APUSH Unit 8 Test
5.0(4)Studied by 36 people
0%Unit 6: Period 6: 1865–1898 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 2:11 AM on 3/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Imperialism
Indicates the __expansion of a nation’s empire__
2
New cards
Naval Act of 1900
Authorized the __construction of battleships that would be clearly offensive in nature__
3
New cards
Spanish-American War
* 1898
* __Cuba is controlled by Spain__
\
* __US has many interests in Cuba__
* Proximity
* Economics (sugar cane)
* Independence
* Yellow Journalism
* __Cuba is controlled by Spain__
\
* __US has many interests in Cuba__
* Proximity
* Economics (sugar cane)
* Independence
* Yellow Journalism
4
New cards
Annexation of Hawaii
* __Forced annexation__, territorial expansion, for __US business__
* Grover __Cleveland says no__, __McKinley convinces Congress__
* 1898
* Grover __Cleveland says no__, __McKinley convinces Congress__
* 1898
5
New cards
Treaty of Paris
* 1898
* __Cuban independence__
* US gets __**Guam**__ and __**Puerto Rico**__ and pays $20 million for the __**Philippines**__
* __Cuban independence__
* US gets __**Guam**__ and __**Puerto Rico**__ and pays $20 million for the __**Philippines**__
6
New cards
Open Door Policy
European Powers had __divided China__ into “__**spheres of influence**__” (territories where the country controls)
* Russia
* England
* __**Japan**__
* Germany
* Austria
* Russia
* England
* __**Japan**__
* Germany
* Austria
7
New cards
Yellow Journalism
* Embraced __dramatic headlines__ and __exaggerated storylines__
* Takes of ripe and __exciting foreign lands__
* Takes of ripe and __exciting foreign lands__
8
New cards
Alfred Thoyer Mahan
* The __Influence of Sea Power upon History__
* __“To be a World power, a great navy is needed”__
* __“To be a World power, a great navy is needed”__
9
New cards
Social Darwinism
* The application of Darwin's theory of __natural selection to society__
* Specifically in __economics and business in America__
* Used by __supporters of imperialism__
* Specifically in __economics and business in America__
* Used by __supporters of imperialism__
10
New cards
White Man’s Burden
(__Pro-Expansionists__)
* US wants to __Christianize the world__
* US wants to __Christianize the world__
11
New cards
Reconcentration
Sent civilians who the __Spanish thought might be potential allies of the rebels__ into __heavily guarded camps__
12
New cards
Jingoism
Combination of __intense American nationalism__ with a __desire for adventure abroad__
13
New cards
USS Maine
* Exploded in Havana Harbor
* __#1 Reason for US involvement__
* US press blames Spain
* __#1 Reason for US involvement__
* US press blames Spain
14
New cards
Rough Riders
__Teddy Roosevelt__ lead this group up __San Juan Hill__ in the most famous event of the war
15
New cards
Teller Amendment
* US has __**NO INTEREST**__ in taking over __Cuba__
* Necessary to appease other countries
* Necessary to appease other countries
16
New cards
Platt Amendment
* US and Cuba
* __US may intervene in Cuban affairs__
* US may maintain naval bases in Cuba (Guantanamo)
* __US may intervene in Cuban affairs__
* US may maintain naval bases in Cuba (Guantanamo)
17
New cards
Panama Canal
* Will __reduce the travel time from Atlantic to the Pacific__
* Helps __trade__ and the __navy__
* Helps __trade__ and the __navy__
18
New cards
Roosevelt Corollary
* The US will __**police**__ the Americans/__**intervene**__ in __**Latin America**__ to protect US interests
* Keep __European powers away__
* Keep __European powers away__
19
New cards
US isolation changes drastically in the late 1800s because
* __**New Industry and Markets**__ (buy and sell with new countries)
* __Yellow Journalism__
* __Religion__ (Christianize the poor heathens, little brown brothers), (White Man’s Burden)
* __Darwinism__ (survival of the fitest)
* __Yellow Journalism__
* __Religion__ (Christianize the poor heathens, little brown brothers), (White Man’s Burden)
* __Darwinism__ (survival of the fitest)
20
New cards
Josiah Strong
__Our Country: Its Possible Future and Present Crisis__
21
New cards
Sanford Dole
__Pineapple King__
22
New cards
Remember…
The US does __**NOT**__ __receive Hawaii in the Spanish-American__
23
New cards
Reasons for US involvement in S-A War
* __Yellow Journalism__
* __Economic Concerns__
* __De Lome Letter__ (Spanish diplomat disses McKinley)
* __**USS Maine explodes in Havana Harbor**__
* __Economic Concerns__
* __De Lome Letter__ (Spanish diplomat disses McKinley)
* __**USS Maine explodes in Havana Harbor**__
24
New cards
Imperialists
Argue US __control of the Philippines will enhance US trade__ in the Pacific/Asia region
* Causes a __huge debate in the US__
* Causes a __huge debate in the US__
25
New cards
Anti-Imperial League
* __Universal presidents__
* __Mark Twain__
* __Samuel Gompers__
* __Andrew Carnegie__
* __Consent of the governed__?
* Why such interest in Asia?
* __Mark Twain__
* __Samuel Gompers__
* __Andrew Carnegie__
* __Consent of the governed__?
* Why such interest in Asia?
26
New cards
Foraker Act
__Puerto Rico__
* __Sets up gov.__
* Future citizenship?
* __Sets up gov.__
* Future citizenship?
27
New cards
Results of S-A War
* __Respect__ from European powers
* National __Pride__
* __**US becomes a power in the Pacific region**__ (__**markets/resources**__)
* __Navy and Army much improved__
* (critical need for a quicker route to the Pacific)
* National __Pride__
* __**US becomes a power in the Pacific region**__ (__**markets/resources**__)
* __Navy and Army much improved__
* (critical need for a quicker route to the Pacific)
28
New cards
Election of 1900
* GOP- __McKinley, T. Roosevelt__ (VP)
* DEM- __Bryan__
* __Imperialism was the biggest issue__
* DEM- __Bryan__
* __Imperialism was the biggest issue__
29
New cards
Russo-Japanese War 1903
* __TR does not want Japan to dominate Asia__ (__**Manchuria**__)
* Portsmouth Treaty
* Nobel Peace Prize
* Portsmouth Treaty
* Nobel Peace Prize
30
New cards
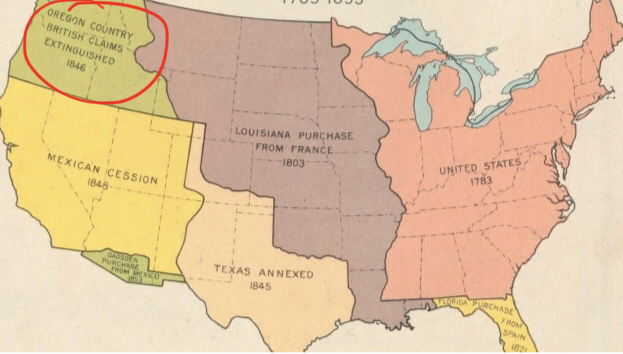
Top Green Corner
Oregon Country British Claims Extinguished
* 1846
* 1846
31
New cards
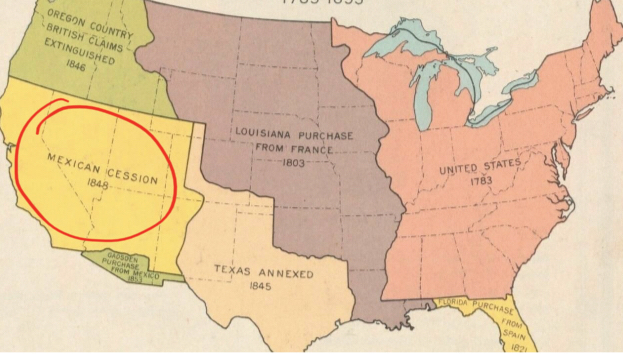
Left Yellow
__Mexico Cession__
* 1848
* 1848
32
New cards
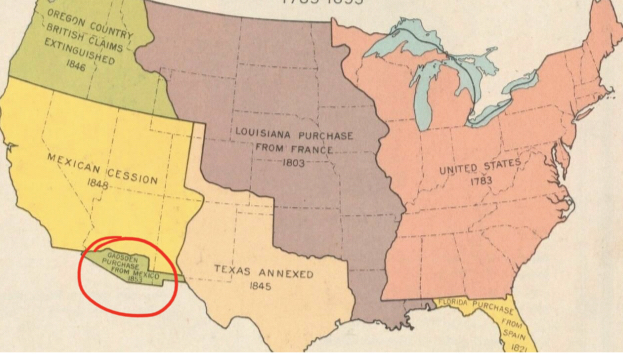
Bottom Green Corner
__Gadsden Purchase__ from Mexico
* 1853
* 1853
33
New cards
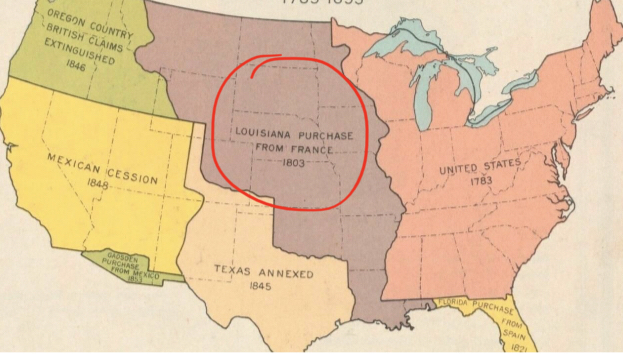
Purple Center
__Louisiana Purchase__ from France
* 1803
* 1803
34
New cards
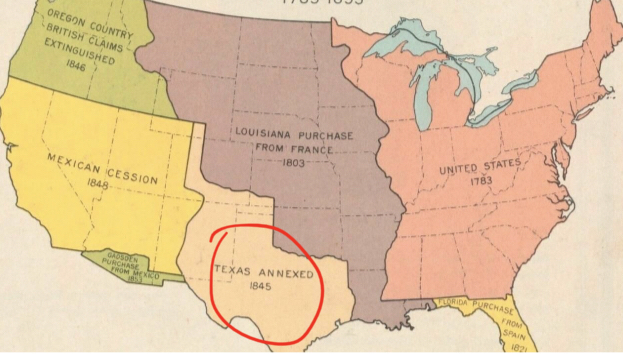
Bottom Light Pink Center
__Texas Annexed__
* 1845
* 1845
35
New cards
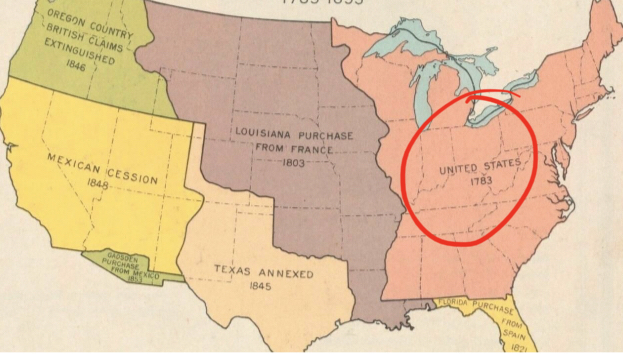
Right Pink
__United States__
* 1783
* 1783
36
New cards
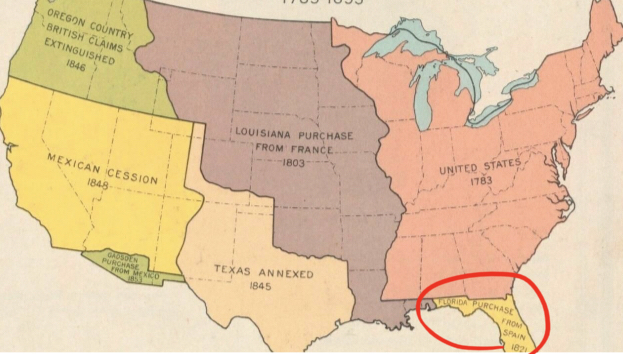
Right Yellow Corner
__Florida Purchase__ from Spain
* 1821
* 1821
37
New cards
William Lloyd Garrison
Showed __how bad slavery is__
38
New cards
Abraham Lincoln
__Doesn’t want slavery to extend__ into western territories
39
New cards
Stephen Douglas
__Popular Sovereignty__
40
New cards
John C. Calhoun
__Nullification__
41
New cards
William Bryan
__Cross of Gold Speech__
42
New cards
Andrew Jackson
__Fought the Seminoles__ in Florida
43
New cards
Teddy Roosevelt
* Big Stick Diplomacy
* __“Speak softly and carry a big stick”__
* __“Speak softly and carry a big stick”__
44
New cards
Hawaii and Philippines
* Hawaii
* __First example of imperialism__
* Philippines
* __Most controversial__
* __First example of imperialism__
* Philippines
* __Most controversial__
45
New cards
What was the Grange and what did it do
* __Organization that formed farmer cooperatives__ to enable members to __enjoy economies of scale by buying and marketing products__
* __Organized politically and sponsored state legislation__ to regulate railroads and grain elevators
* __Organized politically and sponsored state legislation__ to regulate railroads and grain elevators
46
New cards
Insular Cases
Several court cases which __concerned the status of territories acquired by the U.S. during the Spanish–American War__
* The __constitution does not follow the flag__
* The __constitution does not follow the flag__