NYU Science of Happiness (SOH) Final
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
What was involved in the PREP speaker listener technique?
- The speaker has the floor
- Speak, then listener paraphrases
- Each person has a turn
- Goal = to show understanding, ideally allows each partner to understand eachother
What are some names and definitions of thinking traps?
Catastrophizing --> when we believe the only possible outcome is the worst thing imaginable
All-or-nothing thinking --> viewing a situation in only 2 categories, such as "good" or "bad"
Labeling --> we talk about ourselves and others in cruel ways, often using a single word
Mind-reading --> we believe we know what others are thinking and assume the worst
Mental filter --> when you can only see . the downsides in yourself/in a situation
What happens to those who chronically procrastinate?
1st 1/2 of semester --> short term benefits, early stress relief, 1st half of semester lower use of health center
2nd 1/2 of semester --> significant increase in stress, consistently produced lower quality of work/lower grades, early gains were more than offset by later losses. Increase in use of health center
What are mature defenses in therapy?
- Altruism
- Anticipation
- Humor
- Sublimation
- Identification
How do we define a mental health disorder?
The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
What are the top predictors of success in therapy?
- A secure base
- Exploration
- The relationship with therapist
- Connecting the past and present
- Imagining alternatives
What are the definitions of forgiveness and reconciliation?
Forgiveness --> conscious decision to release feelings of anger or resentment towards someone
Reconciliation --> rebuilding trust, coming together to restore a broken or damaged relationship
What is attachment theory?
- Conducted by Harlow (monkeys)
- Study of how human beings respond within relationships when hurt, separated from loved ones, or perceiving a threat.
- Emphasized the feeling that binds us together
What is equity theory?
- Assumes that people calculate costs and benefits involved in interacting with others
- Equitable (equal) relationships last
- The idea that people don't do things simply to receive something in exchange, but rather to reach an equal middle ground
What is the ratio of positive emotions to negative emotions that promotes our relationships with others?
5 positive emotions: 1 negative emotion
What makes avoidance of something we're afraid of so powerful?
Because avoidance reinforces negative emotions/a negative mindset
What is PMR, and what was the exercise for it that we did in lecture?
PMR = progressive muscle relaxation.
You tense everything and then un-tense.
Used in meditation practice.
What is the tetris effect?
Study done where people played tetris for hours on end- the participants eventually found themselves seeing tetris in real life- such as arranging produce at the grocery store.
- Their thoughts, mental images, dreams, and experiences began to be affected by the image of tetris.
- An example of when people spend so much time doing something/on a certain activity, it begins to seem into everyday life
What are our working definitions of mindfulness and mindlessness?
Mindfullness:
- Being situated in the present... sensitive to context and perspective
Mindlessness:
- Past over-determines the present... insensitive to context, trapped in single perspective
What are state and trait changes resulting from mediation?
State changes:
- Deep sense of calm peacefulness
- Cessation or slowing of the minds internal dialogue
- Experiences of perceptual clarity
Trait changes:
- Concentration and self regulation
- Deepened sense of calm , increased comfort, and heightened awareness of sensory field
What are character strengths, and what are three steps for fostering our signature strengths?
Character/signature strengths are individual(s) most notable strengths of character that a person can own, celebrate, and frequently exercise.
Most adults typically identify between 3 and 7 of them.
3 STEPS:
- Aware
- Explore
- Apply
What is challenge response?
- Instead of viewing a thing as a threat, you view it as a challenge. Reappraising our anxiety to be excitement- enhances performance. Has to do with how you respond to stress.
- Through this, you can release a different ratio of stress hormones, and you are more easily able to access mental and physical resources
What are the key qualities of goal setting?
- Resources
- Motivation
- Needs
- Values
All of these things must match one another in order for the goal to be realistic.
What are prevention vs. promotion goals?
Prevention: careful, pessimistic
Promotion: promotes positive view of self, optimistic, more likely to take chances
What is our working definition of meaning, and when does the search for meaning occur in our lifespan?
1. OUR LIVES MATTER
2. OUR LIVES MAKE SENSE
3. WE HAVE A PURPOSE OR A BIAS FOR OUR ASPIRATIONS AND PURSUITS IN LIFE
- Peaks at 18 and 65-- curve in between those times.
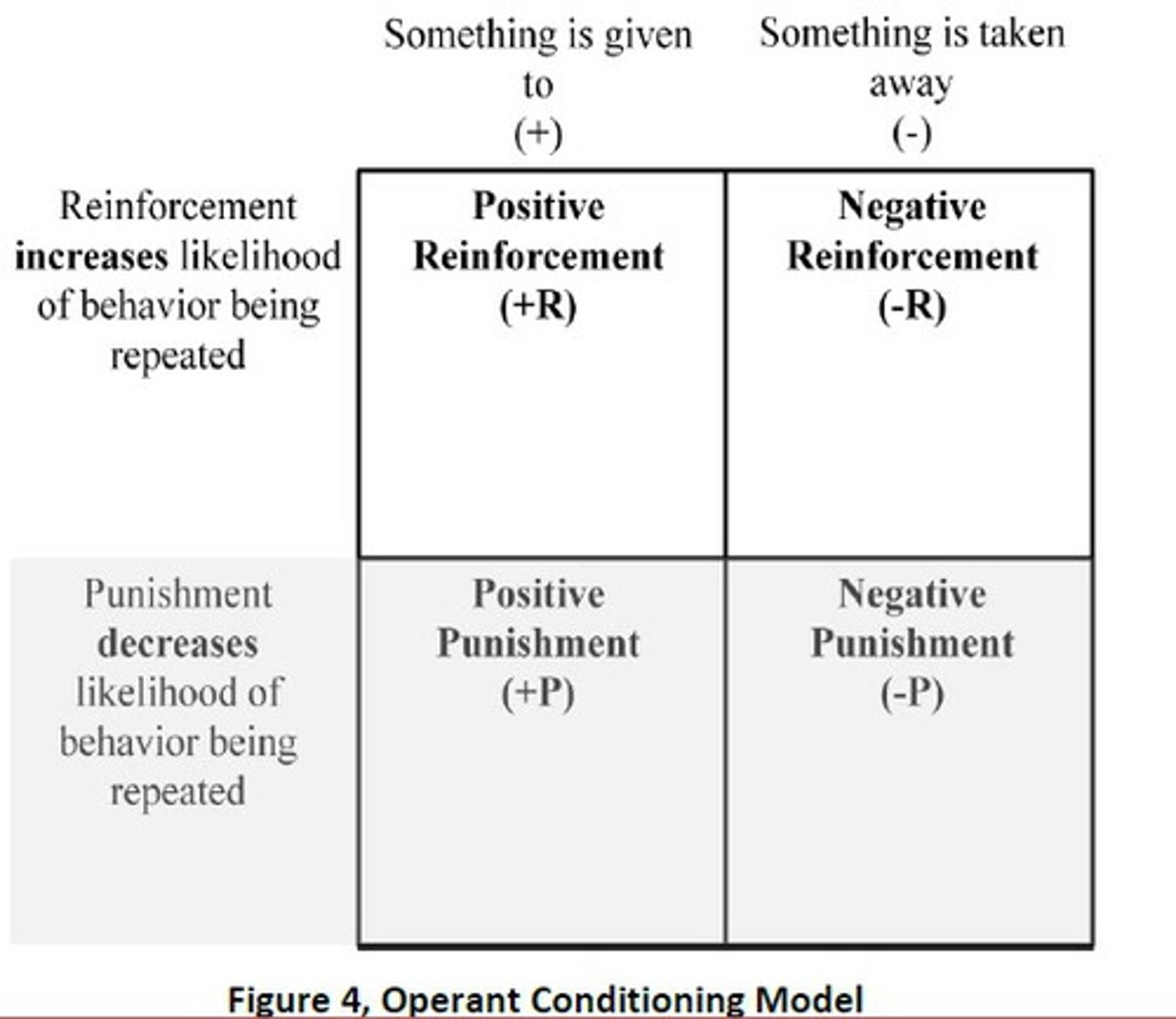
What is operant conditioning for increasing/decreasing the likelihood of behaviors? Draw chart.
What are characteristics of harmonious passion, and what are characteristics of obsessive passion?
Harmonious: you do it because you love it, to learn and grow, not to win or lose
Obsessive: doing it for others or for money, for status, or to win, not because you love it
What are the 4 PREP communication danger signs?
1. Escalation
2. Withdrawal/avoidance
3. Invalidation
4. Negative interpretation
What is ACR, and why is it the best of all 4 styles of responses to good news? Draw chart.
ACR = Active Constructing Response. Most effective way to respond, giving both the deliverer of good news and the listener a positive outcome.

What are the key characteristics of extroverts and introverts?
EXTROVERTS:
- Exterior/external
- Think out loud
- do-think-do
- interaction
- breadth of interests
INTROVERTS:
- internal/interior
- think quietly
- think-do-think
- concentration
- depth of interests
What are the components of optimistic explanatory style vs. the components of pessimistic explanatory style?
OPTIMISTIC:
- Not me: external- life events stem from the external circumstances rather than from individual character traits and actions
- Not always: unstable causes are temporary and are likely to change in the future
- Not everything: specific scope- only a finite portion of a persons life is affected
PESSIMISTIC:
- Me: internal- the problem is with ME, not the external factors
- Always: stable causes are permanent and unlikely to change
- Everything: global scope- every aspect of life is affected
What was the nun study?
- The nuns who wrote about more positive feelings --> lived longer.
- Only positive feelings predicted longevity
What was the Pittsburgh Common Cold Study?
- Individuals injected with the common cold virus
- Negative-minded people felt the effects of the cold for longer than positive minded people
- Shows how positive emotions can make you feel better faster-- negative emotions don't have as much impact on your immune system
What was the chocolate-and-radish experiment?
- One group given chocolate chip cookies, other group given radishes.
- The ones with the radishes were in the same room as those with the chocolate chip cookies
- Both groups had to complete the same task and the group that didn't get cookies didn't do as well as the group that did.
- Proved positive priming
What was the marshmallow study?
- 1960's
- Study of self regulation/willpower
- Child was offered 1 marshmallow immediately or 2 if they waited a certain period of time. If they had the willpower to wait and not eat the first, they'd get a second, doubling their prize.
- Found to be linked to success later in life... delayed gratification = more success
What was the Fiji study?
- 1995
- Exposure of TV to Western community in Fiji
- By 1998, Fijian school girls has body disparagement, body shape preoccupation, and began purging to control weight.
- Study showed how exposure to media causes insecurities-- investigated specific psychological and social mechanisms mediating adverse side effects of media on youth
What was the Napperville Zero Hours study?
- School kids had to do more engaging physical activity before class, and those did better on exams.
- Kids with higher fitness scores have higher test scores (specifically target heart rate)
What is the Yerkes-Dodson Law, and what does it demonstrate about the value of stress?
- The law suggests that there is a relationship between performance and arousal.
- The experiment demonstrated that increasing stress and arousal levels could help focus motivation and attention on the task at hand, but only up to a certain point
What is the mismatch theory about?
- "Evolutionary Hangover"
- Evolved traits that were once useful, such as fight or flight, have become maladaptive, now due to the changes in our environment
What are the common factors in therapy? Can you draw it out?
40% The Client
30% The Relationship between client and therapist
15% Positive Expectancy
15% Therapist Skill
What is PERMA, the theory behind it, and who developed it?
- PERMA is a construct of well-being theory.
- Developed by Martin Seligman
-It stands for Positive emotions, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishments.
- We need to have a little bit of each of these things in our lives... "you need at least one drop in each bucket to thrive, but your buckets don't need to be overflowing-you just need to feel satisfied".
- Each element must have three properties:
1. It contributes to wellbeing
2. People pursue it for its own sake, not merely to get any of the other elements
3. It is defined and measured independently of other measurements
How does positive priming affect performance? Give an example of a study.
It effects performance by making processing faster and speeds up memory retrieval.
(In school, it shows improves memory, better at creative problem solving, answer more questions, answer higher percentage of questions correctly, perceived as more appealing, more likely to talk issues out)
- EXAMPLE: A group of doctors primed with happiness through receiving candy accurately diagnosed patients 2x as fast as group that didn't receive candy
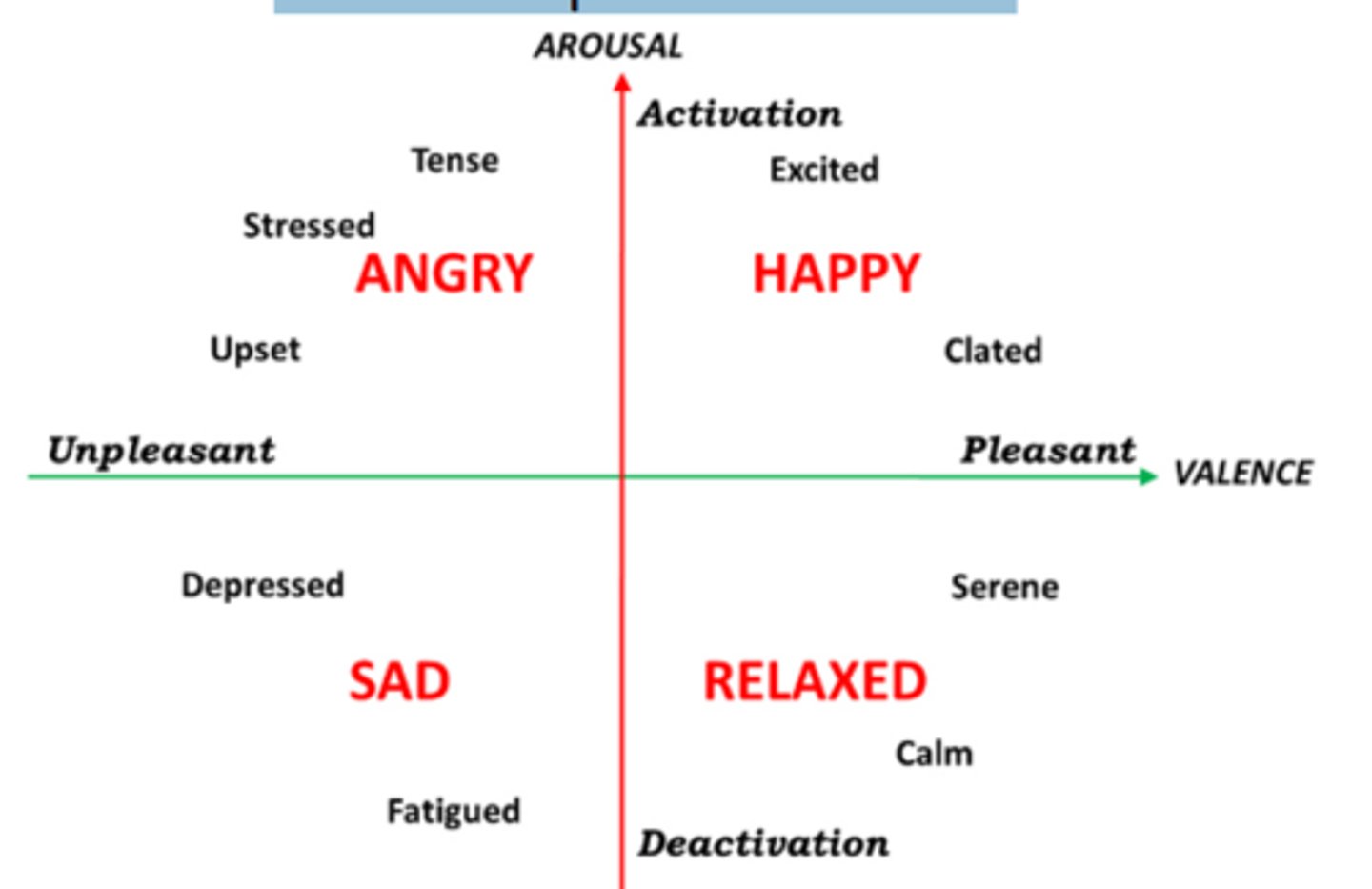
What is the circumplex model of emotions?
Emotions are distributed in a 2D circular space, containing arousal and valence (pleasure/displeasure) dimensions. They have been used to test stimuli of emotion words, emotional facial expressions and affective states.
What characteristics of a growth mindset, and what are the characteristics of a fixed mindset?
GROWTH MINDSET: intelligence is malleable, can be developed and cultivated through effort
- embraces challenges
- persists in the face of setbacks
- sees effort as the path to mystery
- finds lessons and inspiration in the success of others
FIXED MINDSET: intelligence is a fixed trait that cannot be developed
- avoids challenges
- gets defensive of easily gives up when faced with obstacles
- sees effort as fruitless or worse
- ignores criticism (aka useful negative feedback)
What is willpower? Think of the metaphor we use.
- Willpower is the ability to align yourself with the brain system that is thinking about long term goals- thinking about big values rather than short term needs or desires
- Metaphor: willpower is like a muscle- it can be both strengthened and depleted. It can become drained by temptations that you wish to avoid, taking initiatives, and physical depletion. It can get tired with use.
What are essential elements in the theory of deliberate practice?
Definition: Deliberate practice = forced evolution
(Aim to achieve each for its own sake, not for what it will get you)
- Setting goals
- Roles of parents, mentors, etc.
- Access to facilities/materials
- Immediate feedback
- Technique rather than full pieces
What is maximizing and what is satisficing?
Maximizing: seeking & accepting only the best
Satisficing: settling for good enough
(example of studying for a test to get an A vs. to pass)
What is choice paralysis?
A state of overthinking a decision to the point of a choice never being made, creates inaction.
Broaden & build vs. narrow & constrict. Define both.
- Broaden & build: when something good happens, we want to share it with others.
- Narrow & constrict: when something bad happens, we tend to look inwards and keep to ourselves (spiraling)
(Goes with the idea that positive emotions broaden awareness and help build a foundation for more positive emotions)
What are the benefits of sleep on mental health, and what are the barriers to achieving good sleep in modern society?
Benefits: Promotes learning and memory storage, improves decision making and reaction time.
Barriers:
- Sleep machismo
- Blue light/screens
- 24 hour internet access
- Poor societal education on sleepB
What are the benefits of nutrition on mental health? What are the barriers?
Benefits: Elevates your mood through the release of neurotransmitters- it induces FLOW and can serve as a distraction
Barriers:
Stress, depression, and low energy
What are some tips for better sleep (and nap) hygiene?
- Avoid long naps, limit them to 20-30 minutes
- Try to take naps mid afternoon if you're going to take them
- Relaxing before bed (calm music, read a book, mediation, stretch)
- Don't drink coffee 6-8hr before bed
- Avoid screens for 45-60 minutes before bed
- Go to bed at same time every night
- Have an ideal bedtime setting (dark, comfortable, quiet)
What's an adults circadian rhythm like?
90 minute sleep cycle (circadian rhythm = determines sleepiness and wakefulness)
What is the relationship of stress to eating? Draw chart.
**See image on in document
- Bad day --> feel down, stressed out, anxious, worried --> eat to feel better --> feel bad about ourselves, set self up for another bad day --> bad day (cycle starts over)
Where did the freshman 15 originate from?
A Seventeen Mag article in 1985. (Freshman 15 is the idea that you gain weight in your first year of college)
What are leptin and ghrelin?
-LEPTIN: tells you when you're full (found in fat cells)
-GHRELIN: tells you you're hungry (found in gut)
-When you don't sleep, GHRELIN goes up, LEPTIN goes down, so you think you're hungry
What is BDNF, and how do you get more of it?
BDFN = Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor
- Supports existing neurons and encourages growth of them
- Increases long term memory
How to get more of it:
- Exercising/sleeping/meditating
What is the difference between how exercise and sleep affect your brain cells?
Sleep: promotes dendrite spine formation which promotes learning and memory storage
Exercise: Encourages the growth of existing neurons and sympatic plasticity which causes long-term memory to increase
What is the hedonic treadmill? Give an example of when you've experienced it in your life.
(aka hedonic adaptation)
- Humans return to stable level of happiness, regardless of how positive or negative life event might be.
- Eg. when you get a bad grade on a test, the bad feeling won't last because we naturally balance ourselves out.
What is set point theory?
Thee theory that wellbeing is a relatively stable construct of behavior, genetics, and circumstances
What are some empirically sound inventions that change your set point?
Positive interventions such as:
- Conscious acts of kindness, gratitude journals, gratitude visits, three good things (recitation exercises)
PERMA
Properties of Well Being
P: positive emotion-can be so many things, it's a positive construct and contributes to the whole picture of PERMA->constructs limit us
E: engagement-being in the zone, entirely engaged
R: relationships- mixing board that allows people to see how they are doing
M: meaning- living a life that provokes meaning
A: accomplishments- about achieving something, setting small goals and continuing to move ahead, there is some need to accomplish achievements
What do we need to have some of if we want to thrive?
Elements of PERMA
properties of each element of Perma
- Contributes to well-being
- Many people pursue it for its own sake, not merely to get any of the other elements
- Defined and measured independently of the other elements
- You need a drop in each basket to have well-being
Flow
Flow: psychological state that accompanies highly engaging activities; optimal experience in life. When time passes quickly, and your attention is focused on the activity itself. All distractions melt away, and only the present place, time, and action exists.
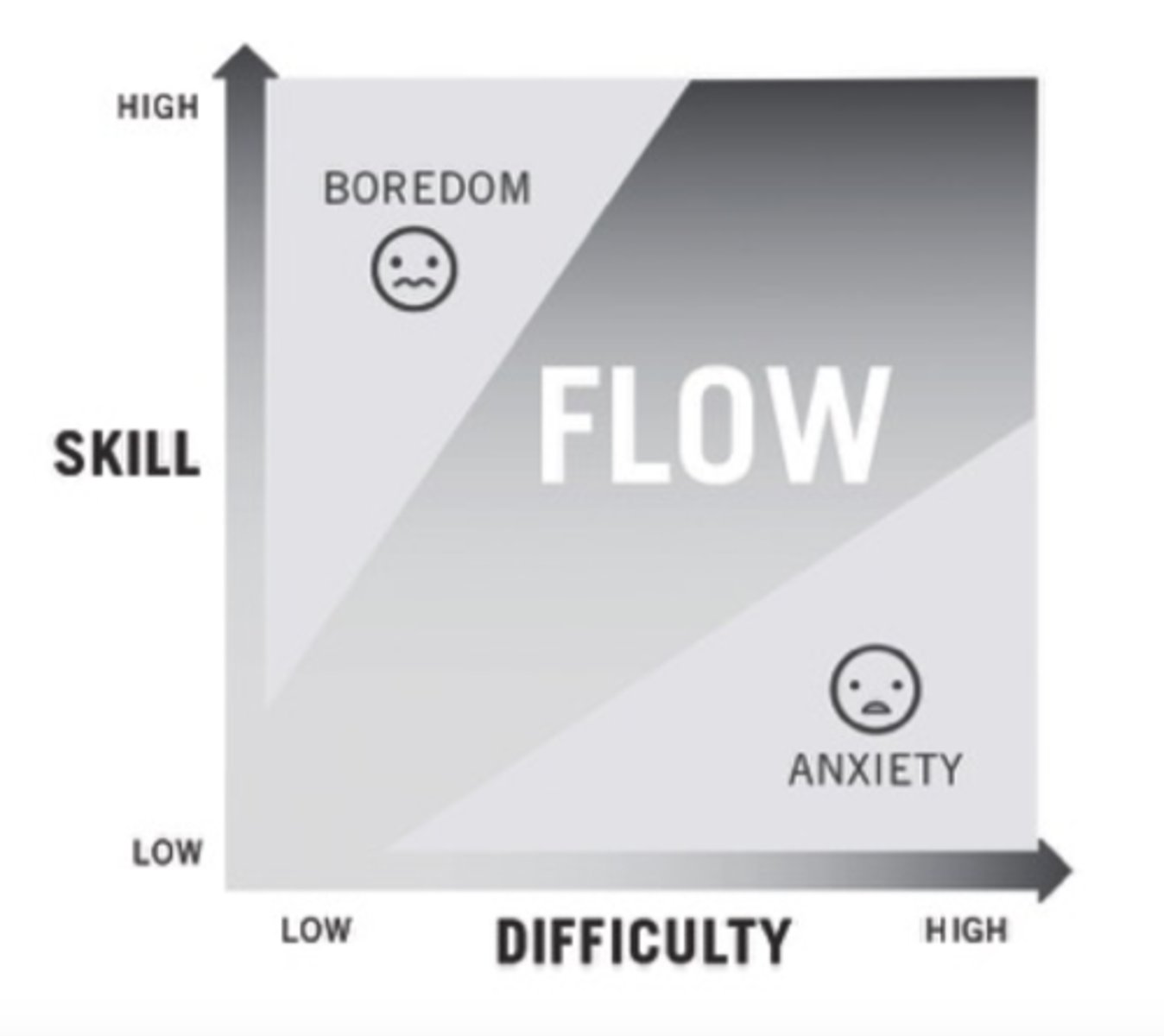
Who came up with flow?
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi
Three parts of flow
1. Mindful
2. Present
3. Focused
Epworth Sleepiness Scale
0 = would never doze
1 = slight chance of dozing
2 = moderate chance of dozing
3 = high chance of dozing
What does the Epworth Sleepiness Scale demonstrate?
- Demonstrates/calculates: your sleepiness through a questionnaire. Calculates your "chance of dozing" when doing certain activities.
- Some items: Sitting and reading, watching TV, inactive in a public space, passenger in a car for an hour without break, sitting and talking to someone, in a car stopped for a few minutes in traffic
- 0-24 scale
Epworth Scale Examples
-sitting and reading
-watching TV
-passenger in car
-lying down to rest in afternoon
-etc.
Epworth Scale analysing scores
0-7: It is unlikely that you are abnormally sleepy
8-9: You have an average amount of daytime sleepiness
10-15: You may be excessively sleepy depending on the situation. You may want to consider seeking medical attention.
16-24: You are excessively sleepy, and you should consider seeking medical attention
Positive Interventions
-five acts of kindness during one day contribute to people feeling much happier with feeling lasting for several subsequent days (conscious acts of kindness)
5 acts of kindness benefits
-We perceive others more positively and charitably
-Fosters a heightened sense of interdependence and cooperation in the social community
-encourages awareness and appreciation for your own good fortune
-... all jump starting an upward spiral of positive consequences
PERMA 4: e in perma is talking about _____ and _____
fulfillment and gratitude
Set Point Theory
-well-being is a relatively stable construct of behavior, genetics, and environment
-genetically determined level of happiness, to which one returns after positive or negative emotional experiences
Set point theory 2: What sets us above our set point?
-food (50)
-sex (100)
-coke (350)
-meth (1200)
Hedonism 1: Hedonic Treadmill
- Definition: the tendency of a person to remain at a relatively stable level of happiness despite a change in fortune or the achievement of major goals; as a person makes more money, expectations and desires rise in tandem, which results in no permanent gain in happiness
-no matter how much hedonism is thrown at you, you can/will adapt back when it is a hedonic pleasure ->you cant beat the hedonic treadmill, you will adapt back and hedonism doesn't encompass happiness
Hedonism 2: what is Hedonism?
The pursuit of pleasure; sensual self-indulgence
Three domains of vitality
food, sleep, exercise
Obsessive Passion
-you do it for others, for status, for glory or for money
-it is your whole life
-you are the best.... or you are nothing
-it controls you
Obsessive Passion Outcomes
-you have more negative emotions
-you feel guitar and show more self-destructive behavior
-you struggle to stay on task
-you are FAR more likely to burnout
Harmonious Passion
-you do it because you love it
-it is just a part of your life
-you do it to learn, not just to win
-you are in control
Harmonious Passion Outcomes
-you are happier and feel more fulfilled
-you enjoy better relationships
-you are more focused in all areas
-you are more energetic and productive
Martin Seligman
-He is referred to as the father of Positive Psychology.
-started off studying helplessness and then shifted to studying optimism and hope
-"Psychology is half- baked." We have baked the side of mental illness, but the side of our strengths and hopes and how to THRIVE is not yet baked.
-If you can teach someone to be depressed, you can also teach them to be hopeful.
William James
- founded the first psychology department at Harvard
- meliorism
- Great Grandfather of positive psychology
- "Excellence is the essential element of social evolution"
- "My experience is what I agree to attend to, only those items which I notice shape my mind without selective interest, experience is an utter chaos"
Abraham Maslow
-started his life in a miserable situation (Parents were very disturbing, referred to him as repulsive, came from intense poverty, food was chained away)
-went to university and became interested in psychology and wanted to study how to make us great/thrive
-founder of the self help movement
the grandfather of positive psychology,
-first to use the term.
-became obsessed with SELF ACTUALIZATION, rather than depression.
Communication: what is most important component
listening
The goal of communication
Is for each partner to feel understood by the other. Is NOT agreement or to solve the problem (yet). Some people just want to get to the solution. But if you spend the time to talk things through you're more likely to solve it. When you put the way we speak ahead, we get to the solution.
Rules for Speaker
-speak for self
-no mind-reading
-be brief
-stop so listener can paraphrase
How to paraphrase
"So, what I hear you saying is..."
"So, from your point of view..."
"It sounds like you..."
"So you..."
"Let me see if I've got it. You feel..."
Rules for listener
-only paraphrase
Positive emotions: advantages to students
-retain more words in a foreign language
-answer more questions and get higher percent correct
-more creativity
-perceived as more appealing
-greater enjoyment in social connections
-more likely to talk issues out
The Nun Study
-130 nuns entering the sisterhood
-had to write a statement why they wanted to enter
-blinded study
-only positive feelings predicted longevity:
Age 85:
-90% of most cheerful quartile alive
-34% of least cheerful quartile alive
Age 94
-54% of most cheerful quartile alive
-11% of least cheerful quartile alive
The Undoing Effect
-subjects were told they were going to speak in front of 100s of people, then were told they weren't. Then were showed 1 of 3 films (Sad, neutral, happy). The people who saw the happy video recovered from their stress level faster.
-if you want to do your best, recovering your stress is shorter/easier when you're around positive emotions
Broaden and Build (vs. Narrow and Constrict)
o Fredrickson's Theory:
- When you feel bummed down, you wallow alone, tend to go in a spiral that supports your level of down-ness; you narrow your views to make the spiral continue to narrow and restrict
- When you feel happy, you broaden and build, you seek out more of what makes you happy and recruit people in
We need more positive interaction vs. negative interaction for our well being.
Barbara Fredrickson
-Undoing Effect
-Broaden and Build
Growth Mindset VS Fixed Mindset
Growth: - Intelligence is a malleable quality that can be developed and cultivated through effort
- Beliefs follow the guidelines of the harder you try the more you will learn and that with effort anyone can change their intelligence levels
- Traits: enjoy learning new things, enjoy challenges, likely to persevere and succeed when challenge arises, develop, learning, they believe they are smart when they are growing
Fixed: - Intelligence is a fixed trait that cannot be developed
- Beliefs follow the guidelines that you are who you are and that you cant change
- Traits: avoid challenges and likely to abandon tasks when faced with set backs, validate what they know because they believe there is no more room for them to grow, proving, smart when flawless-no mistakes can be made
Carol Dweck
-Growth and Broke Mindset
-studied mindset focusing on motivation, personality, and development
Growth mindset allows a person to...
live a less stressful and more successful life
Explanatory Style
-The difference between resilience and helplessness
-Pessimism (internal) V. Optimism (external)
Communication Danger Signs
1. Escalation
2. Invalidation
3. Negative Interpretation
4.Withdraw
Selingman and Peterson together...
-wrote "Primer of Psychology" and "Character Strengths and Virtues"
Martin Selingman
-learned helplessness (dog study; we can learn to be helpless) (if we can learn to be helpless, we can learn to be hopefull)
-Father of Positive Psych
-half-baked psych
Meliorism
"it is about what we can do to change our position, the doctrine that the world or society may be improved and that suffering can be alleviated through rightly directed human effort "
Meliorism: What are the two kinds of meliorism and what are they?
-Mitigative Meliorism
getting rid of what we don't want
-Constructive Meliorism
getting more what what we do want