Shoulder Articulations, Movements, Purpose, Etc..
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
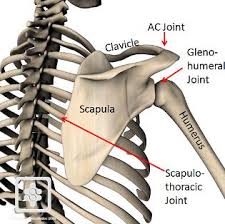
scapula articulations
• Acromion with lateral clavicle (AC joint)
• Glenoid fossa with the head of the humerus (glenohumeral joint)
• Thoracic rib cage, ribs 2-7
scapula purpose
• Provide stability to support upper extremity movement
• Muscular attachment
• Transmit forces from upper extremity to axial skeleton
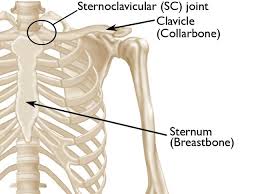
clavicle articulations
• Sternum and first costal cartilage (SC Joint)
• Acromion process (AC Joint)
clavicle purpose
• Holds arm away from trunk
• Transmits forces from upper extremity to axial skeleton
• Muscular attachment
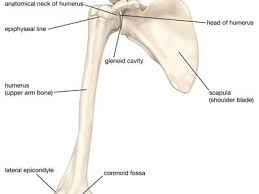
humerus articulations
• Head with glenoid fossa (glenohumeral joint)
• Radius and ulna at distal end (elbow)
humerus purpose
• Primary mover of the shoulder joint
• Allows for reach
• Muscular attachment
sternoclavicular articulation
Medial end of the clavicle
manubriurm sterni
first costal cartilage
sternoclavicular type
Synovial (plane)
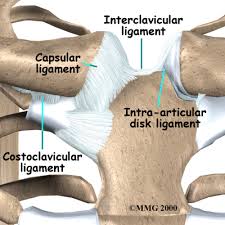
sternoclavicular capsule
• Surrounds joint
• Lined by synovial membrane
sternoclavicular ligaments
• Sternoclavicular
• Costoclavicular
Supraclavicular nerve
• Nerve to subclavius muscle
sternoclavicular innervated by..
• Trapezius
• sternocleidomastoid
• levator scapulae
• rhomboid
action: elevates the scapula/clavicle
Pectoralis minor and subclavius
action: depresses the scapula/clavicle
serrtaus anterior
action: clavicle glides forward
(protracts; anterior)
trapezius and rhomboid
action: clavicle glides back
(retract; posterior)
acromioclavicular joint articulation (AC)
Between acromion and lateral end of Clavicle
AC joint type
Synovial (plane)
AC joint capsule
Surrounds joint
Lined by synovial membrane
AC joint ligaments
• Superior and inferior acromioclavicular
• Coracoclavicular
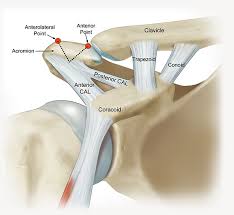
suprascapular nerve
acromioclavicular joint innervated by..
AC joint movement
Gliding movement
• Triggered by scapular rotation or clavicular elevation/depression
glenohumeral joint articulation
Head of humerus and glenoid fossa
• Hyaline articular cartilage
• Fossa is deepened by the labrum
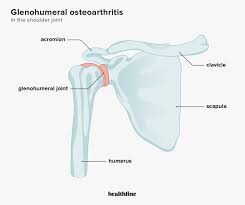
glenohumeral joint type
Synovial ball and socket
glenohumeral joint capsule
• Medial attachment - margin of glenoid fossa
• Lateral attachment - anatomical neck of the humeral head to the medial side of humeral shaft
glenohumeral ligaments
• Transverse humeral ligament
• Coracohumeral ligament
• Coracoacromial ligament
glenohumeral joint synovial membrane
• Lines capsule
• Surrounds biceps tendon
• Forms a tubular sheath around the long head of biceps brachii
• Forms the subscapularis bursa
Axillary nerve and suprascapular nerve
glenohumeral joint is innervated by..
anterior fibers of the deltoid,
pectoralis major,
biceps, and
coracobrachialis
action: flexes shoulder/arm
posterior fibers of deltoid,
latssimus dorsi,
and teres major
action: extension of shoulder/arm
middle fibers of deltoid and supraspinatus
action: abduction of the shoulder/arm
pectoralis major,
latssimus dorsi,
teres major,
and teres minor
action: adduction of the shoulder/arm
infraspinatus,
teres minor,
and posterior fibers of deltoid
action: laterally rotates arm/shoulder
subscapularis,
latssimus dorsi,
teres major,
anterior fibers of deltoid,
pectoralis major
action: medially rotates arm/shoulder
trapezius origin
from medial third of superior nuchal line of occipital bone
external occipital protuberance
ligamentum nuchae; from spine of seventh cervical vertebra
spines and supraspinous ligaments of all thoracic vertebrae
trapezius insertion
upper fibers - lateral third of clavicle
middle fibers - acromion and upper border of spine of scapula
lowest fibers - medial end of spine of scapula
trapezius nerve supply
motor fibers from spinal part of accessory nerve (i.e. cranial nerve XI)
sensory fibers from third and 4th cervical nerves
trapezius action
• upper fibers elevate scapula
• middle fibers pull scapula medially
• lower fibers pull medial border of scapula inferiorly resulting in glenoid cavity facing in anterosuperior directon
latissimus dorsi origin
from posterior part of iliac crest
lumbar fascia
spines of lower six thoracic vertebrae (deep to trapezium); from lower three or four ribs
few fibers from inferior angle of scapula
lattismus dorsi insertion
tendon wraps around lower border of teres major muscle and inserted into floor of bicipital groove of humerus
thoracodorsal nerve
(a branch of posterior cord of brachial plexus)
latissimus dorsi is innervated by..
latissimus dorsi action
extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
levator scapulae origin
Transverse process of upper four cervical vertebrae
levator scapulae insertion
Medial border of scapula (opposite of supraspinous fossa)
3rd & 4th cervical nerve,
dorsal scapular nerve
levator scapulae innervated by..
levator scapulae action
Pulls scapula medially and superiorily
• Acts with middle fibers of traps and rhomboids
• Braces shoulder joint during flexion
rhomboid minor origin
Lower part of ligamentum nuchae and spine of 7th cervical and first thoracic vertebrae
rhomboid minor insertion
medial border of scapula
dorsal scapular nerve
rhomboid minor is innervated by..
rhomboid minor action
• Elevates medial border of scapula
• Pulls scapula medially