bohr model of the atom
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
describe bohrs model of the atom
the electron moves around the nucleus in a fixed orbit, and the energy associated with each orbit has a fixed value. by absorbing energy, an electron could move from one orbit to another further out from the nucleus, and by emitting energy it could move to an orbit closer to the nucleus. however, only certain orbits are allowed, and the electron cannot lie between them.
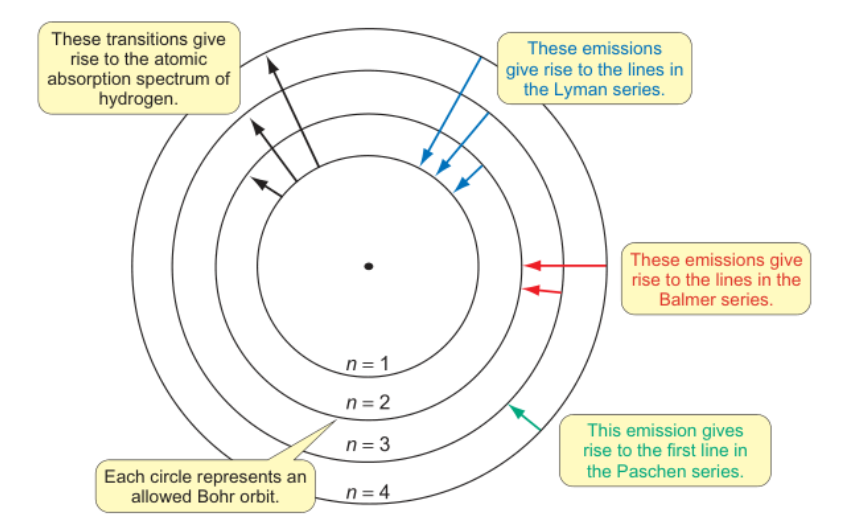
diagram of bohr’s model including the transitions that give rise to:
-atomic emission spectrum
-lyman series
-balmer series
-paschen series
bohr’s equation for energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom
me is mass of electron, e is charge on electron, n is principal quantum number
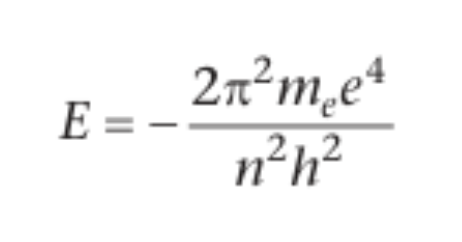
how and why is bohr’s expression simplified
π, me, e and h are all constants, so simplifying them into one constant, k, means the electronic energy is determined only by n
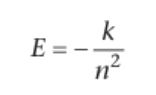
problems with bohrs model
-he could not explain the quantisation condition for angular momentum
-classically, an orbiting chartged particle would emit EM radiation, lose energy and fall into the nucleus
-bohr could not extend this model to apply to atomic spectrums for atoms other than hydrogen
examples of the wave-particle duality of electrons
wave behaviour - electron diffraction patterns: a beam of electrons is fired at a thin sheet of graphite. the electrons pass through and hit a luminescent screen, producing the pattern of rings associated with diffration
particle behaviour - Young’s double slit experiment - the same pattern of bright and dark lines occurs if electrons are directed at a double slit
what is de broglies equation and what is it used for
used to show that for the wave behaviour of matter (including electrons), the wavelength is inversely proportional to the momentum
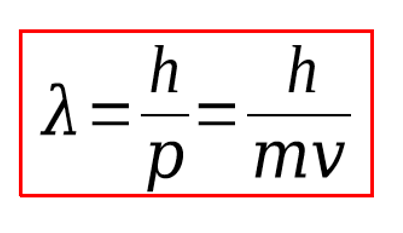
order of magnitude of electron wavelengths compared to light
can be up to 105 times smaller than visible light
which 3 classical physics concepts did bohr use
angular momentum (L)
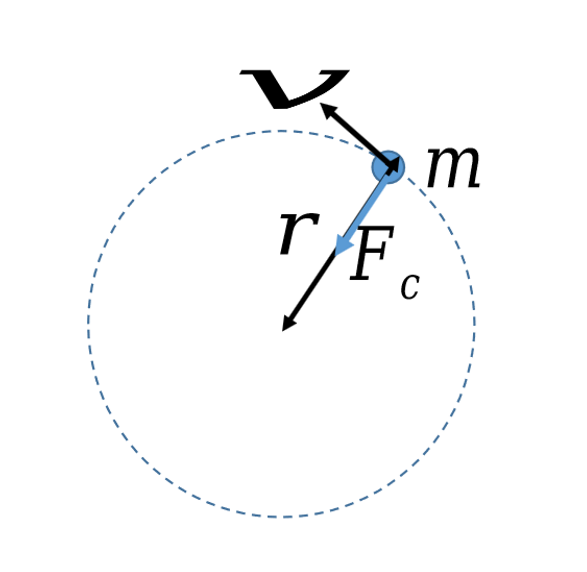
centripetal force (Fc)
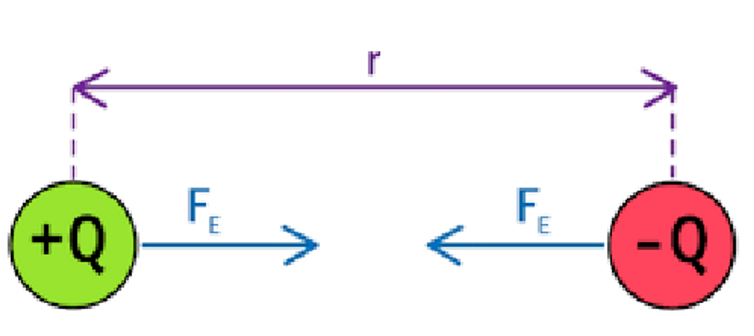
electrostatic force (Fe)
angular momentum equation and diagram
L = mvr
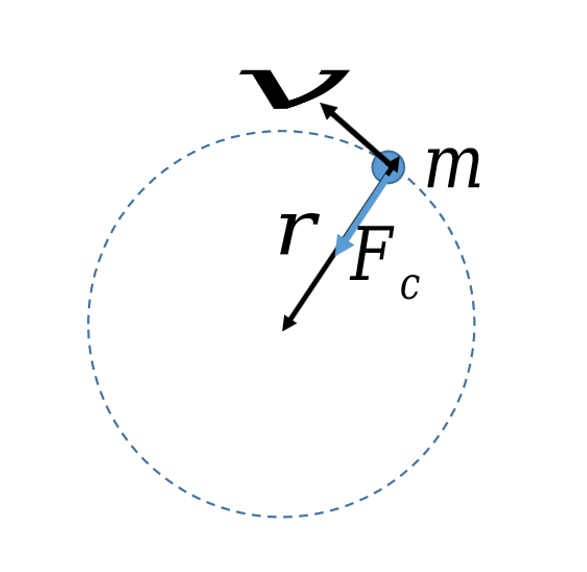
centripetal force equation and diagram
Fc = mv2/r
electrostatic force equation and diagram
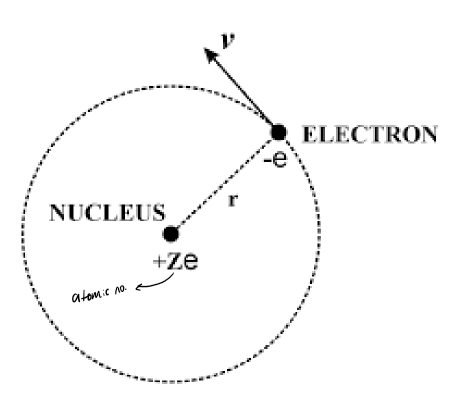
how is it expressed for electrons in an atom?
FE = Q1Q2/4πε0r2
atom: FE = Ze2/4πε0rn2
potential energy equation + why
as E=Fd
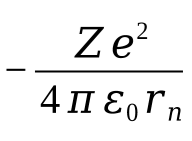
what is ε0? units?
permittivity of free space (value on formula sheet)
units = Fm-1 = C2N-1m-1
constructive and destructive interference equations (allowed/forbidden orbits)
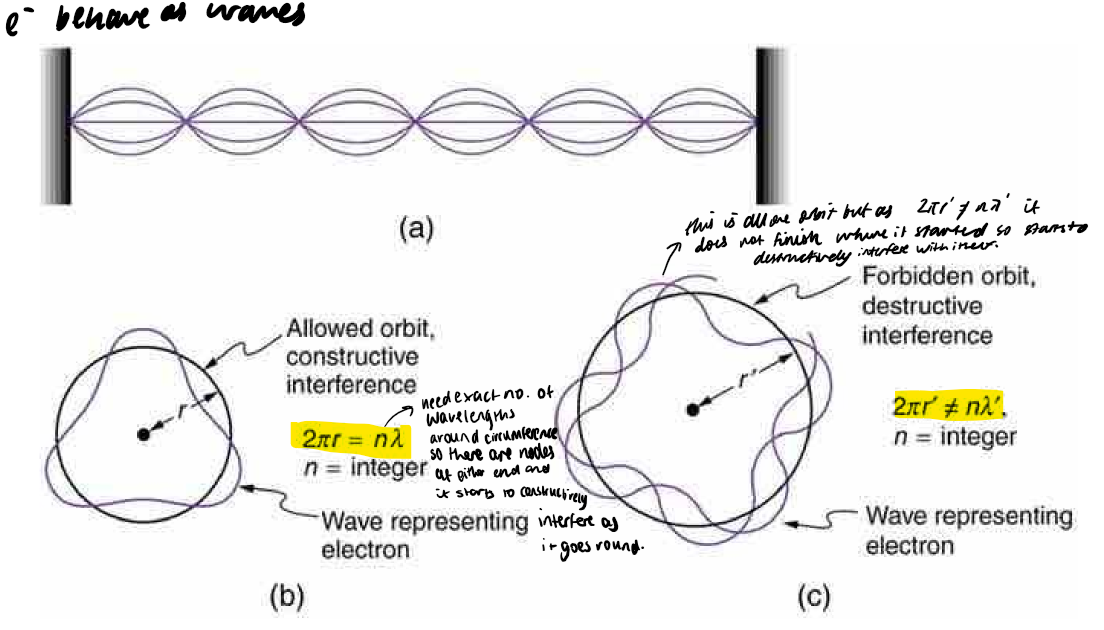
angular momentum in terms of constructive interference
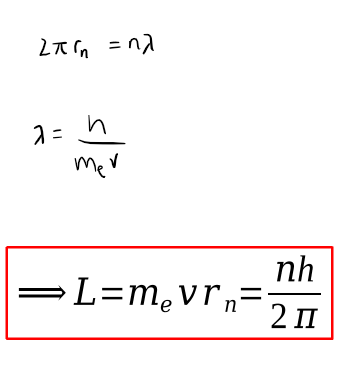
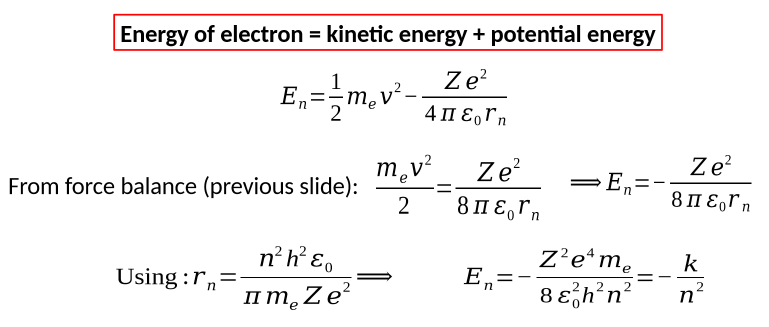
bohr radius equation + derivation
centripetal force is due to the electrostatic force so they are equal
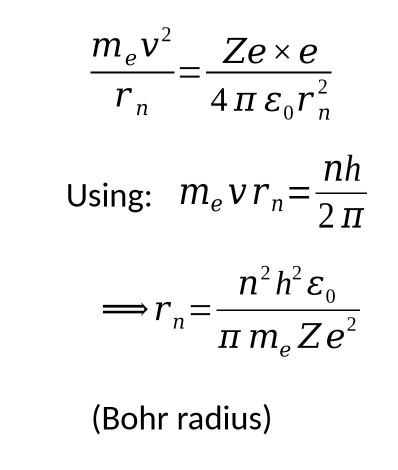
energy of electron general equation (words and symbols)
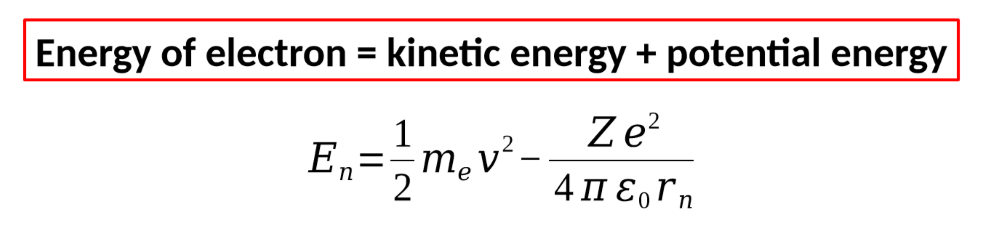
energy of electron for bohr model equation + derivation
rn when n=1 and Z=1
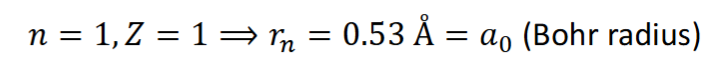
3 equations for frequency when electron moves from E1 to E2
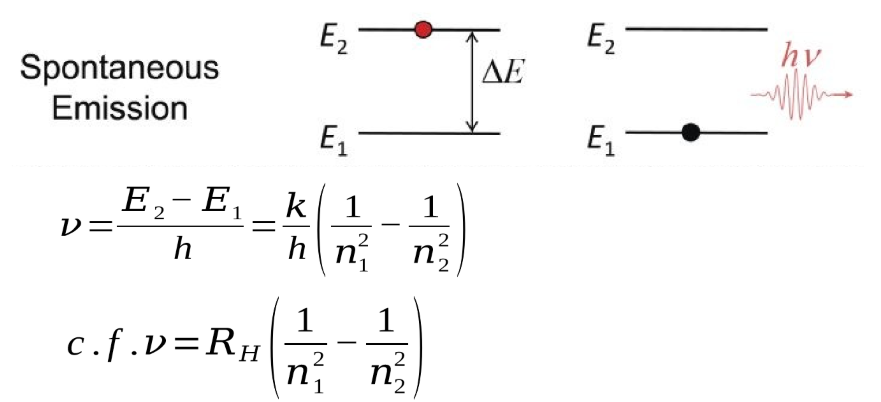
what is RH? (incl value) units?
Rydberg constant
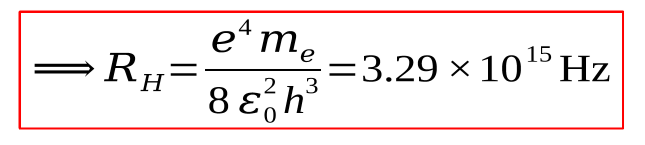
problems with bohr’s model
he could not explain the quantisation condition for angular momentum - classically an orbiting charged particle would emit electromagnetic radiation, lose energy and fall into the nucleus
while the model could explain the atomic spectrum of hydrogen it could not predict the spectra of other atoms