Bu111 MIDTERM
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
The internal features of an organization __________
are what allow you to execute your strategy.
-strategy is the plan for your business
_What are the 6 Critical Success Factors?_
1. Creating a Distinct Competitive Advantage
2. Building Quality Products and Services
3. Achieving Financial Performance
4. Gaining Employee Commitment
5.Encouraging Innovation and Creativity
6. Meeting Customer Needs
//Achieving Financial Performance//
-Maximizing profit, reaching financial goals, maximizing efficiency (ROI, PROFITS, GROWTH OVER TIME)
-Expansion of growth= continued profit
//Meeting Customer Needs//
Understanding customer needs, fulfilling those needs, and anticipating those needs
-If you don't meet customer needs your competitor will be more successful
//Gain Employee Commitment//
Having passionate, loyal employees is important because those employees will do better work for you
-Customers will be treated well by the employees which will allow for more customer loyalty
//Encouraging Innovation and Creativity//
Being innovative and creative can give you an advantage and help you stand apart from your competition
-allows you to remain current and get ahead of competing organizations
//Building Quality Products and Services//
Customers expect value for their money, regardless of what the customer is paying they expect performance on an ongoing basis. Thus, they expect reliability.
-
//Creating a distinct competitive advantage//
Something that sets your business apart that makes you unique in comparison to your competitors. This creates value
- possibly allows you to charge higher prices
Joes Java Critical Success Factors
-Achieving Financial Performance
-Meeting Customer Needs
High Tech Bar Top Critical Success Factors
-Innovation & Creativity
-Creating a distinct Competitive advantage
_Why is each critical success factor Important?_
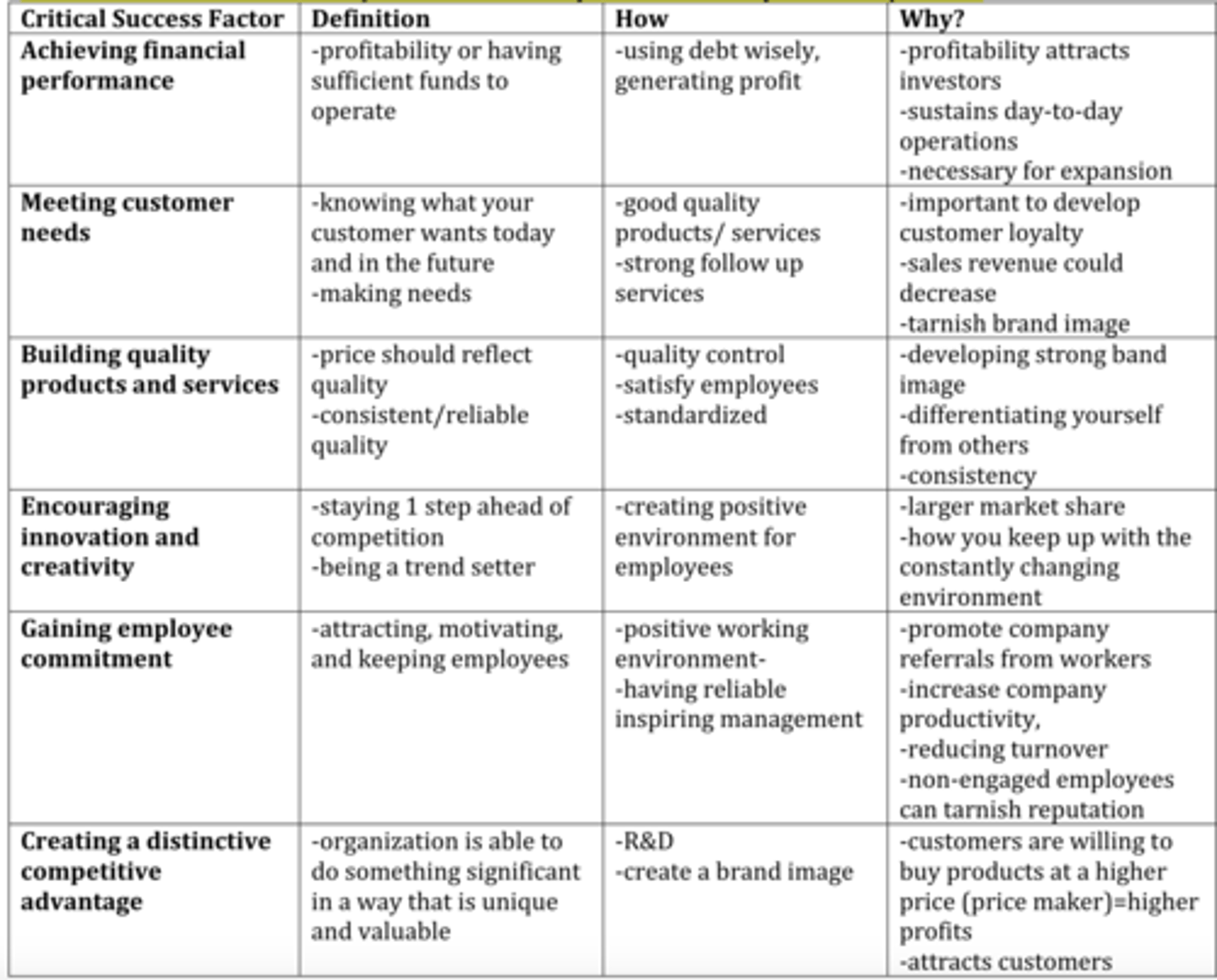
_Overall, Why are the critical success factors important?_
-Critical success factors guide our strategic and daily details
- Ensures holistic thinking , it requires you to think about how everything connects
- Ensures success over time by if you are not looking at all 6 success factors
- They are all connected/related, if one fails there will be a domino effect
_How is each critical success factor connected to eachother?_
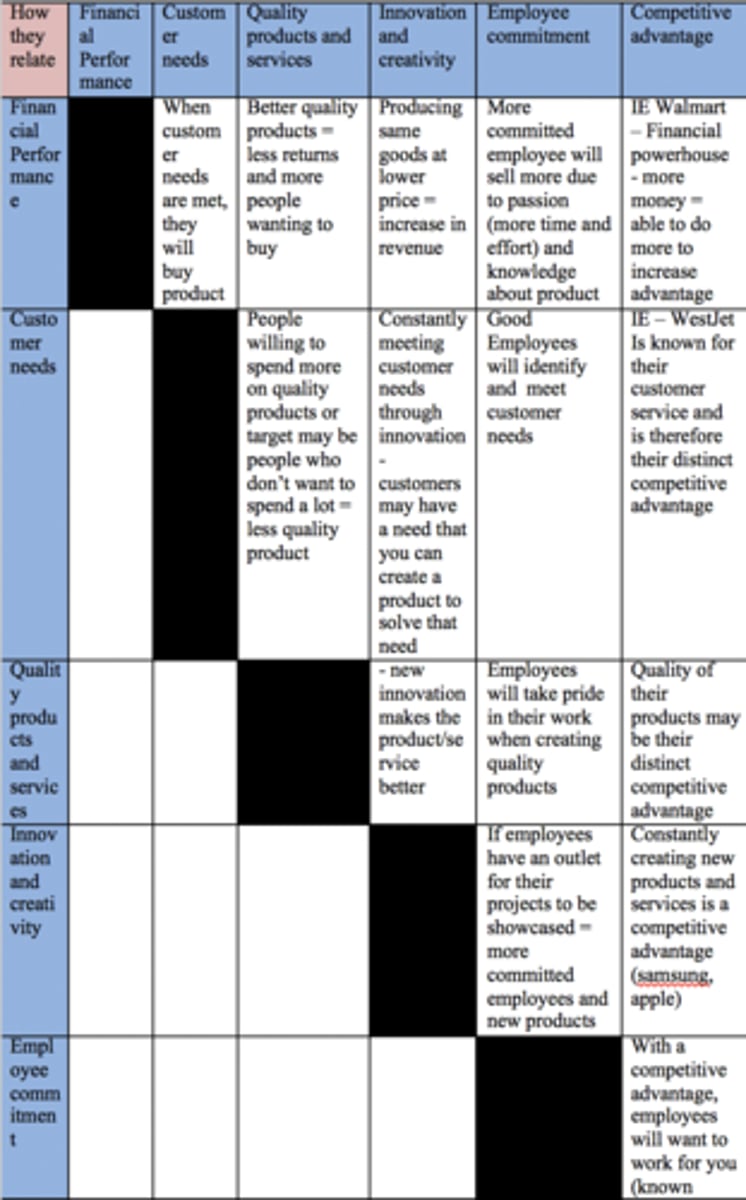
//Vision//
and how does it guide your strategy ?
- Should align with organizational values and culture
-Guides strategy by keeping focused on desired future
//Mission//
How does it guide your strategy
- Mission is the HOW to achieving your vision
-Guides strategy by listing goals and approaches
_Diamond-E Framework_
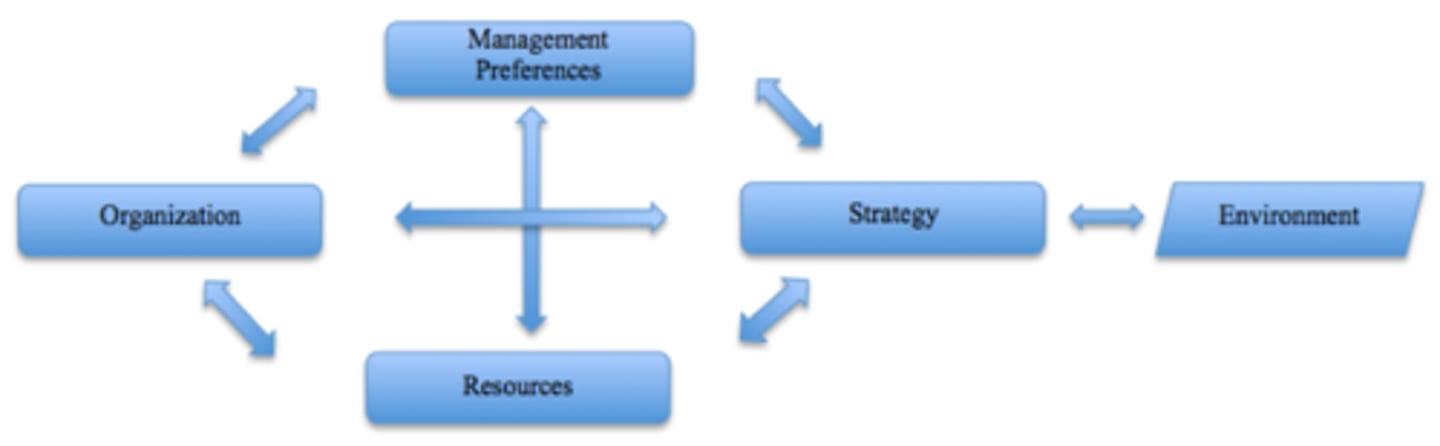
Every factor on the internal side of the Diamond-E Framework (ex, strategy, mgmnt. pref, organization...) consists of ___________________ & _____________________ ?
Strengths and Weaknesses
_What are the purpose/uses of the Diamond-E_
- Assess your strategy, Generate new strategic proposals, and Evaluate strategic proposals
-However, your strategy has to make sense given the environment (environment is always changing)
//Strategy// in the Diamond-E
-Is the linking variable in the Diamond- E on what you can and should do
-Strategy is based on the environment and needs to be adjusted based on the environment
-Determines and is determined by internal qualities
//Management Preferences// in the Diamond-E
-Determines the decision making process for the organization
-Ambitions (what they see for company)
-Management sets the vision and mission for the company and you need to follow that
//Organization// in the Diamond- E
Consists of the Culture, Capabilities, and Structure of company
1. Culture - vision and mission of company, how employees connect
2. Capabilities - What the organization can do (ex. management says what the company is going to focus on)
3. Structure- The way you structure your organization is the way you focus on your attention
//Resources// in the Diamond- E
1. Financial resources- how we get resources and where we spend them
2. Capital resources- How many locations and where they are located
3. Human resources- Management decides if human resources are local or international, what kind of skills are they going to hire
//Environment// in the Diamond- E
- Must conduct a process of scanning and evaluating the external environment, and examine opportunities & threats which is called an External Analysis
- Market size & Growth, #of rivals/substitutions
-Cost Factors (economy/economies)
The variables in the diamond- E can either ___________ or ___________ a strategy
Constrain or Drive
//MORSE//
MORSE - a "two way code" helps the internal and external aspects "communicate" (plus it keeps strategy in MOR and Environment)
_How do the variables in the Diamond- E Framework connect to each other?_
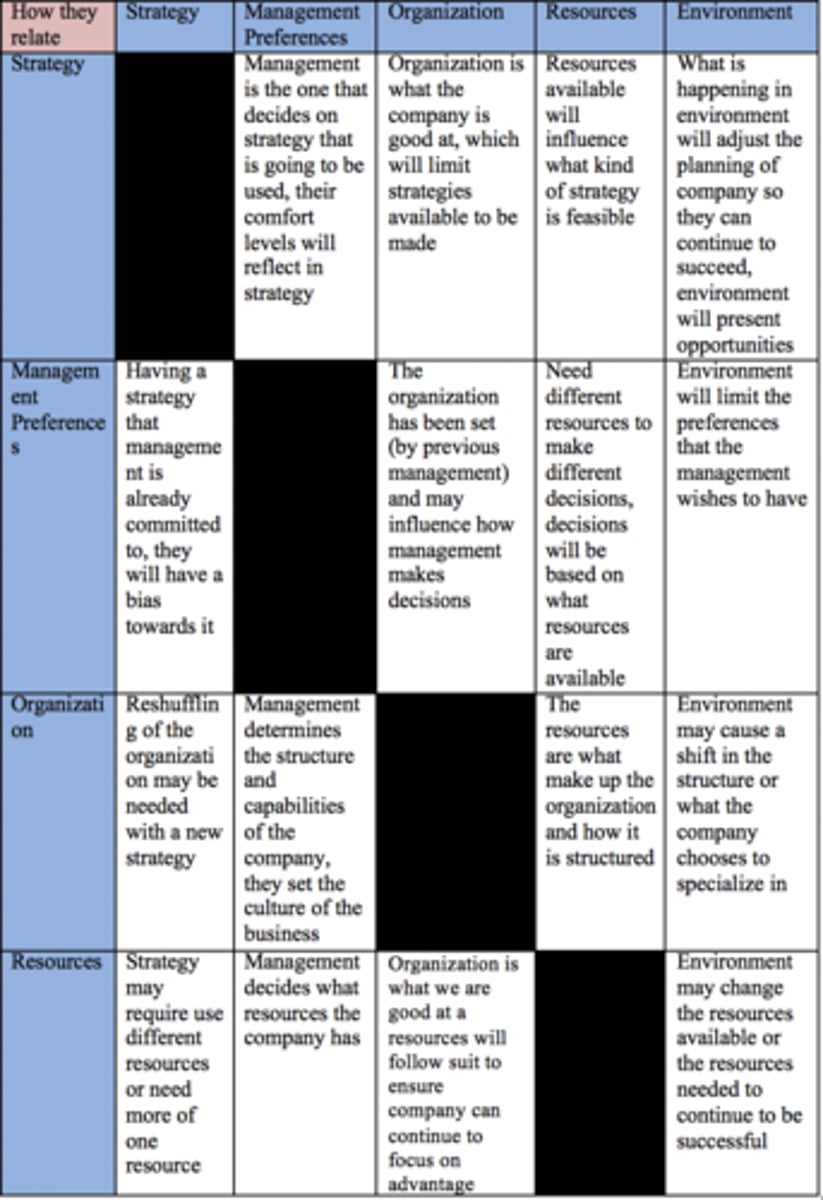
Diamond- E - //Principal Logic//
Principal Logic behind the Diamond- E is Consistency or Alignment
Consistency internally leads to performance
Alignment externally ensures strategy is right given that environment
-Consistency internally leads to performance only when there is alignment between strategy & environment
- 2 way relationship exists where If your strategy isn't consistent with the resources, it doesn't matter how well aligned strategy is with the environment as it will not be feasible anymore
1. _What was the Principal Logic behind Blockbuster?_
2. _Why/ How?_
1. Inconsistent/ no or little alignment
2.
-Movies started moving towards online streaming or TV
-Nobody wanted to go to the store to rent when you already had it at home
Thus, Blockbuster did not evolve/adapt to the environment
1. _What was the Principal Logic behind IKEA's strategy?_
2. _Why/ How?_
1. Consistency/ Alignment
2.
-Affordable, durable, easy to build/use
-Had extensive resources supporting them
Since the Environment was full of people living in small spaces and they had the resources to correspond with their strategy, it aligned with the environment which = success!
1. _What was the Principal Logic behind P&G's Strategy in 2000?_
2. _Why/How?_
1. Inconsistency
2.
-Had capabilities and resources but > moved into new product lines
-The Manager was aggressive and missing parts
Since, the Environment was not suitable (recession) and didn't support new products P&G in 2000 failed to succeed
Example of rivalry companies where one succeeded and one failed?
Kodak Vs Canon
-Kodak made money through film and devoted to making better film
-Canon saw that the environment was changing and made the risk to go the digital route. At first it didn't pay off for Canon, but now they are doing extremely well and Kodak is struggling
//External Analysis//
- The process of scanning and evaluating the external environment
-How managers determine opportunities (positive external trends) or threats (negative external trends)
1. //General Environment//
2. //Specific Environment//
General Environment - Affects all businesses (ex. employment, tax rates, exchange rates)
Specific Environment- Affects industry participants
_What model should you use to do an external analysis based on the type of environment you're in?_
- For the //General Environment// use the PEST model (identifies general trends and changes in an economy)
- For the //Specific Environment// use the Porter's Five Forces Model (analyzes competition and predicts industry profitability)
_5 Benefits of External Analysis_
1. Makes managers proactive
2. Provides information used in planning
3. Helps organization get needed resources (on time)
4. Helps organization cope with uncertainty
5. Improves consistency and performance
_Challenges of External Analysis_
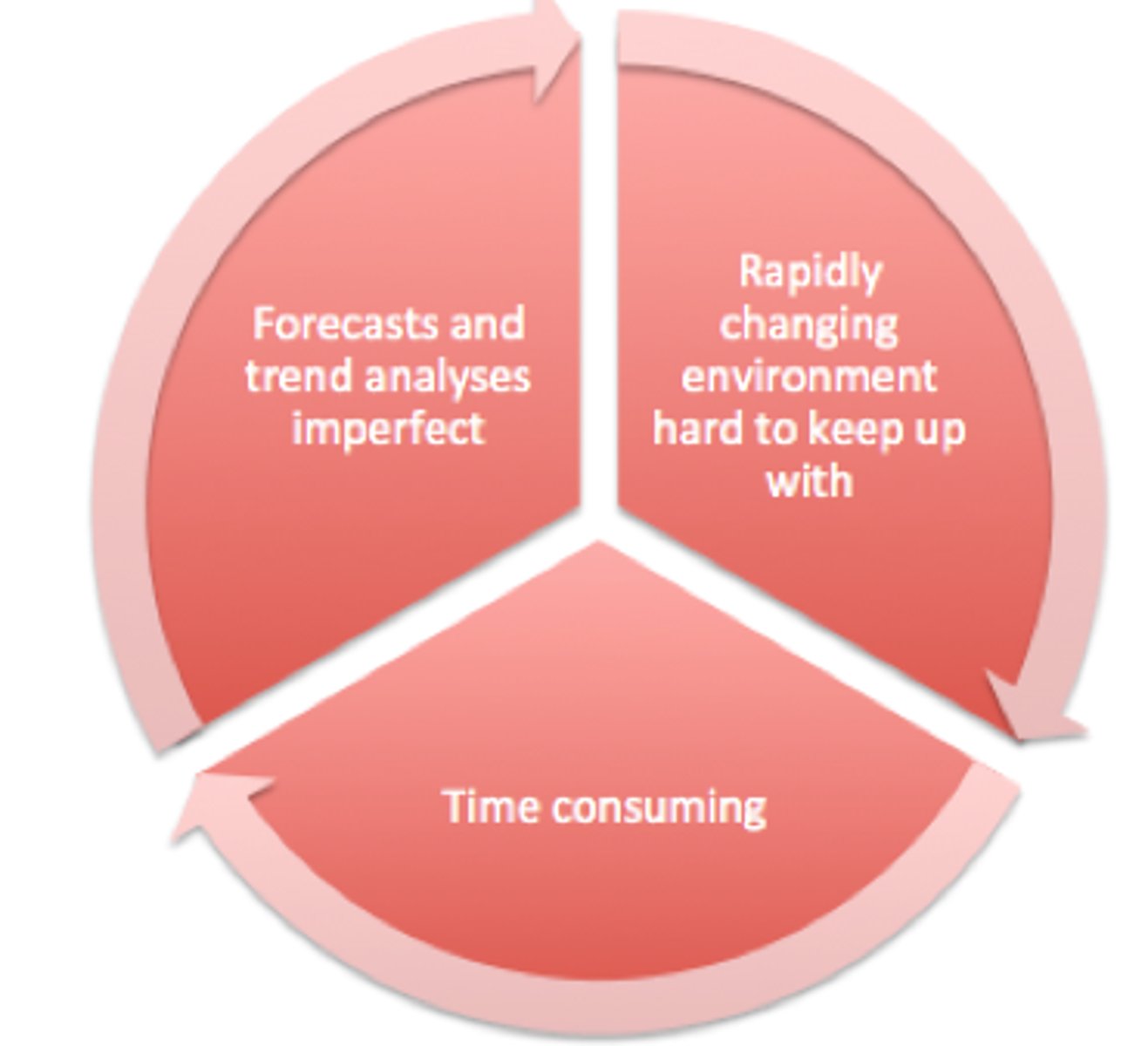
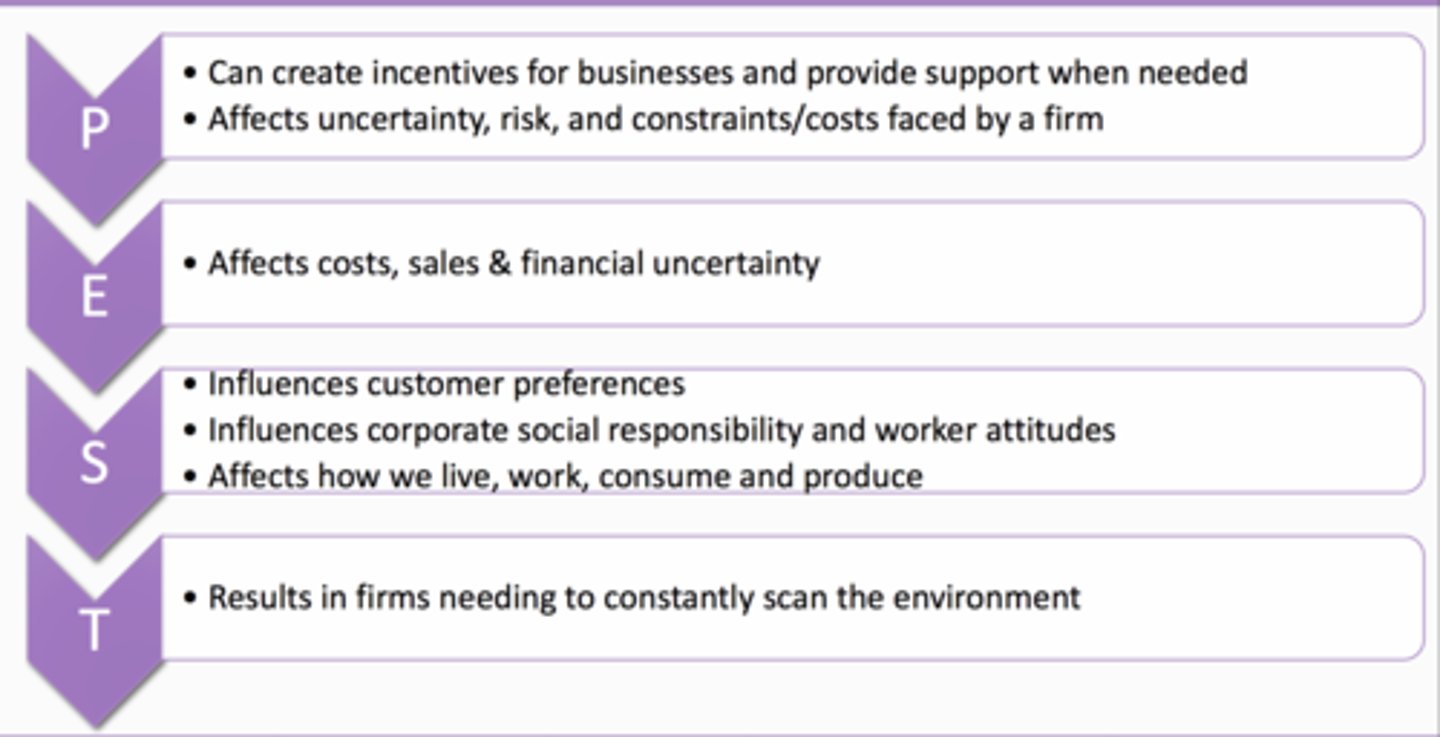
//PEST//
Political- Legal, Economical, Social, Technological Factors
Why //PEST//?
-Framework for analyzing General environment
-Identifies opportunities/ threats
-Helps managers identify opportunity and prepare for threats in environment
_What is the significance of the //Political-Legal// factors?_
-Protects consumers, support/ protection and regulation of domestic businesses, opportunity creation in foreign markets
Elements of //Political- Legal// factors
1. Laws
-Constraints/rules on what businesses are allowed to do in any environment
2. Taxes
-Higher business taxes= lower drive to do that business
3. Trade agreements or conditions
-Competition gets more competitive if other companies can sell with out duty and you can't
4. Political System
-ex. under a communist government, they have all of the control
5. Political Stability
-ex. Political instability an creates unpredictable environment making it undesirable for companies
Elements of //Economic Factors//
1. Inflation/ Deflation
-When prices inflate, there are higher costs (expenses)
2. Interest Rates
-When it goes up it costs more to borrow money
3. Employment Rates
-When unemployment rates increase, fewer people have jobs and have less money to spend on your products
- 3-4% unemployment is healthy
4. Exchange Rates
-Important for international trade
-CAD $ is lower than US $. If you shop in USA, you are spending more than you should
5. Balance of Trade
-Balance of trade refers to net imports compared to exports
6. Productivity (what % inputs are you putting in to what % outputs you get out)
-High productivity means it costs you less to produce a product
Elements of //Social Factors//
1. Customs
-Influence what we spend time and money on
2. Values
-How much we value a certain thing (ex. Do we value being employed?)
3. Attitudes
- i.e. Smoking >> change in attitude changes how we react
4. Demographic Characteristics
-Women vs men, age groups, levels of education
Elements of //Technological Factors//?
1. Internet
-affects buying/selling and communication
2. Information Technologies
-Suppliers connect with companies through technology (ie when a product is running low, supplier can see because they have access to inventory website)
3. Not limited to computers and Information
-Product doesn't need to be technologically innovative in terms of computers and information
-ie Mechanical Pencils
Business Implications of //PEST// Factors
Questions to answer from //PEST//

Michael //Porter's Five Forces Model//
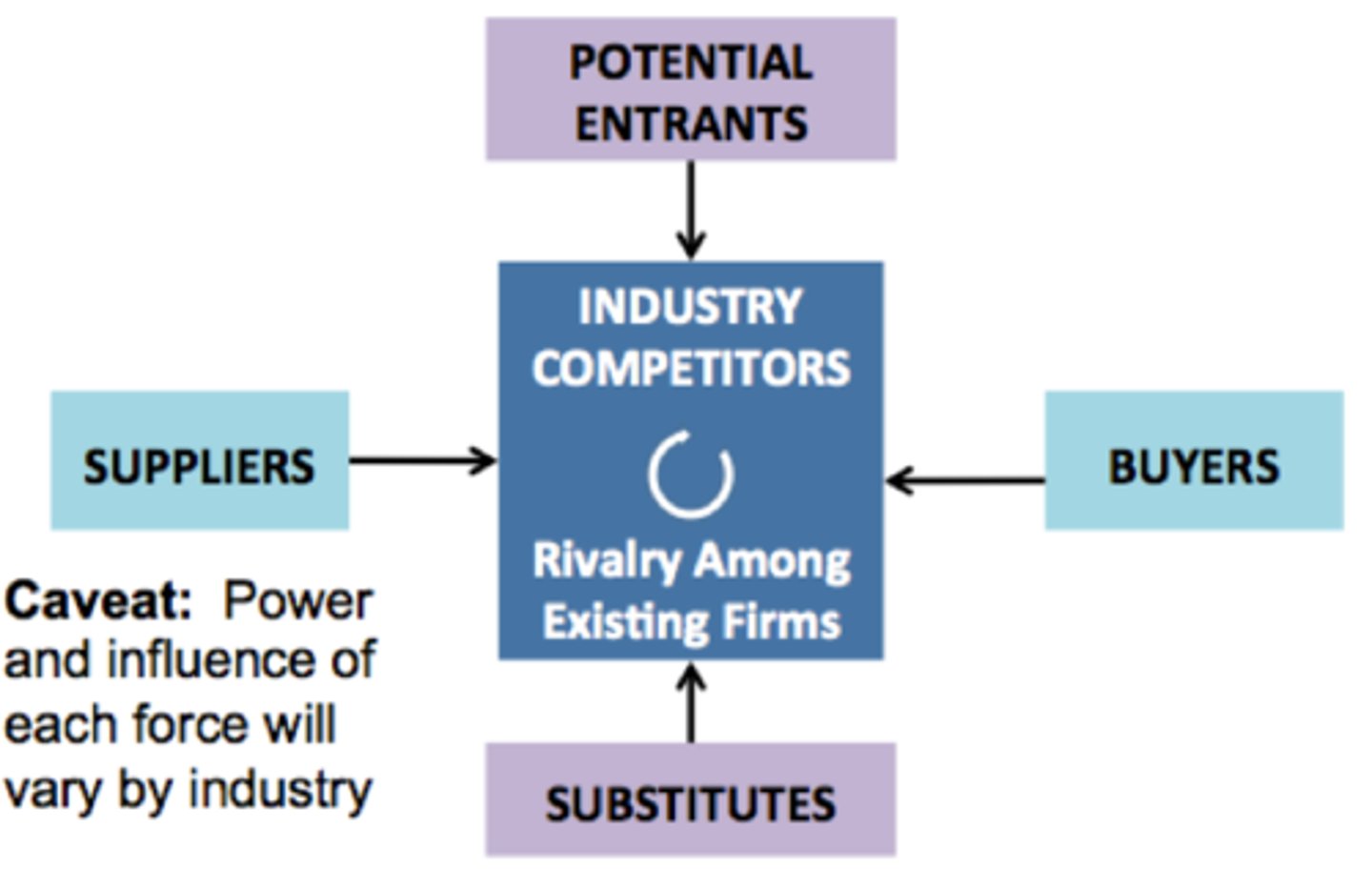
_What are the Porter's Five Forces? _
1. Competitors
2. Potential Entrants
3. Substitutes
4. Suppliers
5. Buyers
Why Porter's?
- Analyzes the Specific Environment which analyzes competition and predicts profitability
//Rivalry/Competition//
Competitors = more intense rivalry
1. lowers revenues
2. Not a big market to share
3. Downward pressure on price
-Most powerful of Porter's Five Forces
//Potential Entrants//
1. More people entering industry
2. The easier it is for people to enter, there is more downward pressure on price; thus, lower profitability
//Suppliers//
- Organizations or people that provide "key inputs"
1. If they are able to increase the price they charge you, your profitability goes down
2. If you are able to negotiate, you will have advantage in profitability
//Buyers//
1. When consumers have a lot of bargaining power, you will have lower profitability
2. If you have the upper hand (lots of people want to buy your product at a set price) then buyers don't have ability to negotiate
//Substitues//
1. If there are more substitutes, there are more consumers willing to buy that product and not yours, thus causing lower profitability
2. You need more time and energy to convince buyers to buy your product
North - South on Porter's Five Forces model =_________?
Competition
West- East on Porter's Five Forces model = ________?
Supply Chain
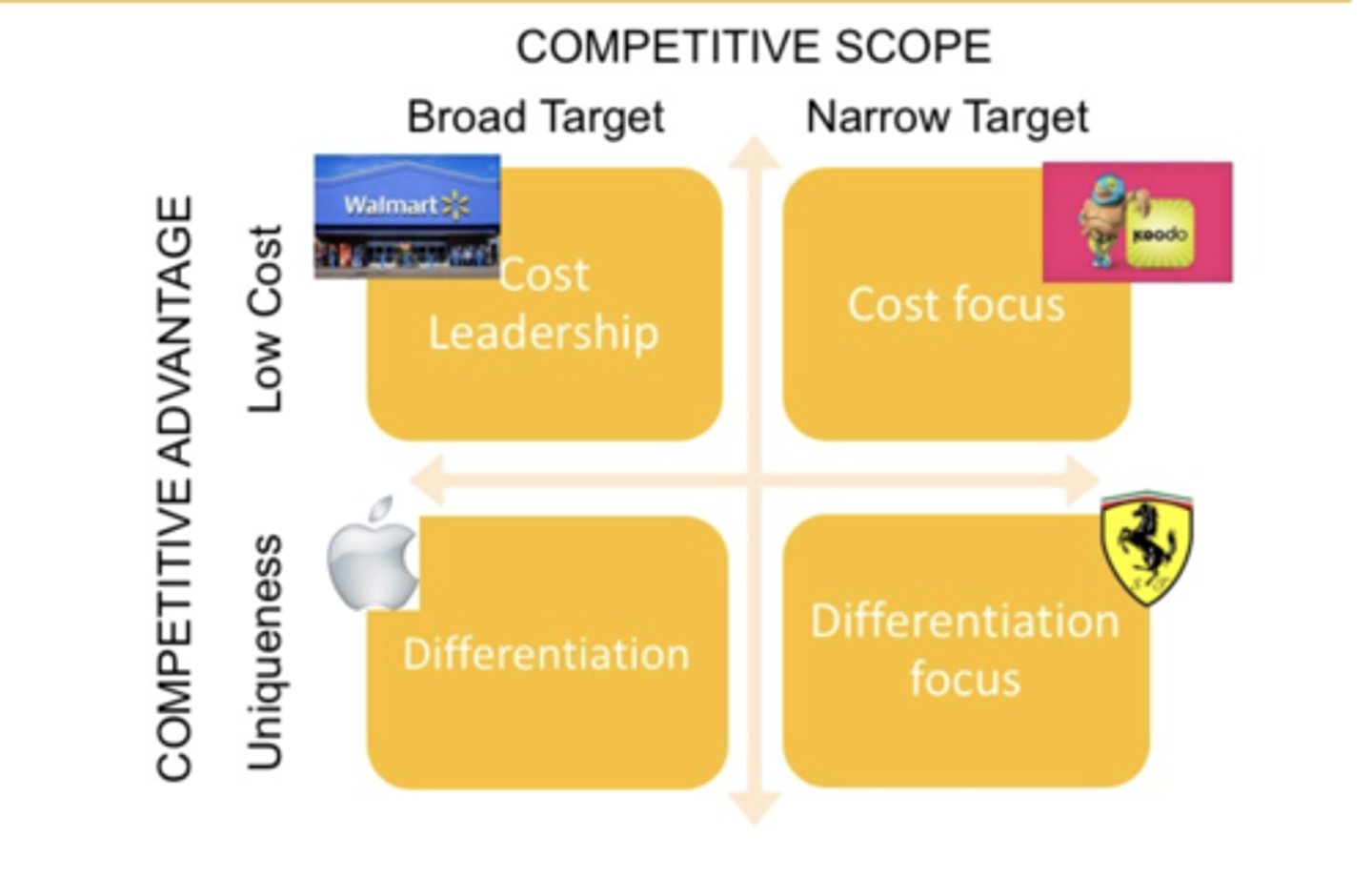
Porter's Generic Strategies
//Rivalry among Existing Firms (Competition)// Effects
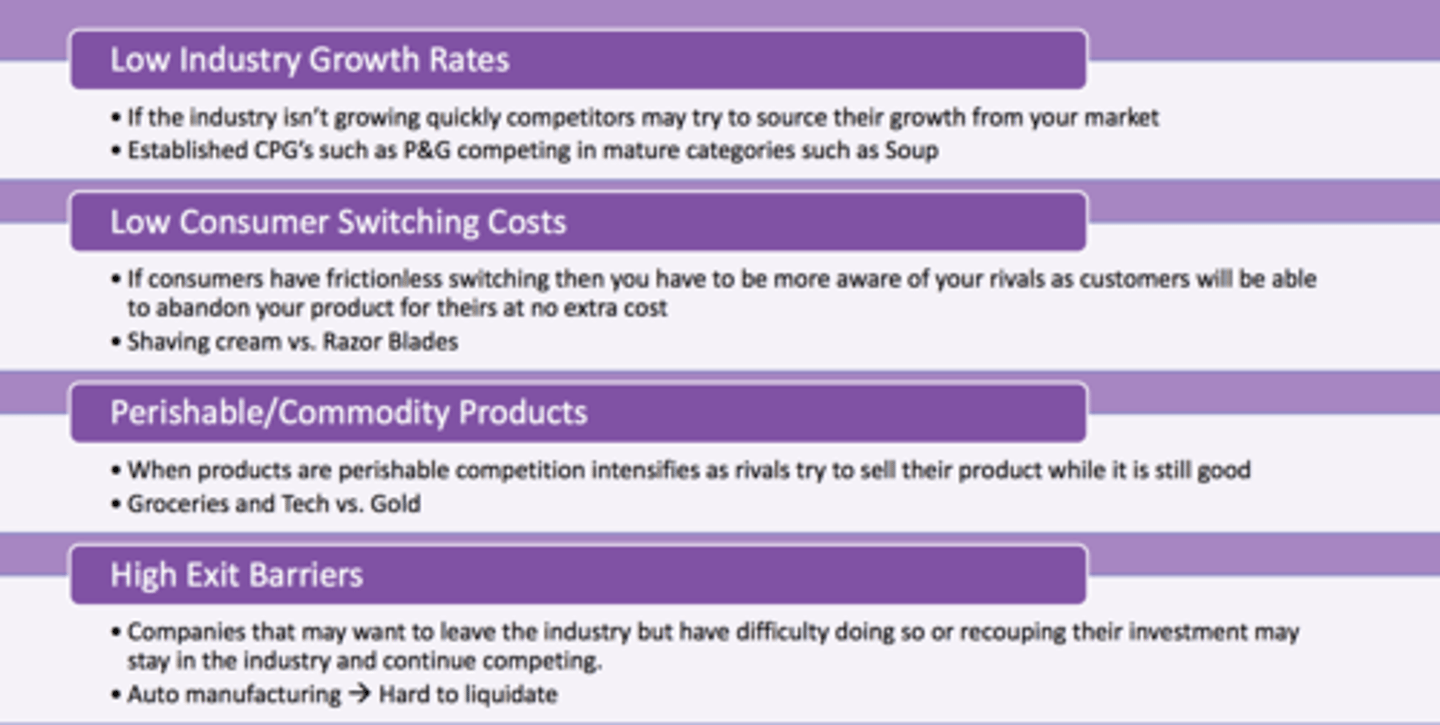
//Rivalry among Existing Firms (Competition)// Solutions to fix Profitability

//Suppliers// Effects on industry profitability

//Suppliers// Solutions to fix profitability

//New Entrants// Effects on industry profitability

//Substitutes// Effects on industry profitability

//New Entrants// Solutions to fix profitability

//Substitutes// Solutions to fix profitability
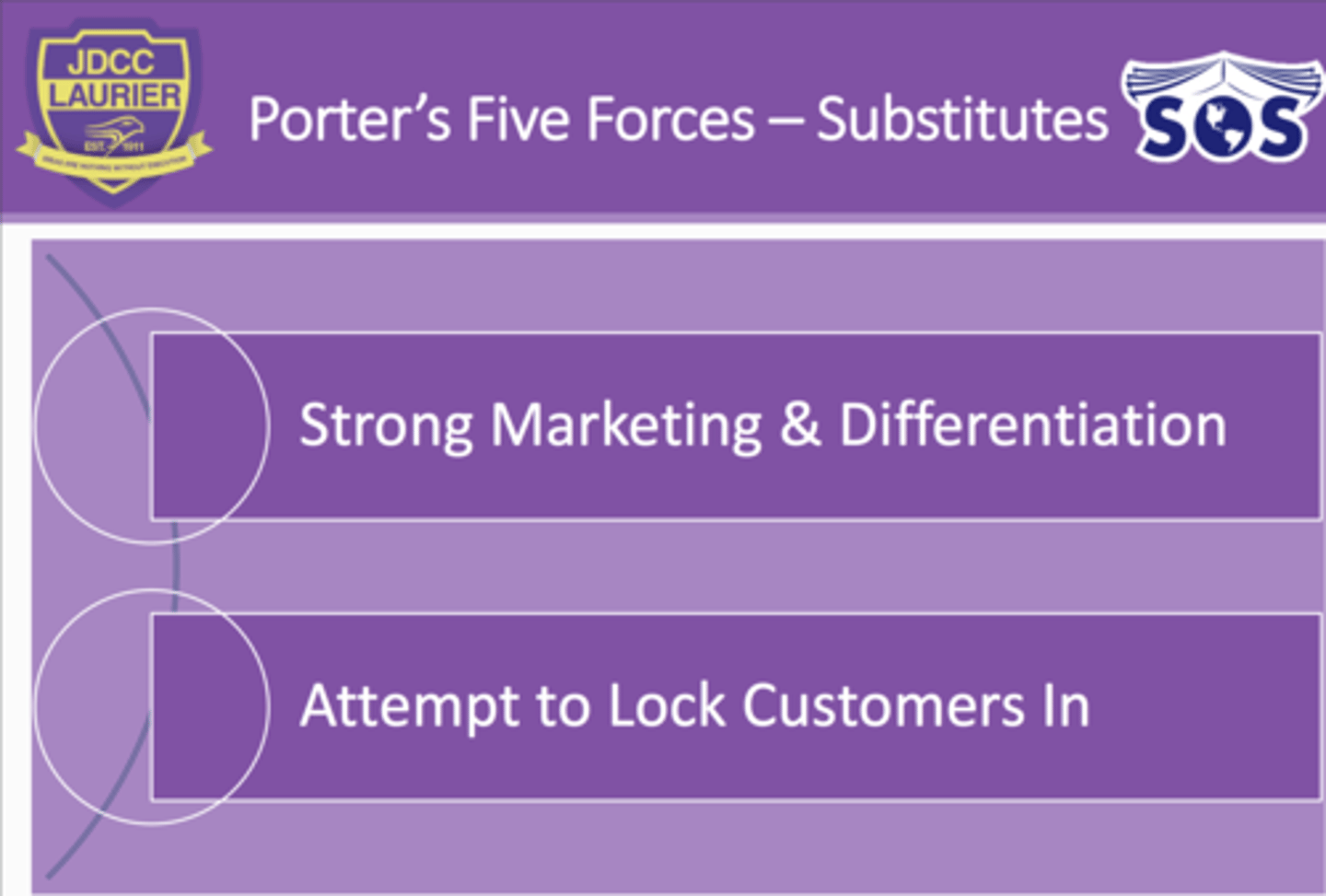
//Buyers// Effects on Industry profitability

//Buyers// Solutions to fix profitability

Define //New Venture//
-recently formed commercial organization that sells goods/services
Define //Entrepreneurship//
-identify an opportunity and accessing resources to capitalize on it
1. _How old is a new firm?_
2. _How many employees does a small firm have?_
1. less than 5 yrs old
2. Less than 100 employees
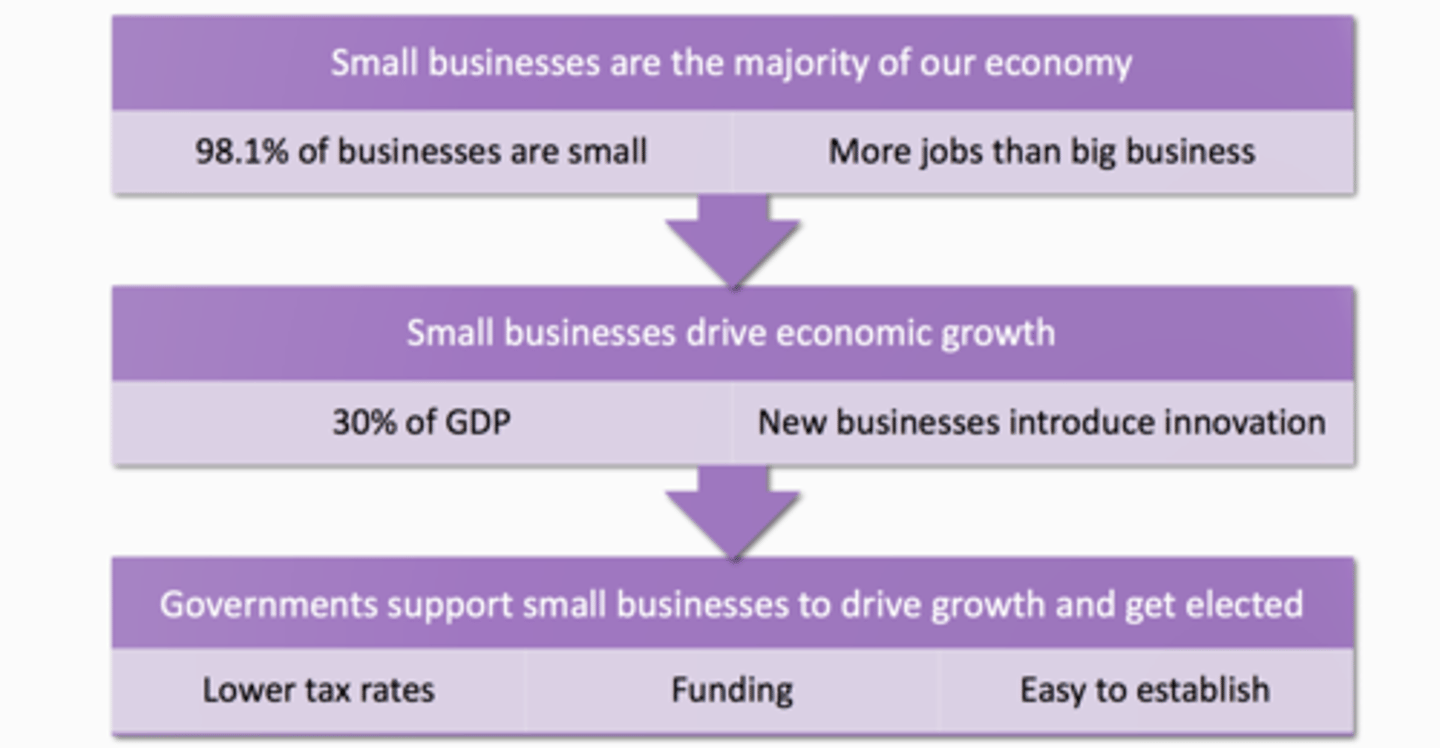
_Importance of Entrepreneurship ?_
1. 98.1% of CDN biz are small
2. Contribute 30% annually to GDP
3. Provide more jobs than large businesses
4. New ventures lead in new products and services
_ The Government supports Small biz by?_
1. Lower tax rates
2. Resources - advice and sometimes funding
3. Ease of establishment
Ex. Government of Ontario supports young entrepreneurs (Summer Company) and offers them ease of establishment/ resources
_Why are Small Businesses supported by the Government?_
_What is the Entrepreneurial Process?_
-Influenced by PEST, Successful only when entrepreneur, resources , and opportunity fits
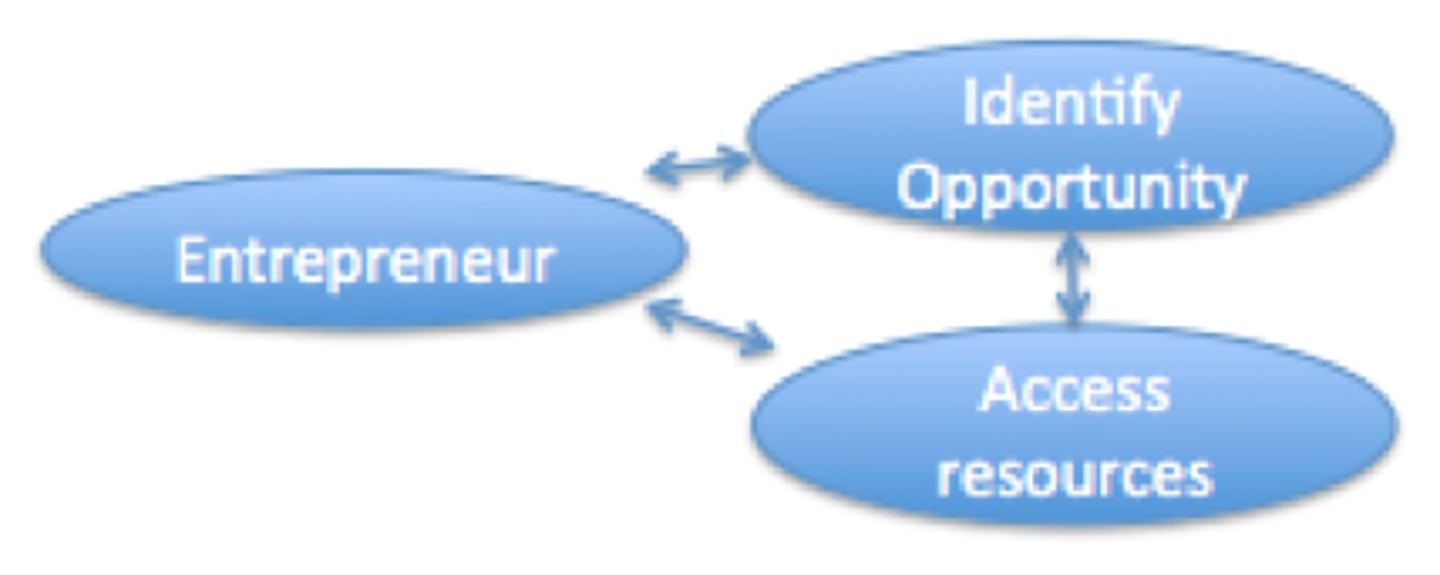
//Entrepreneur// in the Entrepreneurial Process
-Their capabilities are what the company can do
-An individual willing/able to seek out opportunity and execute
//Access Resources// in the Entrepreneurial Process
-Having access to necessary resources to make business a reality
//Identify Opportunity// in the Entrepreneurial Process
-Seeking out an opportunity typically using External Analysis (e.g PEST or Porter)
_What must the //Entrepreneurial Process// achieve?_
-The Entrepreneurial Process must achieve alignment among the three factors (they must fit together)
_How does the //Entrepreneurial Process// begin?_
- Begins with an opportunity being identified and then accessing the resources to fulfill that opportunity
_How is the //Entrepreneurial Process// similar to the //Diamond-E//?_
-Both need alignment for success
- Entrepreneur = Management Preferences, and Organization's capabilities
-Resources= Resources
-Identifying Opportunity = Strategy and Environment
Opportunity Recognition
_Idea Generation_
-Paradigm Shifts (change in approach)
-Solving Daily Problems (related to work, life, hobbies etc.)
-Combining Features
_Screening_
- 3 component Screening Process
- Eliminates Bad Ideas
- Saves Time + $$$
//Three Component Screening Process// (You know you have a good idea when?)
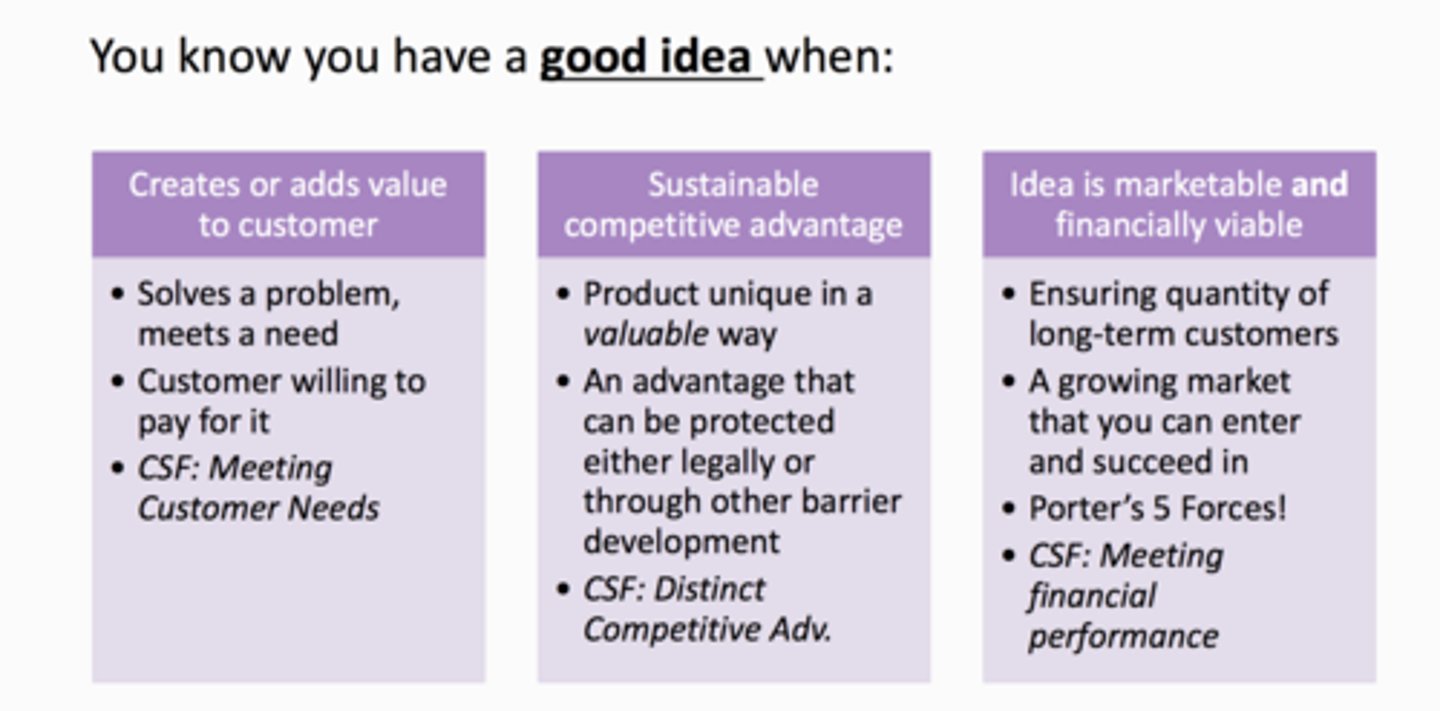
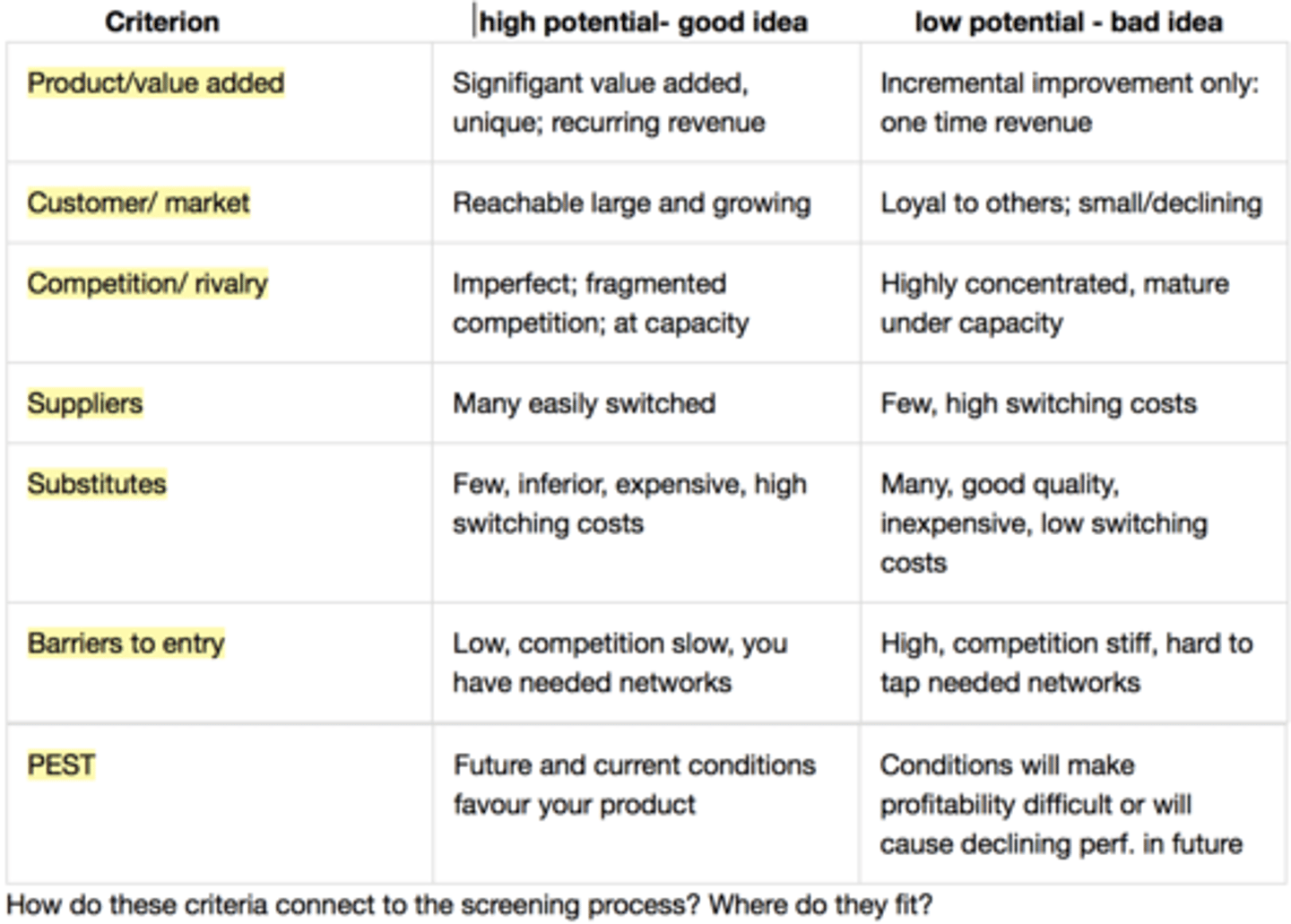
High Potential New Venture vs Low potential New Venture
- put these into the three component screening process
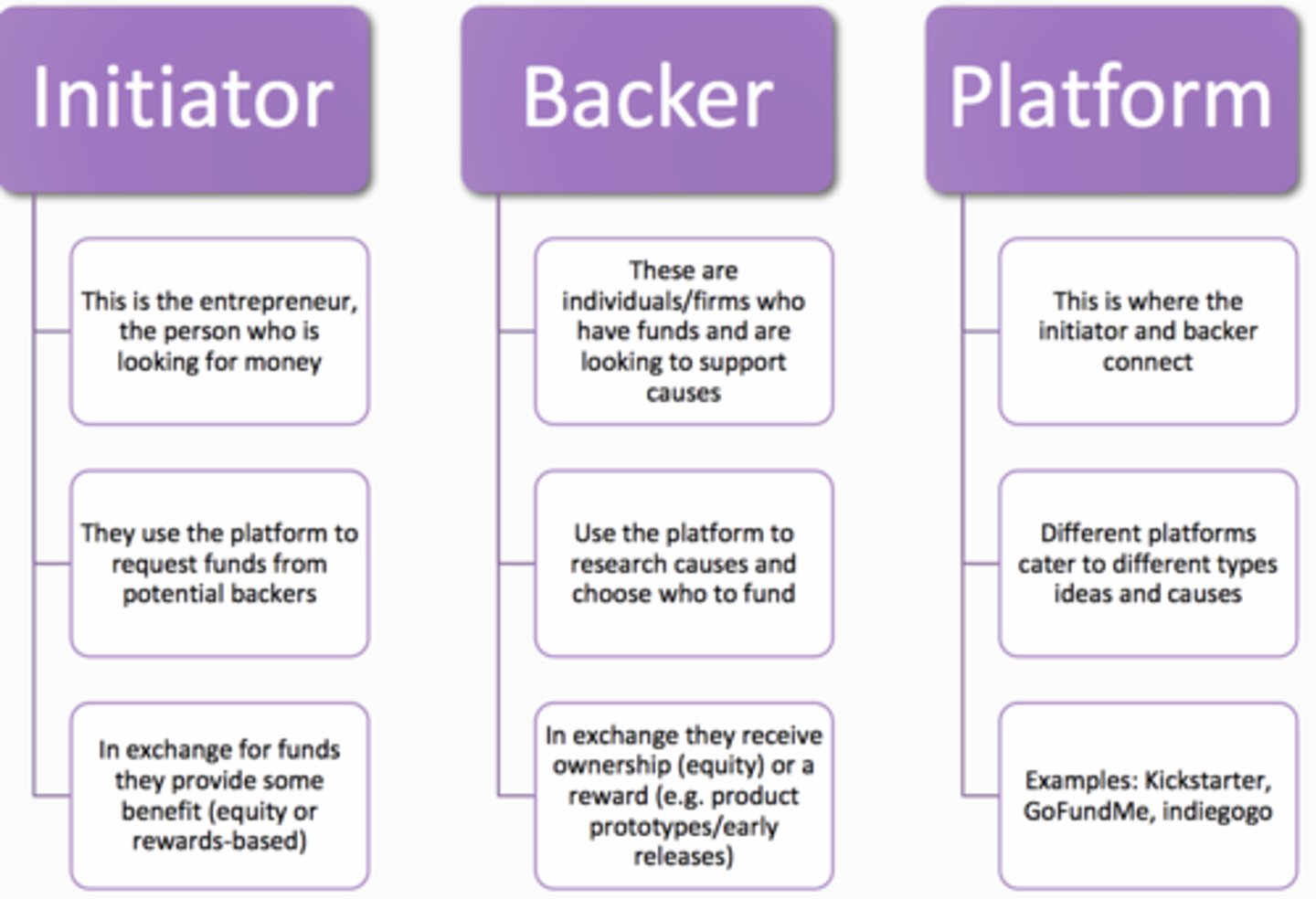
Accessing Resources - //Bootstrapping//
Doing more with less
-Make do with as few resources as possible
-Use other peoples resources where possible
-Find/ Use free stuff
Accessing Resources - //Equity//
Equity is selling a % ownership in your business (ex. Dragons den)
Sources: Savings, Private Investors, Angel Investors, Venture Capital
Accessing Resources - //Debt//
Debt is essentially an IOU- Receive money now, and pay it back later
-Keep control of your business, but have to pay interest rates on top of the money your borrow
Sources: Financial Institutions (banks), Suppliers
Accessing Resources - //Crowdfunding//
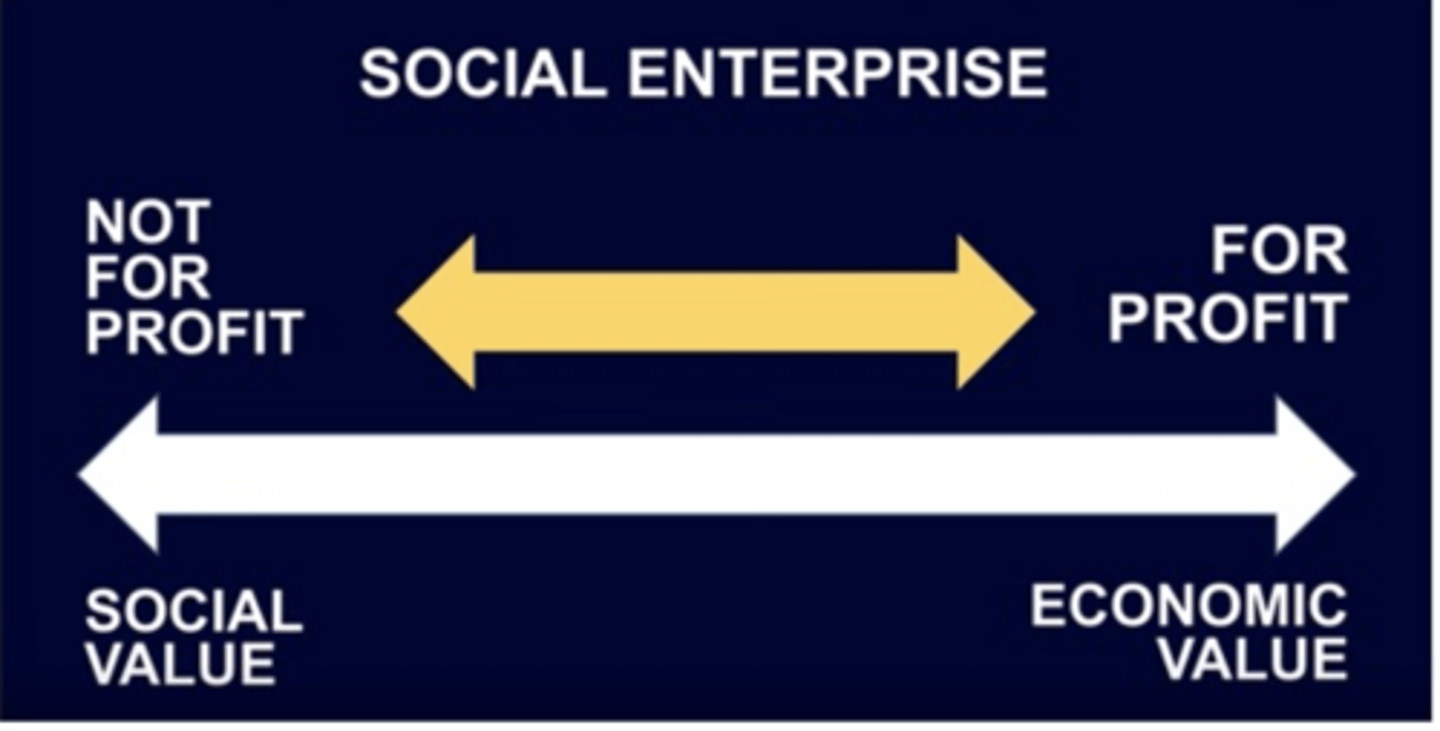
//Social Enterprise//
-In-between a For Profit and a Not For Profit
-Thus, Social Enterprises social value while operating with a financial discipline
//Social Entrepreneurs//
• Society's change agents: a creator of innovation that disrupts the status quo and transforms our world for the better
• Addressing needs in the world (environmental/social)
What are the Key Facets of //Social Entrepreneurship// (what is it)

//Traditional Entrepreneurship// vs //Social Entrepreneurship//
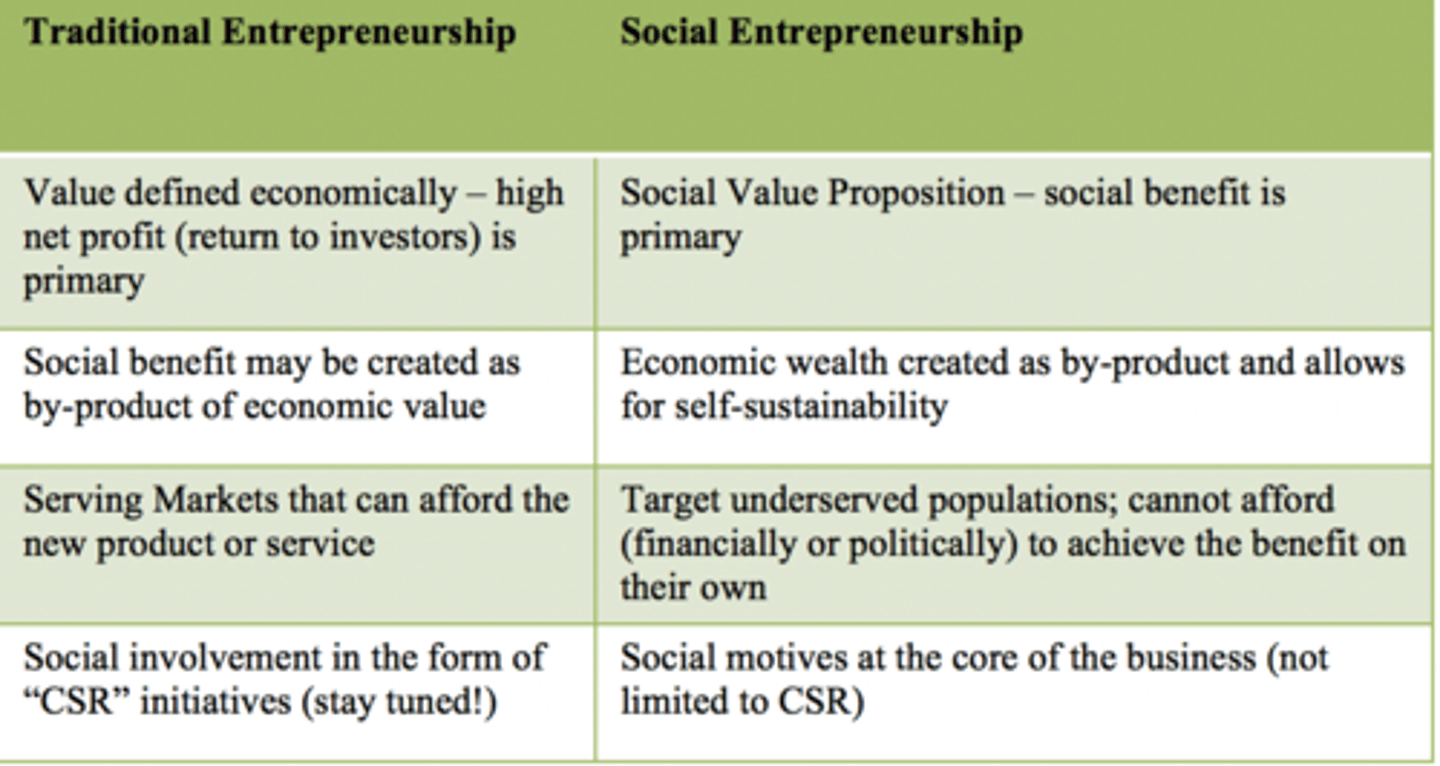
Example > _Grameen Bank_ - providing loans to women in impoverished areas of Bangladesh
Unique- These people do not have access to small loans
Social Value - women are able to invest in their children's education and overall life
Self- Sustaining - loans are repaid and capital given to other members
Example > _Students Offering Support (SOS)_ -
Unique Value to Customer- offers students with support/ exam prep
Social Value- funds educational development in Latin America
Self- Sustaining- Uses Students $$ and funds education in Latin America
Bootstrapping - Using University Resources and Volunteers (these do not cost anything)