Atomic structure
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
what are atoms
very small particles made up of three main subatomic particles (protons, neutrons and electrons)
2
New cards
where are protons and neutrons found in an atom
in the nucleus (small dense central region)
3
New cards
charge of a proton
\+1
4
New cards
charge of a neutron
0
5
New cards
charge of an electron
\-1
6
New cards
where is the electron found in an atom
outside the nucleus (on shells)
7
New cards
which one is the mass number and the atomic number
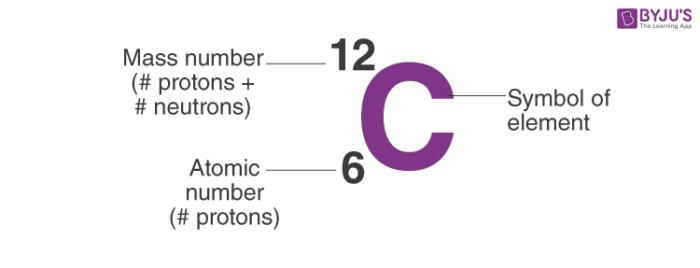
8
New cards
why is the nucleus positively charged
it contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons
9
New cards
why are all atoms neutral
they contain equal numbers of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons
10
New cards
what is the atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus
11
New cards
what is the mass number
number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus
12
New cards
what are elements
substances made up of only type of atom
13
New cards
how to figure out no. of neutrons of an atom
mass no. - atomic no.
14
New cards
what are isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
15
New cards
why do isotopes of an element have different masses
due to the different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
16
New cards
why do isotopes of an element behave the same way in chemical reactions
since the number of electrons determines the way an atom reacts (have same no. of electrons and protons - atomic no.)
17
New cards
what differs or stays the same between isotopes of an atom
different - no. of neutrons
same - no. of electrons and protons
same - no. of electrons and protons
18
New cards
how to figure out no. of protons of an atom
mass no. - no. of neutrons (atomic no. = no. of protons)
19
New cards
order of maximum electronic configuration
2,8,8,2
20
New cards
what do lewis diagrams include
only valence electrons
21
New cards
what are valence electrons
electrons in the outer most shell (highest occupied energy level)
22
New cards
what number of valence electrons is not exceeded
past 8 valence electrons
23
New cards
what electrons are involved in chemical reactions
only valence electrons
24
New cards
what tends to happen when atoms have the same number of valence electrons
they have similar chemical properties
25
New cards
what is the period of a periodic table
the same row across the periodic table
26
New cards
what is the group of a periodic table
same column down the periodic table
27
New cards
how to figure out valence electrons for group 1 and 2
no. of valence electron = group number eg. group 2 has 2 valence electrons
28
New cards
how to figure out valence electrons for group 13 to 18
no. of valence electron = group number - 10 eg. group 17 has 7 valence electrons
29
New cards
what does the number of valence electrons do across a period
increases
30
New cards
what does the number of valence electrons do down a group
remains the same
31
New cards
what are cations
positively charged ions (have fewer electrons than protons)
32
New cards
when do cations form
when atoms or a group of atoms lose electrons
33
New cards
what are anions
negatively charged ions (have more electrons than protons)
34
New cards
what groups of the periodic table are metals found in
groups 1, 2 and 13
35
New cards
what trend do metals usually do (link cations)
tend to lose electrons to form monatomic cations (one atom)
36
New cards
what groups of the periodic table are non-metals found in
groups 15, 16 and 17
37
New cards
what trend do non-metals usually do (like anions)
tend to gain electrons to form monoatomic anions
38
New cards
whats special about group 18 elements
they are unreactive towards most other elements (do not tend to from ions)
39
New cards
what are polyatomic ions
ions that consist of a stable group of atoms with an overall charge eg. NH4
40
New cards
what is the valency of an ion
the magnitude or size of the charge of the ion eg. sodium ion valency is +1
41
New cards
what can transition metals do
can form a range of cations with different valencies eg. copper or iron
42
New cards
what groups are non-metals found
groups 14-17