Unit 4 - States & Changes of Matter
Gases
- Kinetic-Molecular Theory
- Gases are a large number of constantly and randomly moving particles
- Most of the volume of a gas is empty space
- There is no force of attraction/repulsion between particles
- All collisions are perfectly elastic
- No energy is gained/loss during collisions
- Kinetic Energy - The energy of movement [of particles]
- Average kinetic energy is directly proportional to temperature
- KE = (1/2)mv^2
- Ideal Gas - A theoretical gas composed of randomly moving particles that don’t interact with each other
- Describes the behavior of most gases under common conditions
- Fits the description of the Kinetic-Molecular Theory
- Real gases deviating from this model under extreme conditions
- Properties of Gases
- Compressibility
- Change in pressure → change in volume
- No fixed shape/volume
- Expands to fit container
- Property Relationships
- Pressure & Volume have an inverse relationship
- Volume and Number of Atoms(# of moles) have a direct relationship
- Pressure and Temperature have a direct relationship
- Collision with container walls cause pressure
- More/harder collisions = more pressure
- Pressure = Force / Area
- Volume and Temperature have a direct relationship
- Pressure and Number of Atoms(# of moles) have a direct relationship
- Diffusion - Movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
- Effusion - Movement of gas through a smaller opening into a larger volume
- Graham’s Law - Rate of effusion is inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass
Liquids
- Kinetic energy of individual particles is similar to that of the intermolecular attraction between them
- Properties
- More dense than gases
- Have a fixed volume
- Particles aren’t fixed in place
- Can flow freely
- Viscosity - The thickness / resistance to flow of a liquid
- Directly related to intermolecular force
- Directly related to size of molecules
- Inversely related to temperature
- Takes the shape of their container
- Surface Tension - The tendency for a liquid to resist penetration
- Directly related to intermolecular force
- Surfactant - chemical compounds that can decrease surface tension
- Incompressible
- Can be used to transmit force, i.e hydraulics
- Dissolvability - When a solid, liquid, or gas becomes integrated into a host liquid
- Dissolved particles are dispersed evenly throughout the liquid
- Miscible Liquids - liquids that are able to dissolve into each other
- Immiscible Liquids - liquids that are not able to dissolve into each other
- Intermolecular Forces
- Caused by uneven electron distribution
- Affects interactions between particles
- The stronger the force, the more kinetic energy particles need to move
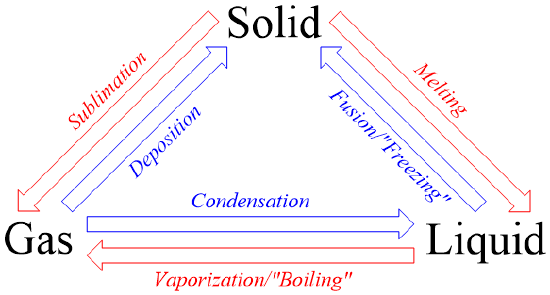
- Condensation - Gas → Liquid
- Caused by intermolecular force > kinetic energy, meaning particles are pulled in towards each other
- Evaporation/boiling - Liquid → Gas
- *Evaporation is when small amounts of particles randomly gain enough energy, boiling is when the entire substance as a whole gains enough energy to change
- Caused by kinetic energy > intermolecular force, meaning particles are pulled away from each other
- Boiling point has a direct correlation w/ boiling points
- Higher intermolecular force → higher boiling point
- i.e ionic and polar covalent compounds have higher boiling points like non-polar covalent compounds
- Freezing - Liquid → Solid
- Caused by intermolecular force > kinetic energy
- Melting - Solid → Liquid
- Caused by kinetic energy > intermolecular force
Solids and Plasmas
- Solids
- Properties
- Low energy
- Rigid structure
- Molecules vibrates instead of move
- Fixed shape & volume
- Crystal - A solid whos components make up a highly ordered microscopic structure
- Long Range Order - A property of crystals where their atomic particles show a periodic (recurring) pattern or shape
- Lattice - A regular arrangement of atoms, molecules, etc
- Amorphous Solids - Solids with particles arranged in non-uniform patterns
- Can be caused by rapid cooling such that particles do not have time to fully arrange into a crystalline structure
- Lack of long range order
- Compressible
- No definitive properties like boiling points due to changing pattern of molecules throughout
- Molecules can shift & move past each other over time
- Plasmas
- Properties
- Composed of ionized (high-energy) particles
- EXTREMELY HOT (high temperature)
- Conducts electricity
- Compressible
- No definite volume/shape
- Examples: Lightning, Stars, Auroras, Fluorescent Lights, Ion Thrusters, Arc Welders, Plasma Displays (plasma TVs), Plasma Balls, etc
- Thermal Equilibrium - Temperature is equal to its surroundings
- Plasma can be “cold“ when:
- Their electrons break off from their nucleuses and move extremely quickly, dissipating the energy quickly
- The energy in the electrons gets converted to light
- Only a small percentage of the overall substance is ionized into a plasma
- Comparisons
- Conduct Electricity - Plasmas always conduct electricity, only some solids do
- Density - Plasmas have low density, solids have high density
- Shape & Volume - Solids have fixed shape and volume, plasmas don’t
- Kinetic Energy - Plasmas have high kinetic energy, solids have low kinetic energy
- Composition - Plasmas are made of electrons and cations, solids are made of neutral particles or cation/anion pairs
Phase Changes
- Most of the phase changes are covered previously, so the only information here is going to be non-covered vocab and concepts
- Vapor Pressure - The pressure exerted by the gas in equilibrium with a liquid
- Changes based on altitude; higher pressure → harder to boil
- Higher vapor pressure → more likely to evaporate
Properties of Water
- Water = H2O
- Has a total of 8 valence electrons; stable
- There are single bonds between the oxygen and each hydrogen, and two pairs of non-bonded electrons on the other side of the oxygen atom
- “Tetrahedral“ electron-domain geometry
- “bent“ molecular geometry
- Bond Angle of 104.5*
- Properties
- Oxygen --- Hydrogen bonds are highly polar → water is a polar molecule
- Oxygen is partial negative, hydrogens are partial positive
- Allows for hydrogen bonds
- Strong solvent
- Like dissolves like → Water mostly dissolves ionic and polar covalent compounds
- Process of dissolving
- Dissociation - Water breaks an ionic compound into cations and anions
- Hydration - Water surrounds “broken apart“ substances
- Adhesion/Cohesion - Intermolecular forces; polar “stick“ to polar
- Adhesion is with other molecules, cohesion is with itself
- Strong surface tension
- High specific heat capacity
- Uses


