SLP Praxis
1/672
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
673 Terms
Perlocutionary Period
The stage of a child’s development when they begin to communicate through unintentional behaviors like crying, cooing, and smiling. It lasts from birth to about 8 months of age.
Secondary Behaviors
Eye movements, twitching, and phonation breaks are overt examples of what?
Syllable structure processes
Staying “top” for /stap/ and “poon” for /spun/ are characteristic of which phonological processing errors?
Frontal
Which lobe of the cerebrum is critical for speech production?
Missing an intended target
What is a typical symptom of cerebellar involvement?
Cohesive adequacy
What pragmatic component may be used to evaluate “complete ties”?
Cricothyroid
Control over the fundamental frequency of the laryngeal tone is most closely related to the activity of what muscle?
Pressure
According to the Bernoulli effect, constriction of the glottis increases airflow speed which in-turn decreases what?
Global aphasia
Which form of aphasia is caused by extensive lesions affecting all language areas and results in severe impairments in both comprehension and expression?
Recognize syntactic ambiguity
Sentences such as “Visiting friends can be a nuisance” are especially useful to test a person’s ability to…
Maximal oppositions
A phonemic approach based on operant conditioning that expands upon an individual’s underlying knowledge of sound system and features
CN XII
Which CN innervates all intrinsic muscles of the tongue and all but one extrinsic muscle?
Working memory
Ability to hold a given amount of info for immediate processing
Short term memory
Retention of info for longer than 30 seconds lasting hours
Long term memory
Retention of info for months and/or years
Declarative memory
Recall of facts
Episodic memory
Recall of specific and recent events
Procedural memory
Recall of sequences necessary for given tasks
Focused attention
Ability to focus on and respond to stimuli and info
Sustained attention
Ability to sustain or hold and manipulate information
Selective attention
Ability to attend and select information within a larger set
Alternating attention
Ability to switch or alternate attention between tasks
Divided attention
Ability to attend and divide focus on multiple things at once
Non fluent aphasia
Lesion in posterior inferior frontal gyrus in left hemisphere. Effortful, telegraphic speech. aka Broca’s or expressive aphasia
Fluent aphasia
lesion in posterior, superior left temporal lobe. Fluent speech with poor auditory comprehension. aka Wernike’s or receptive aphasia
Dementia
Persistent or progressive deterioration of cognitive functions. memory deficits are most characteristic. may also impact language, emotions, etc
Right Hemisphere Dysfunction
Visuospatial deficits, anosognosia (denial/poor awareness of impairment), Prosodic, inferencing, and discourse deficits. Sustained and selective attention deficits
Apraxia
Inferior posterior left hemisphere damage. Deficit of motor planning with normal speech musculature. Groping, inconsistency, and sound/syllable sequencing errors.
Dysarthria
Slowness, weakness, and speech musculature incoordination. Divided into flaccid, spastic, ataxic, hypokinetic, hyperkinetic, and unilateral UMN
Anomia
Word finding problem. Symptom of aphasia
Phonemic Paraphasia
Paraphasia with a few phoneme mistakes, but mostly correct
Semantic Paraphasia
Paraphasia of a word substituted for a word with similar meaning
Neologistic paraphasia
Paraphasia of a word substituted with a made up word
Perseveration
Inappropriate repetition of a word/idea previously produced
Agrammatism
Grammar deficits, inadequate sentence production.
Alexia
Acquired reading impairment after brain damage
Agraphia
Acquired writing impairment after brain damage
Neologism
New word is created
Circumlocution
Talking around the intended word or idea
Jargon
Continuous fluent utterances that make little sense but appear to make sense to the speaker
Frontal Lobe
If damaged, leads to deficits in executive function. Memory loss, consciousness, impulse control, motor planning
Parietal Lobe
If damaged, can lead to sensory deficits. Difficulty reading/writing, spatial relationships, mathematical deficits
Temporal Lobe
If damaged, leads to deficits in auditory perception/sensation/integration.
Occipital Lobe
If damaged, leads to visual deficits, including alexia and agraphia
Basal Ganglia
If damaged, can lead to hypokinetic or hyperkinetic dysarthria
Hippocampus
If damaged, can lead to memory impairments, as well as increased anxiety
Anterior Cerebral Artery Stroke
Leads to deficits in memory, emotion, sensation, and motor speech. Cortical = apraxia. Subcortical = dysarthria
Brainstem
Damage leads to attention deficits, consciousness, and non-voluntary function damage. Midbrain damage = parkinson’s (Hypokinetic dysarthria)
Cerebellum
Damage leads to motor coordination and balance deficits. Ataxia (Slurred speech)
Broca’s area
Light Blue area?
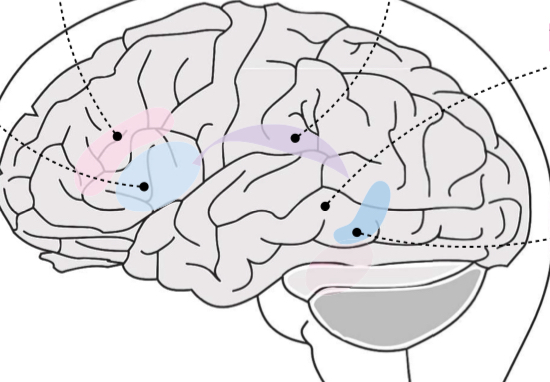
Transcortical motor
Pink area?
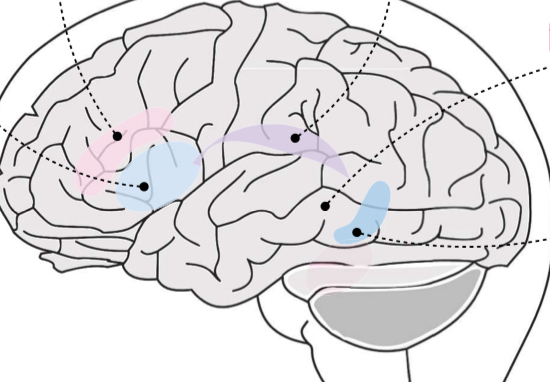
Arcuate fasciculus
Purple area
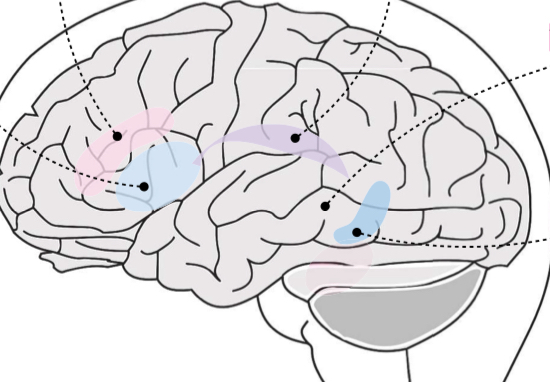
Wernicke’s area
Gray area?
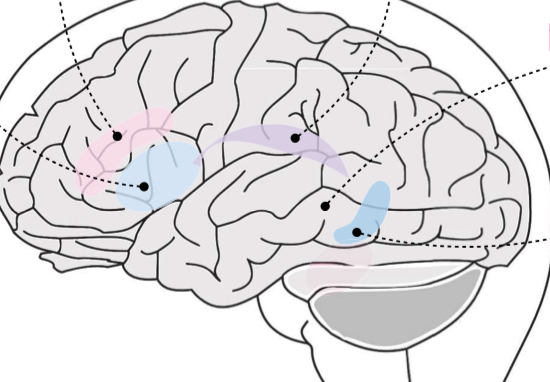
Transcortical sensory
Dark blue area?
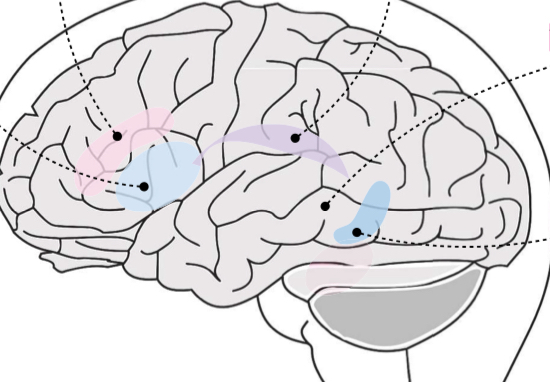
Broca’s
aphasia with impaired fluency, repetition. Intact comprehension
Wernicke’s
Aphasia with intact fluency, impaired comprehension, repetition.
Transcortical motor
Aphaisa with impaired fluency. Intact comprehension, repetition.
Transcortical sensory
Aphasia with intact fluency, repetition. Impaired comprehension.
Conduction
Aphasia with intact fluency, comprehension. Impaired repetition.
Transcortical mixed
Aphasia with impaired fluency, comprehension. Intact repetition
Global
Aphasia with impaired fluency, comprehension, and repetition.
Flaccid
Dysarthria from lower motor neuron lesions. Hypernasality with nasal emissions. Slow and slowed DDKs and tongue fasciculations
Spastic
Dysarthria from bilateral upper motor neuron lesions. Hypernasality and a strained-strangled voice
Ataxic
Dysarthria from cerebellum lesion. Slow, slurred speech, irregular incoordination, distorted vowels, and prolonged phonemes
Hypokinetic
Dysarthria from basal ganglia lesion - depetion of dopamine. Short rushes of speech
Hyperkinetic
Dysarthria from basal ganglia lesion - dopamine excess. Involuntary movements and voice stoppages
Unilateral Upper Motor Neuron
Dysarthria from unilateral upper motor neuron lesions. Unilateral facial weakness
Narrowing valleculae space
Placing a bolus in the mouth, tilting the head back, and sallowing results in what anatomical change?
Ask fewer open ended questions
Compared with children who do not have language disorders, children with language disorders tend to…
Maubrium
Which part of the sternum provides attachment for the clavicle and the first rib?
Hard glottal attack
What is the most appropriate therapeutic strategy for an SLP to use with a man needing voice treatment after medialization thyroplasty for a paralyzed vocal fold?
Phonology
Smallest unit of language that can change meaning of words but does not have meaning on it sown is known as:
Present progressive -ing, regular plural -s
What are 2 grammatical morphemes that are acquired first in typically developing children
Manual depression of the larynx
What would be effective in remediating a falsetto voice for an adult male with a severe bilateral hearing loss?
Athetosis
What type of cerebral palsy is characterized by slow, arrythmic writhing and involuntary movements of the extremities?
Dendrites
Which part of the neuron receives neural impulses from other neurons?
Aided
AAC with an external aid (communication board, books, voice output device, etc)
Unaided
AAC produced by the body (vocalizations, gestures, signs, etc)
10 months
At about what age to infants begin to send intentional and purposeful messages via babbling and gesturing?
24 months
At about what age do typically developing children have about 200-300 words in their expressive vocabulary?
Occlusion
The way two dental arches come together when a person “bites down”
Levator veli palatini, musculus uvulae, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, superior pharyngeal constrictor
Muscles for velopharyngeal closure
Palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus
Muscles that oppose velopharyngeal closure
Cerebrum
Front area of skull composed of two hemispheres
Cerebrum
“Thinking portion” of brain; most complex cognitive function
Brainstem
Base of brain-cerebrum juncture and spinal cord: midbrain, pons, and medulla
Brainstem
Automatic reflexes/vegetative functions
Cerebellum
Hangs off back of brainstem under occipital lobe
Cerebellum
Voluntary movements; balance, coordination, posture, attention
Medulla
Lower portion of brainstem, below pons
Medulla
Regulates respiration, heart rate, and reflexes such as vomiting, swallowing
Pons
Middle portion of brainstem
Pons
Attachment between cerebellum and rest of CNS
Midbrain
Upper most part of brainstem
Midbrain
Houses substaintial nigra (production of neurotransmitter - dopamine)
Basal Ganglia
Deep within cerebral hamispheres; telencephalon
Basal ganglia
Fine-tunes voluntary body movements, motor coordination, posture
Spinal Cord
Housed within bony vertebral column, PNS begins here
Spinal Cord
Allows afferent impulses to transmit to brain and efferent from brain-body
Thalamus
Top of brainstem; core of diencephalon