economics test 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
macro vs micro
\
Microeconomics deals with the economic problem from an individual POV. “a smaller perspective”
Macroeconomics deals with the economic problem from a society’s POV.
They are the same because they both study the economic problem, they are different because the economy is studied at 2 different POV.
Microeconomics deals with the economic problem from an individual POV. “a smaller perspective”
Macroeconomics deals with the economic problem from a society’s POV.
They are the same because they both study the economic problem, they are different because the economy is studied at 2 different POV.
2
New cards
economic problem
Economic problem:
The economic problem exists when there is limited resources for unlimited needs and wants.
The economic problem exists when there is limited resources for unlimited needs and wants.
3
New cards
scarcity
Scarcity:
Scarcity means unlimited need or wants but limited resources (e.g the lack of pink diamonds in aus, and hence the increased price)
Scarcity means unlimited need or wants but limited resources (e.g the lack of pink diamonds in aus, and hence the increased price)
4
New cards
relative scarcity
Refers to the scarcity of a good in relation to demand for it.
5
New cards
free good
Are goods that are not scarce and therefore and free (e.g ice in north pole)
6
New cards
why is the economic problem a problem of choice
The economic problem is a problem of choice because resources are limited, consumers have the make decisions on how to utilize resources at the cost of other resources foregone.
7
New cards
Would more g+s be produced if more aud is produced?
Would more g+s be produced if more aud is produced?
No, because money doesn’t produce goods, also other factor’s cost would increase and everything in general would cause inflation.
No, because money doesn’t produce goods, also other factor’s cost would increase and everything in general would cause inflation.
8
New cards
purpose of an economic model
Economic models are based on assumptions on which theories can be formulated
However, they provide a simplifies framework which makes it easier to study fundamentals.
However, they provide a simplifies framework which makes it easier to study fundamentals.
9
New cards
ceteris peribus
Economist predictions are based on this concept, meaning only true if no other variables are affected. Economists use it to predict trends between cause and effect between 2 variables.
10
New cards
opportunity cost
Opportunity cost:
Opportunity cost Is the value of the next best alternative you give up.
Opportunity cost Is the value of the next best alternative you give up.
11
New cards
economics and social science
Economics is a social science because it is based on economic models which help to formulate theories, it studies the human behaviors however it isn’t a physical science like chem, in that it can’t conduct controlled experiments.
12
New cards
positive and normatative
Positive: based on what’s factual info, had testing and data collected done on, can be proved. E.g what is the unemployment rate.
Normative: subjective, based on valued judgments and opinions. E.g is the UE rate too high?
Normative: subjective, based on valued judgments and opinions. E.g is the UE rate too high?
13
New cards
Factors of production: improve FOP= productivity
Land: Natural resources by nature used to produce g+s. (oil and coal)(urbanization and soil composition can ruin supply)
Labor: The efforts, physically or mentally, that people contribute to produce g+s(teacher, doctor)(poor health and less education can ruin it)
Capital: The manmade goods used to produce the g+s(hammers and machines)(labor availability and profits)
Enterprise: human effort that co-ordinates all the other factors of production(Elon musk, mark Zuckerburg)(education and govt policies)
Labor: The efforts, physically or mentally, that people contribute to produce g+s(teacher, doctor)(poor health and less education can ruin it)
Capital: The manmade goods used to produce the g+s(hammers and machines)(labor availability and profits)
Enterprise: human effort that co-ordinates all the other factors of production(Elon musk, mark Zuckerburg)(education and govt policies)
14
New cards
Which group owns the FOP in the circular flow?
\- Households
15
New cards
incomes
Capital= resources, interest (not materials)
Land= rent
Labor= wages
Enterprise= money, profit
Talk about opt cost, choices and scarcity
Land= rent
Labor= wages
Enterprise= money, profit
Talk about opt cost, choices and scarcity
16
New cards
allocating resouces
Marginal analysis is used to best allocate limited resources and to increase net profit.
Law of diminishing: As you consume more amounts of something, the marginal benefits decrease (decline), and the marginal costs increase.
Law of diminishing: As you consume more amounts of something, the marginal benefits decrease (decline), and the marginal costs increase.
17
New cards
Should we keep building more hospitals as long as total benefits exceed total cost?
No, we should allocate resources till we maximize net benefit because resources are scarce, we should allocate them in such a way to get the best value from their use.
18
New cards
The Production possibility frontier
Economists use a model PPF, to help illustrate the economic problem and opportunity cost, and efficient resource allocation.
It shows the combination of g+s produced, when using all resources efficiently and illustrates a trade-off.
It shows the combination of g+s produced, when using all resources efficiently and illustrates a trade-off.
19
New cards
what is assumed in a ppf
1. Economy’s resources are fixed.
2. Tech is fixed.
3. The economy is only producing 2 goods (pizza and burger)
20
New cards
what a ppf demonstrates
· Efficiency is shown because resources are used efficiently
· Opportunity cost is shown by the decrease in one good when another is increased
· Economic growth, when the frontier is moved outwards
· Capital vs production
· Opportunity cost is shown by the decrease in one good when another is increased
· Economic growth, when the frontier is moved outwards
· Capital vs production
21
New cards
Why does the frontier always have a negative slope:
negative slope= because of limited resources, an increase of opportunity cost (increase in the cost of 1 resource to obtain the other) overtime as resource are limited, we have to give up a higher quantity of other resources (a) to obtain (b) (increased opt cost)
22
New cards
constant opportunity cost
the resources to make goods A and B are similar
23
New cards
increasing opportunity cost
the resources to produce goods A and B are very different, to gain 1 unit of good A you must sacrifice 2 units of good B.
24
New cards
changes in pff and economic growth
When the frontier moves outwards, right, more of both goods can be produced, meaning there must have been an increase in quantity or quality of resources that affects the production of both goods. An increase of tech can also shift outwards the frontier.
25
New cards
economic system
An economic system is the way in which a country’s resource are allocated to deal with the economic problem
26
New cards
An economy system must answer these questions:
what to produce
how to produce
who to produce for
how to produce
who to produce for
27
New cards
planned economy
most often equates with communism, operates using a planning bureau to answer what, how much, how and who questions.
28
New cards
traditional economy
center around the passing down of customs and beliefs. Economic questions are answered by tradition. Eg. Tribes. No govt system. Adv= less stress, more time. Dis adv= lack of innovation, limited economic and living standard growth.
29
New cards
socialist system
state owns all the resources
30
New cards
capitalist
resources are owned privately, decision made by owners of resources based on their interest.
31
New cards
command economy
resources are owned collectively, decisions made by a planned authority.
32
New cards
mixed economies
combine elements of both market and planned economies.
33
New cards
role of markets
\- A market is said to exist when buyers and sellers meet to organize an economic transaction. A market is composed of buyers (demand) sellers (supply) and something to exchange.
34
New cards
characteristics of market economy
· Three vital elements:
Buyers (demand) sellers (supply) and something to exchange.
· Voluntary exchange
You get to chose what to buy and produce
· Price mechanism
The price (price mechanism) is the signal to consumers and producers of the intentions of each other, and the needs to change the quantity bought or sold in the market. Therefore, price is a signal as to where the allocation of resources is best suited or most efficient.
The role of price (The consumers determine what will be produced- consumer sovereignty)
Buyers (demand) sellers (supply) and something to exchange.
· Voluntary exchange
You get to chose what to buy and produce
· Price mechanism
The price (price mechanism) is the signal to consumers and producers of the intentions of each other, and the needs to change the quantity bought or sold in the market. Therefore, price is a signal as to where the allocation of resources is best suited or most efficient.
The role of price (The consumers determine what will be produced- consumer sovereignty)
35
New cards
Distinguish between product and factor markets
Factor markets – refer to the market where the factors of production (capital, enterprise, land & labour are exchanged for the payment of income (rent, profit, wages and interest).
Product markets: deads with the buying and selling of goods and services, consumers represent the demand side of market, producers represent the supply side of market. Firms produce and sell to cosnumers.
\
the demand side of market
Product markets: deads with the buying and selling of goods and services, consumers represent the demand side of market, producers represent the supply side of market. Firms produce and sell to cosnumers.
\
the demand side of market
36
New cards
demand
refers to the buying intentions of consumers. (different to want, many ppl wants rolex but most aren’t willing to pay the price)
37
New cards
4 factors of demand
Demand is made up of 4 factors:
* Price consumer is willing to pay
* At a particular price
* At a particular point in price
* The quantity of g+s
* Price consumer is willing to pay
* At a particular price
* At a particular point in price
* The quantity of g+s
38
New cards
law of demand
The Law of Demand States that price and demand have an inverse relationship (ceteris paribus) as prices rise the quantity demanded falls.
39
New cards
Factors of the slope on the demand curve-income
* When prices rise consumers are not willing to buy as much (as their purchasing power or real income falls)
* (eg, if you have 100 dollars, your real income is 10 pizzas if one is 10 dollars, if pizza increases to 20 dollars, your real income is 5 pizzas) when your real income falls, you are poorer, therefore you will purchase lesser)
* Works both directions: when price of good falls, your real income and you will purchase more.
* (eg, if you have 100 dollars, your real income is 10 pizzas if one is 10 dollars, if pizza increases to 20 dollars, your real income is 5 pizzas) when your real income falls, you are poorer, therefore you will purchase lesser)
* Works both directions: when price of good falls, your real income and you will purchase more.
40
New cards
Factors of the slope on the demand curve- substitution
* When prices of one good increases, consumer will switch to cheaper substitute products.
* (e.g, when fuel price increases, consumers will choose public transport)
* Work in reverse, Weaker if less substitutes available, Stronger if there are more substitutes.
* (e.g, when fuel price increases, consumers will choose public transport)
* Work in reverse, Weaker if less substitutes available, Stronger if there are more substitutes.
41
New cards
Factors of the slope on the demand curve-law of diminishing marginal utility
* Economists refer to satisfaction as utility.
* As more of a good or services is consumed, additional satisfaction derived diminishes. (eg, one pizza slice slaps, but 8th piece is dh asf)
* As more of a good or services is consumed, additional satisfaction derived diminishes. (eg, one pizza slice slaps, but 8th piece is dh asf)
42
New cards
relationship
\- Price and quantity have a negative relationship, as price increases the quantity demanded decreases, ceteris paribus.
43
New cards
demand curve
\- The Demand Curve is a graph reflecting the price consumers are willing to pay and the quantity consumers are willing buy.
44
New cards
market demand
\- __Market Demand__ includes the individual demand curves of all the participants in a particular market added together
45
New cards
expansion
Expansion:
If the price of the good decreases, then there will be an expansion in demand due to more consumers being included in the market.
If the price of the good decreases, then there will be an expansion in demand due to more consumers being included in the market.
46
New cards
conteaction
If the price of a good increases, then there will be a contraction in demand, due to more consumers being excluded from the market.
47
New cards
demand shifts
a shift occurs when the quantity demanded of good changes by a non-price factor. (Price is constant)
48
New cards
non price factors that affect the demand curve
* Income levels
* Substitution (A substitute good is a good that can be used in replacement to meet a need or want. For example a motor bike is a substitute for a car (mode of transport)
* A complimentary good is a good that is used in conjunction with another good. For example sock and sneakers)
* Tastes and preference
* Advertising
* Availability of credit
* Amount of disposable income
* Weather+ season
* Substitution (A substitute good is a good that can be used in replacement to meet a need or want. For example a motor bike is a substitute for a car (mode of transport)
* A complimentary good is a good that is used in conjunction with another good. For example sock and sneakers)
* Tastes and preference
* Advertising
* Availability of credit
* Amount of disposable income
* Weather+ season
49
New cards
normal vs inferior goods
* Normal: when income increases demand increases
* Inferior: when income increases demand decreases (e.g Coles brand rice)
* Inferior: when income increases demand decreases (e.g Coles brand rice)
50
New cards
supply
Supply is the amount of goods and services producers are willing and able to produce at a particular price and point in time.
51
New cards
supply curve
The Supply Curve is a graph reflecting at different prices quantity producers are willing to sell to the consumers at different prices.›
The relationship between supply and price is a positive one.
The relationship between supply and price is a positive one.
52
New cards
law of demand
› As prices fall, we see a Fall in Supply.
› If price rises, there will be a Rise in Supply.
› If price rises, there will be a Rise in Supply.
53
New cards
why supply curve upward sloping
The profit motive: When the market price rises, it becomes more profitable for businesses to increase their output
Production and costs: When output expands, a firm's production costs tend to rise, therefore a higher price is needed to cover these extra costs of production.
New Market Entrants: Higher prices may create an incentive for other businesses to enter the market leading to an increase in total supply.
Production and costs: When output expands, a firm's production costs tend to rise, therefore a higher price is needed to cover these extra costs of production.
New Market Entrants: Higher prices may create an incentive for other businesses to enter the market leading to an increase in total supply.
54
New cards
Movement along curve: Caused only by price.- price increase
If price increases, expansion in supply, quantity supplied of a good rise.

55
New cards
Movement along curve: Caused only by price.- price decrease
If price decreases, contraction in supply, quantity supplied of a good fall.

56
New cards
non price factors affecting supply
Non price factors affecting supply:
Tech: improvement in tech enables firm to produce more quantity at same price. Shift to right
Cost of production: If raw materials price increases, then firm cant produce the same quantity at the same price, this causes a shift to left. (vice versa- low cost ^ high supply)
Change in the Price of an Alternative Product:
If the price of butter rises, there will be an increase in demand for margarine, which will increase supply (shift to the right) without a change in price.
Complimentary: a rise in lamb supply increases, this will mean more wool is supplied even though the price of wool didn’t rise. ‘
Erratic weather: when weather impacts a supply of good, e.g tornado causes loss of supply of crops, causing shift to left. Whereas perfect weather results in lots of supply of bananas, shift to right.
Production in other countries:
An increase of supply can cause more cars sold in aus. Shift to right
Govt. Intervention: business tax can cause a decrease of supply, shift to left./ Subsides, cause shift to right
Future expectations: If producers expect prices of their products to rise in the future, they may decrease supply now (stockpile) so that they can increase the supply when prices are higher.
Tech: improvement in tech enables firm to produce more quantity at same price. Shift to right
Cost of production: If raw materials price increases, then firm cant produce the same quantity at the same price, this causes a shift to left. (vice versa- low cost ^ high supply)
Change in the Price of an Alternative Product:
If the price of butter rises, there will be an increase in demand for margarine, which will increase supply (shift to the right) without a change in price.
Complimentary: a rise in lamb supply increases, this will mean more wool is supplied even though the price of wool didn’t rise. ‘
Erratic weather: when weather impacts a supply of good, e.g tornado causes loss of supply of crops, causing shift to left. Whereas perfect weather results in lots of supply of bananas, shift to right.
Production in other countries:
An increase of supply can cause more cars sold in aus. Shift to right
Govt. Intervention: business tax can cause a decrease of supply, shift to left./ Subsides, cause shift to right
Future expectations: If producers expect prices of their products to rise in the future, they may decrease supply now (stockpile) so that they can increase the supply when prices are higher.
57
New cards
shifts in demand and supply at equalibrium
Shifts in demand and supply and at equilibrium:
Demand shift increases (right): price increases, quantity increases.
Demand shift decreases (left): price decreases, quantity decreases
Supply shift increases ( ):price decreases, quantity increases
Supply shift decreases (up): price increases, quantity decreases
Increased demand and supply: P= interdependent, quantity increases
Demand decreases and increased supply: Price decreases, quantity interdependent
Demand increased and supply decreases: Price increases, quantity interdependent
Demand and supply decrease: Price interdependent and quantity decreases.
Demand shift increases (right): price increases, quantity increases.
Demand shift decreases (left): price decreases, quantity decreases
Supply shift increases ( ):price decreases, quantity increases
Supply shift decreases (up): price increases, quantity decreases
Increased demand and supply: P= interdependent, quantity increases
Demand decreases and increased supply: Price decreases, quantity interdependent
Demand increased and supply decreases: Price increases, quantity interdependent
Demand and supply decrease: Price interdependent and quantity decreases.
58
New cards
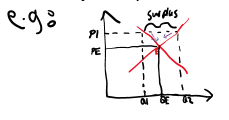
How would you explain:
\
If market prices rise to P1 there is a surplus of supply, the producers will react and the price would decrease from P1-PE to get rid of excess stock, meaning that quantity demanded will expands from Q1-QE because they see the same product for a cheaper price. The supply would contract from Q2-QE. Meaning new equilibrium in reached (PE-QE)