Module 2- Foundations in Biology
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
3D or 2D?
- 2D
3D or 2D?
- 3D
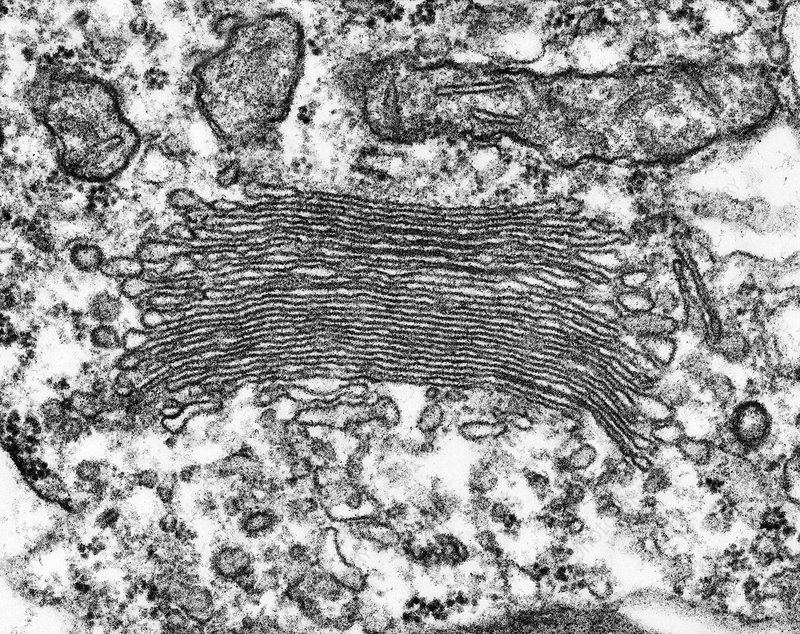
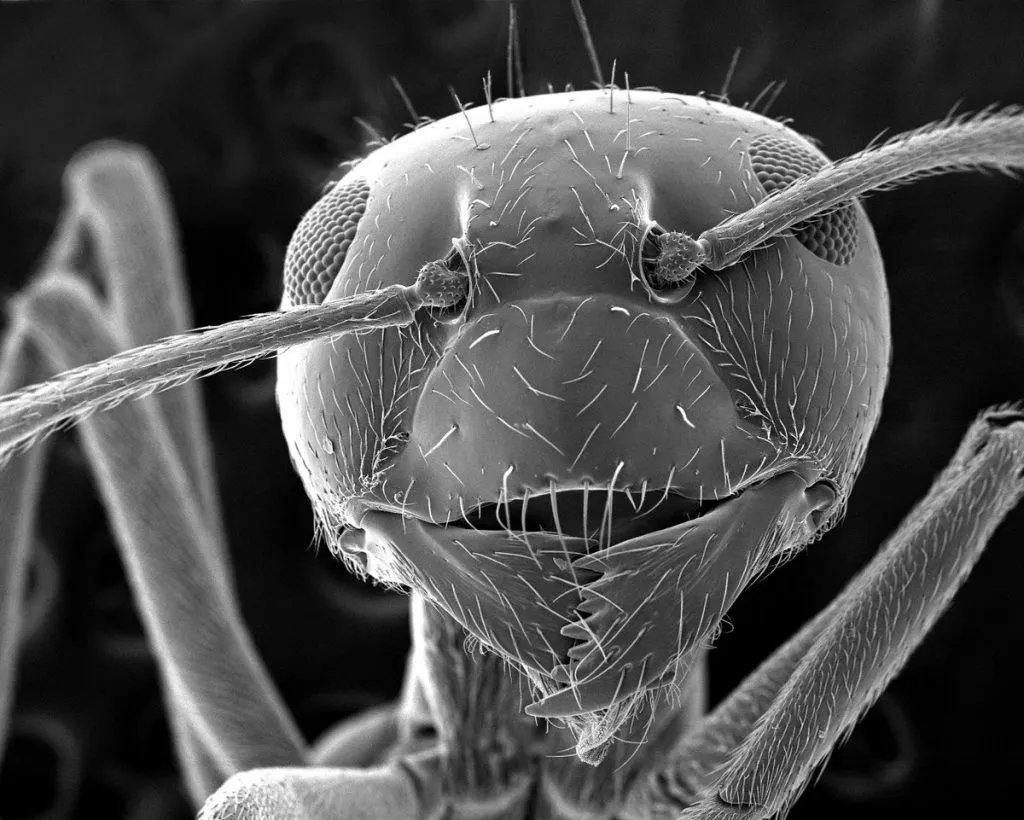
Why are stains used on specimens?
Why would a wet mount be used for a specimen?
- Cell wall
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Nuclear envelope
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondria
- lysosomes
- centrioles
- involved in the organisation of spindle fibres during cell division
- Chloroplasts
5 points
* Protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm
* Mitochondria- grows and divides, increases in number
* In plant cells - grow and divides, increases in number
* Normal metabolic processes carry on occurring
S
G2
4 things
Cell grows in size
Organelles are replicated
Protein synthesis
3 things
Energy stores increase
Duplicated DNA checked for errors
Cytokinesis
DNA of the cell may be damaged
Senescent cells
\
(4points)
\- grown to the correct size
\- that replicated DNA is error free,
\- chromosomes are in their correct positions during mitosis
\- to ensure that 2 identical daughter cells are created from the parent cell
3 points
\- nutrients
\- growth factors
\- DNA damage
\- Cell size
\- DNA damage
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts
What type of proteins are enzymes, globular or fibrous?
Globular
What is an anabolic reaction?
Metabolic reactions that construct molecules from smaller units
Which type of reaction requires energy from ATP hydrolysis?
Anabolic reactions
What is a catabolic reaction?
Metabolic reactions that break molecules down into smaller units
Which type of reaction releases energy
Catabolic or anabolic?
Catabolic
Which reaction builds molecules and requires energy?
Anabolic reaction
Which reaction breaks up molecules and releases energy?
Catabolic
Define metabolism
The sum of all of the different chemical reactions that take place in living cells
What is the name which describes
“Enzymes can only increase the rate of a reaction up to a certain point”?
Vmax
What does Vmax mean in enzyme action?
The maximum initial rate of the enzyme catalysed reaction
What must happen in order for an enzyme controlled reaction to happen?
Substrate and enzyme molecules must collide
What is meant by specificity of enzymes?
Enzymes are specific to particular substrates, and have specific active sites complementary to the substance they catalyse the breakdown of
What is activation energy?
The energy required to begin a reaction
What do enzymes do?
Reduce the activation energy required
What are the two models of enzyme action?
lock and key model
Induced fit hypothesis
What forms when the substrate is bound to the enzyme?
An enzyme substrate complex
Summarise the lock and key model (3 points)
Enzyme and substrate are complementary
Specific enzyme ‘fits’ into the active site of the enzyme
Products released leaving the enzyme unchanged
What is the induced fit hypothesis?
A modified lock and key explanation for enzyme action where the enzyme becomes slightly modified in shape when binding to the substrate
What an intracellular enzyme?
An enzyme that acts within the cell
Give an example of an intracellular enzyme…
Catalase
What is catalase an example of?
An intracellular enzyme
What does catalase do?
Breaks down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water
Which enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide?
Catalase
True/False ?
“ Catalase is an extracellular enzyme”
False, intracellular
Why is catalase important? (2)
Because it breaks down hydrogen peroxide in plant and animal tissues
Hydrogen peroxide is toxic
What is an extracellular enzyme?
Enzymes that work outside the cell that made them
Usually extracellular enzymes work outside the cell that made them, how does this differ in fungi? (3 steps)
In fungi the enzyme is secreted outside of the body
Organic matter is broken down
Then it is absorbed and used by the fungi for growth
Give 2 examples of extracellular enzymes involved in digestion .
Amylase, trypsin
Why are extracellular enzymes necessary?
Because large molecules that cannot enter cells directly through the cell surface membrane need to be broken down into smaller components first
State 2 types of organisms that rely on extracellular enzymes to gain nutrition
Single celled, multicellular
Why is starch digested in 2 steps?
Because two enzymes are needed, each enzyme catalyses 1 reaction
In the first step of digestion of starch what are starch polymers broken into?
A disaccharide; maltose
Which enzyme is involved in the breakdown of starch into maltose?
Amylase
Where is amylase secreted? (2)
Saliva in the mouth
pancreatic juice in the small intestine
After starch is broken down into maltose by amylase; what happens next?
Maltose is broken down into glucose by maltase
What does maltase break maltose down into?
Glucose
True or false
“Maltose is a monosaccharide”
If false, give the correct answer
False, disaccharide
Where can maltase be found?
In the small intestine