multi engine ch 2a - diesel, prop, and fuel systems
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
type of fuel metering systems
**fuel injection** and **carburetors**
2
New cards
when does induction system icing occur?
it is more common in engines with carburetors
3
New cards
how to prevent carburetor ice
use carburetor heat as recommended in the POH and whenever you suspect that carburetor icing could occur
4
New cards
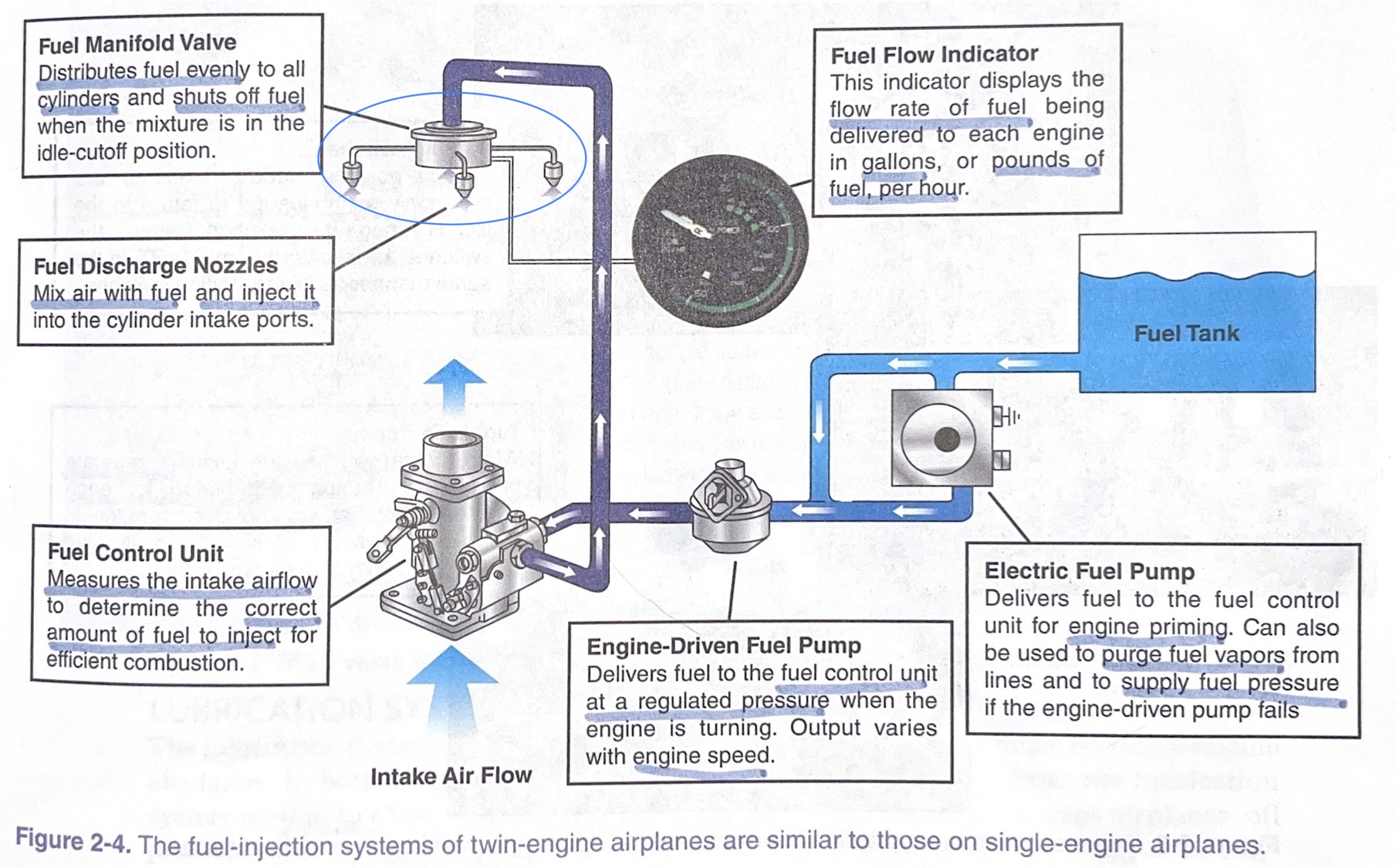
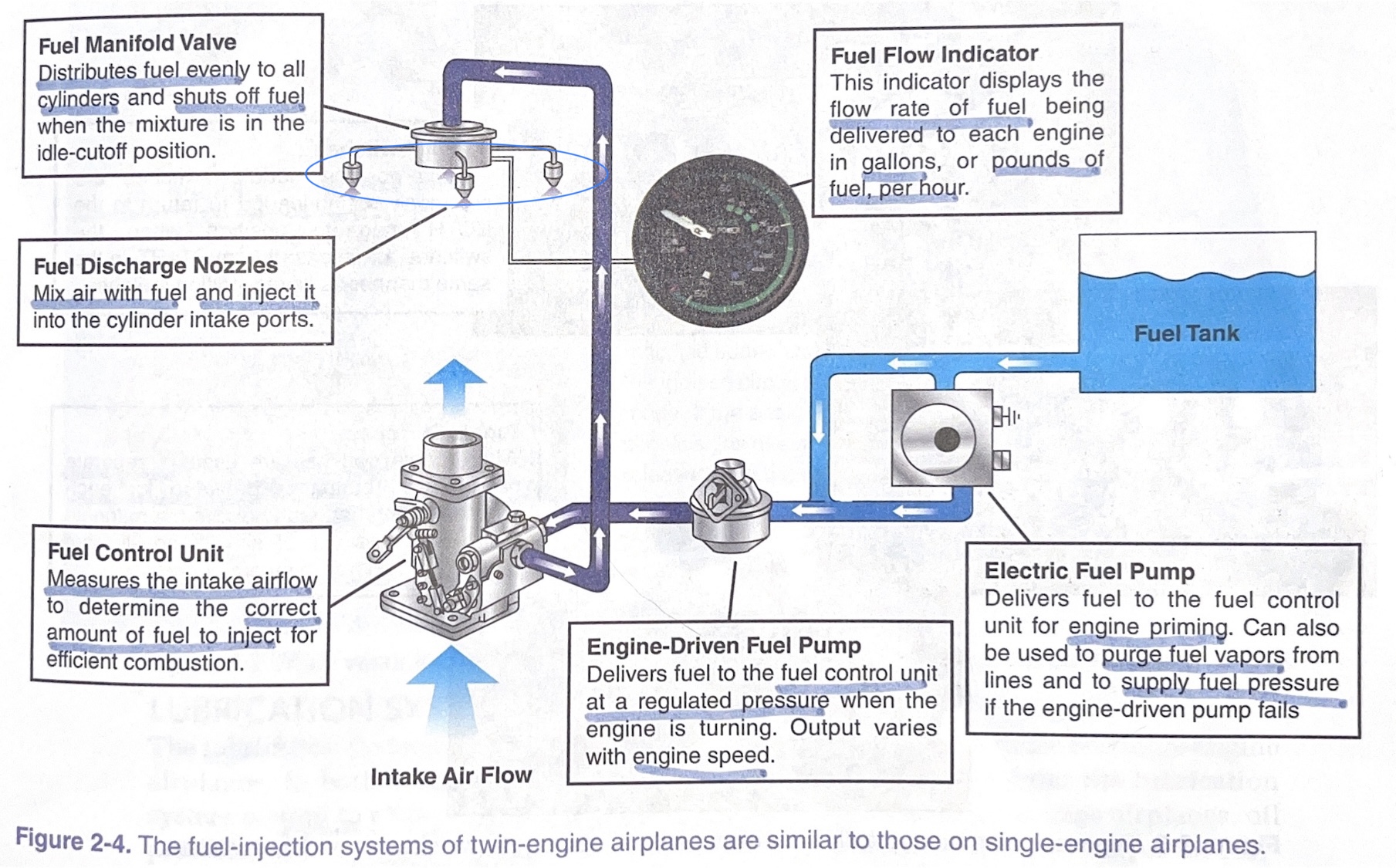
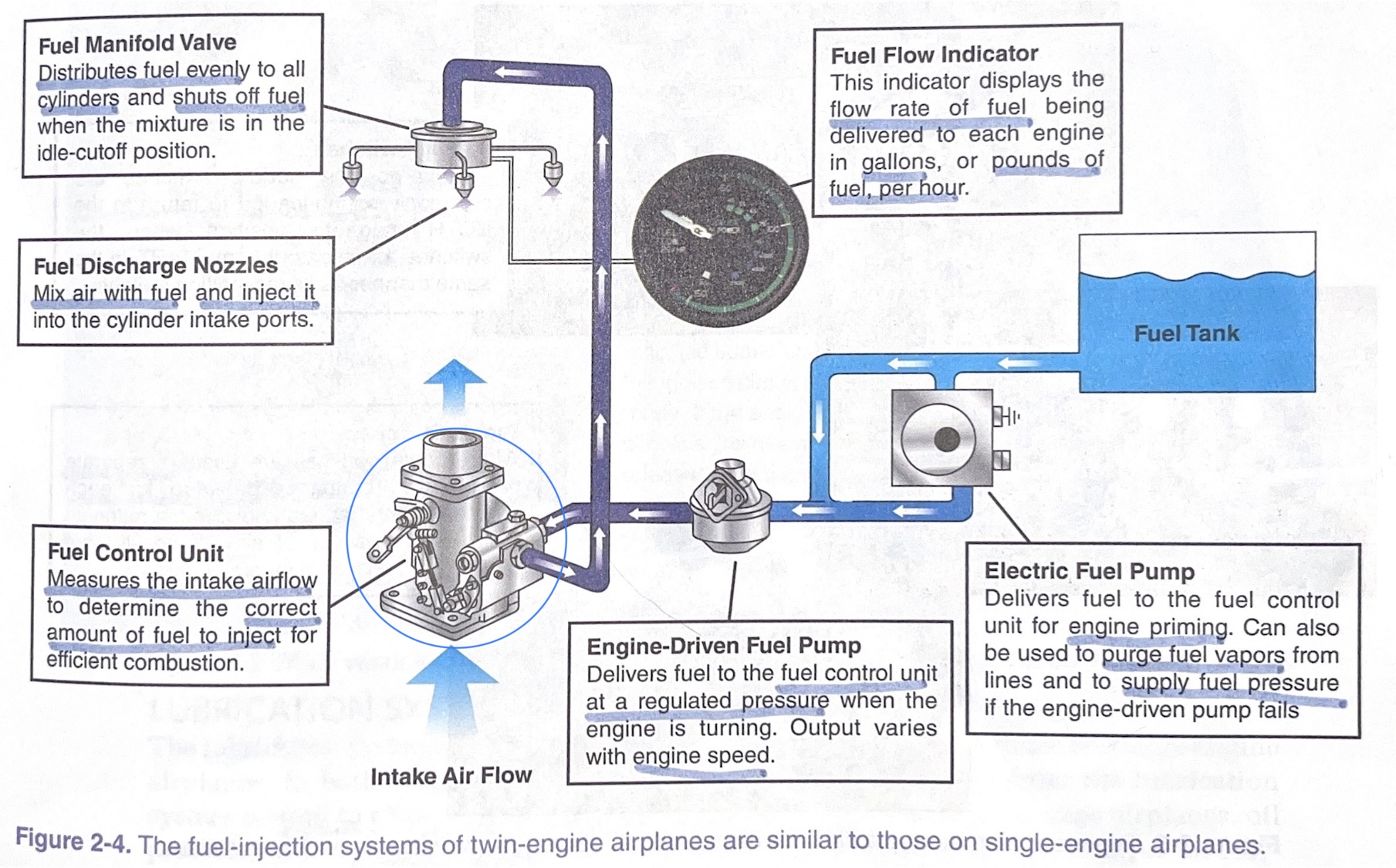
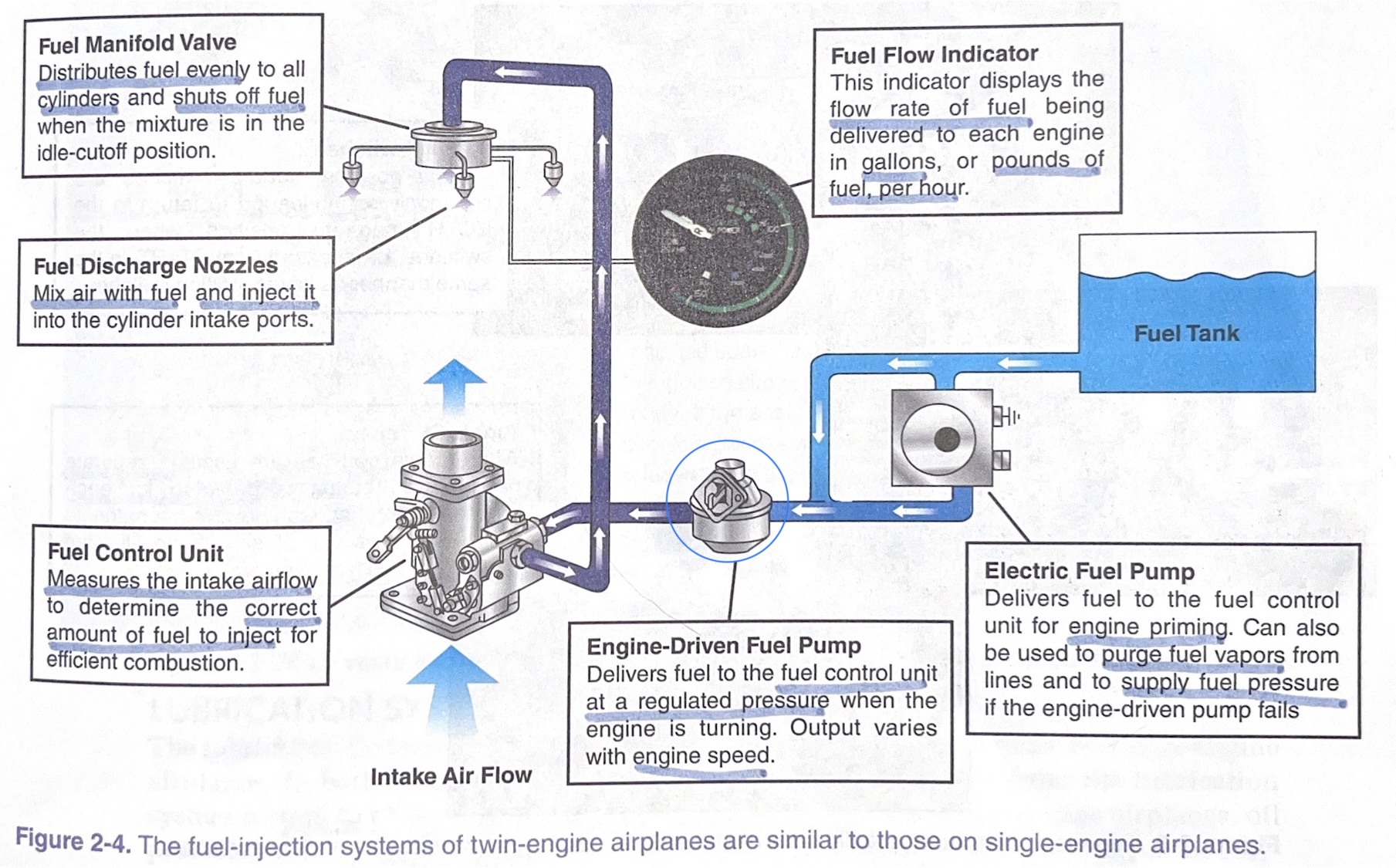
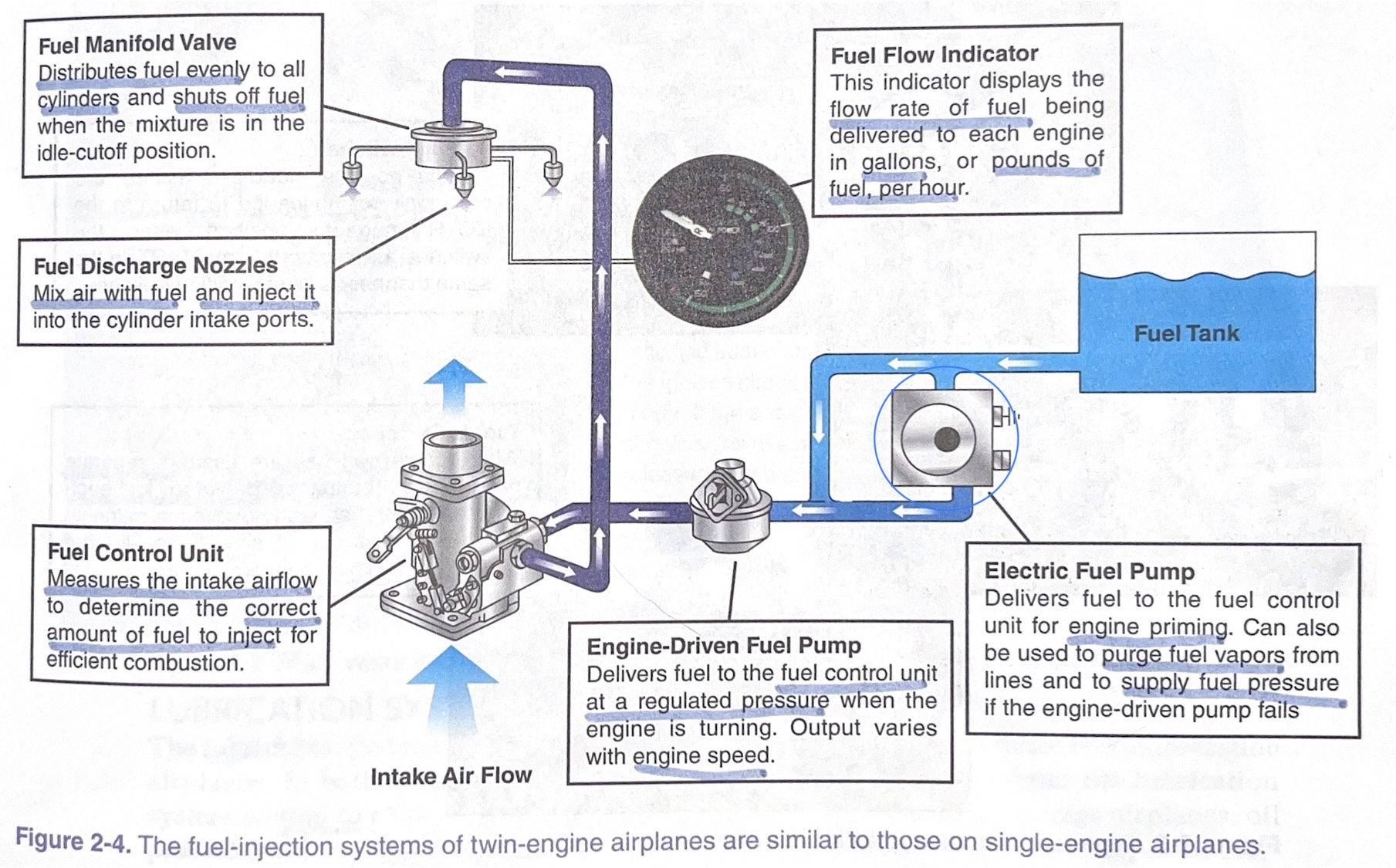
fuel manifold valve
distributes fuel evenly to all cylinders and shuts off fuel when the mixture is in the idle-cutoff position
5
New cards
fuel discharge nozzles
mix air with fuel and inject it into the cylinder intake ports
6
New cards
fuel control unit
measures the intake airflow to determine the correct amount of fuel to inject for efficient combustion
7
New cards
engine-driven fuel pump
* delivers fuel to the %%**FUEL CONTROL UNIT**%% at a regulated pressure when the engine is turning.
* output varies with **engine speed**
* output varies with **engine speed**
8
New cards
electric fuel pump
* delivers fuel to the fuel control unit for %%**ENGINE PRIMING**%%.
* can also be used to purge fuel vapors from lines and to supply fuel pressure if the engine-driven pump fails
* can also be used to purge fuel vapors from lines and to supply fuel pressure if the engine-driven pump fails
9
New cards
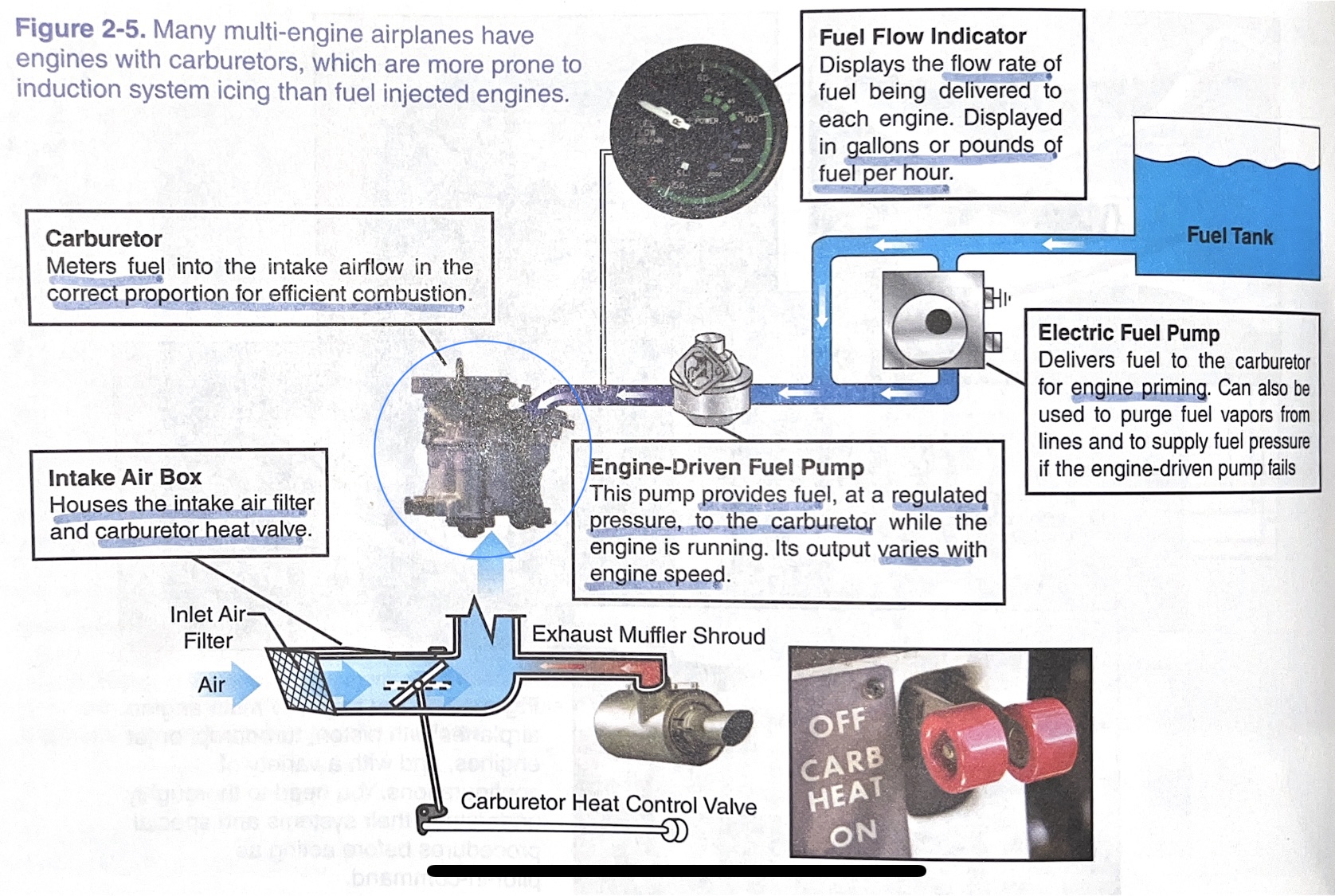
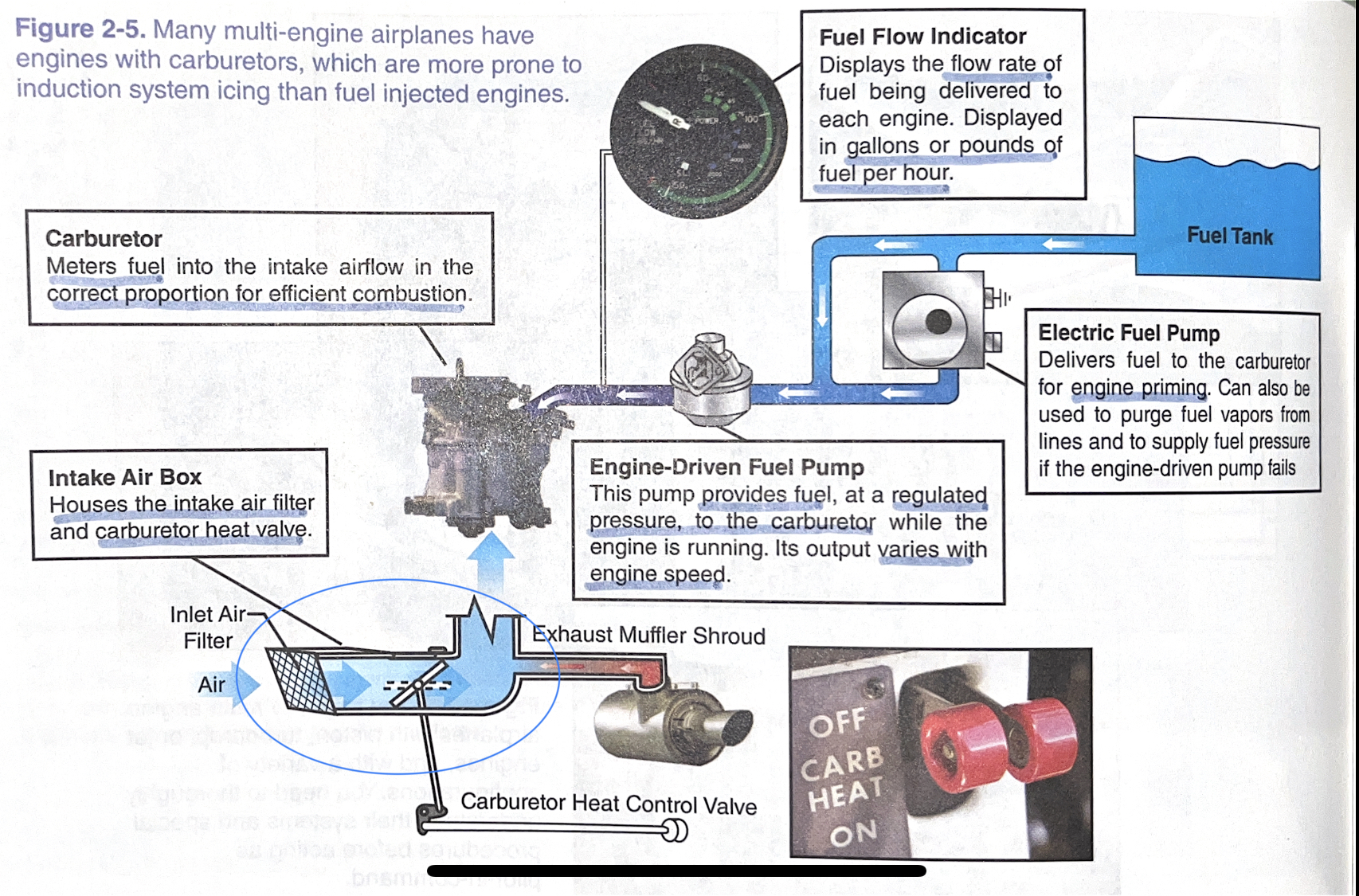
carburetor
meters fuel into the intake airflow in the correct proportion for efficient combustion
10
New cards
intake air box
houses the intake air filter and carburetor heat valve
11
New cards
paddle switches
multiple-position paddle switches are commonly spring-loaded to return to the BOTH magneto position when the switches are released from START
12
New cards
toggle switches
when toggle switches are used, a separate push-to-start button is provided for each engine
13
New cards
gang bar
a bar found above the magneto switches that allows you to simultaneously shut off all the magnetos in an emergency
14
New cards
how are engines traditionally numbered?
* left to right. left engine is number one, right is number 2.
* if the manufacturer does not prescribe a specific order, start the engine that is closest to the BATTERY COMPARTMENT first
* if the manufacturer does not prescribe a specific order, start the engine that is closest to the BATTERY COMPARTMENT first
15
New cards
why do you start the engine that is closest to the battery compartment first?
the shorter electrical wiring between the battery and engine improves starting performance
16
New cards
how do planes change the pitch of the propeller blades
oil pressure from the lubrication system
17
New cards
types of induction systems
normally aspirated or turbocharged
18
New cards
why should you limit carburetor heat on the ground?
to avoid sucking dirt and other foreign objects into the engine. it draws air from around a heat exchanger, bypassing the air filter
19
New cards
signs of carburetor icing
* often a slight loss of engine power, indicated by lower manifold pressure.
* this is because most multi-engine airplanes have constant-speed propellers
* this is because most multi-engine airplanes have constant-speed propellers
20
New cards
what do fuel-injected engines have instead of carb heat
* an alternate air source in case an air filter or inlet becomes obstructed.
* bypass doors might open automatically when sufficient differential pressure exists, or it will be a manual alternate air control
* bypass doors might open automatically when sufficient differential pressure exists, or it will be a manual alternate air control
21
New cards
what is the use of turbocharged air?
they enable higher altitude operations where greater airspeeds are possible and where it is easier to avoid adverse weather
22
New cards
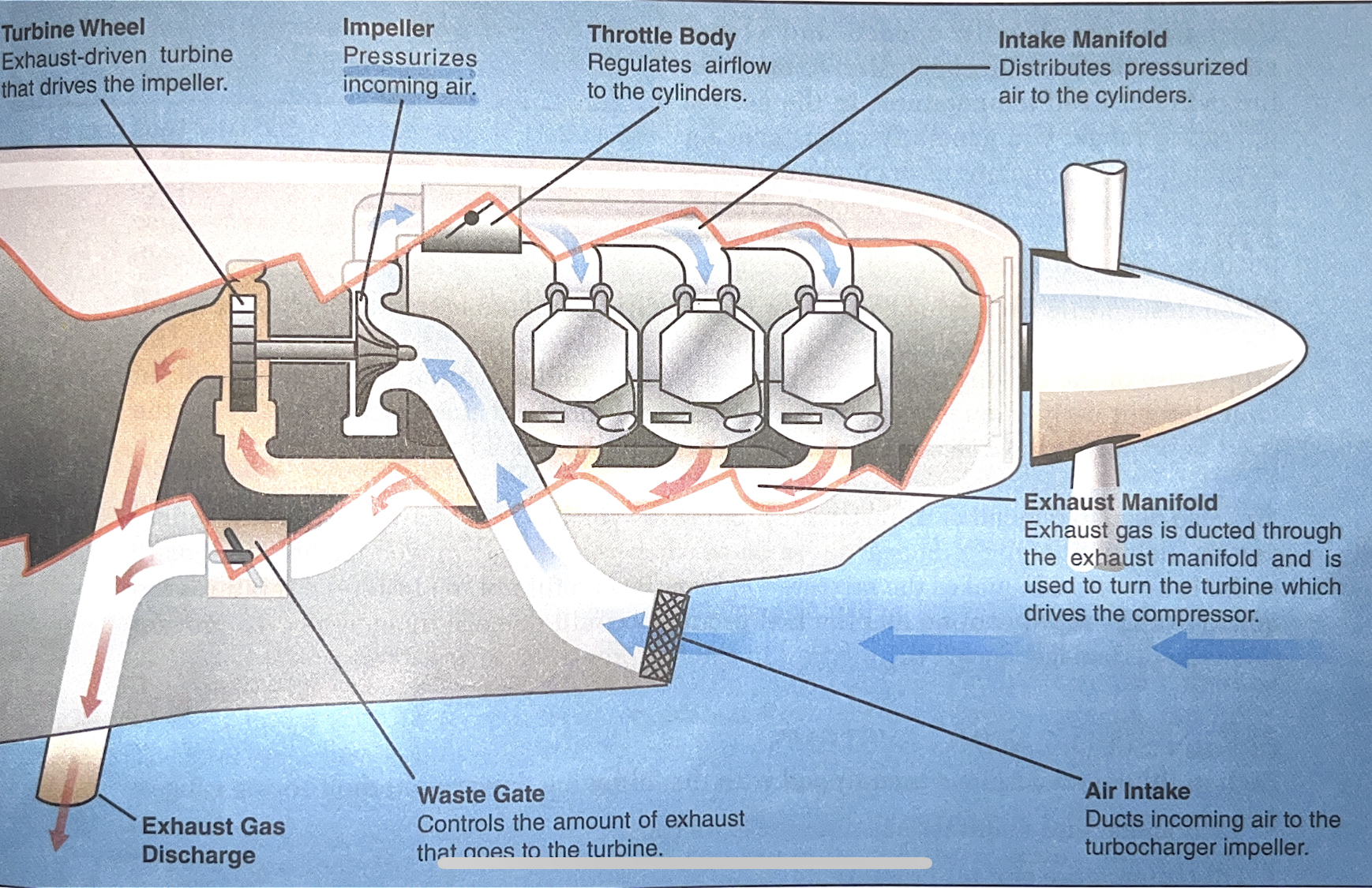
how do turbochargers work?
1. it uses exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which turns an impeller in the induction system.
2. the impeller boosts the induction air to a higher pressure, making it possible to achieve sea-level engine performance at higher altitudes
23
New cards
what are the operational differences between turbocharged single- and multi-engine aircraft at takeoff?
* the turbochargers in a multi-engine plane may not accelerate (spool up) at the same rate. this causes the thrust produced by each engine to vary.
* the thrust variations can cause so much yaw that it becomes difficult to maintain directional control
* the thrust variations can cause so much yaw that it becomes difficult to maintain directional control
24
New cards
how do you prevent differential acceleration in turbocharged multi-engine planes?
making sure the engine oil is sufficiently warm before you apply takeoff power. cold oil tends to cause sluggish operation in the turbocharger control system
25
New cards
types of cooling systems
most are air cooled; some have liquid cooling systems
26
New cards
augmentor tubes
installed around and aft of exhaust stakes, it allows the flow of exhaust gases through it to pull more cooling air through the engine compartment
27
New cards
how does air density affect the mixture?
higher air density leans the mixture; lower air density enriches the mixture
28
New cards
engine accessory systems
they provide the primary source of electric, pneumatic and hydraulic power to operate the aircraft systems
29
New cards
what do aircraft diesel engines run on?
a derivative of kerosene; jet fuel
30
New cards
how do diesel engines start?
* instead of a spark plug, they depend on the heat generated by compression to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
* in order to obtain this temperature, diesels have much higher compression ratios than gasoline-fueled engines.
* in order to obtain this temperature, diesels have much higher compression ratios than gasoline-fueled engines.
31
New cards
how does the higher compression ratio benefit diesel engines?
because jet fuel contains more energy per gallon than avgas, a diesel engine can provide greater fuel economy than an engine using avgas
32
New cards
what propellers do multi-engines most often use?
constant-speed, controllable-pitch, full-feathering propellers
33
New cards
full-feathered propellers
* each blade is rotated so that its chord line is nearly parallel to the relative wind over the aircraft
* this stops the propeller from windmilling, greatly reducing drag and stopping rotation of a damaged engine
* this stops the propeller from windmilling, greatly reducing drag and stopping rotation of a damaged engine
34
New cards
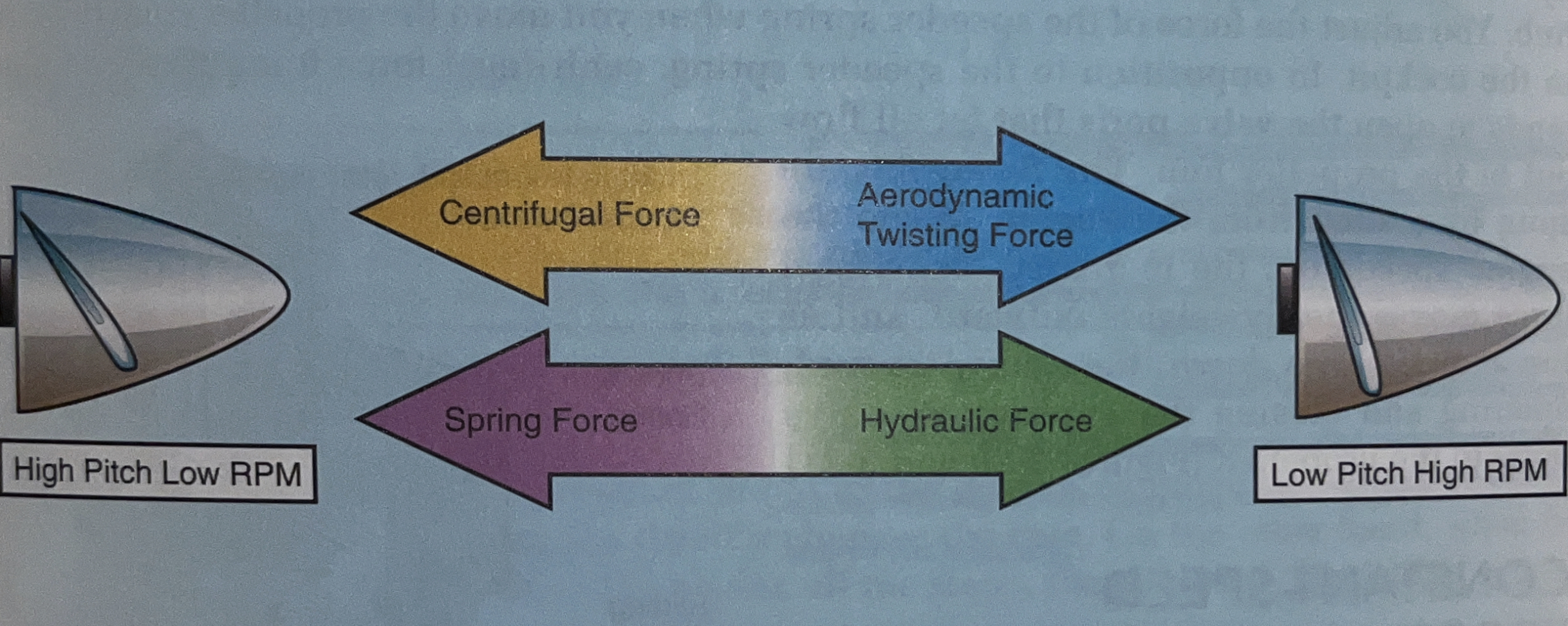
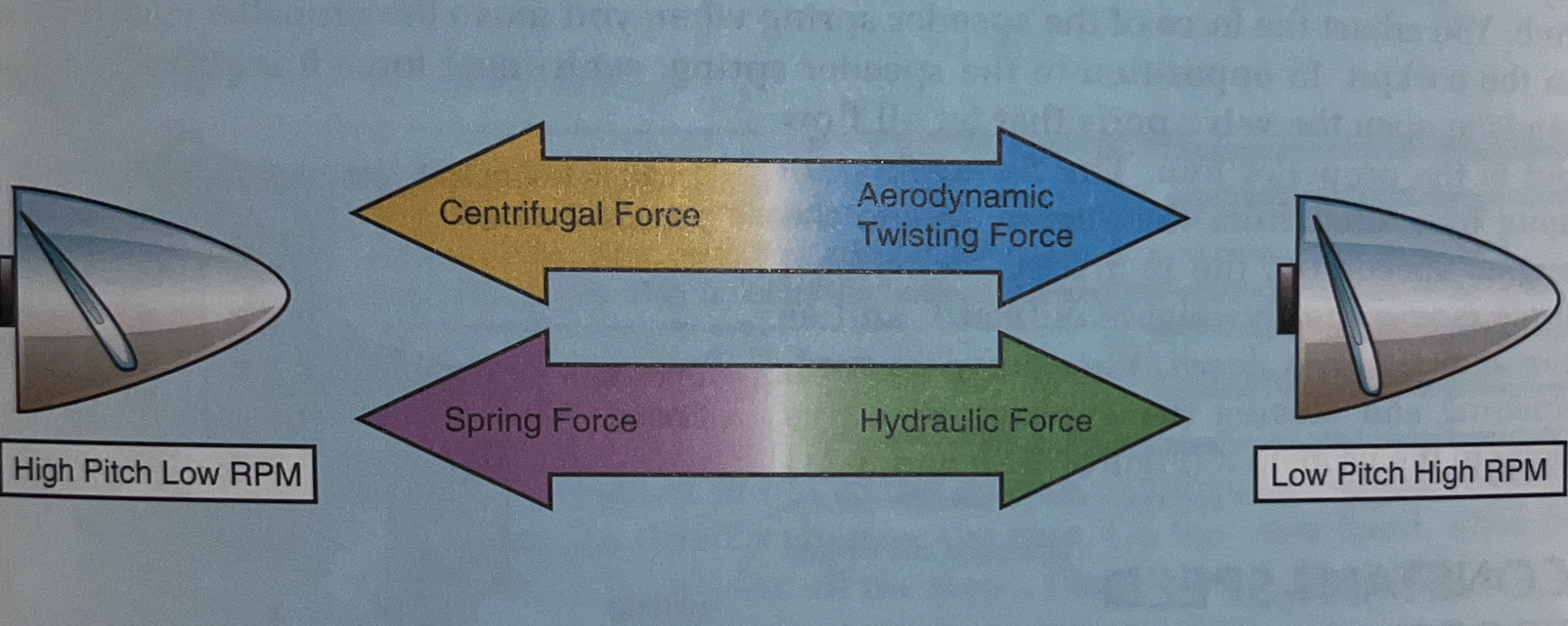
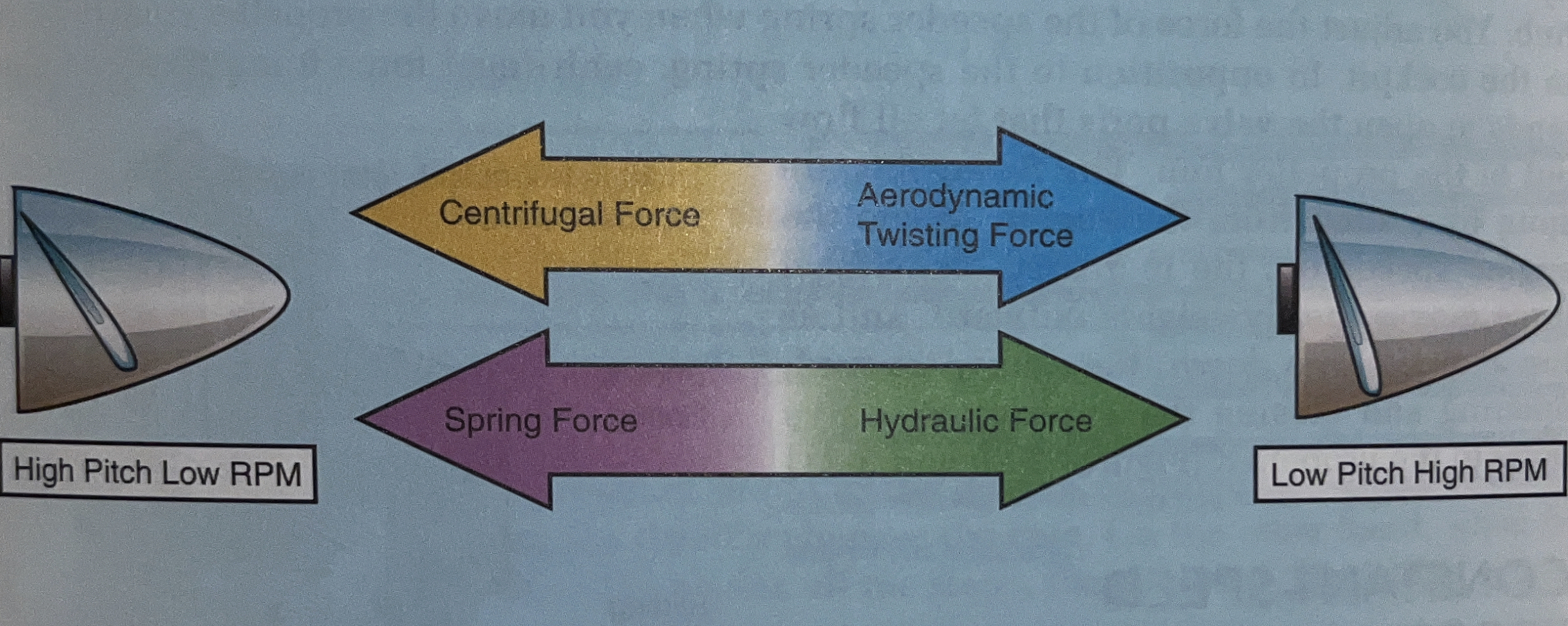
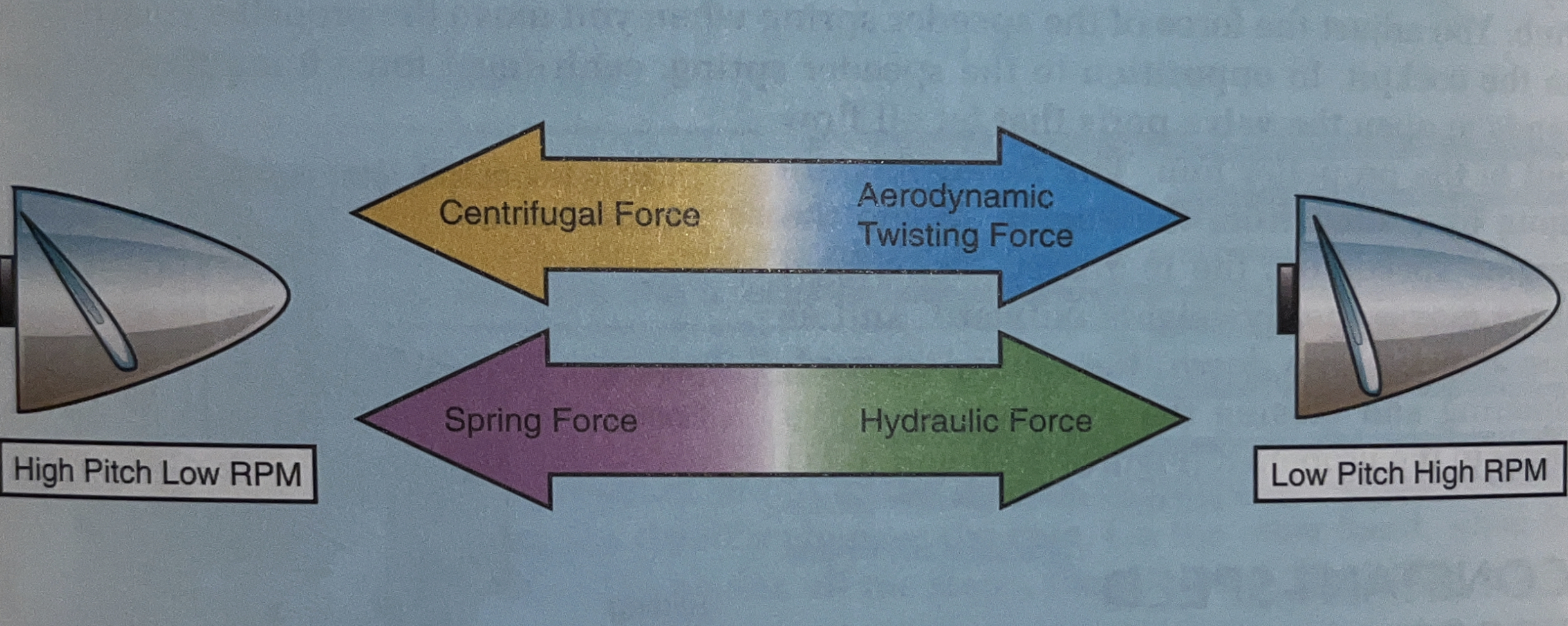
what forces reduces the blade pitch
aerodynamic twisting force + hydraulic force
35
New cards
aerodynamic twisting force
results from the spinning propeller blades tending to align themselves with the relative airflow in a low pitch angle that produces no thrust
36
New cards
hydraulic force
results from oil pressure moving the pitch change mechanism in the propeller hub
37
New cards
what forces increase the blade pitch
* spring force applied by mechanical springs, gas springs, or a combination of both
* centrifugal force coming from counterweights mounted on the blade designed to overcome the aerodynamic twisting forces
* centrifugal force coming from counterweights mounted on the blade designed to overcome the aerodynamic twisting forces
38
New cards
governor
maintains rpm
39
New cards
how does the governor work
it works by using a combination of %%centrifugal force%% and %%spring pressure%% to move a valve that allows pressurized oil to travel into or out of the propeller hub
40
New cards
how do constant-speed props work?
1. the %%prop control lever%% selects the rpm for the governor to maintain
2. the **pitch stops** of the propeller limit the range of constant-speed operation
3. when the propeller is **out of the governing range,** it functions like a **fixed-pitch propeller;** moving the throttle changes the RPM
4. the governor can control rpm by changing the blade pitch
41
New cards
moving the lever forward in a constant-speed prop…
sets a **low** %%**pitch angle**%%**,** which **increases** the %%engine rpm%%
42
New cards
define **full authority digital engine control (fadec)**
* replaces many mechanical engine and propeller control systems with computer-controlled electronic systems
* in light GA planes, typically can control:
* throttle valve position
* fuel injection
* fuel-air mixture
* spark timing
* turbocharger waste gate position
* also replaces %%**throttle, mixture,** and **propeller rpm levers**%% w a single power lever for ^^each engine^^
* there are **no manual overrides or backup controls**
* in light GA planes, typically can control:
* throttle valve position
* fuel injection
* fuel-air mixture
* spark timing
* turbocharger waste gate position
* also replaces %%**throttle, mixture,** and **propeller rpm levers**%% w a single power lever for ^^each engine^^
* there are **no manual overrides or backup controls**
43
New cards
**propeller synchronizer systems**
* most are controlled by a switch mounted near the propeller control levers
* to use:
* set power as usual, adjusting within 50 rpm of each other
* turn on the synchronizer
* to use:
* set power as usual, adjusting within 50 rpm of each other
* turn on the synchronizer
44
New cards
**type 1 prop synchronizer**
* drives an electric motor on one propeller control to **match** the rpm of one prop to another
* **slaved** to the other propeller
* **slaved** to the other propeller
45
New cards
**type 2 prop synchronizer**
* no master-slave relationshhip
* reduces the rpm of the faster prop while simultaneously increasing the rpm of the slower prop until their speeds match
* reduces the rpm of the faster prop while simultaneously increasing the rpm of the slower prop until their speeds match
46
New cards
what do **governor checks** do?
* reveals a malfunctioning governor before takeoff
* to perform check:
* increase the engine rpm into the prop’s governing range (specified by manufacturer)
* after the speed has stabilized, leave the prop control in position and advance the throttle
* if functioning properly, you can hear the prop pitch change, and the rpm remains at its original setting
* to perform check:
* increase the engine rpm into the prop’s governing range (specified by manufacturer)
* after the speed has stabilized, leave the prop control in position and advance the throttle
* if functioning properly, you can hear the prop pitch change, and the rpm remains at its original setting
47
New cards
what are **unfeathering accumulators**
* store oil under pressure when the engine is running, before you feather the propeller
* when moving the prop control out of feather, the accumulator releases the oil into the %%**prop hub**%%, which rotates the blades so that the propeller begins windmilling
* allows you to restart the engine **without using the starter**
* when moving the prop control out of feather, the accumulator releases the oil into the %%**prop hub**%%, which rotates the blades so that the propeller begins windmilling
* allows you to restart the engine **without using the starter**