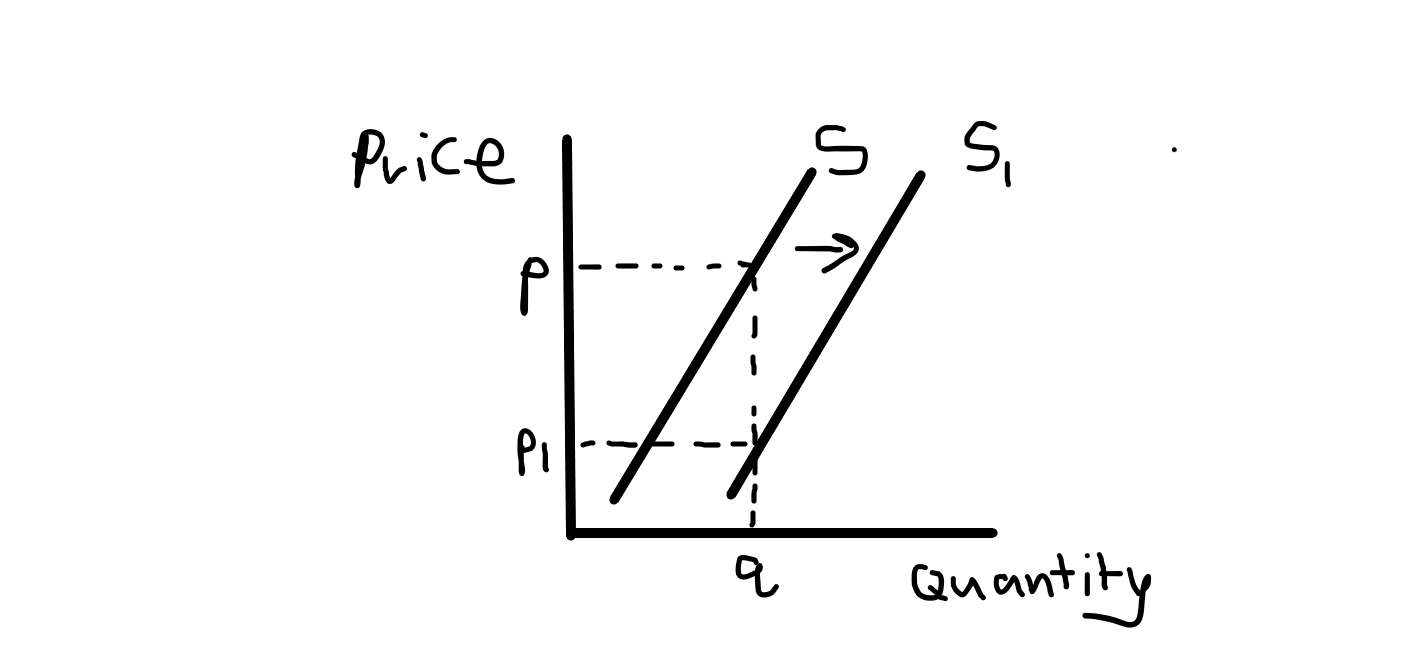
What is producer surplus?
The difference between the price the producers are willing to sell at + the price they actually sell at (for the producer who got a good deal)
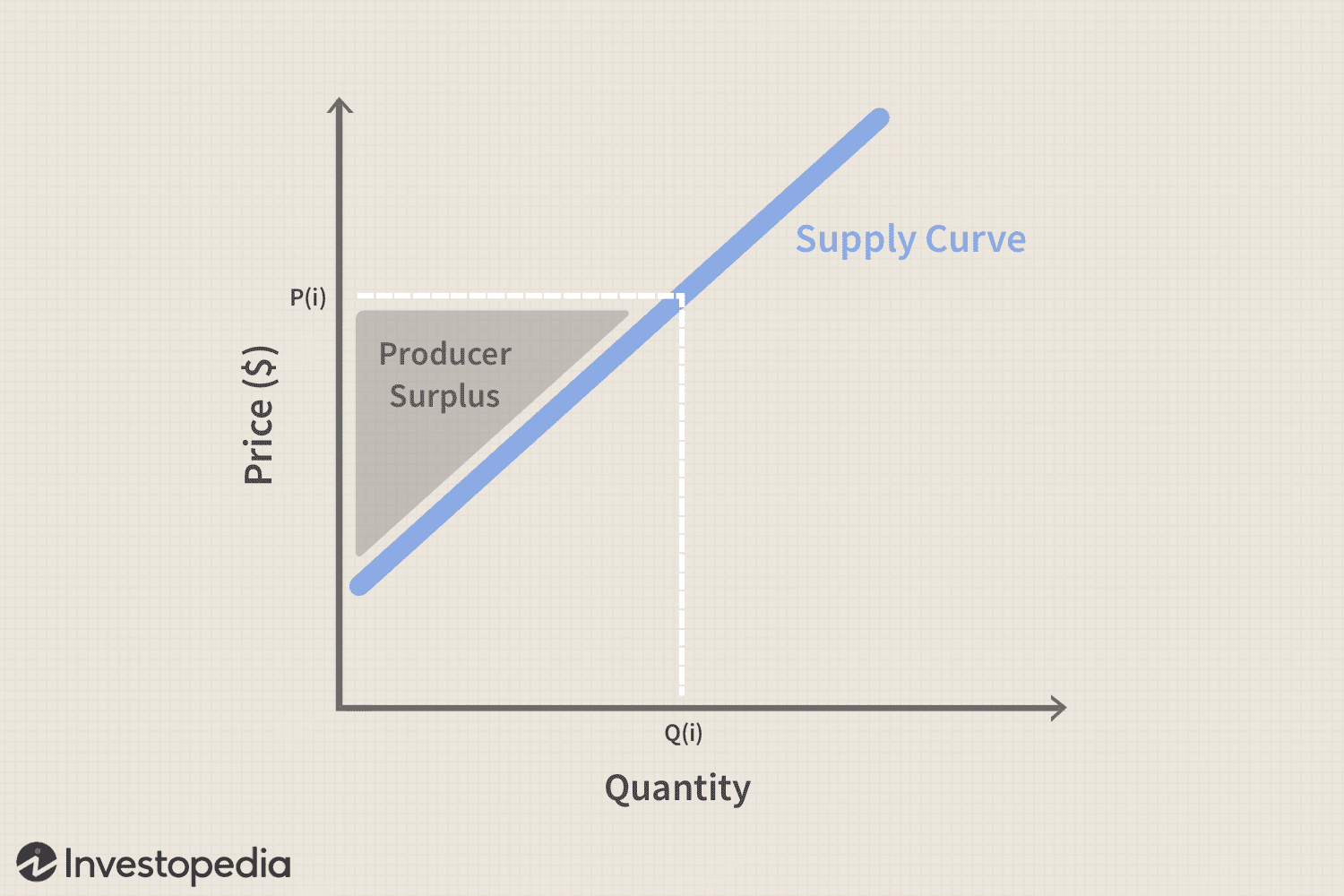
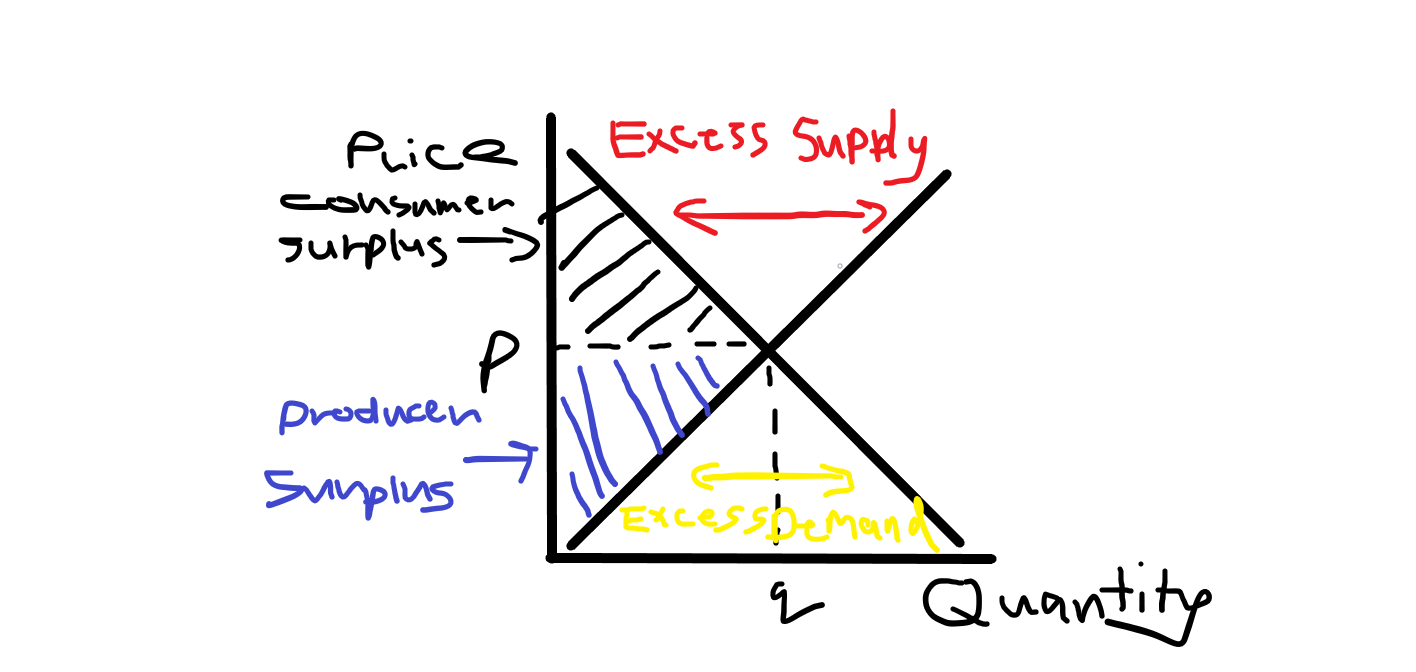
What does the price mechanism graph look like?
Equilbrium price - demand = supply
Excess demand - quantity demanded is greater than supply at the current price
Excess supply - quantity demanded is less than supply at the current price
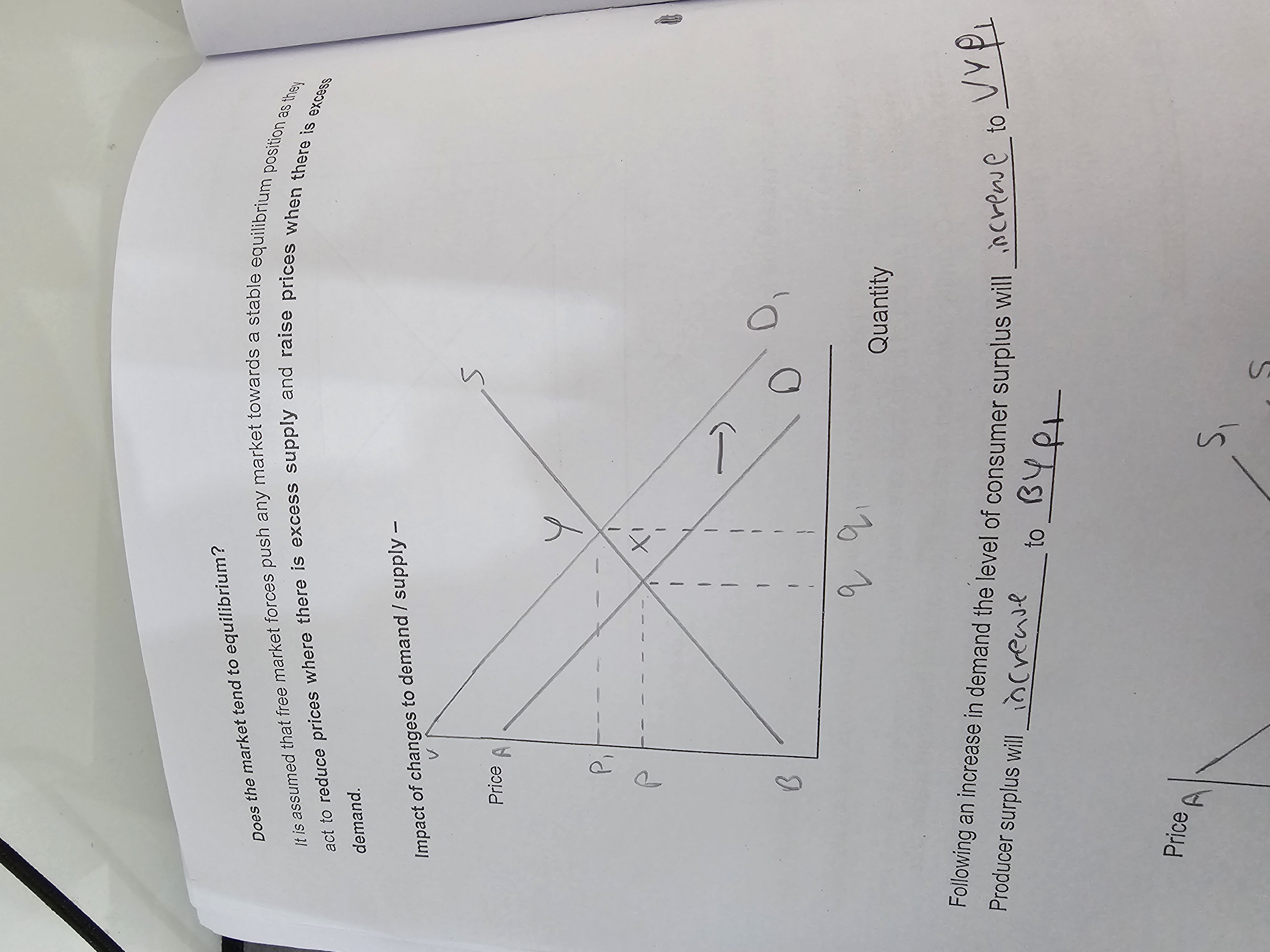
What happens to consumer + producer surplus when there’s an increase in demand?
Consumer surplus increases to UVp1
Producer surplus decreases to BY1
What are the three roles of the price mechanism?
Signaling - signals which goods/services to allocate Factors of Production to
Incentives - rising prices → attracts producers to supply resources
Rationing - spread resources to different good/services
What are two advantages of the price mechanism?
Allocates resources naturally
Efficient over time
What are two disadvantages of the price mechanism?
Buyers/seller don’t have full info
Irrational decisions
Immobile factors of production → can’t allocate resources fast enough
What are the five relationships between markets?
Complements - consumer likely to buy another good when buying one (e.g golf clubs supply increases → golf balls demand increases)
Substitutes - competitors (e.g coke supply increases → pepsi demand decreases)
Derived (Joint) demand - good demanded because it is needed for another product (e.g yoghurt demand increases → milk demand increases)
Composite demand - good needed for multiple products (e.g steel for cars demand increases → steel for boats demand decreases)
Joint supply - one good supplies two different products at the same time(e.g beef demand increases → leather supply increases)
What are three reasons consumers don’t act rationally?
Consideration of other people’s behavior - trends
Habitual behavior - don’t try new stuff even if better/cheaper
Consumer weakness at computation - consumers have difficulty calculating best price