Rutgers Nutrition Final Exam: Blueprint Based Study guide
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What are the six classes of nutrients?
carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, water
Which nutrients are organic?
carbs, fats, proteins, vitamins
What are the three energy yielding nutrients? How much energy is yielded from each one? Bonus: how much energy is yielded from alcohol?
Carbs: 4 kcal/g
Fats: 9 kcal/g
Protein: 4 kcal/g
Alcohol (not a nutrient): 7 kcal/g
What is the standard kind of experiment used is the scientific method?
Double-blind (neither researchers nor subjects know who is in control group or experimental group)
* allows for a randomized assortment of study subjects
How does the placebo effect work?
Patients who believe that the treatment they receive will be effective can experience better symptoms than those who do not
What is the average daily amount of a nutrient that meets the requirement for half of the population?
The EAR (Estimated Average Requirement)
What is the difference between the RDA and AI?
RDA- use this for nutrients we have more extensively studied and determined an EAR for (meets needs of 98% of the population)
AI- based on scientific judgments and not much concrete evidence; determined by observing the level of a nutrient that healthy people consume
What are the AMDRs?
Carbs: 45-65%
Fats: 20-35%
Proteins: 10-35%
What are the four components of a nutrition assessment?
history (health, drugs, and diet), anthropometric measurements, physical examinations, lab tests
What is a primary vs. a secondary deficiency of a nutrient?
Primary: comes from diet
Secondary: comes from something else other than diet (like a disease that impairs absorption)
Is fat-free milk, cheddar cheese, or turnip greens the most nutrient-dense in regards to calcium content?
Turnip greens (6.7 mg/kcal) > fat free milk (3.5 mg/kcal) > cheddar cheese (about 1/2 as nutrient dense as the milk)
What are the major (five) food groups and nutrients from each?
fruit (Vitamin A, C, B9, and potassium, carbs), vegies (same as fruit but also Vitamins K, E, and magnesium), grains (complex B vitamins, carbs), protein foods (protein, iron, zinc, magnesium, B vitamins), dairy (calcium, Vitamin b12, riboflavin)
What parts of bread are removed when making refined flour?
Bran, germ, and husk (only leaves endosperm: mostly carbs and some protein)
What are reference values of nutrients created by the FDA for use on food labels?
Daily values
How are health claims different from structure-function claims?
health claims: describe relationships between food and disease (based on research and FDA approval)
Structure-function claims: characterize relationship between nutrients and their roles in the body (no disease can be mentioned; no FDA approval required)
What nutrients may vegans be deficient in?
protein, iron, zinc, vitamin B12, calcium, Vitamin D, omega-3s
Describe the path of food down the digestive tract?
Mouth -> Pharynx -> past epiglottis -. upper esophageal sphincter -> esophagus -. lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter -> stomach -> pyloric sphincter -> small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), ileocecal valve -> large intestine (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid) -> rectum -> anus
What reaction is used by digestive enzymes to break down food?
hydrolysis
Where are most nutrients absorbed? What structures in particular help with absorption?
small intestine (villi and microvilli)
How do the nutrients from the digestive system reach the rest of the body (describe the pathway of blood vessels used)?
Digestive capillaries -> hepatic portal vein -> liver -> hepatic vein -> heart -> pulmonary and systemic circulation
How do water soluble vs. fat-soluble nutrients get absorbed?
water-soluble: directly into bloodstream
Fat-soluble: through lymphatic system first, then into blood
What are the three major hormones used in digestion and their roles?
Gastrin: enables the secretion of HCl into the stomach to lower pH
Secretin: enables bicarbonate-rich juice to be secreted from pancreas into small intestine to maintain alkaline pH
Cholecystokinin (CCK): enables secretion of bile to emulsify fat, and helps to slow GI motility to digest fat and protein
What methods can be used to relieve constipation?
drink more water, eat more fiber, increase exercise
What are the three disaccharides and their components?
sucrose: glucose + fructose
maltose: glucose + glucose
lactose: glucose + galactose
How is fiber different from starch?
Vertical bonds make fiber indigestible in the body
What food group (out of the five is the best source of carbs)
grains
What enzyme helps to digest carbs in the mouth?
salivary amylase
What carbs should people with IBS avoid?
FODMAP (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccarides, and polyols)
What hormones help to balance blood sugar? What is the action of each one?
insulin: lowers it, glucagon: raises it
Cause of Type 1 v. Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1; auto-immune disorder that attacks beta cells
Type 2: insulin resistance
What % of calories should come from added sugar?
at most 5%
What are three benefits of sugar alcohols over sugar?
1. low glycemic index response
2. usually calorie free
3. do not cause dental caries
How can fiber help lower risk of diabetes and heart diisease?
It slows the absorption of glucose into blood and binds to excess cholesterol in the blood for excretion
What are the three types of lipids? Which are most abundant in the diet?
triglycerides (most abundant in diet), steroids, phospholipids
What is the basic structure of a fatty acid?
a chain of carbons with a carboxyl group on one end and a methyl group on the other (end with methyl group is used for naming omega fatty acids)
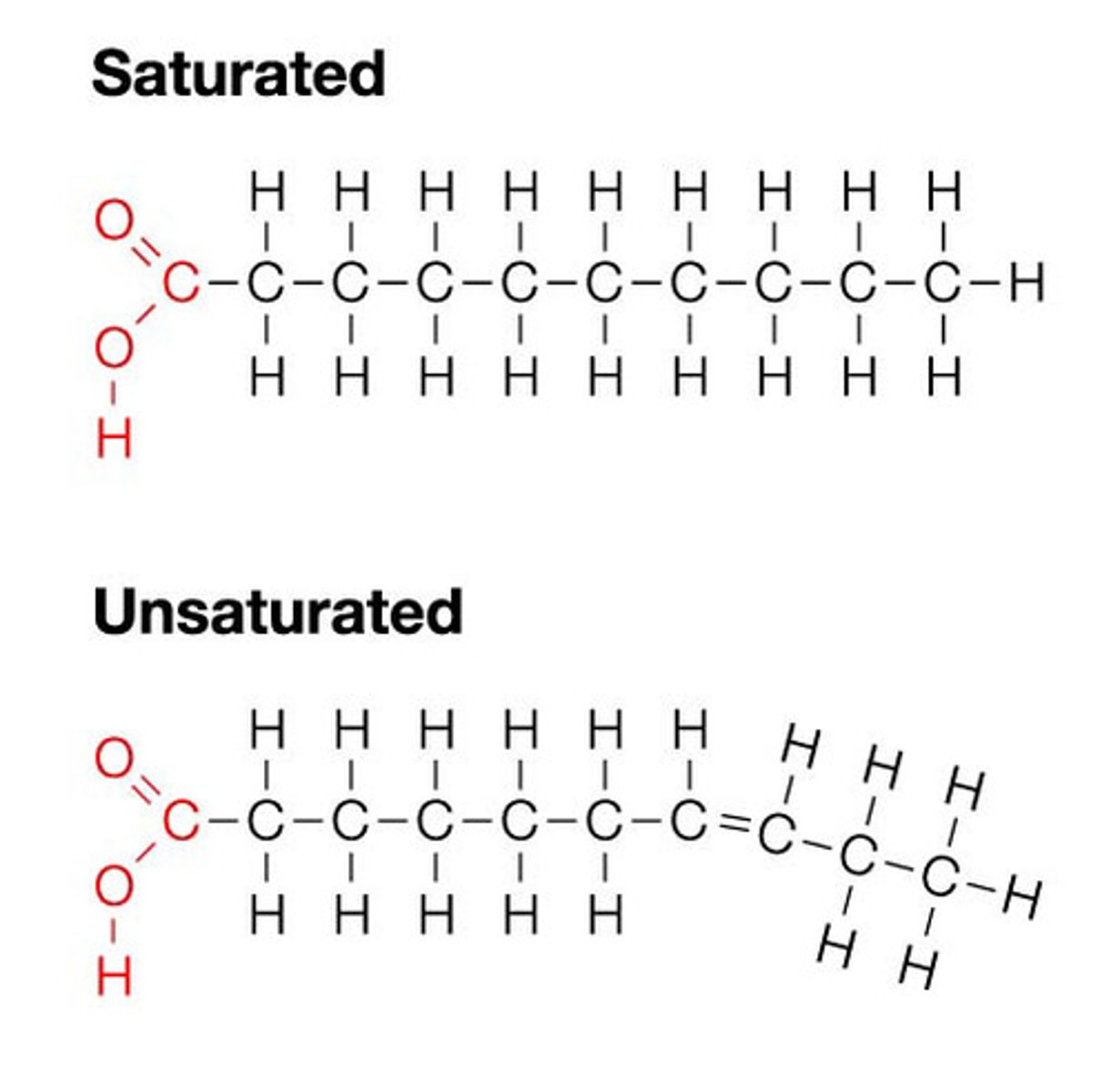
What are some basic differences between stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid?
Stearic acid; saturated (mostly from animals)
Oleic acid: Monounsaturated (olive oil, avocado oil)
Linoleic acid: polysunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid (2 double bonds: found in soybean, corn, safflower, and canola oil)
Linolenic acid: polysunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid (3 double bonds: found in flaxseed oil, walnuts, and fatty fish)
Are saturated or unsaturated fats more stable?
saturated (no double bonds: These unstable bonds are prone to oxidation)
What are some roles of phospholipids in the body and industrially? What is the best known phospholipid?
Roles: cell membrane structure, emulsification
Most popular: lecithin
Where does the major digestion of fat start? What process is necessary before digestion of fat begins?
Small intestine; emulsification of fat by bile
What structures bring fat into intestinal cells for absorption?
Micelles
What are the four types of lipoproteins in order of largest to smallest and what does each one transport?
Chylomicrons: transport dietary fat (triglycerides) into bloodstream from digestion
VLDL: used to transport lipids synthesized form liver. to the cells (half triglycerides)
LDL: mostly transports cholesterol to cells from liver
HDL: mostly made up of protein, used to deliver cholesterol to the liver for excretion
What is the difference between essential and nonessential amino acids? How many amino acids are essential?
Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body; 9
Where does protein digestion start? What begins the process?
Stomach: HCl denatures proteins and activates pepsinogen to form pepsin enzyme to digest protein
Where do amino acids that are not being used by intestinal cells go?
To the liver (amino acid pool)
What can proteins regulate fluid balance? How can lack of protein cause edema?
They increase osmotic pressure wherever they are located. Lack of protein causes plamsa proteins to move into the interstitial flued, where can cause swelling.
What steps are involved in ridding the body of excess protein?
Deamination (removal of amine group) -> ammonia formation from amine group -> conversion of ammonia to urea by liver -> disposal of urea by kidneys
Are plant proteins or animal proteins higher quality? Why?
Animal: more easily digestible and more likely to be complete (contain all essential amino acids)
How can high protein intake contribute to osteoporosis?
High protein levels increase excretion of calcium
What organ is the major metabolic center of the body?
liver
What are the two major reactions involved in energy metabolism?
anabolism: synthesis via energy input
catabolism: energy output via breakdown
What reaction occurs during glycolysis? what is the net ATP yield?
glucose -> 2 pyruvate (2 ATP gained)
What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic glucose metabolism?
Aerobic: in mitochondria, produces more ATP, and last longer
Anaerobic: produces less ATP, lasts less time, occurs in cytoplasm, forms lactate
What can glycerol be converted directly into?
glucose or pyruvate
What is the major breakdown product of fat?
Acetyl CoA
What compound starts and ends the TCA cycle?
oxaloacetate
How can excess nutrients be handled during feasting?
1. Replenish protein stores (excess protein)
2. Replenish glycogen (excess glucose)
3. Accumulation of fat (all macronutrients in excess, happens after other 2 steps occur)
When you fast, how does produce sources of energy for the cells?
1. turns protein into glucose
2. Makes ketone bodies from fat
What is the recommended daily intake of alcohol?
1/2 ounce ethanol (5 oz. wine, 12 oz. beer, 10 oz. wine cooler, 1.5 oz. liquor)
What nutrient does alcohol readily get converted into? Where can this cause major damage?
Fat; liver (fatty liver disease -> fibrosis -> cirrhosis)
How do we maintain energy balance?
calories in = calories out
What is the difference between satiation and satiety? What nutrients promote each principle?
satiation: triggers fullness during a meal (protein)
satiety: keeps you full after meal stops (protein, fat: CCK)
List the components of energy expenditure in order of how much energy they expend?
Basal metabolism (2/3)
Physical activity (1/4 -> 1/2: varies b activity level)
Thermic effect of food (10%)
Adaptive thermogenesis (minor)
What BMI values correspond with underweight, healthy weight, overweight, and obese?
Underweight: under 18.5
Healthy: 18.5 - 24.9
Overweight: 25 - 29.9
Obese: 30+
What is the key indicator of how much energy they will expend?
lean body mass (muscle is more active than fat)
What are some consequences that can come with being underweight or overweight?
Under: wasting of lean tissue, malnutrition
Over: diabetes, obesity, heart disease, cancer
What eating disorder involves a cycle of binging followed by purging?
Bulimia nervosa
What are the differences in the fat cells of the healthy-weighted and the obese?
The obese have more and larger fat cells
The increased activity of what hormone in the obese makes it easier for them to store fat?
lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
What are the roles of ghrelin and leptin in weight management?
Ghrelin (hunger hormone): stimulates appetite, increases food intake, and decreases energy expenditure
Leptin (satiety hormone): suppresses appetite, decreases food intake, and increases energy expenditure
What risk factors may an overweight or obese individual possess before a healthcare professional recommends them to lose weight?
hypertension, Fatty liver disease, hypertension, diabetes/prediabetes, sleep apnea
What drug affects serotonin utilization in the brain to reduce appetite?
sibutramine
What are the requirements for a person who is obese to need aggressive treatment like drugs or surgery?
Clinically severe obesity (BMI of 40+ or BMI of 35+ combined with medical problems)
What surgical procedure for weight loss involves removing the majority of the stomach and stapling the remaining parts together to limit food intake?
sleeve gastrectomy
What is the recommended body % of weight a person who is aiming to lose weight should target to lose every year?
5 - 10 %
Why is it important for underweight people to strength train?
So they can build muscle mass
What should a person trying to lose weight do to increase food volume and fullness when eating?
Pick foods with more water content
How are vitamins different from the other organic nutrient?
1. They are needed in small amounts (micronutrients)
2. They are individual units (not polymers like the other organic molecules)
3. they do not yield energy
What vitamins are absorbed into the lymph before the bloodstream and are less likely to reach deficiency levels?
Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
What is the function of most B vitamins?
They act as conezmyes
What is the major source of riboflavin?
Dairy
What deficiency disease is associated with a lack of niacin? What are the signs of this disease?
Pellagra (Dementia, Dermatitis, Diarrhea, Death)
What type of anemia results from Vitamin B12 and/or folate deficiency?
Macrocytic anemia (RBCs cannot properly divide)
What are two early signs of Vitamin C deficiency? What disease is caused by Vitamin C deficiency?
Bleeding gums and pinpoint hemorrhages (due to lack of collagen); scurvy
What is the precursor to vitamin A? In what foods is it found?
Beta-carotene (deep orange and dark green vegies: sweet potato, carrot, spinach, broccoli etc.)
What is the difference between the deficiency in Vitamin A that causes night blindness and the deficiency that causes total blindness (xerophthalmia)?
Night blindness: caused by vitamin A deficiency in retina
Total blindness: caused by vitamin A deficiency in cornea
What is the major function of vitamin D?
To increase the absorption of calcium from the bones, intestines, and kidneys
What disease is caused by vitamin D deficiency in children?
rickets
What is the major form of active Vitamin E in the body
alpha-tocopherol
What disease is caused by a deficiency of Vitamin E? Explain why.
Erythrocyte hemolysis (polyunsaturated fatty acids in the membrane of RBCs get oxidized, destroying the cells)
What are the major sources of Vitamin K?
Green leafy vegetables, bacterial production
What are the functions of vitamin K?
aids in blood clotting and the metabolism of bone proteins (including osteocalcin)
What are the four major types of fluid in the body? How much (give a fraction) of the total blood fluid does each one make up?
Intracellular: 2/3
Extracellular: 1/3
Interstitial: most of extracellular fluid
Intravascular fluid: plasma, minor component of ECF
What is the adrenal hormone that increase reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys when BP is low?
aldosterone
What is the body's obligatory water excretion to dispose of wastes?
500 ml
What sources does the body use for the intake and excretion of water?
Intake: beverage, foods, metabolism (dehydration synthesis)
Excretion: urine, sweat, breath, feces
True or false: Fatigue is an early sign of dehydration.
True
True or False: Water intoxication can cause hypernatremia.
False (hyponatremia, since the concentration of sodium would be dilute)
What is the recommended intake of sodium to reduce risk of chronic disease?
2300 mg/day (1 teaspoon of salt)
What are the major cations in the ICF and ECF?
ICF: potassium
ECF: sodium
What Major minerals are involved are in water balance, impulse conduction, and muscle contraction?
sodium, potassium, chloride