Theme 3
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are the reasons for planned growth?
To increase profits
To achieve economies of scale
Increase market share
Increase profitability
Increased market power over customers and suppliers
What are the 2 types of economies of scale?
Internal - economies within a business such as managerial, purchasing and technical economies
External - economies that occur in the industry e.g. improved infrastructure
What are some problems linked to growth?
Diseconomies of scale (average costs rising)
Overtrading
Why do diseconomies of scale occur?
Poor communication
Poor employee motivation (alienation)
Poor management
Organic growth
When a firm grows from within, using its own resources
Inorganic growth
When a firm grows from merging or acquiring another company
Advantages for organic growth
More control
Minimises risk
Gives staff opportunities to advance = better motivation
Disadvantages for organic growth
Slow growth
Limited by internal resources
Harder to respond to competition
What is a merger?
When 2 firms of a similar size agree to join forces permanently creating a new company
What is a takeover?
One firm buys the majority of shares in another
What is vertical integration?
When one firm takes over/merges with another in a stage of production in the same industry
What is horizontal integration?
When a firm buys out another in the same industry (e.g. a competitor)
What is conglomerate integration?
When one firm buys out another with no clear connection to industry
Why do businesses remain to stay small?
Product differentiation or USPs
Flexibility
Maintain customer service level
Forward vertical integration
Buying out a customer
Backward vertical integration
Buying out a supplier
Mission statement
Brief statement that summaries the aims, purpose and core values of a business
Ansoff’s Matrix
A tool used to help a business decide how to grow. The 4 strategies are:
Market penetration
Market development
Product development
Diversification
Market penetration
An existing product within a market
Help to improve economies of scale
Strengthens existing
Limited ceiling for sales
Product development
New product in your existing market
Meets evolving customer needs
Expands product portfolio
Product may fail
Market development
New market using an existing product
Increases economies of scale
Boosts revenue and brand image
Market may reject the product
Diversification
New product in a new market
New revenue streams
Potential synergies - links to industries
High risks
High costs
Distinctive capabilities
Businesses can gain competitive advantage by 3 ways:
Architecture - strong relationships and networks of trust
Reputation - strong brand images build over time through quality and customer loyalty
Innovation - developing new ideas to gain an advantage
Porter’s 5 forces
Help businesses evaluate the attractiveness and potential profitability of an industry
Industry rivals
Threat of new entrants
Buying power
Supplier power
Threat of substitutes
Threat of new entrants
Measures the ease of how easily new competitors can enter the market and disrupt existing businesses - depends on the barriers of entry
Threat of substitutes
The risk of customers switching to alternative products or services that meet the same need - not in direct competition but serve the same customer needs
Buyer power
Influence customers have over prices and business decisions based on demand
Supplier power
Control suppliers have over pricing, quality and availability of key resources - businesses can consider backwards vertical integration
Industry rivals
The level of competition among existing markets in the industry
Corporate culture
The shared values, beliefs and behaviours that shape how employees interact and work within a business
Strong culture
When employees align with the company’s values creating a unified workforce
Weak culture
When employees do not share the company’s values, leading to a lack of cohesion and higher employee turnover rates
How corporate culture is formed
Leadership style
Type of ownership e.g. plcs or sole traders
Type of product
Recruitment policies
Power culture
Centralised, with one person or a small group of people making key decisions shaping the culture
Quick decison making with clear direction from the leader
Lack of employee involvement decreases motivation
Employees may become reliant on the leader
Role culture
Structured and hierarchical system where employees have clear roles and responsibilities based on their job title
Efficient in large complex businesses by improving department coordination
Allows employees to specialise in their roles
More rules and procedures = slower decision making which can hinder innovation
Task culture
Employees are allocated projects or tasks, emphasising teamwork and problem solving in a flexible structure
Higher motivation as expertise is valued
More innovation
Lacks clear authority
Person culture
When an organisation prioritises individuals over the company, employees work indepently
Lots of freedom = greater motivation
Hard to implement in large businesses
Lack of direction
Shareholder approach
Prioritises maximising profits and returns for shareholders, often focusing on short term performance
Can be seen as unethical
Lacks long-term sustainability
Stakeholder
Individuals who have interest in, or are affected by a business’ activities and decisions
Stakeholder approach
Considers the interest of all stakeholders rather than focusing solely on profit
Consultation with stakeholders
Long term gain
Stakeholder objectives
Consumer - best quality products at the cheapest price
Employees - increased wages and development
Suppliers - shorter payable days and higher payments
Ethics
Businesses making decisions that priotise doing the morally right thing rather than maximising profits
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Benefits a business’ stakeholders, by addressing social and environmental concerns in operations and decision making
An active choice, not ethics
Quantitative sales forecasting
Estimating future sales figures based on past trends and patterns
Purpose of moving averages
Help to smooth out fluctuations in data to identify trends more clearly
Extrapolation
The process of using past data to predict sales, extending the trend line on a graph
Limitations of quantitative sales forecasting
Assumes past trends will be the same as the future
The further into the future, the harder it is to predict
Start ups cant use it
Payback period
How long it takes for an investment to recover its initial cost
Month of payback formula

Average rate of return formula (ARR)
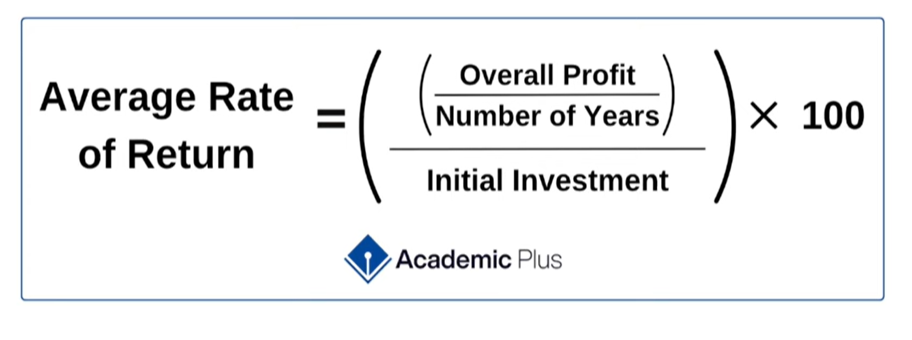
Net present value (NPV)
Financial metric that evaluates the value of the investment against interest rates and time
Limitation of decision trees
They rely on estimated probabilities which can be inaccurate, and their reliability depends on the accuracy of data used
Critical path analysis (CPA)
A network diagram that shows how activities within a project can be done simultaneously and which can be done consecutively
EST
Earliest start time for an activity to be started
LFT
Latest finish time a task can be completed before it delays the activity
SWOT analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Internal
External
Opportunities
External factors that a business can exploit for growth such as emerging markets and changing trends
PESTLE analysis
Strategic tool used to assess external factors that can impact a business’ performance and decision making:
Political
Economic
Social
Technological
Legal
Environmental
Gearing
Measures how reloiant a business is on borrowing money
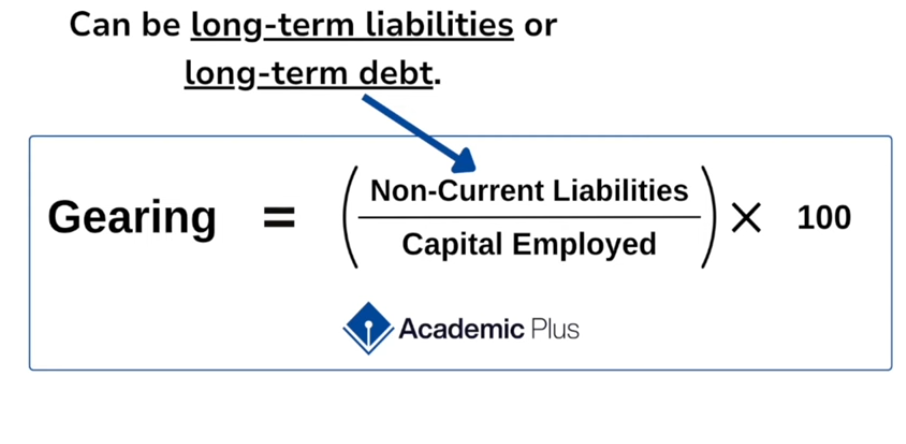
Capital employed
Long term investments made in a business to support its operations and growth

High gearing
Over 50%
Increased interest rates
Poor cash flow
Likelihood of insolvency
Low gearing
Under 25%
Limited growth potential as avoiding risks