Ch08 Signal Transduction & Neuronal Integration
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APK2105 @ UF | Dr. Nguyen | Module 2 | Ch 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
electrical synapse
A type of synapse where electrical “coupling” of cells w/ similar functions occurs at gap junctions and is less common.
chemical synapse
A type of synapse were neurotransmitters communicate w/ neurons, muscles, or glands, and is the most common.
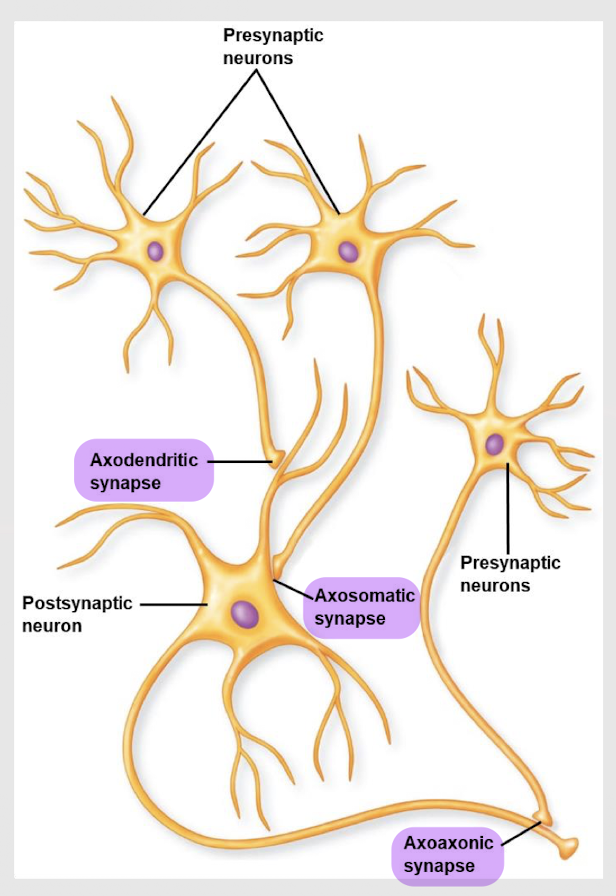
axodendritic, axosomatic, axoaxonic
What are the 3 types of chemical synapses?
axon terminal
The more Ca2+ allowed into the _______ _________, the more neurotransmitter released.
frequency; Ca2+; axon terminal
The greater the ________ of action potentials, the more _____ channels open in the _____ __________, leading to greater neurotransmitter release.
reuptake molecule
Protein that takes up neurotransmitters from the synapse into the presynaptic axon terminal for recycling
SSRIs
Medication that prevents the reuptake of serotonin in the synapse to increase serotonin, alleviating symptoms of depression
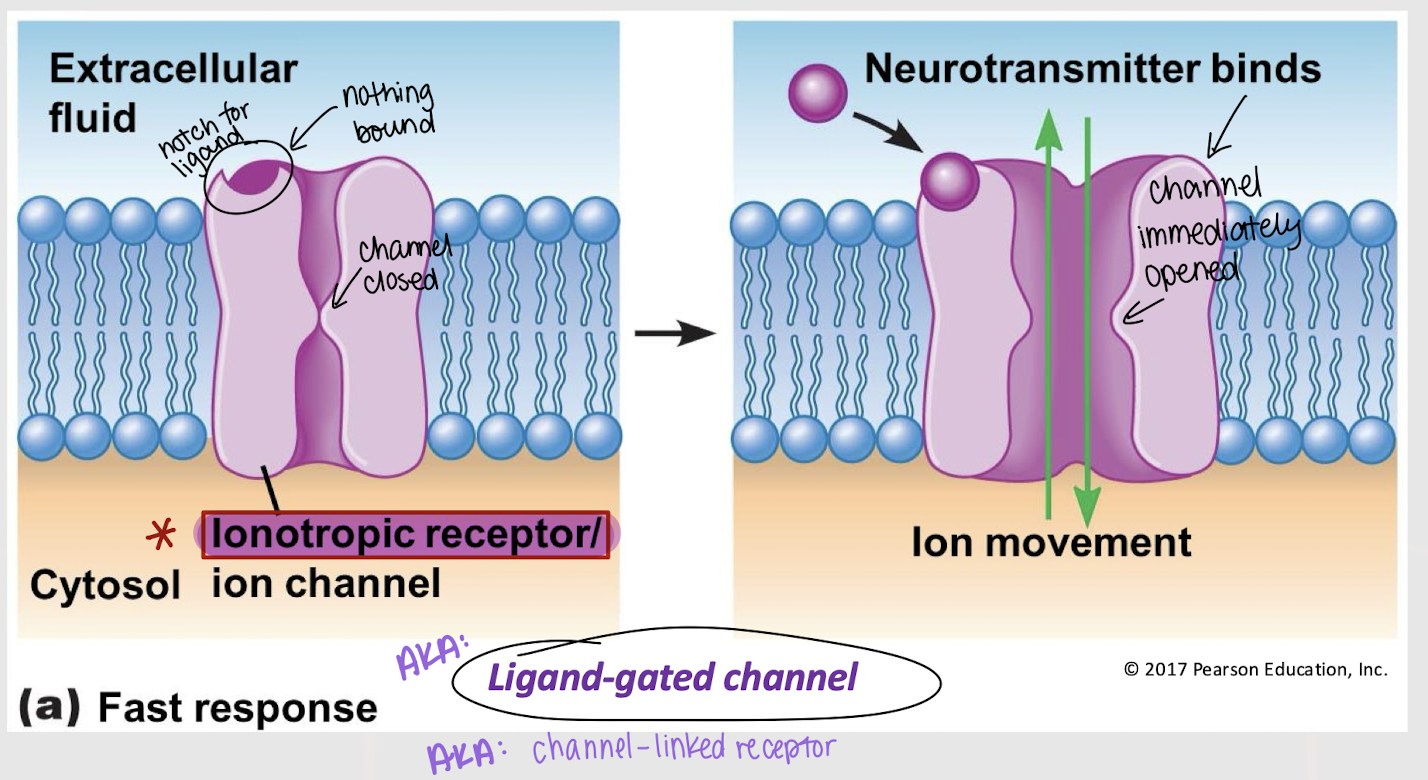
ionotropic receptor; fast
What is another name for a ligand-gated channel / channel-linked receptor? Does this receptor act fast or slow?
post-synaptic potential (PSP)
Change in membrane potential Vm in the postsynaptic neuron due to neurotransmitter binding, which can be excitatory (EPSP) or inhibitory (IPSP)
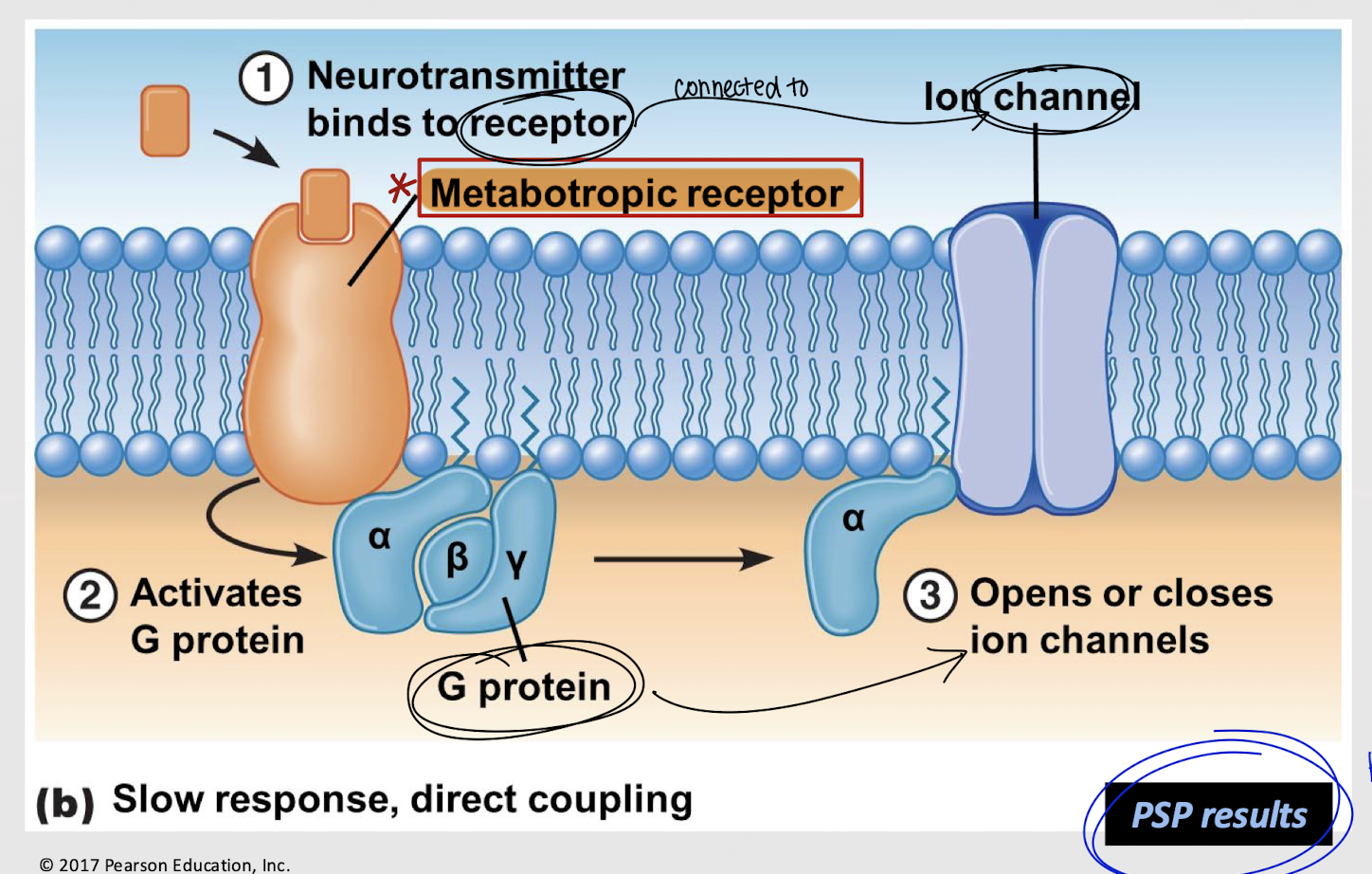
metabotropic receptor
What is another name for a G-protein linked channel?
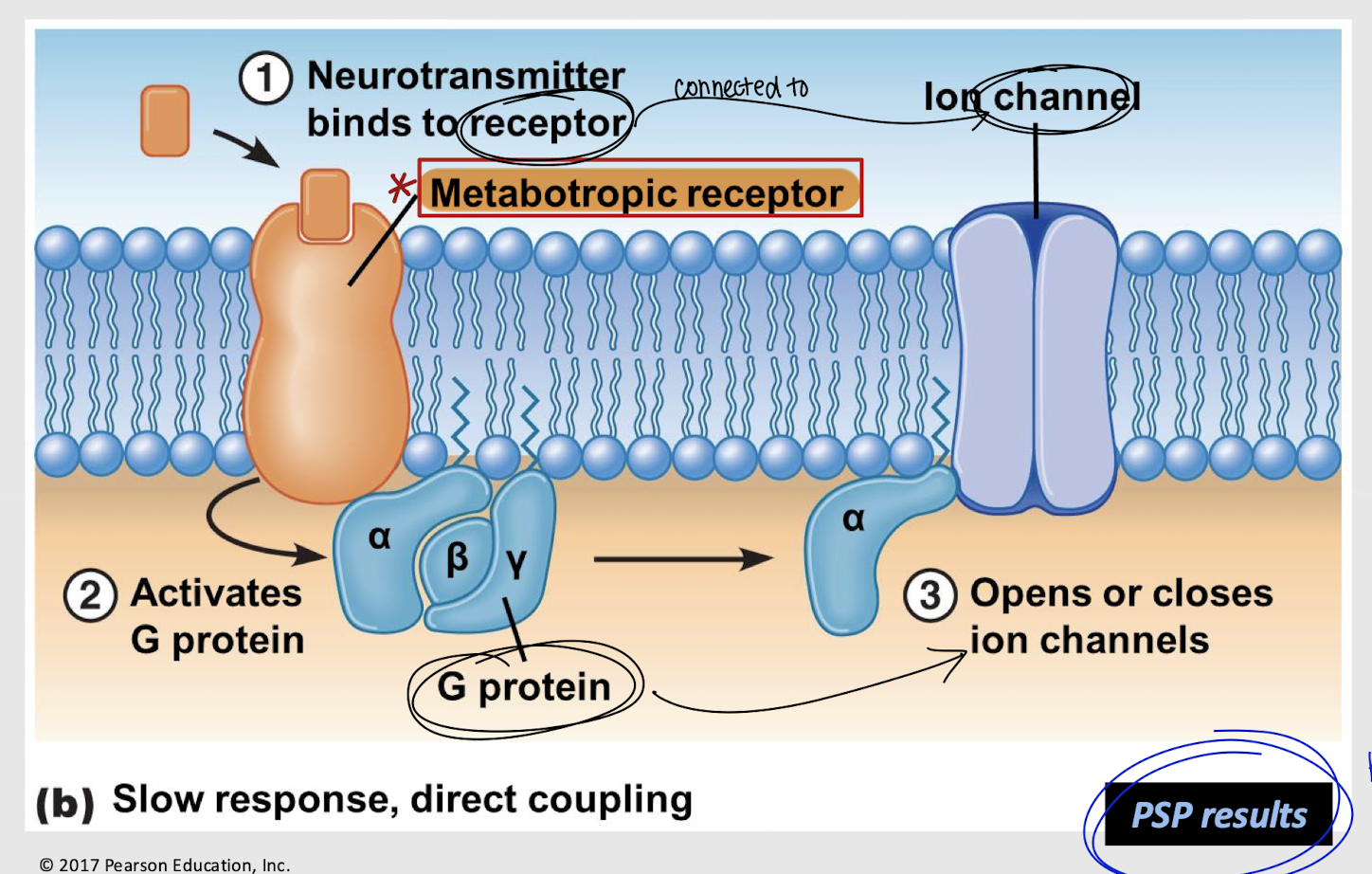
direct coupling
Type of coupling where a receptor and channel are linked through a G-protein
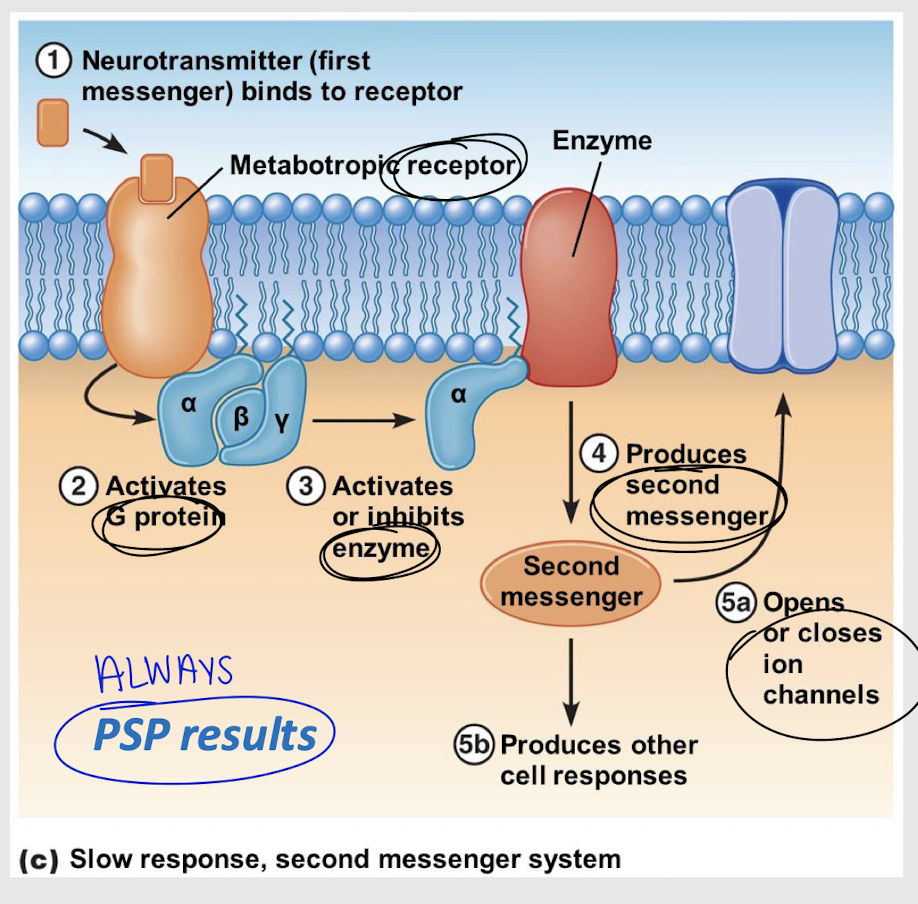
indirect coupling
Type of coupling where a second messenger system mediates the signal between a receptor and an ion channel.
postsynaptic potential (PSP)
Signal transduction at chemical synapses will always result in a…
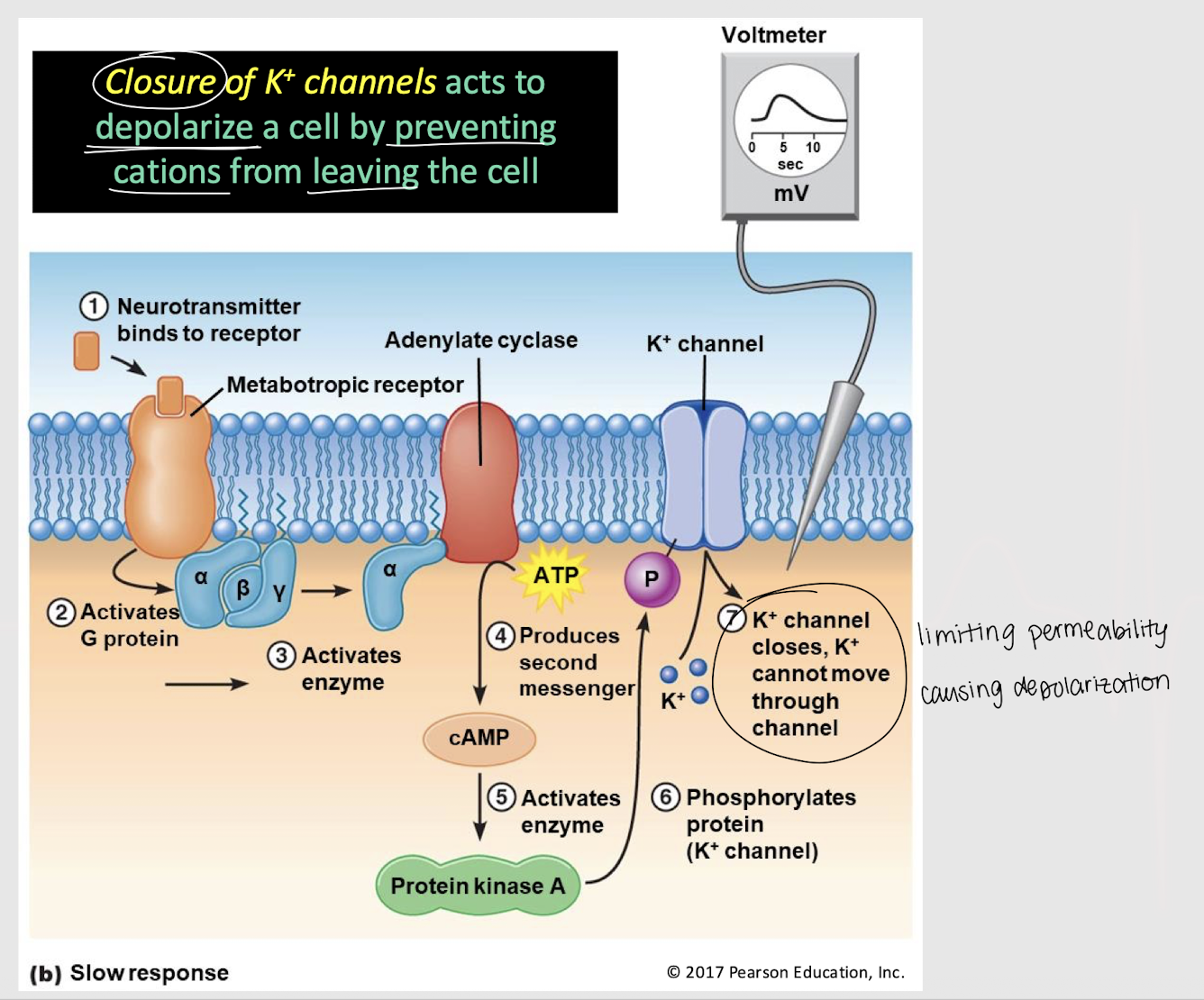
depolarize; cations
Closure of K+ channels acts to __________ a cell by preventing _______ from leaving the cell.
stabilize
IPSPs can hyperpolarize the cell or __________ the Vm
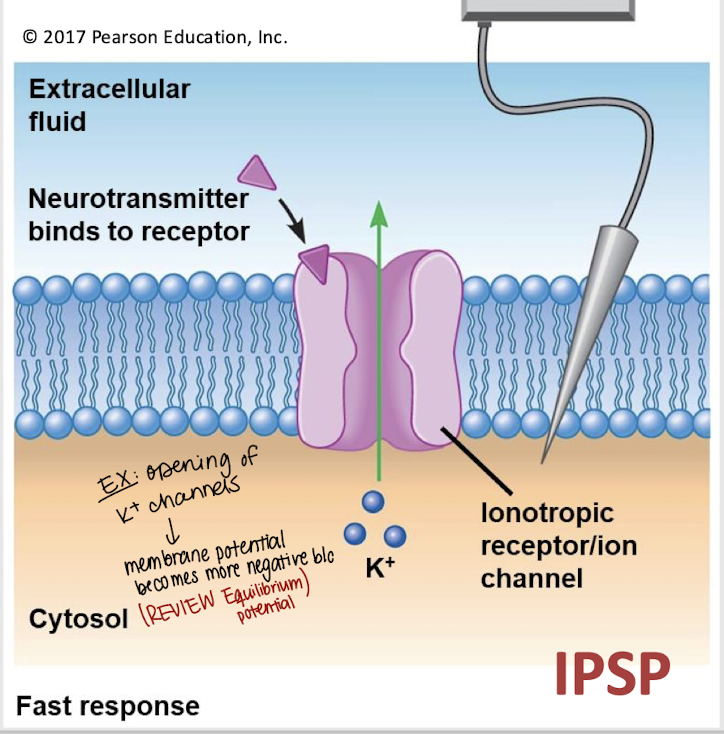
K+; Ex
Opening of ____ channels leads to an IPSP because the increased permeability will drive the Vm closer to an ion’s _____.
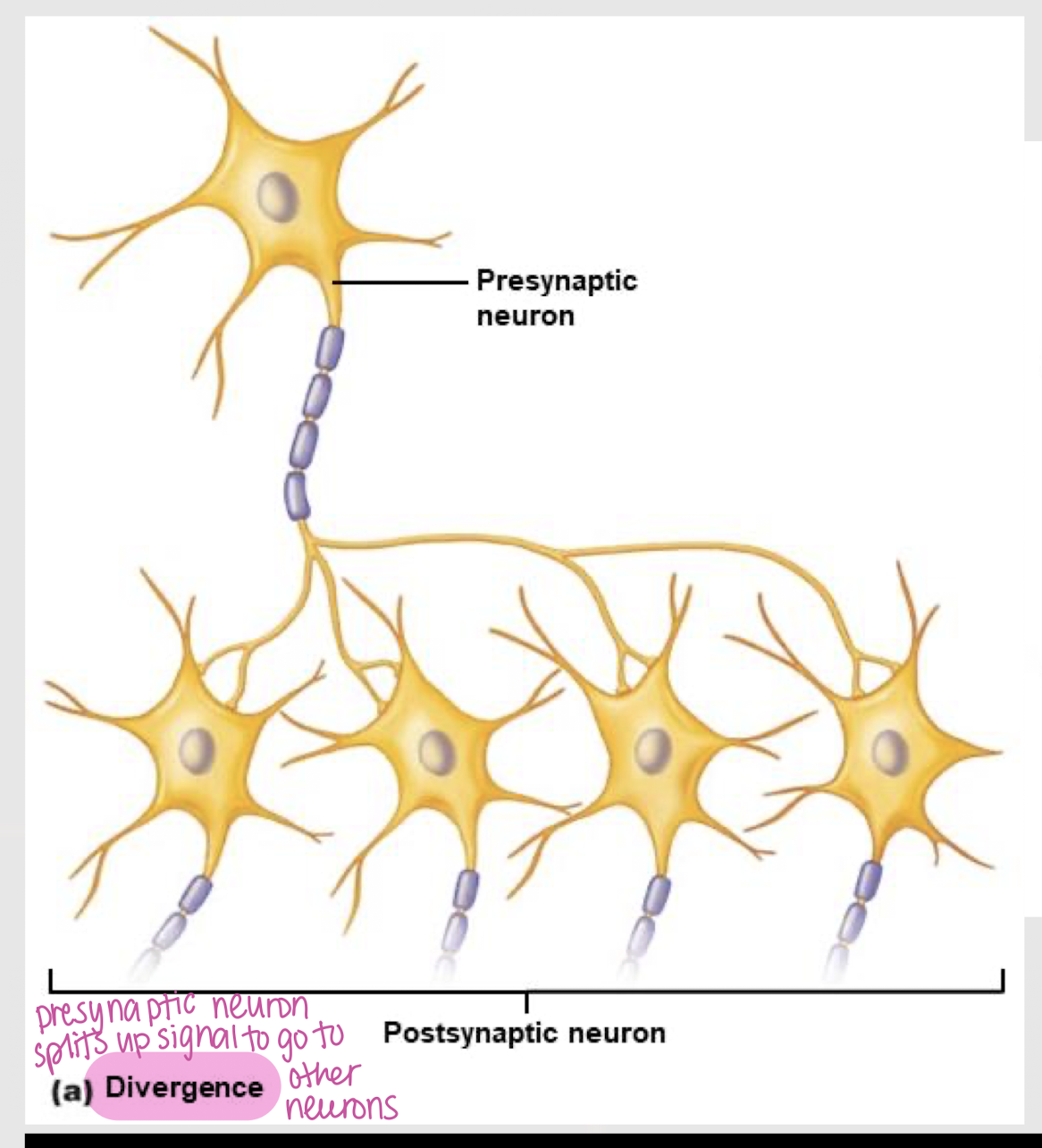
divergence
Feature of neurons in which a presynaptic neuron sends a signal to many other neurons
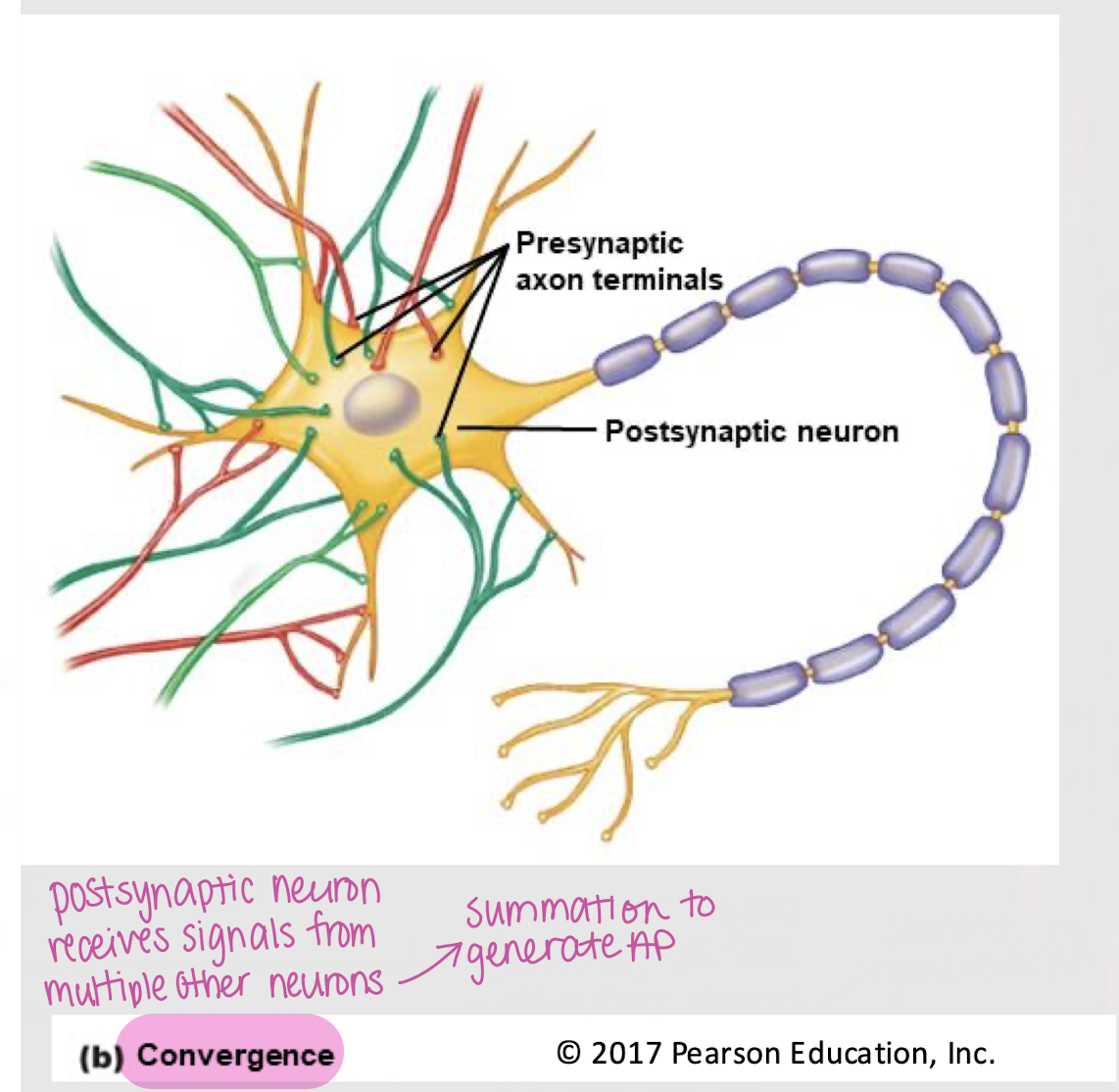
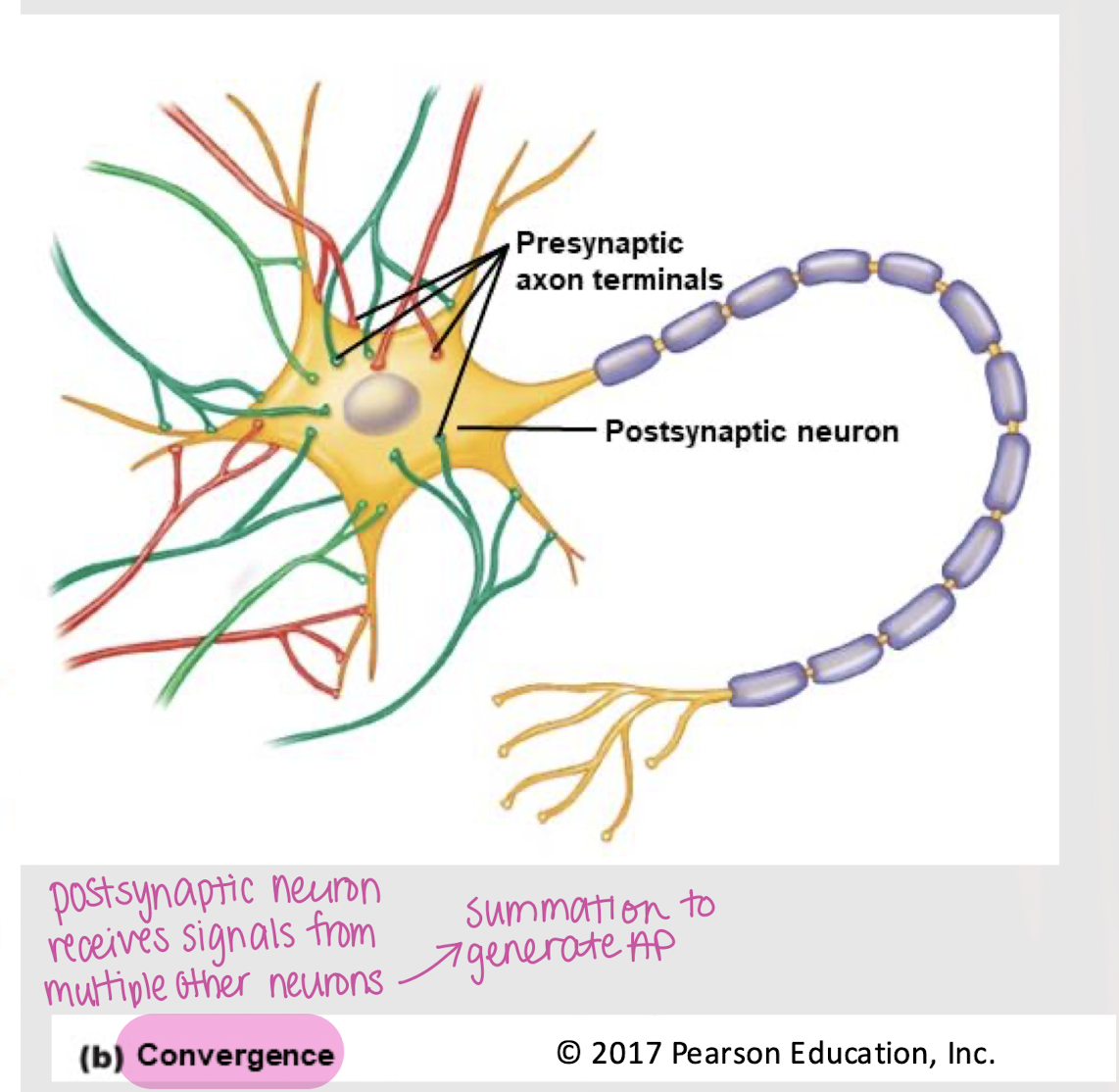
convergence
Feature of neurons in which a postsynaptic neuron receives signals from multiple other neurons.
convergence
Does divergence or convergence allow for the spatial summation of action potentials?
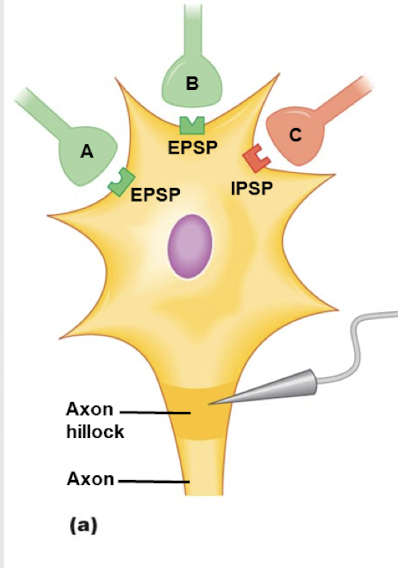
B; it’s farther away
If a single AP in each presynaptic neuron A and B results in an 8-mV depolarization at the axon hillock, which presynaptic neuron had to produce the larger EPSP at the synapse? Why?
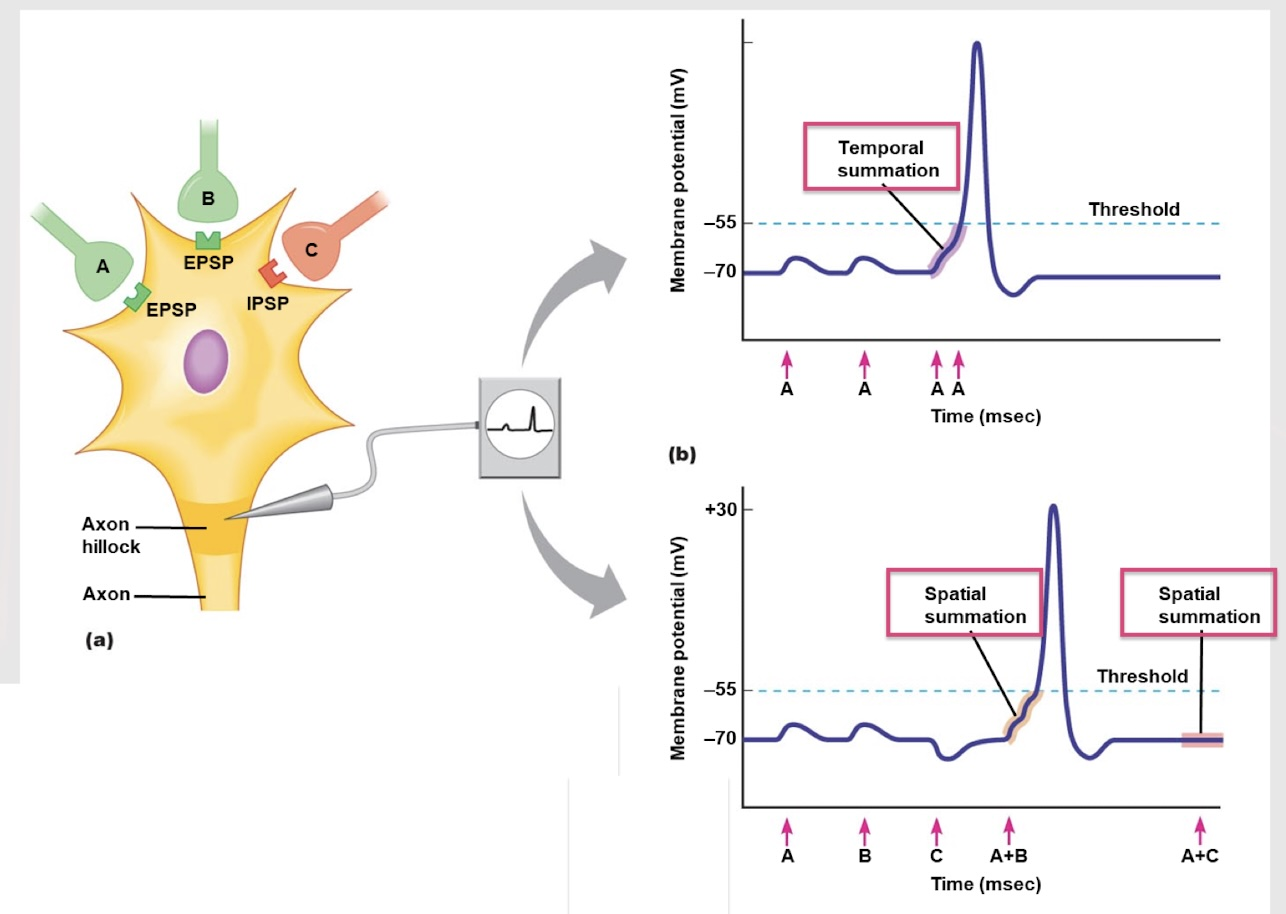
temporal summation
If neuron A sends two signals very close to each other, an action potential is produced due to which type of summation?
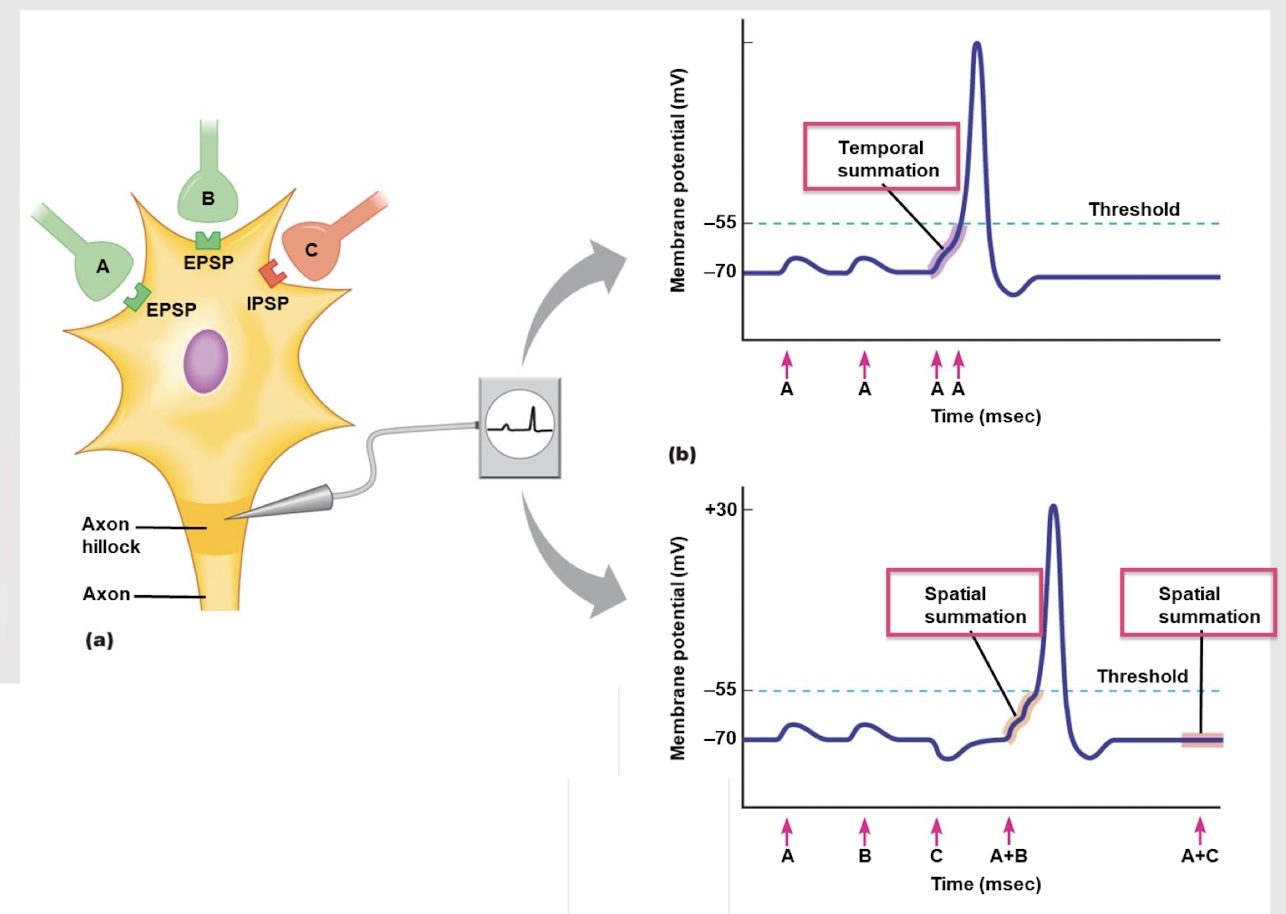
spatial summation
If both neuron A and B send a signal at the same time, an action potential occurs due to which type of summation?
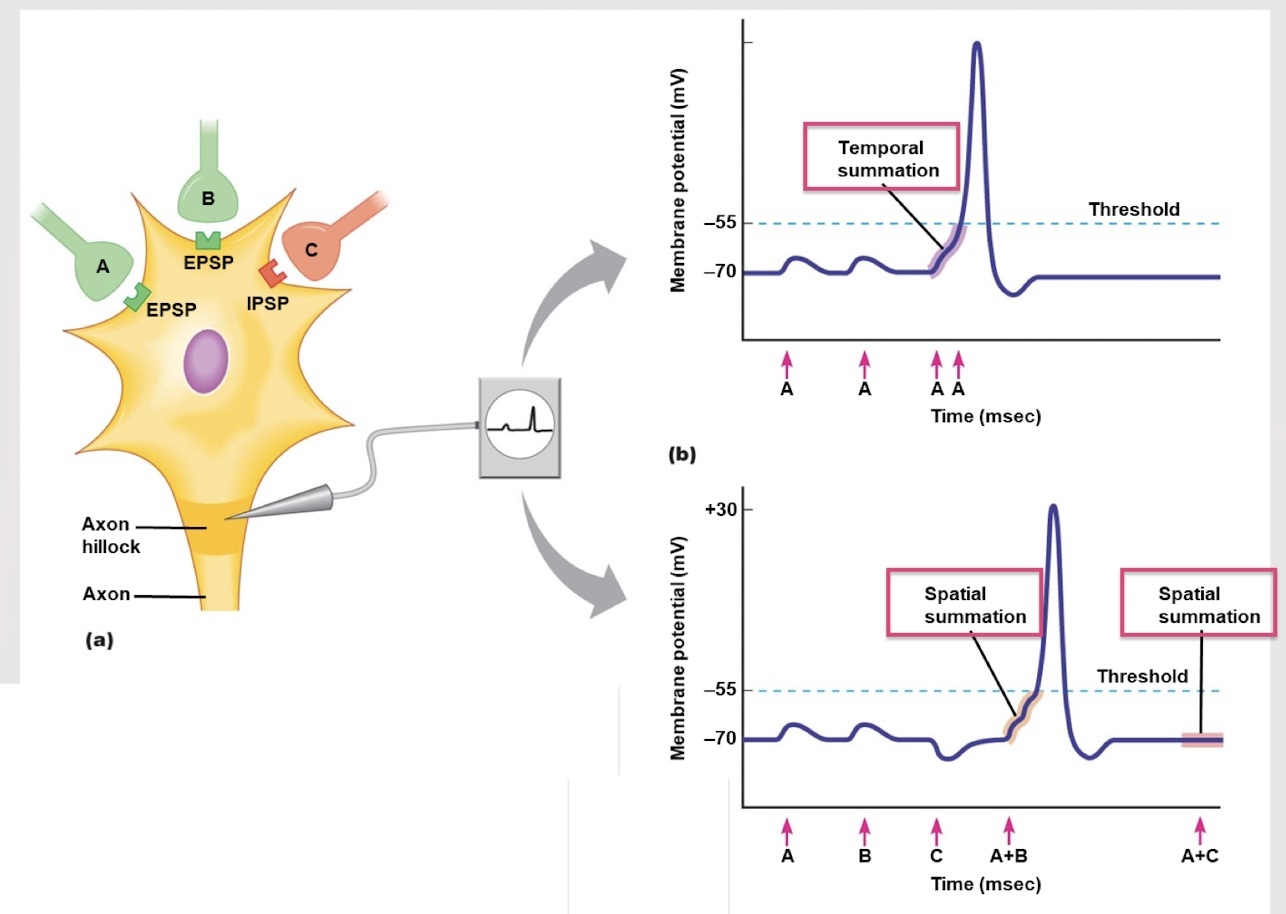
spatial summation
If neurons A and C both fire a signal, which type of summation is at play?
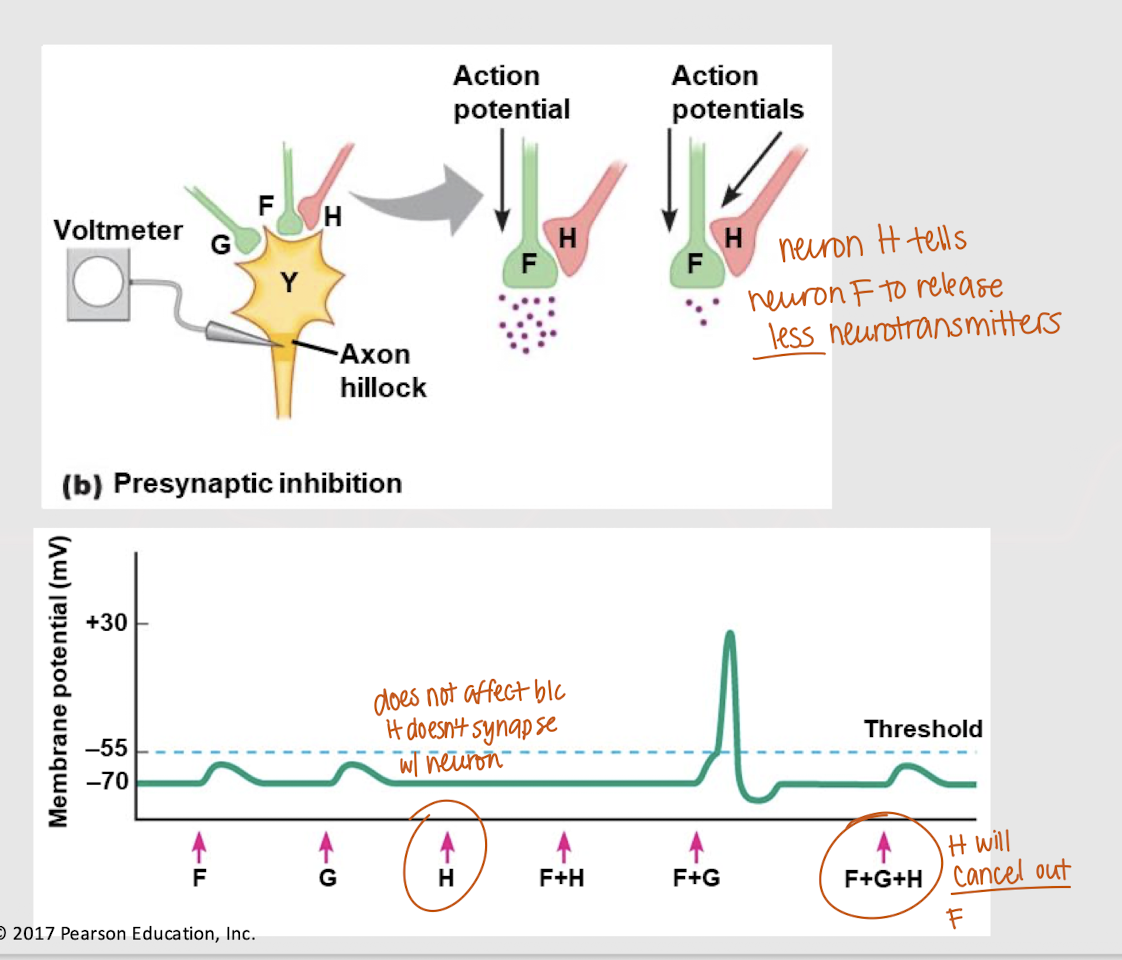
presynaptic modulation
Mechanism that modulates the amount of neurotransmitter release via axoaxonic synapses
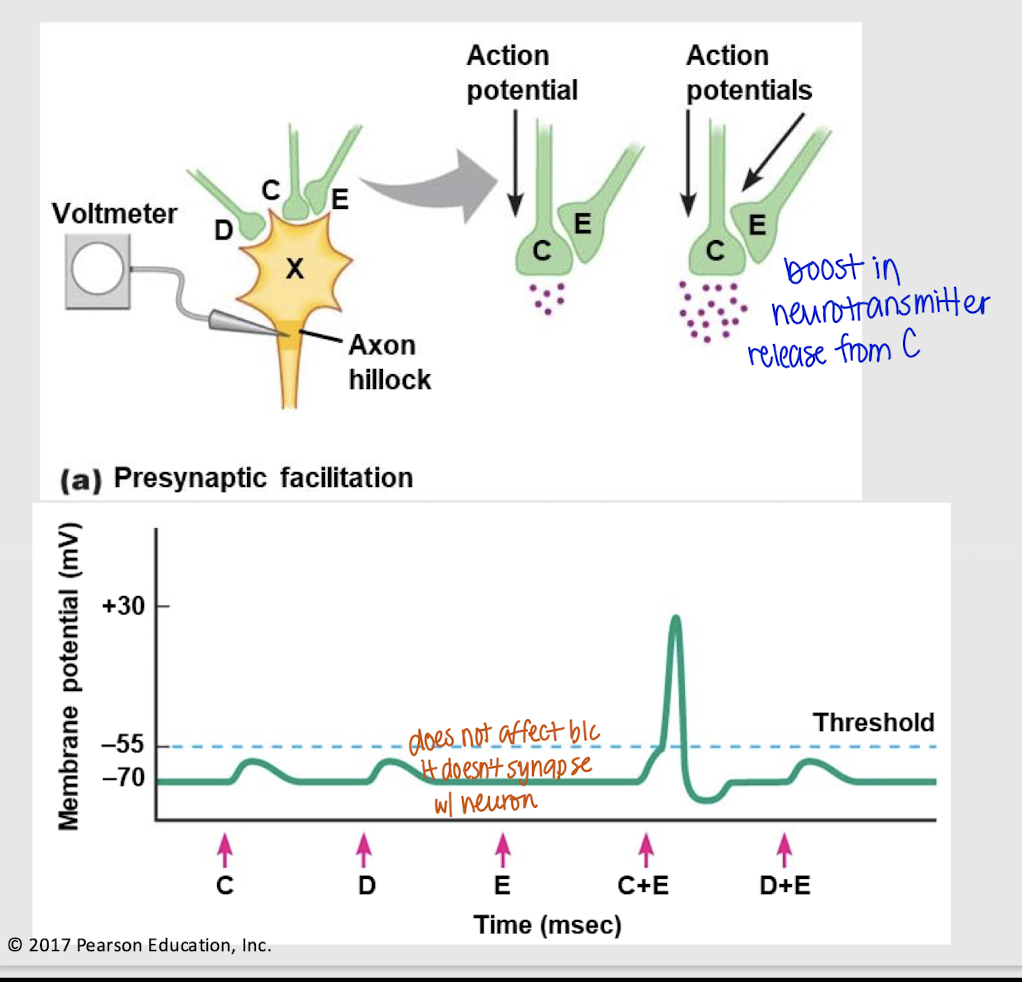
presynaptic facilitation
Presynaptic modulation at axoaxonic synapses that signals a postsynaptic neuron to release more neurotransmitters.
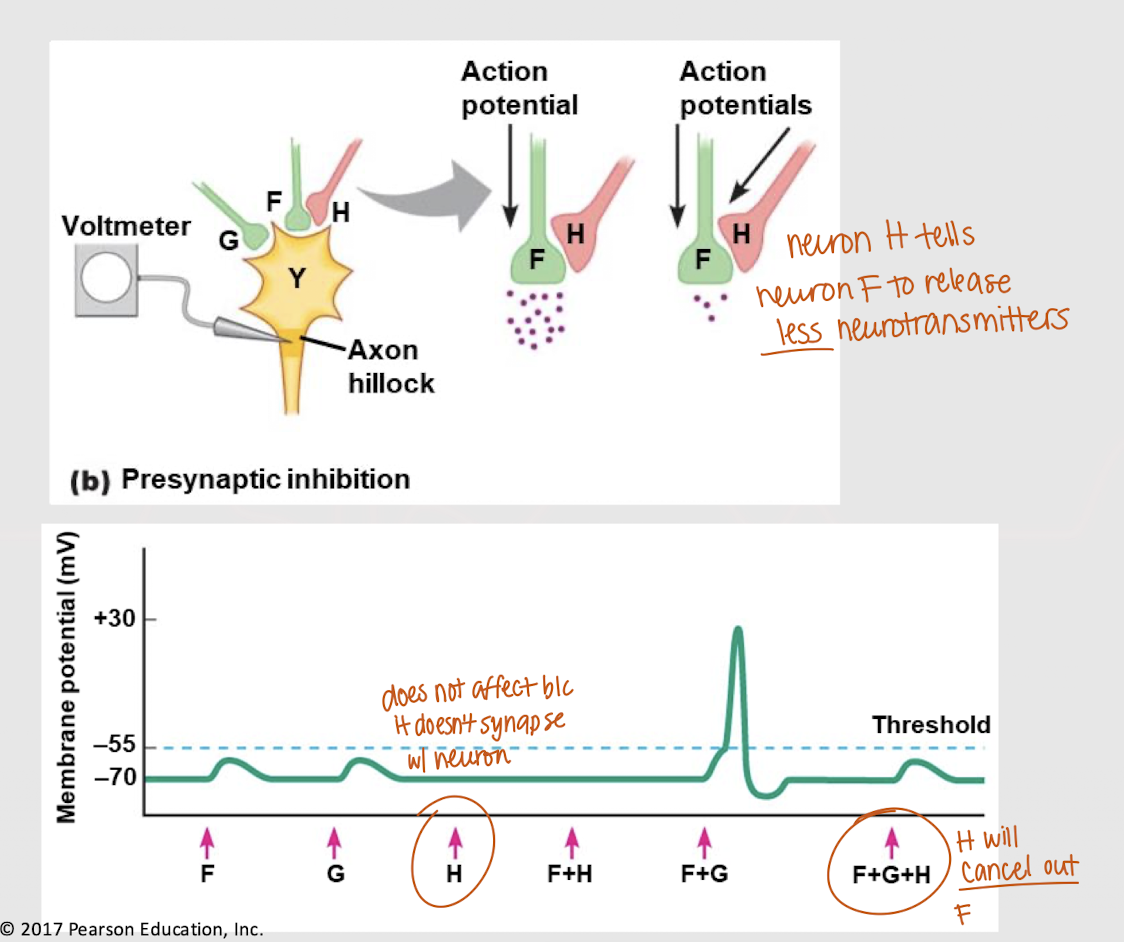
presynaptic inhibition
Presynaptic modulation at axoaxonic synapses that signals a postsynaptic neuron to release less neurotransmitters.
No
Will a presynaptic neuron at an axoaxonic synapse affect membrane potential (Vm)?
Yes
If both neuron C and E send signals, will an action potential occur?
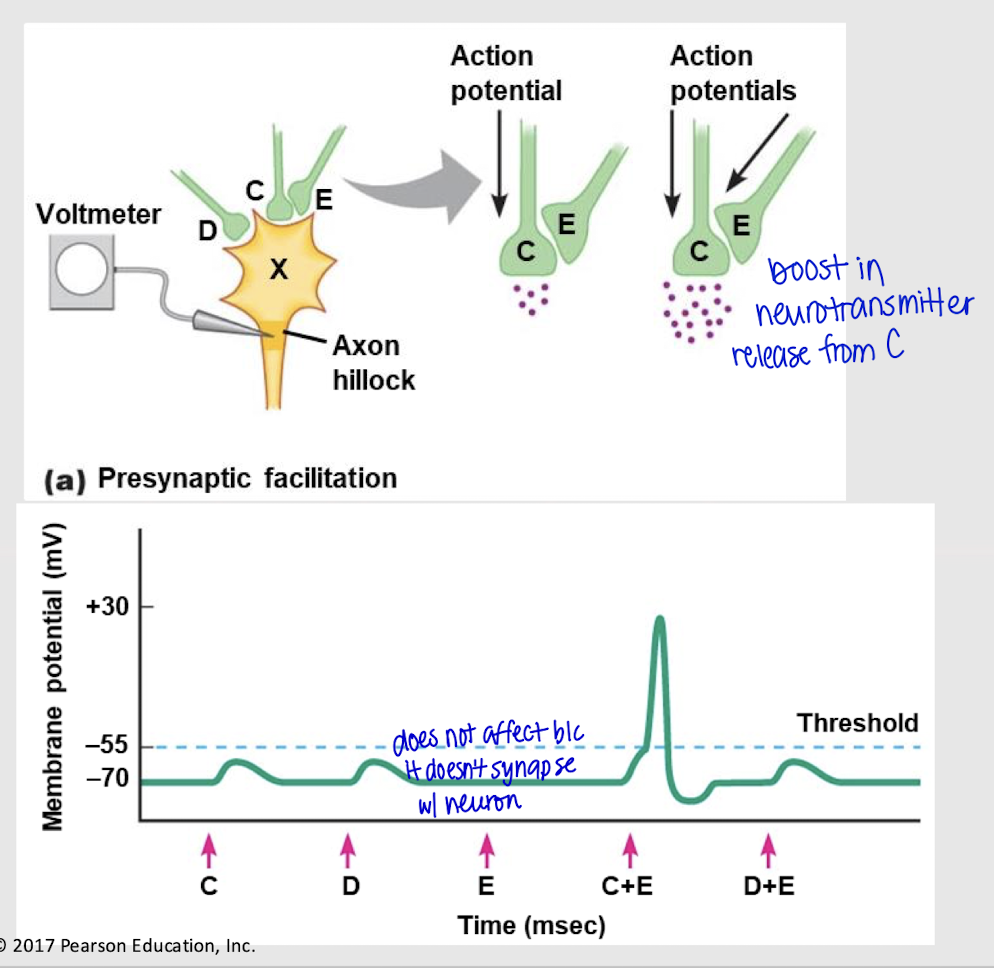
depolarization; no
If both neuron D and E send a signal, what happens? Does E have an effect?
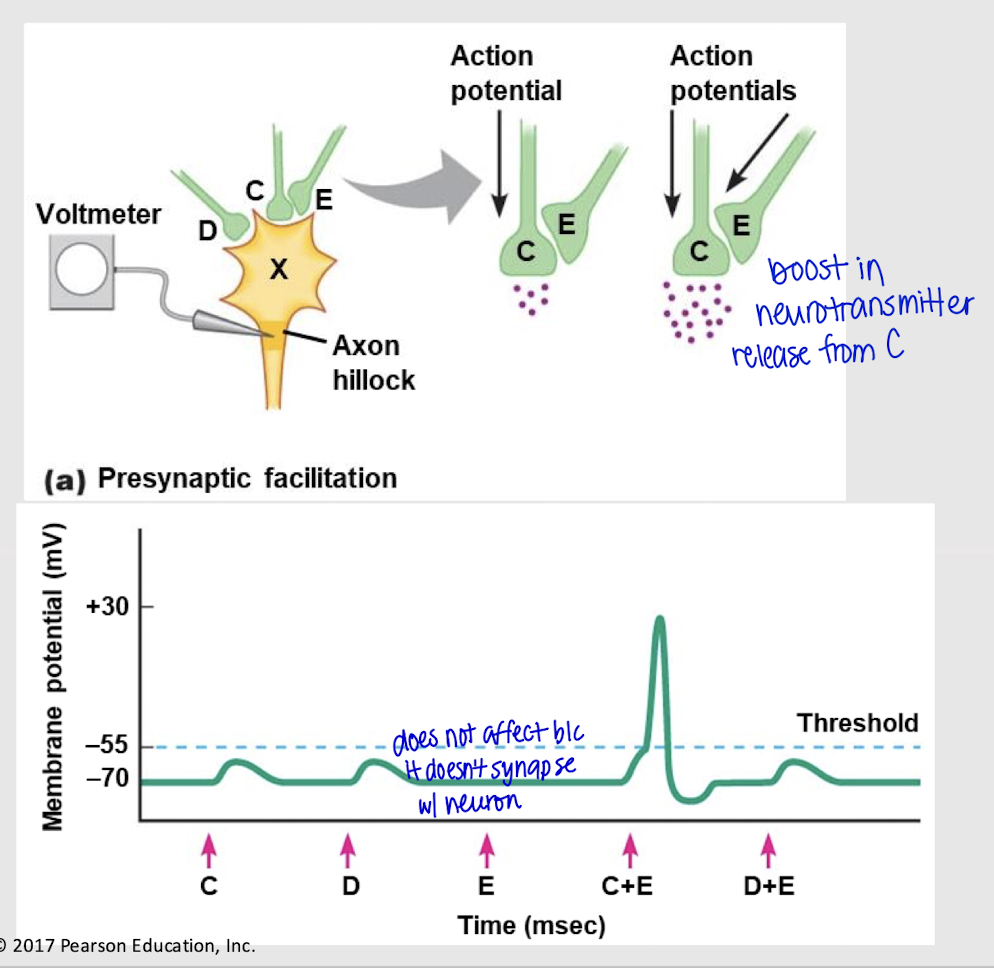
yes
If both neuron F and G send a signal, will an action potential occur?
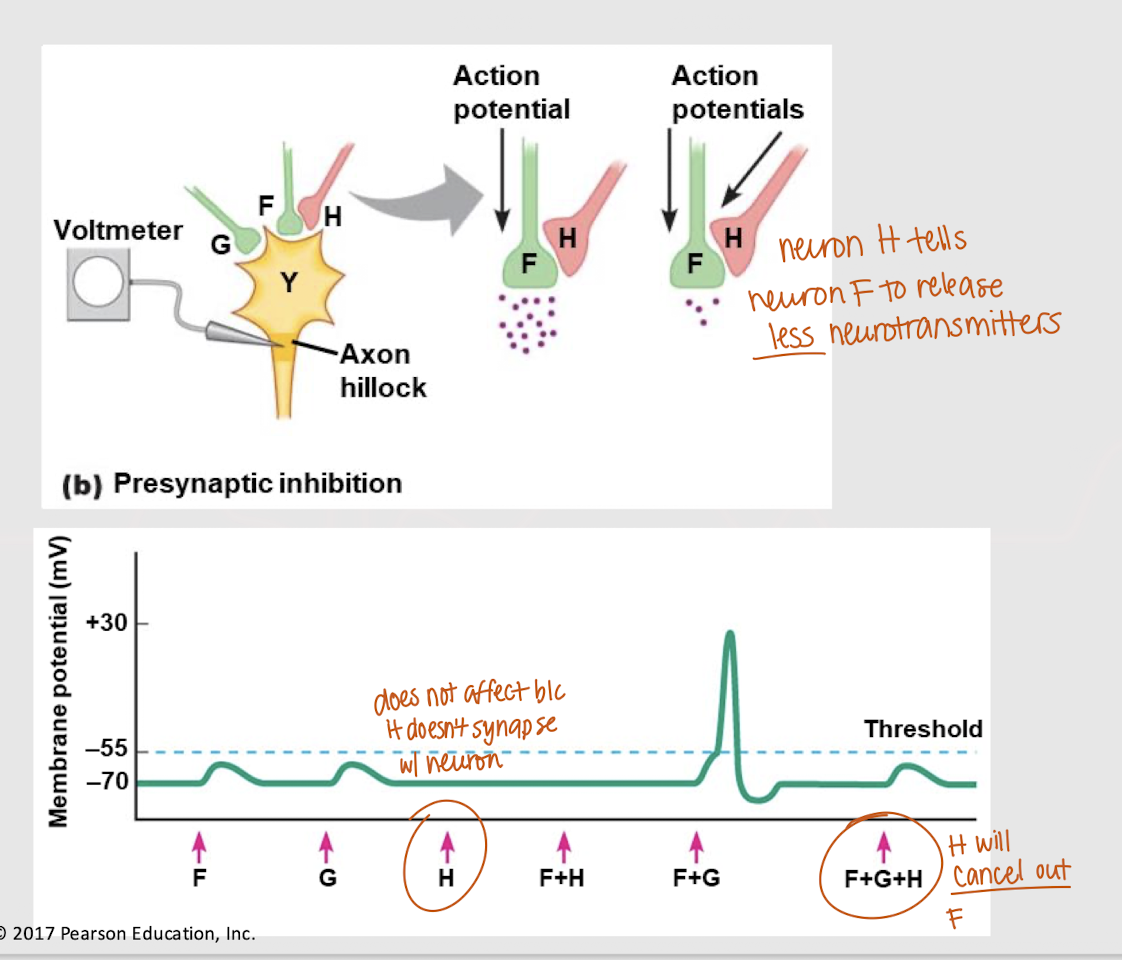
No
If both F and H send a signal, will an action potential occur?
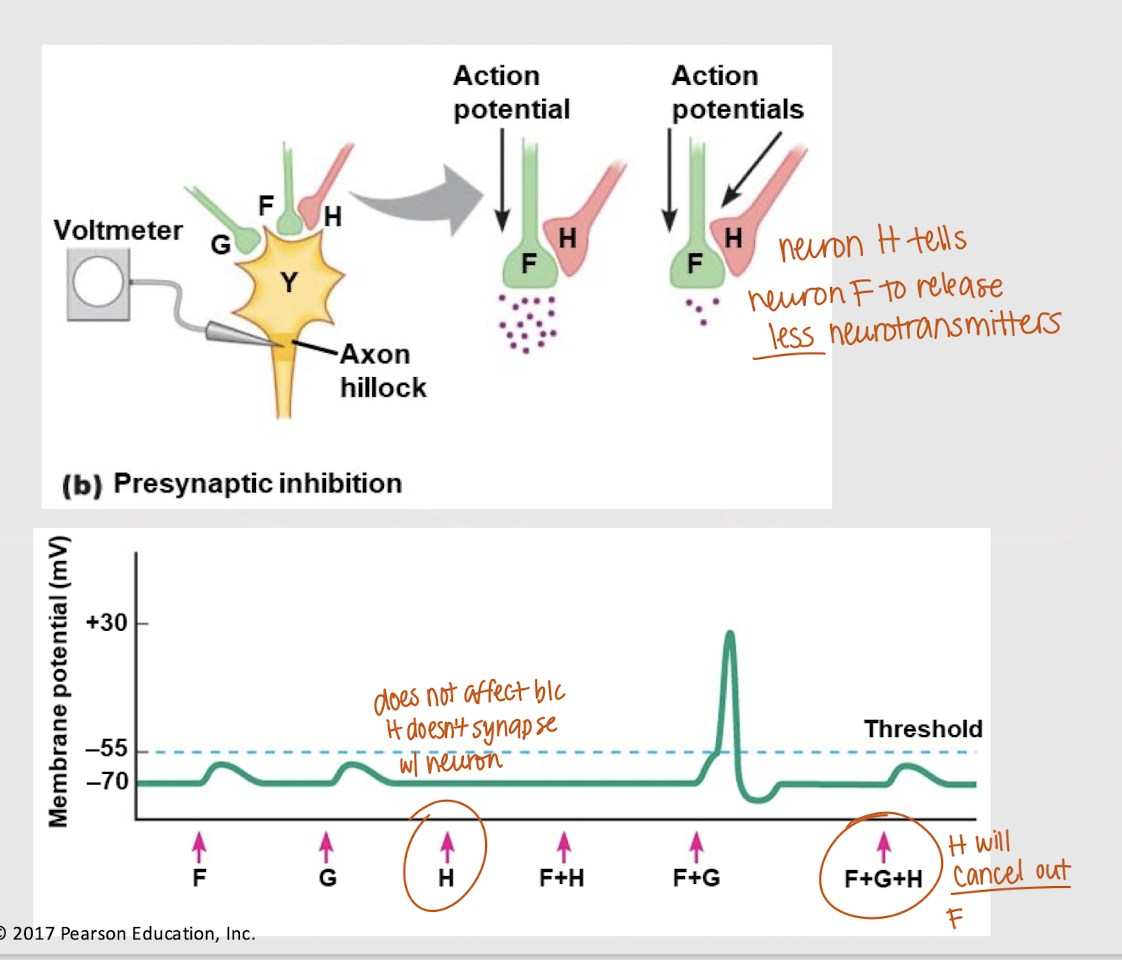
depolarization
If all neurons send a signal, what happens?
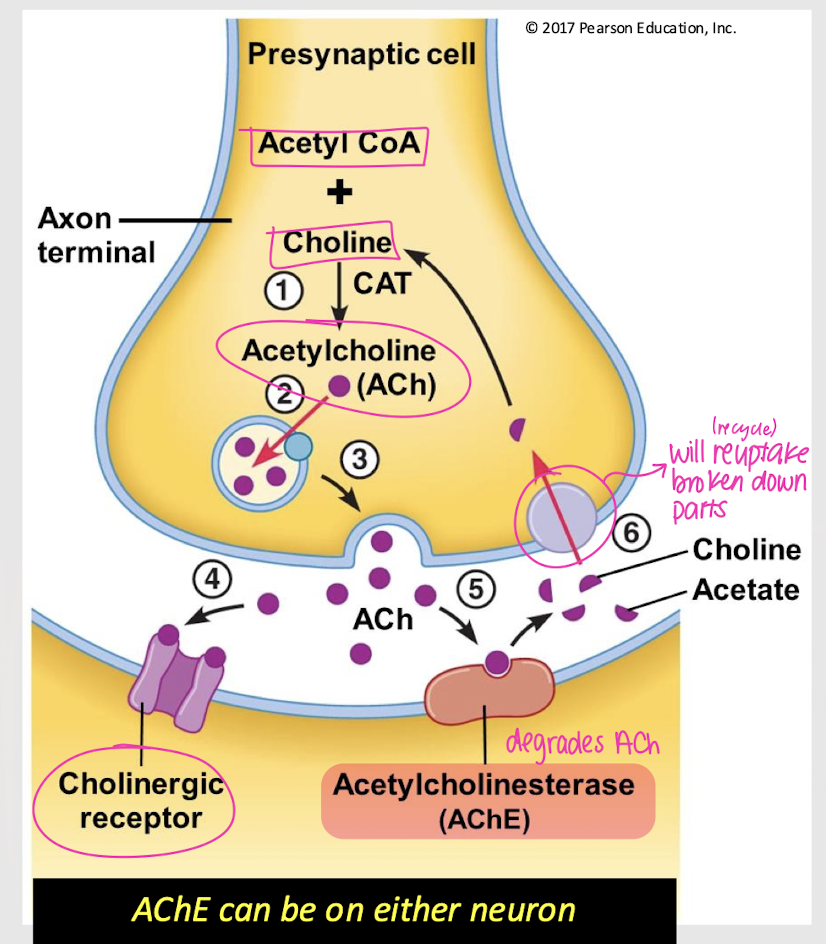
axon terminal cytosol
Where is ACh synthesized?
PNS
ACh is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the…
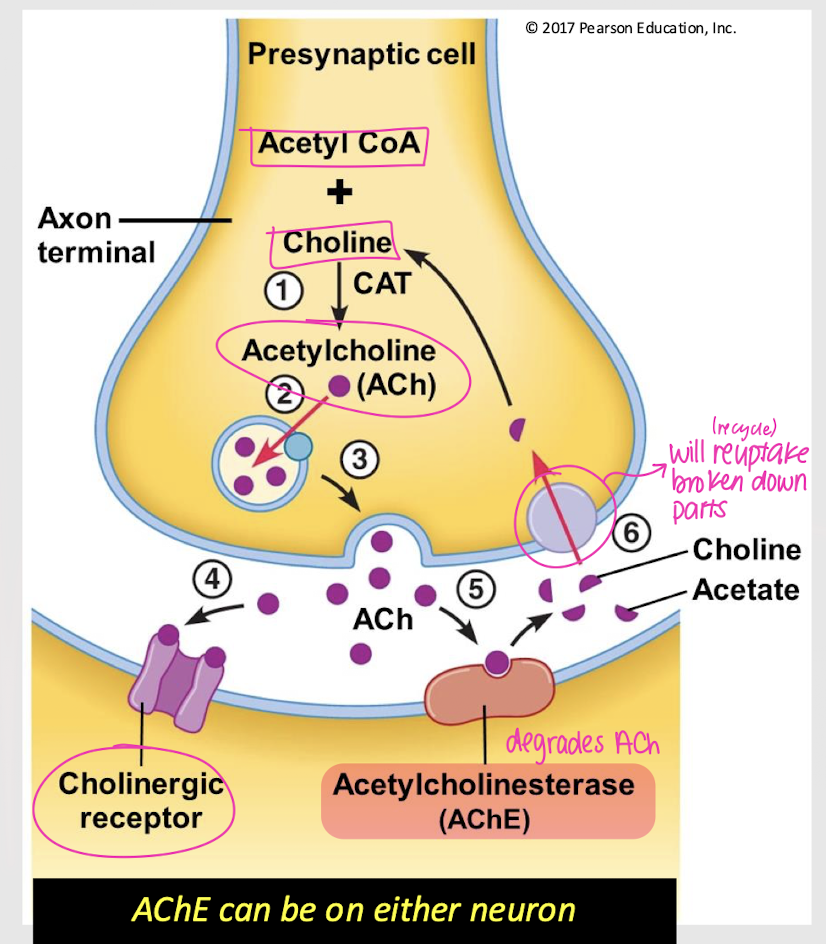
cholinergic receptors
What type of receptors will ACh bind to?
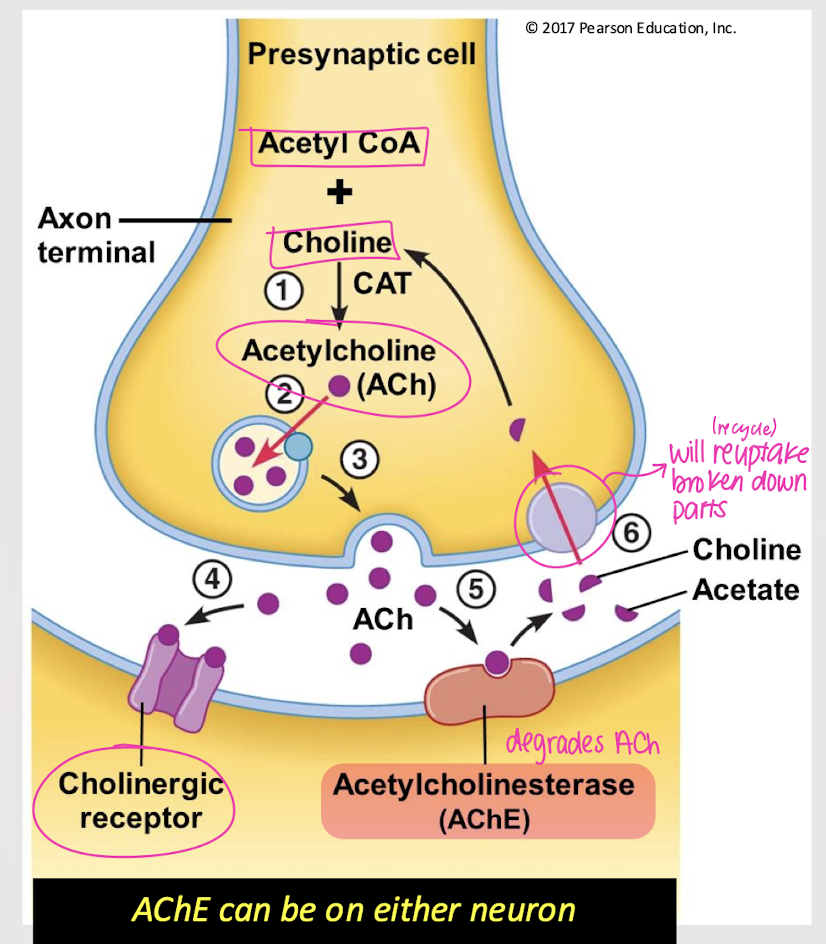
acetylcholinesterase (AChE); either
What enzyme degrades ACh at the synapse? Is it located on the presynaptic neuron, the postsynaptic neuron, or either?
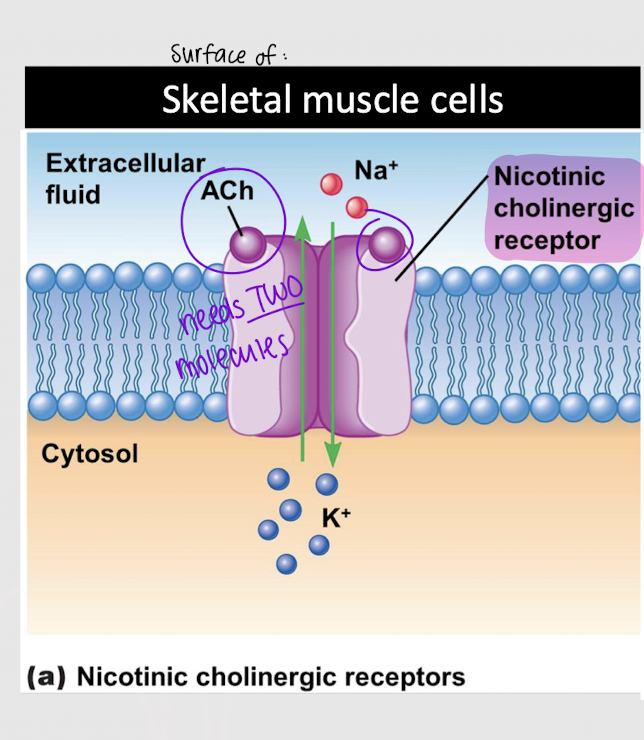
nicotinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor requires two Ach molecules to bind to it?
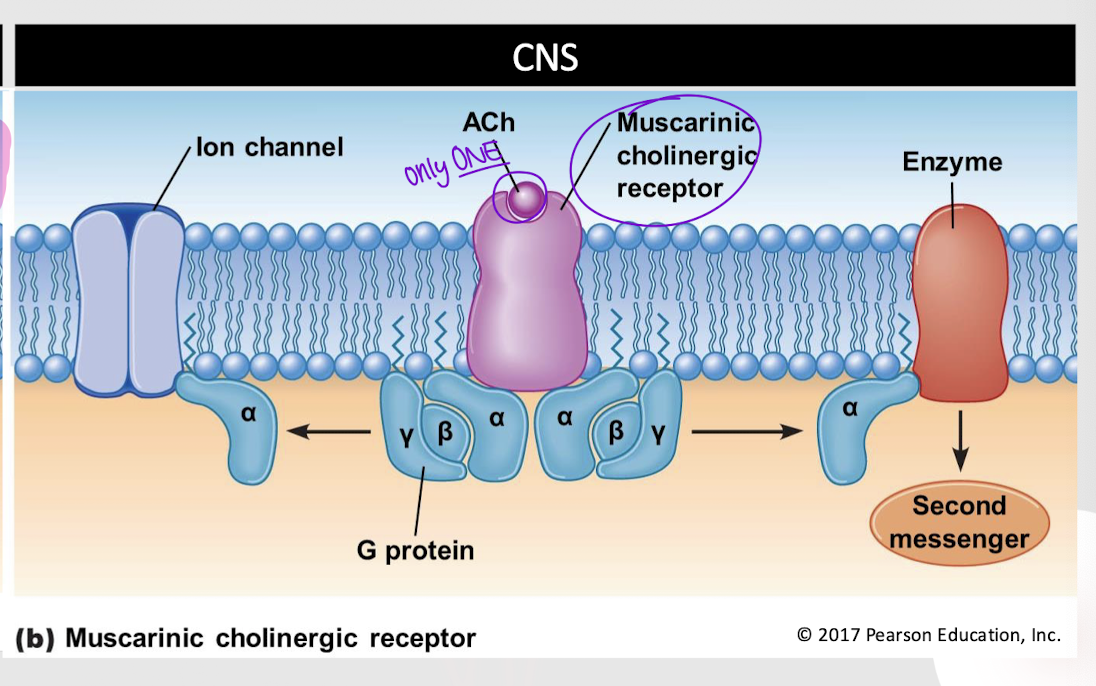
muscarinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor requires one ACh molecule to bind to it?
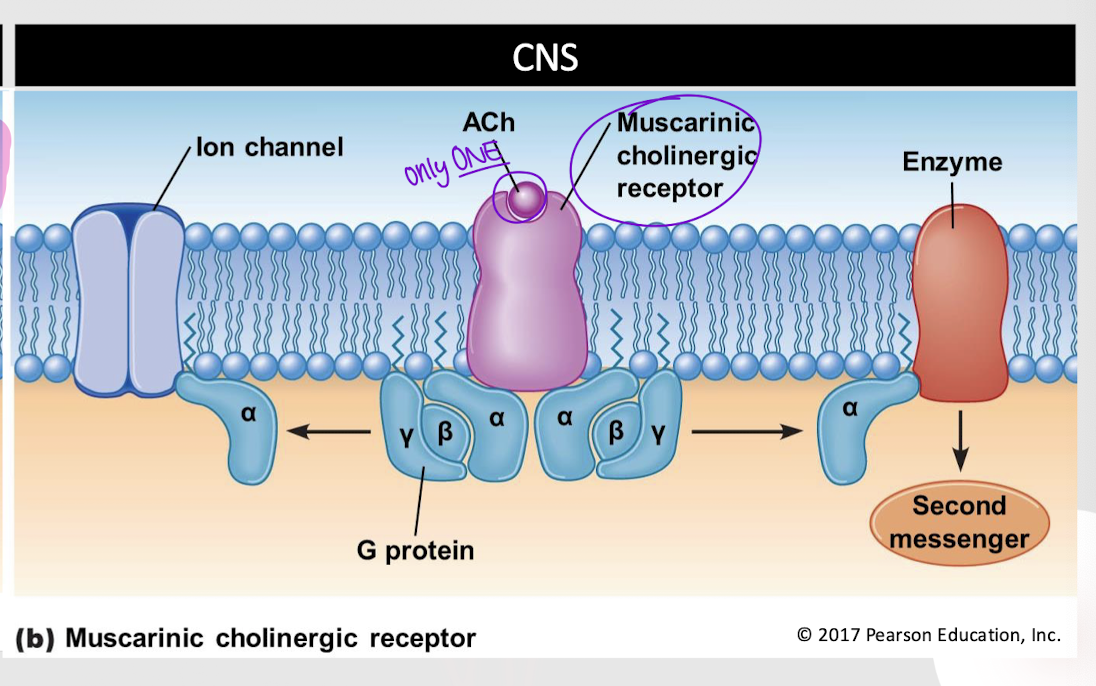
muscarinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor activates a G-protein?
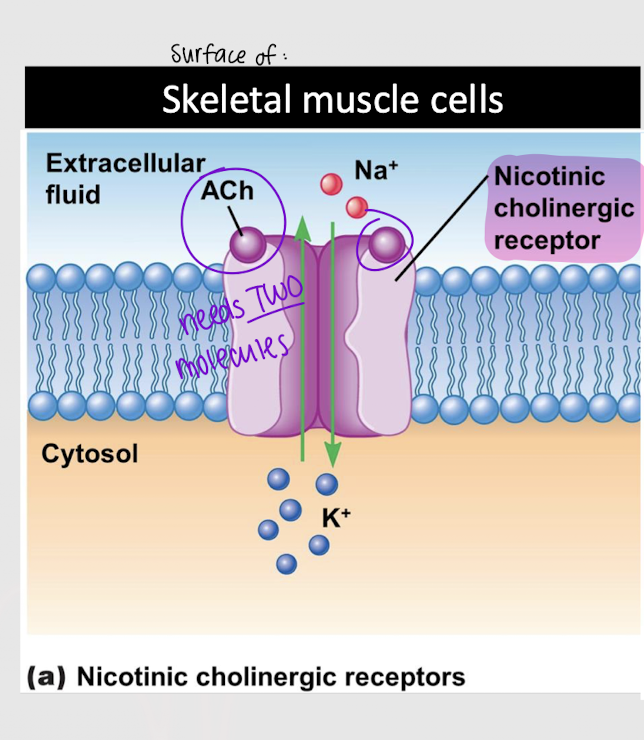
nicotinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor produces a fast response?
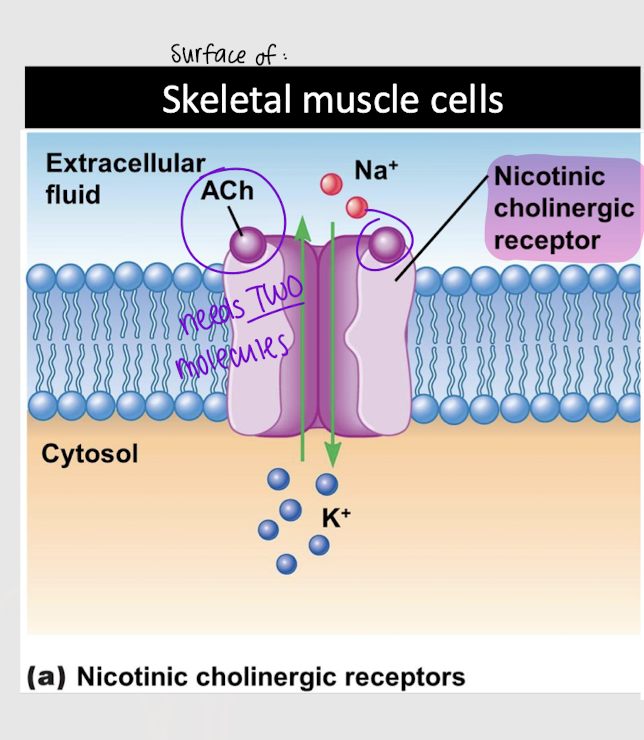
nicotinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor is found on skeletal muscle cells?
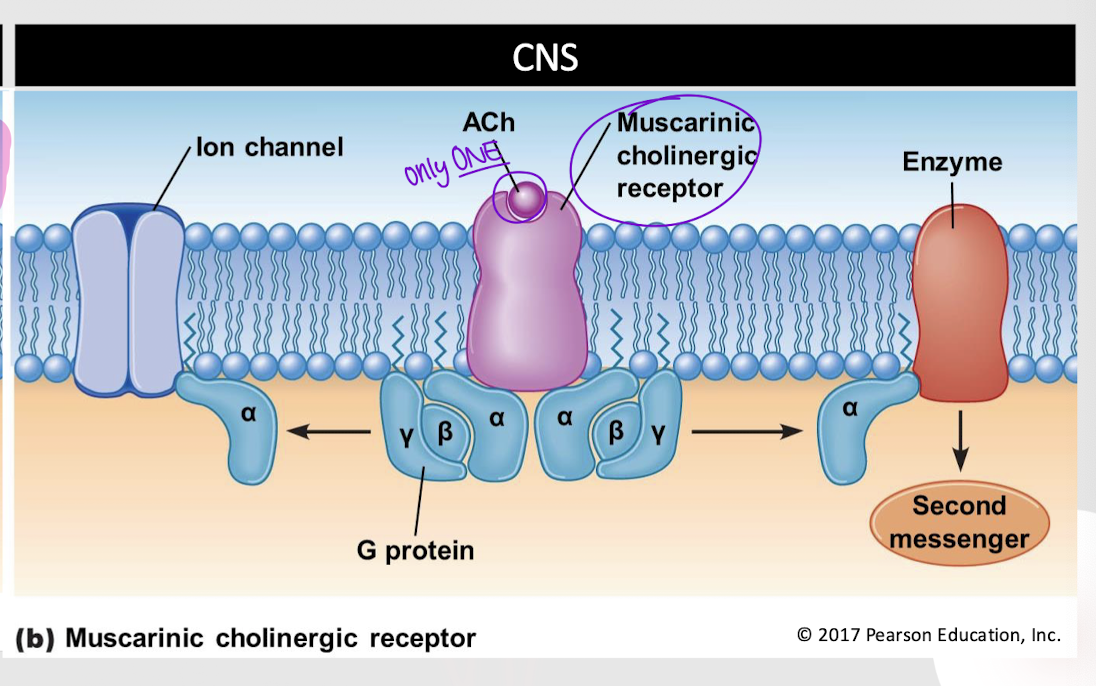
muscarinic cholinergic receptor
Which type of cholinergic receptor is found in the CNS?