1.13 Assessment of Aortic Regurgitation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is the first thing that must be done when AR is identified?
Determining the etiology of the regurgitation.
AR is due to what?
Either to disease of valve leaflets or abnormalities of the aortic root.
What are some primary causes of aortic leaflet dysfunction?
Bicuspid aortic valve
Rheumatic disease
Endocarditis
Calcified disease
Systemic diseases
Aortic root enlargemnt resulting in AR may be due to what?
Marfan Syndrome
Familial aortic aneurysm
Hypertension or aortic dissection
What are the views AR should be evaluated in?
Parasternal LAX
Parasternal SAX
Apical 5 and/or 3
SSN, Subcostal, RSB (to determine if there is flow reversal in diastole)
Physiological or mild degrees of mitral, tricuspid, and pulmonary regurgitation is…
common in the normal population.
Are physiological or mild degrees of AR normal in the population?
No, they are not normally seen. Therefore, whenever AR is present, close inspection of the aortic valve and aortic root are necessary.
What are the steps associated in the assessment of AR?
Determine the etiology of the lesion
Assess the LV size and systolic function
Measure the aortic dimensions
Estimate the severity of AR
Regurgitant severity should be evaluted using the integration of what methods?
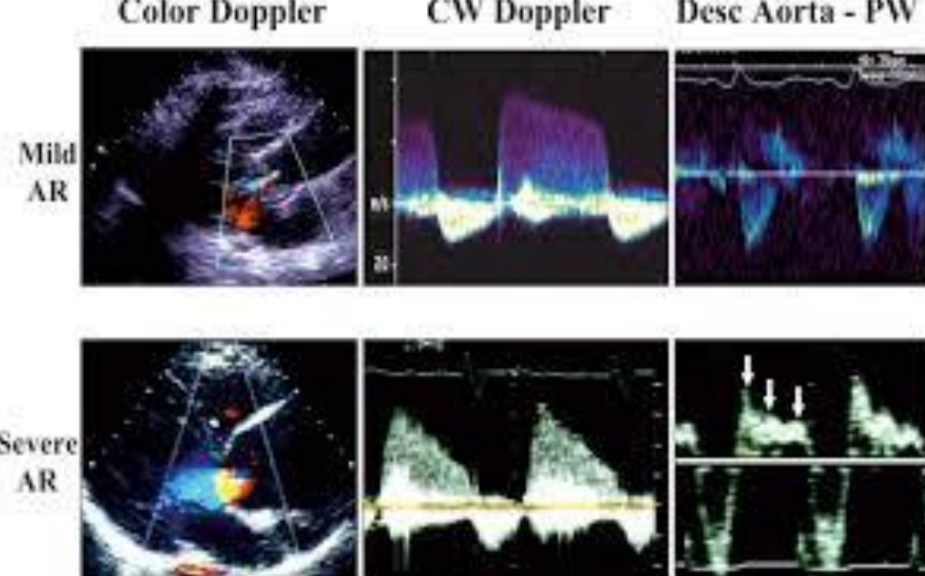
Colour Doppler
Vena contracta
PHT
AR jet/LVOT height
AR jet area/LVOT area
Flow reversal in the descending aorta
In addition to Doppler, what are other important parameters used in clinical decision making with AR?
The cause of the regurgitation and the LV size and systolic function.
What is the method of choice for detecting AR?
Colour Doppler (along with other methods of Doppler).
What views may allow you to identify the exact origin of the regurgitant jet in addition to the width and cross-sectional area of it?
Parasternal LAX and SAX.
What views are best for assessing AR with Doppler?
Apical 5 and 3 because this is where both spectral and colour Doppler are parallel to flow.
In what view is the vena contracta best measured in?
Parasternal LAX view on TTE.
How is vena contracta measured?
Image is zoomed and a narrow sector is used to improve the measurement accuracy.
A Nyquist limit of 50-60 cm.sec is typically used.
Cineloop through captured image to find the best vena contracta.
Measure.

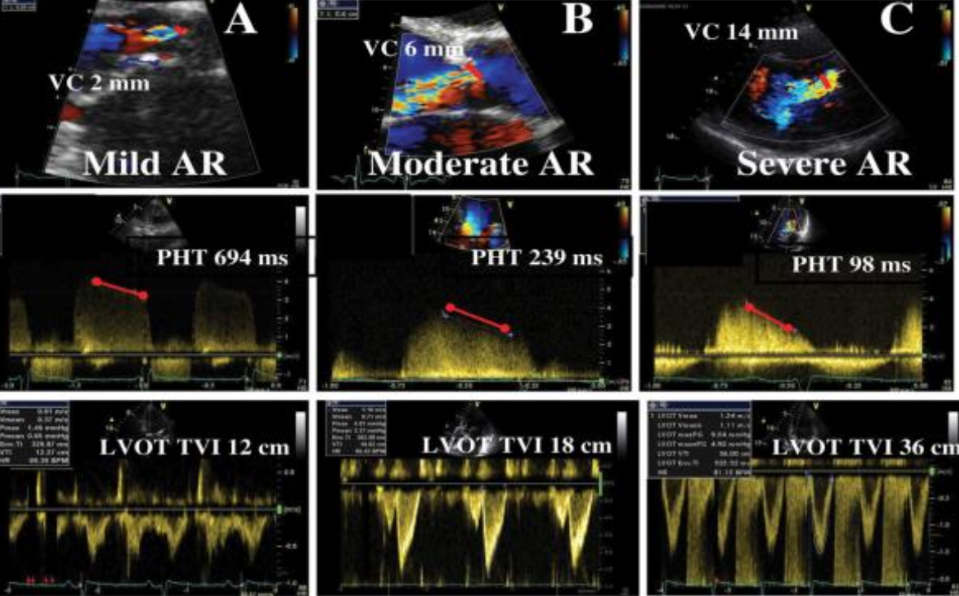
A vena contracta width less than 0.3 indicates what?
Mild AR.
A vena contracta with a width greater than 0.6 cm indicates what?
Severe AR.
A vena contracta with measurements between 0.3-0.6 cm/sec indicates what?
These are intermediate measurements and thus, they cannot rule out moderate AR. Therefore, further quantification is required.
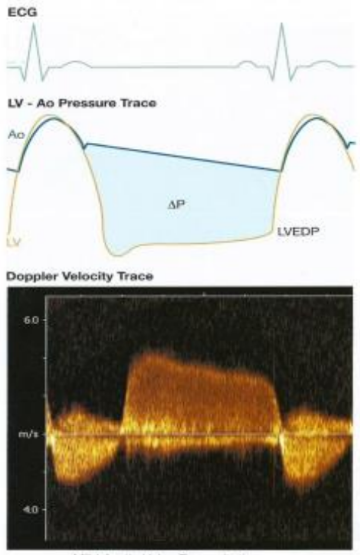
How is PHT used to calculate AR?
Done the same way it is used to calculate MS, however, the only difference is that the steeper the waveform the more severe the AR.
Why does Mild AR have a flatter slope in PHT?
Because the pressure difference gradually decreases as the AR slowly moves back through the closed AOV into the LV.
Why does severe AR have a steeper slope in PHT?
Because the larger the opening of the closed AOV, the faster the aorta empties into the LV, the faster the aortic pressure drop, the faster the LV pressure rises.
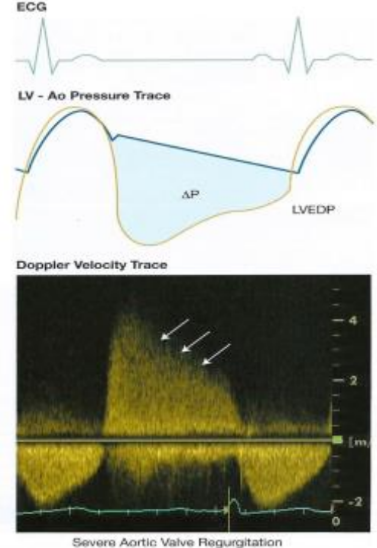
AR CW Doppler signal represents the gradient between what?
The LV and Aorta in diastole.
What is the diatolic pressure in the aorta normally at?
80 mmHg.
What is the diastolic pressure in the LV normally at?
10 mmHg.
What is the PHT for mild AR?
> 500 ms.
What is the PHT for moderate AR?
350-500 ms.
What is the PHT for severe AR?
< 200 ms.
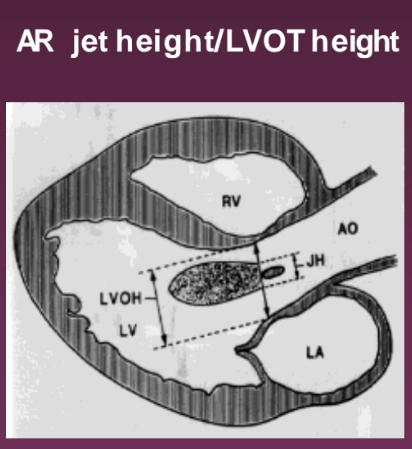
What view is used to look at the AR jet height/LVOT height?
Parasternal LAX. It compares the regurgitant jet height to the LVOT height.
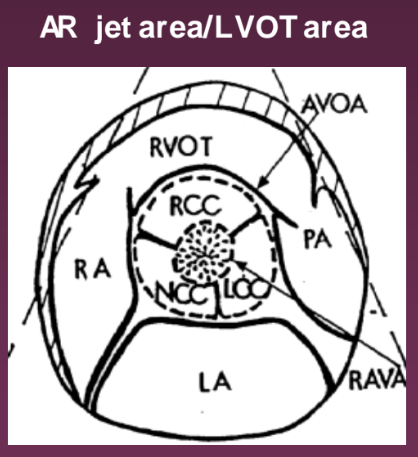
What view is used to look at the AR jet area/LVOT area?
Parasternal SAX. It compared the regurgitant jet area to the LVOT area.
What percentage identifies mild AR jet height/LVOT height?
< 25 %
What percentage identifies moderate AR jet height/LVOT height?
25-46%
What percentage identifies moderate to severe AR jet height/LVOT height?
47-64%
What percentage identifies severe AR jet height/LVOT height?
> 65%
What percentage identifies mild AR jet area/LVOT area?
< 4%
What percentage identifies moderate AR jet area/LVOT area?
4-24%
What percentage identifies moderate to severe AR jet area/LVOT area?
25-59%
What percentage identifies severe AR jet area/LVOT area?
> 60%
Holodiastolic flow reversal in the proximal abdominal aorta is highly specific to what?
Severe AR.
Holodiastolic flow reversal in the descending thoracic aorta is seen where?
In some patients with moderate AR as well as those with severe AR.
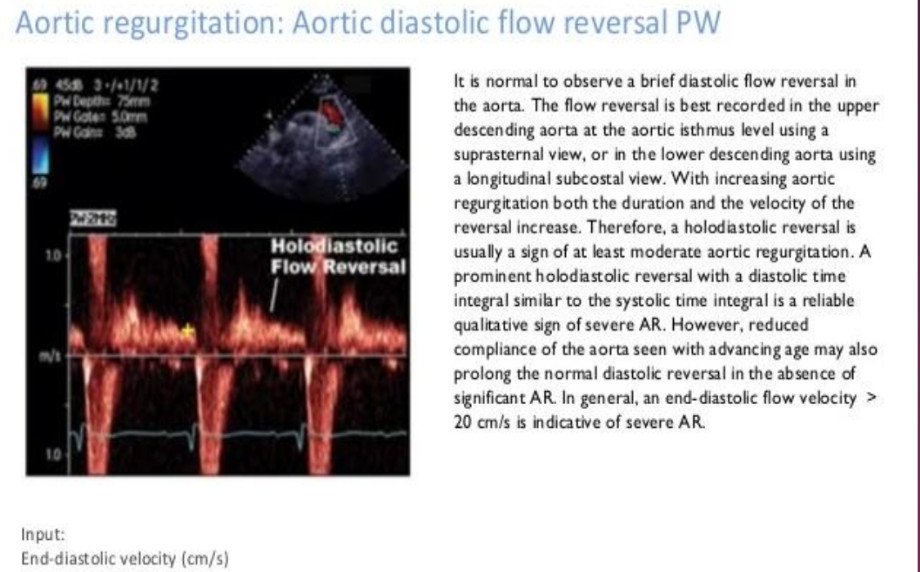
Early diastolic flow reversal in the descending aorta is…?
Normal and should not be mistaken for AR.
What does mild vs severe AR look like with various Doppler forms?