Endocrine System II
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
two types of feedback control
negative
positive
positive feedback control
response to stimulus amplifies the stimulus
negative feedback control
response to stimulus reduces the stimulus
endocrine signaling
a cell targets a distant cell through the bloodstream
neuroendocrine signaling
neurosecretory cell produces neurohormones that go to the bloodstream and then in everywhere in the body
two kinds of hormonal effects
tropic
non-tropic
tropic effect
act on another endocrine gland to stimulate the release of other hormones
non-tropic effect
act directly on target tissue
hyposecretion of hormones
hormone production too low
hypersecretion of hormones
hormone production too high
hypothalamus
in brain
neuroendocrine
controls most hormone activity
two modes of action for the hypothalamus
produces & releases releasing hormones (RH) and inhibiting hormones (IH)
produces antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT)
SEQ hypothalamus production and release of RH and IH
into pituitary portal veins
anterior pituitary (target tissue)
SEQ hypothalamus production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin
ADH & OT produced in cell bodies
axons extend into posterior pituitary
stored in vesicles in axon terminals until neuron is stimulated
released by posterior pituitary
Posterior pituitary involves which hormones?
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT)
ADH stimulus
dehydration
ADH target tissue
kidneys;
returns more water to blood → less urine produced
oxytocin target tissues
uterine → contractions
mammary glands → milk
brain → behavior (maternal care, pair bonding)
Anterior pituitary involves the ____ gland.
endocrine
Endocrine gland produces hormones into…
bloodstream
Every anterior pituitary hormone is controlled by at least one…
releasing hormone (RH)
GnRH (Gonadotropin RH) → LH → (target) → (effects)
target = reproductive system
effects = stimulates production of sex hormones by gonads
GnRH (Gonadotropin RH) → FSH → (target) → (effects)
target = reproductive system
effects = stimulates production of sperm and eggs
TRH (Thyrotropin RH) → TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) → (target) → (effects)
target = thyroid gland
effects = stimulates the release of thyroid hormone (TH), which regulates metabolism
GHRH (growth hormone RH) → GH → (target) → (effects)
target = liver, bone, muscles
effects = induces targets to produce insulin-like growth factors (IGF), which stimulate body growth & a higher metabolic rate
CRH (Corticotropin RH) → ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) → (target) → (effects)
target = adrenal cortex
effects = induces targets to produce glucocorticoids which regulate metabolism and the stress response
thyroid gland
2 lobes on the surface of the trachea
What are the two hormones produced by the thyroid gland?
T3 & T4
thyroid hormone (TH)
T3 & T4
target cells throughout the body
T3 & T4
derived from tyrosine (amino acid) & iodine
What does the thyroid gland do?
stimulates metabolism
maintains normal BP, HR, muscle tone
regulates digestive & reproductive functions
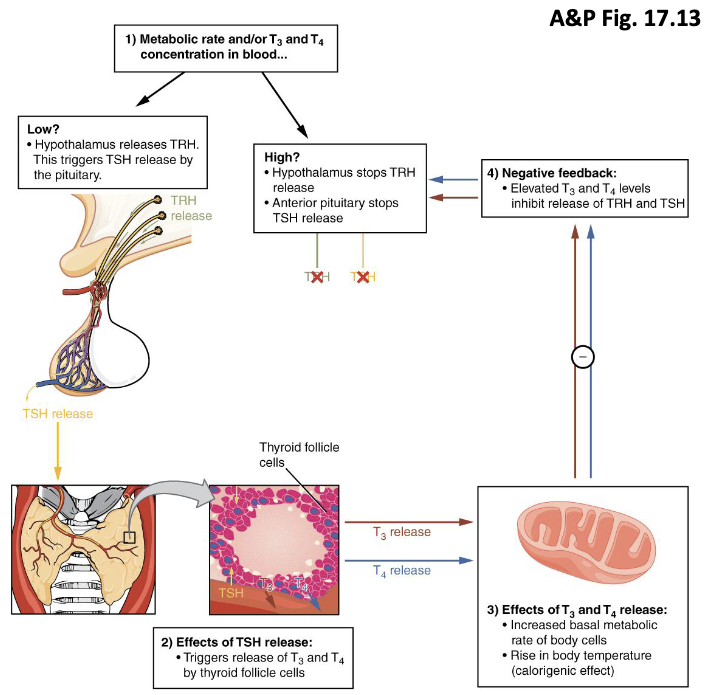
SEQ regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin RH (TRH)
anterior pituitary secretes thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) into blood
thyroid gland (tropic effect)
T3 & T4
cells throughout the body
response
draw the regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
hypothyroidism
decreased metabolic rate = weight gain & lethargy
goiter
goiter
enlarged thyroid gland
caused by iodine deficiency
hyposecretion → anterior pituitary increased TSH → thyroid gland enlarged
hyperthyroidism
high body temp & sweating → weight loss & high BP
Grave’s disease
Grave’s disease
autoimmune disease;
abnormal antibodies bind to & stimulate TSH receptors → hypersecretion of hormone
Thyroid detects if blood Ca2+ levels are too high and secretes _____.
calcitonin
calcitonin target tissues
bone → inhibits Ca2+ removal
kidneys → increases Ca2+ removal
What is the major target of the growth hormone?
liver
What is the response when growth hormones reach the liver?
release of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), which stimulates bone & cartilage growth
If growth hormone levels in the blood are high, the hypothalamus secretes…
growth hormone inhibitor hormone (GHIH)
→ anterior pituitary releases less GH
If growth hormone levels in the blood are low, the hypothalamus secretes…
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
→ anterior pituitary releases more GH
Hyposecretion of growth hormones in childhood leads to…
pituitary dwarfism
pituitary dwarfism
small, correct proportions
treatment for pituitary dwarfism
before puberty;
human GH from cadavers;
recombinant DNA tech hGH gene inserted into bacteria
Hypersecretion of growth hormones during childhood leads to…
gigantism; normal proportions
Hypersecretion of growth hormones during adulthood leads to…
acromegaly;
not taller;
abnormal bone growth in hands, feet, and head
Where are the adrenal glands?
on top of each kidney
What are the two parts of the adrenal glands?
adrenal cortex (outer)
adrenal medulla (middle)
Adrenal cortex responds to _____ signals.
endocrine
Adrenal medulla responds to _____ signals.
nervous
Adrenal cortex is used during ____ stress.
chronic
Adrenal medulla is used during ____ stress.
acute
What happens in the adrenal cortex during chronic stress?
hypothalamus secretes corticotropin RH (CRH)
anterior pituitary releases ACTH
adrenal cortex produces corticosteroids
corticosteroids
synthesized from cholesterol
What are the two main types of corticosteroids?
glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids regulate…
glucose metabolism
Mineralocorticoids regulate…
mineral metabolism
How do glucocorticoids regulate glucose metabolism?
breaks down muscle proteins
liver converts amino acids into glucose
glucose is released into blood
How do mineralocorticoids regulate mineral metabolism?
aldosterone regulates water/sodium balance in blood
alarm reaction
fight or flight response
What are the two hormones involved with the adrenal medulla?
epinephrine (Epi) = adrenaline
norepinephrine (NE)
What happens in the adrenal medulla during acute stress?
sudden stimulus
hypothalamus
activates adrenal medulla via nerve impulses
Epi & NE released
What is the response when epi and NE are released?
increased blood to brain, muscles, heart
breakdown of glycogen
increased metabolic rate
increased oxygen delivery by:
increased heart rate and stroke volume
increased breathing rate
How many glands are in the tissue surrounding the thyroid (parathyroid glands)?
4
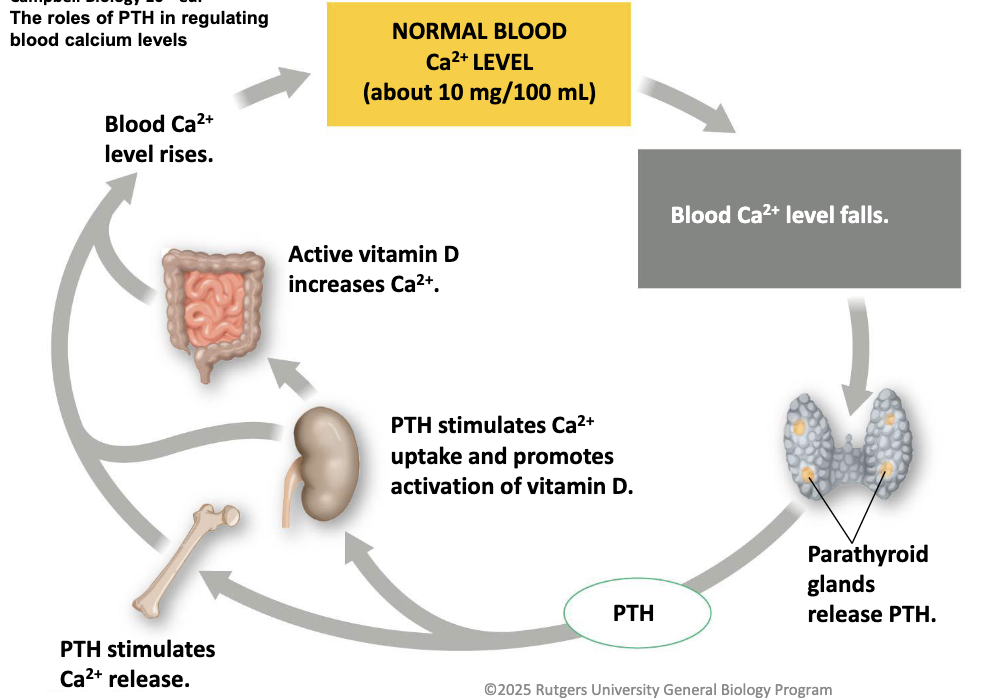
What do the parathyroid glands do?
detect blood Ca2+ levels
What do the parathyroid glands do when Ca2+ levels are too low?
releases parathyroid hormone (PTH)
What are the direct effects of releasing the parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
bone releases Ca2+
kidneys don’t release Ca2+ in urine
What are the indirect effects of releasing the parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
kidneys are stimulated to activate vitamin D
vitamin D acts on intestine
intestines increase uptake of Ca2+ from blood
draw the effect of the parathyroid glands on low blood Ca2+ levels
PTH and calcitonin are…
antagonistic
Pancreas maintains…
glucose homeostasis
draw the pancreas and how it works