JUNE SCIENCE EXAM
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
SHOW YOUR WORK
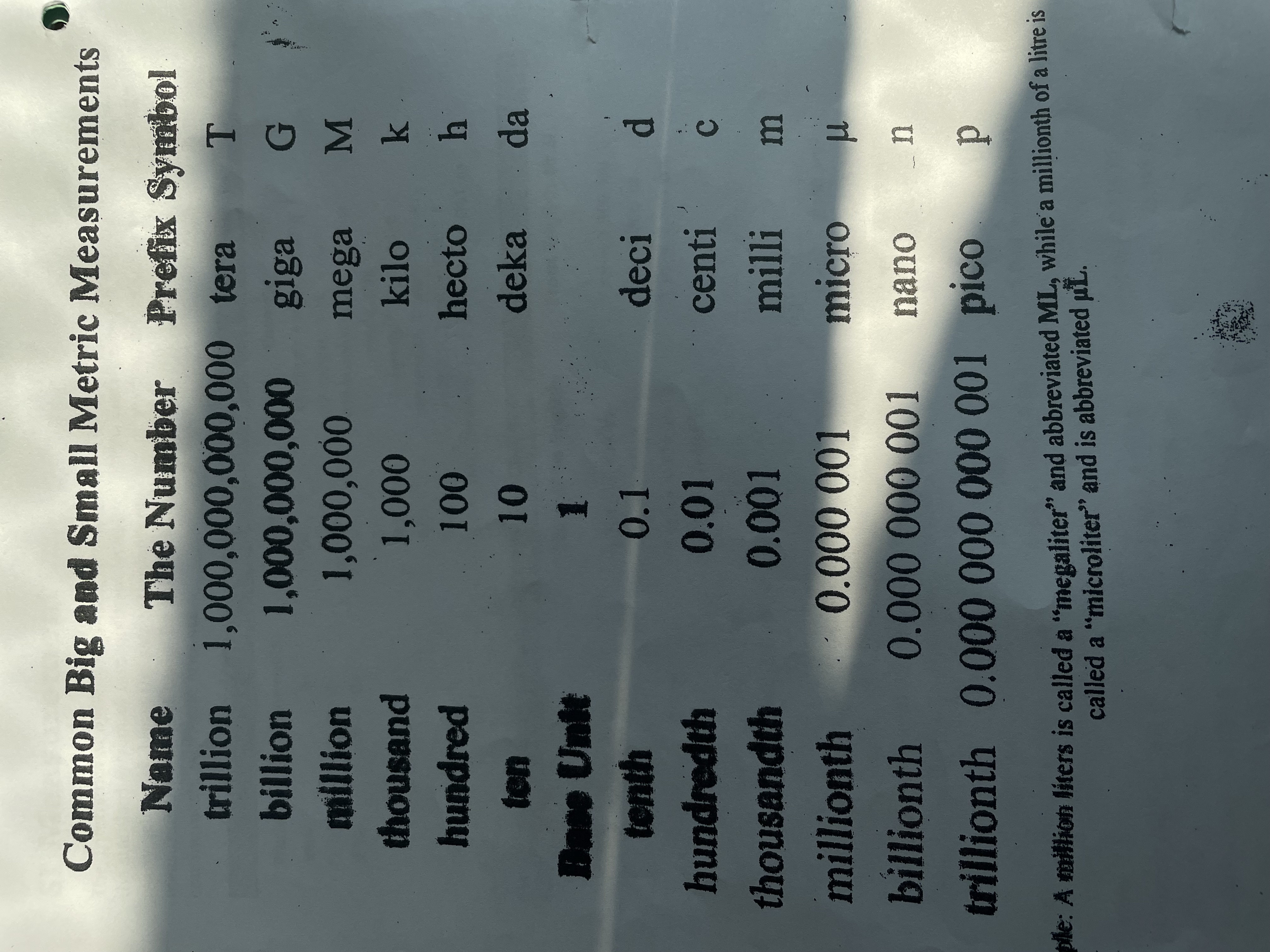
What is the metric conversions table?

SHOW YOUR WORK
Calculating electricity

TRUE/FALSE
Matter
Anything that takes up space, has volume and mass.
Ex: solid; ice, liquid; water, gas; steam
TRUE/FALSE
Pure substance
Is made up of particles that are alike. Since all the particles are the same, all samples of a pure substance will always have the same properties.

TRUE/FALSE
How to read chemical formulas
Counting subscripts
H₂O
C₆H₁₂O₆
2 Hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom
6 Carbon atoms, 12 Hydrogen atoms, 6 Oxygen atoms

TRUE/FALSE
Asexual reproduction
Mitosis: Requires a single parent, producing offspring identical to its parent
TRUE/FALSE
Sexual reproduction
Meiosis: two individuals contribute genetic material to produce offspring with unique genetic combinations
TRUE/FALSE
Do all cells have nucleus?
Difference of cell structure between animal cell and plant cell
No
animal: circular
plant: rectangular
TRUE/FALSE
Homogeneous mixture
provide example
A mixture where the molecules of each substance are equally mixed, and you can’t see the difference of the mixture.
ex: sugar dissolving water
TRUE/FALSE
Heterogeneous mixture
provide an example
A mixture where the substances aren’t evenly mixed
ex: salad
TRUE/FALSE
Static electricity
a buildup of electrons
stays in one place until it jumps to an object
does not need a circuit
Lightning is static electricity
TRUE/FALSE
Trait inheritance and alleles (dominant and recessive)
A gene is a segment of a chromosome, encoded by DNA. Genes come in pairs called alleles, and each allele is a variation of that gene.
homozygous dominant: AA
homozygous recessive: aa
Heterozygous: Aa
TRUE/FALSE
Solute/solvent
A solute is the substance that gets dissolved, and the solvent is the substance that dissolves the solute.
TRUE/FALSE
5 different types of asexual reproduction
Binary fission
budding
vegetative propagation
regeneration
sporulation
TRUE/FALSE
differences between genes, traits and alleles.
Genes are made of DNA that determine traits.
Traits are observable characteristics passed down from parents to offspring.
Alleles are different versions of a gene, which can result in variations of a trait
TRUE/FALSE
Covalent and Ionic bonds
(what happens to the atoms charges)
IONIC BOND:
when an atom gains or loses electrons, the atom is no longer neutral
COVALENT BOND:
chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms
Types of animals that use external fertilization
Fishes, amphibians, invertebrates
Ex: fishes release both eggs into the water during spawning
SHORT ANSWER
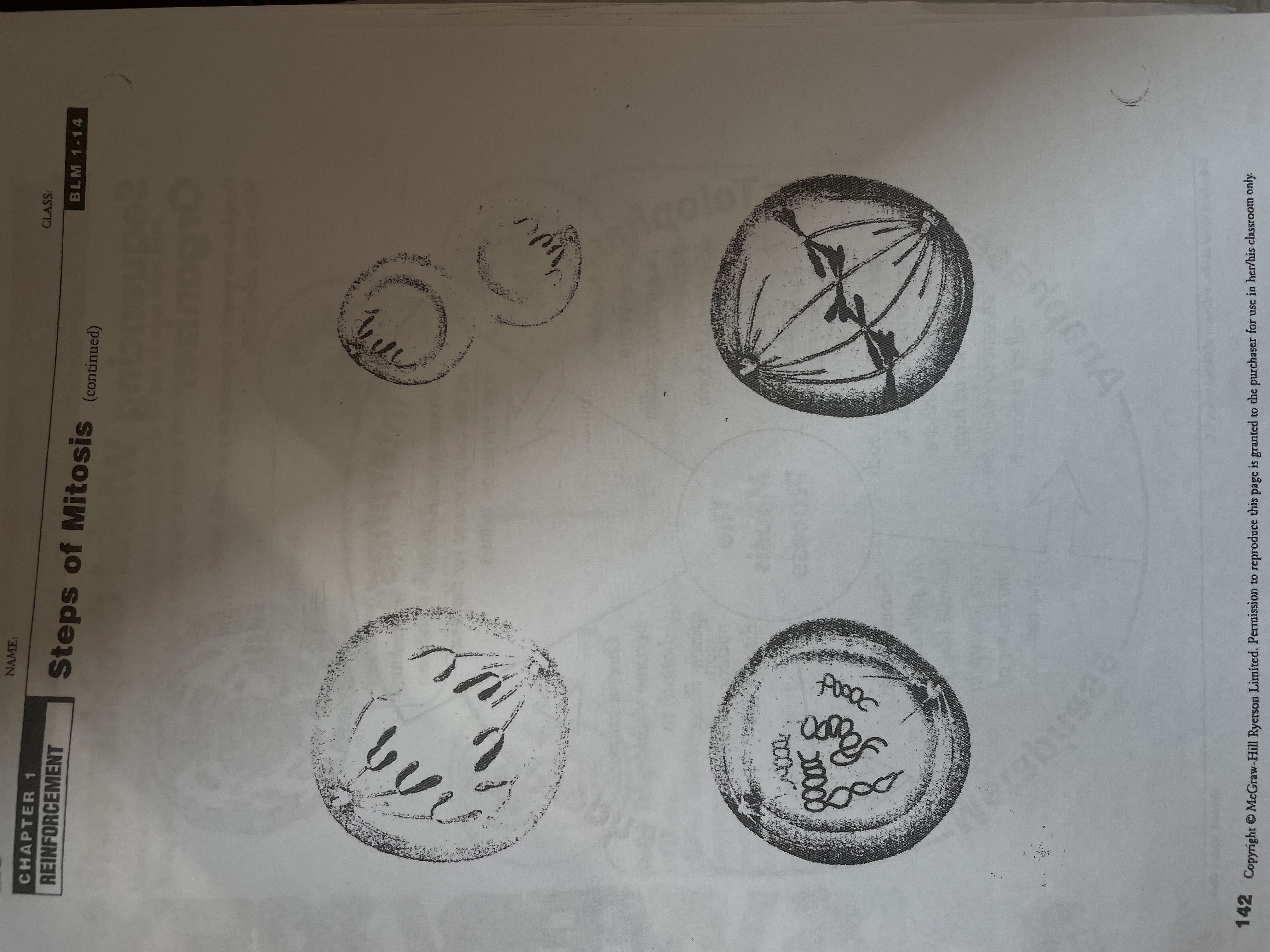
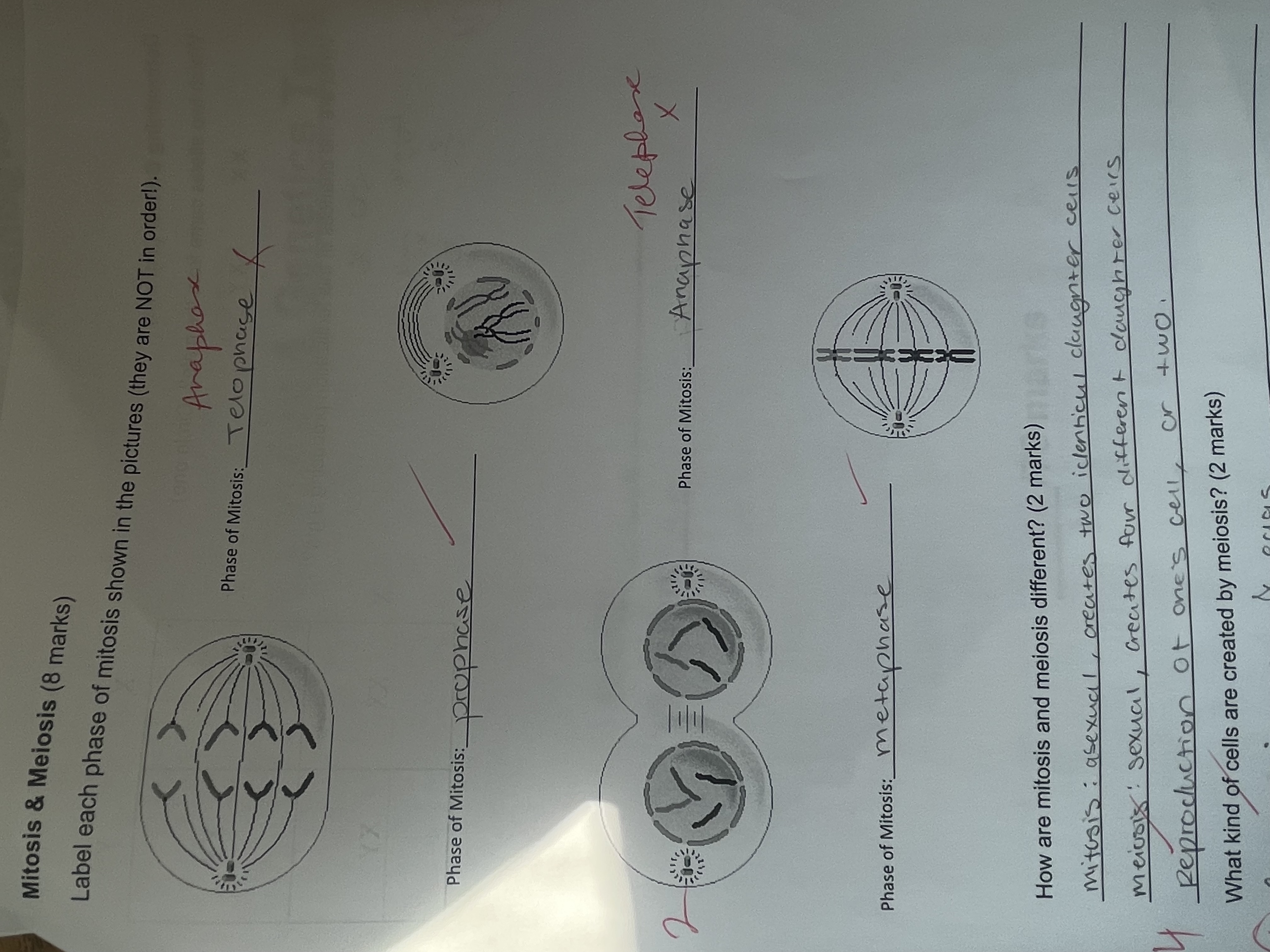
Review stages of PMAT
Prophase: first stage, chromosomes become visible, membrane disappears
Metaphase: chromosomes are pulled by spindle fibres
Anaphase: there are now twice as many chromosomes in the cell
Telophase: Nuclear membrane reappears, spindles disappear
Interphase: cell grows, replicates DNA and prepares for cell division

SHORT ANSWER
Diagram of PMAT

SHORT ANSWER
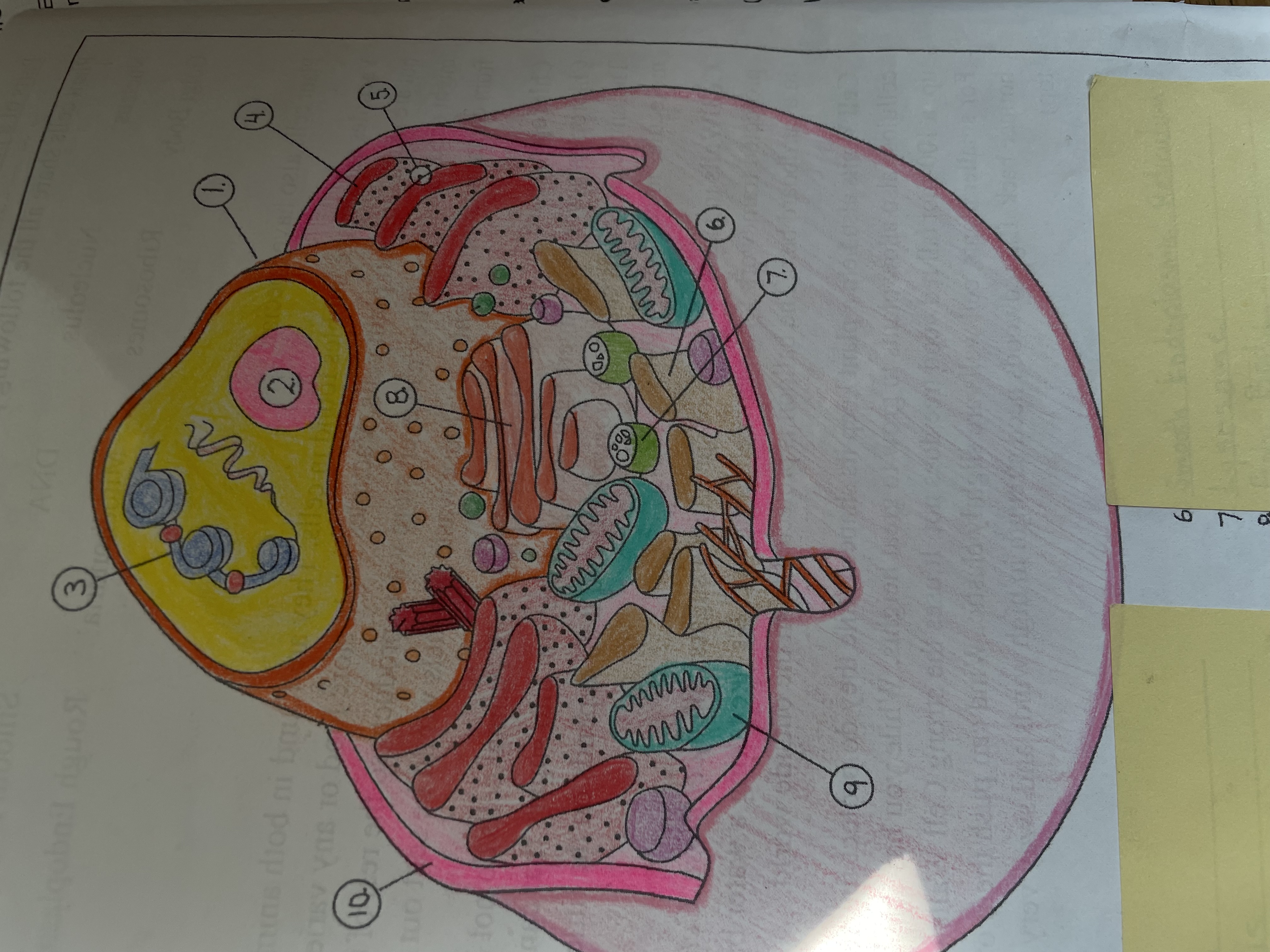
Know your cell organelles and their functions

SHORT ANSWER
Animal cell diagram

SHORT ANSWER
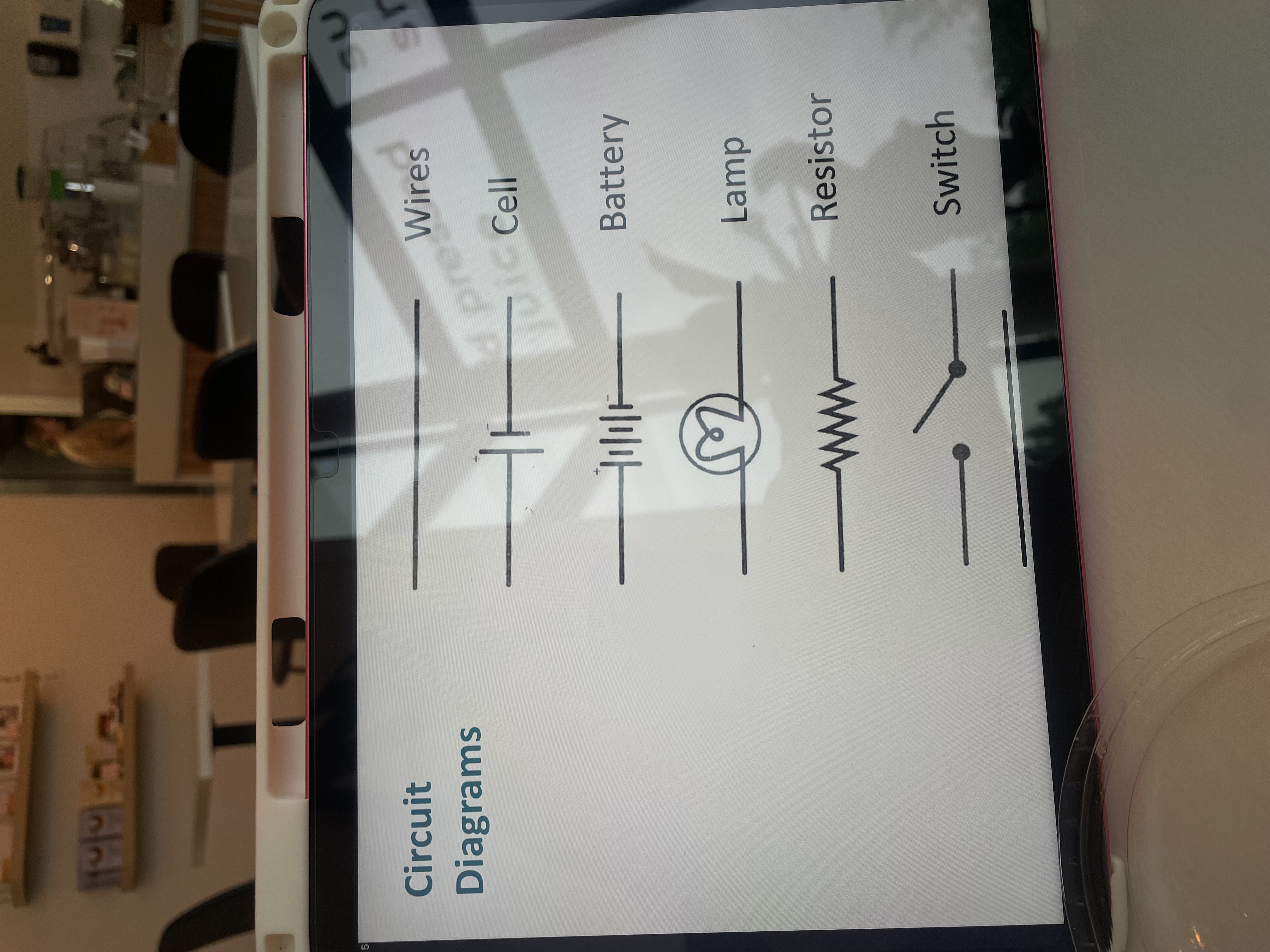
Circuit diagrams and matching them with identifiers (light bulbs, resistors, parallel/series circuit)
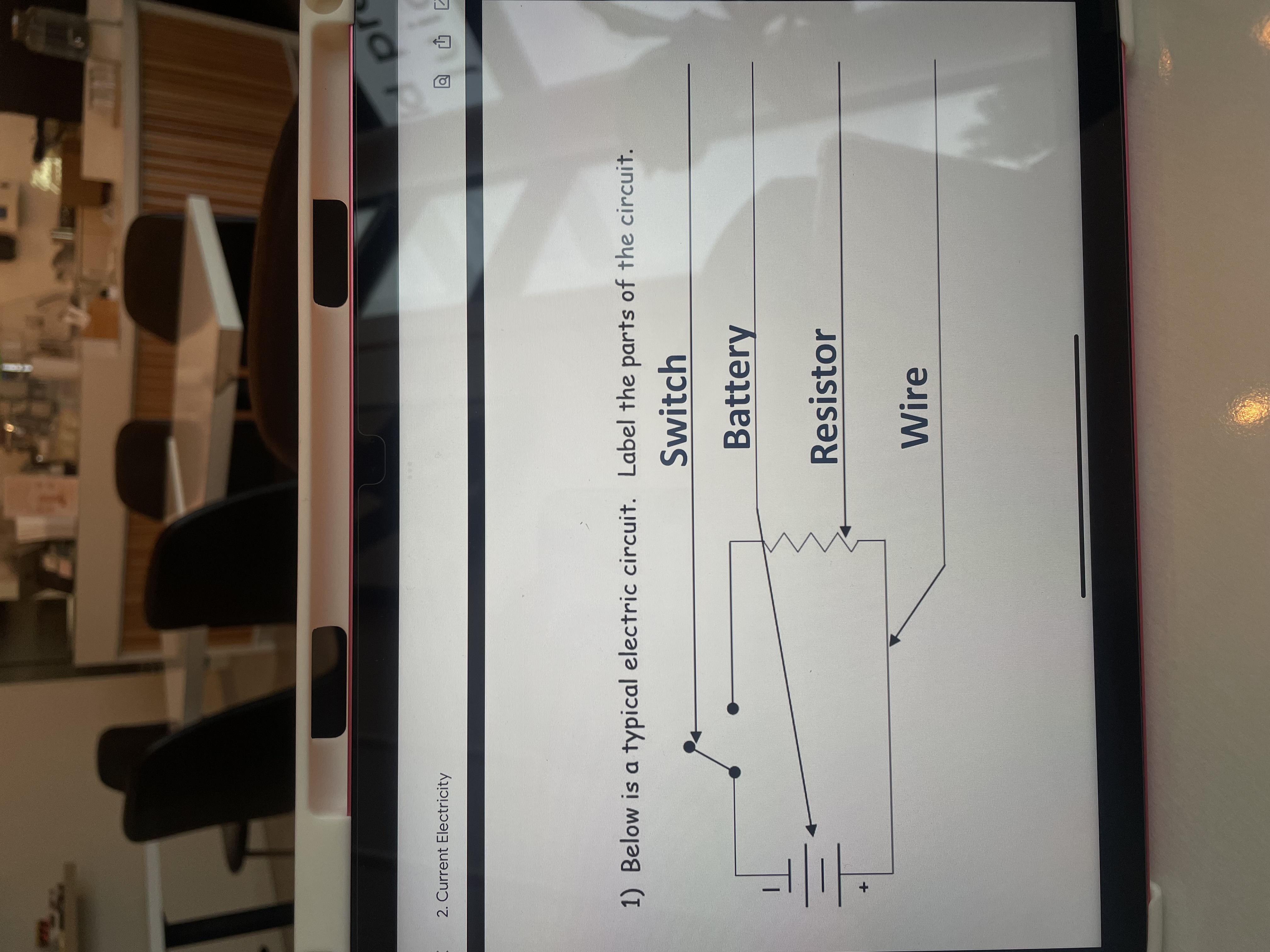
SHORT ANSWER
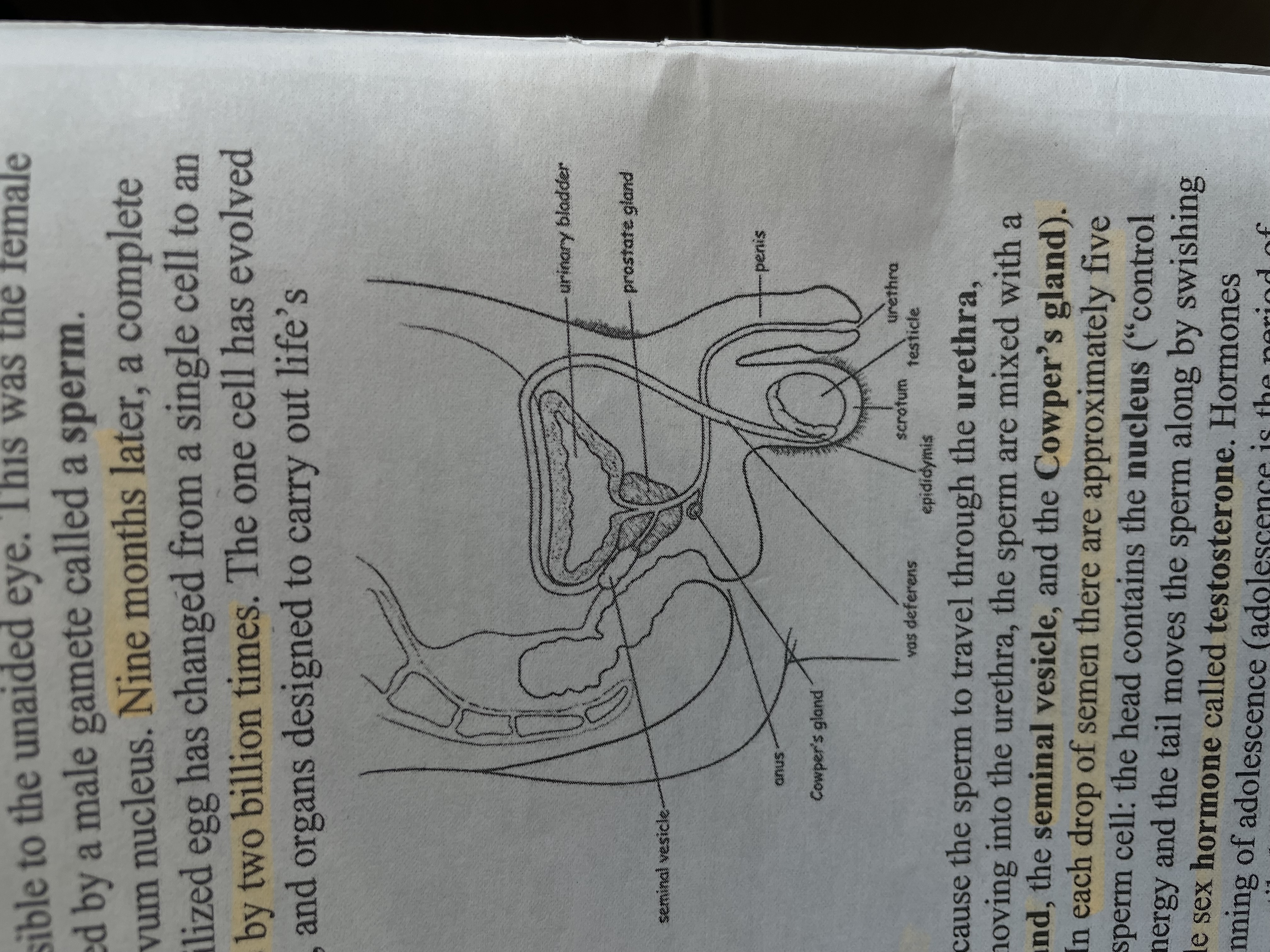
Male reproductive structure
SHORT ANSWER
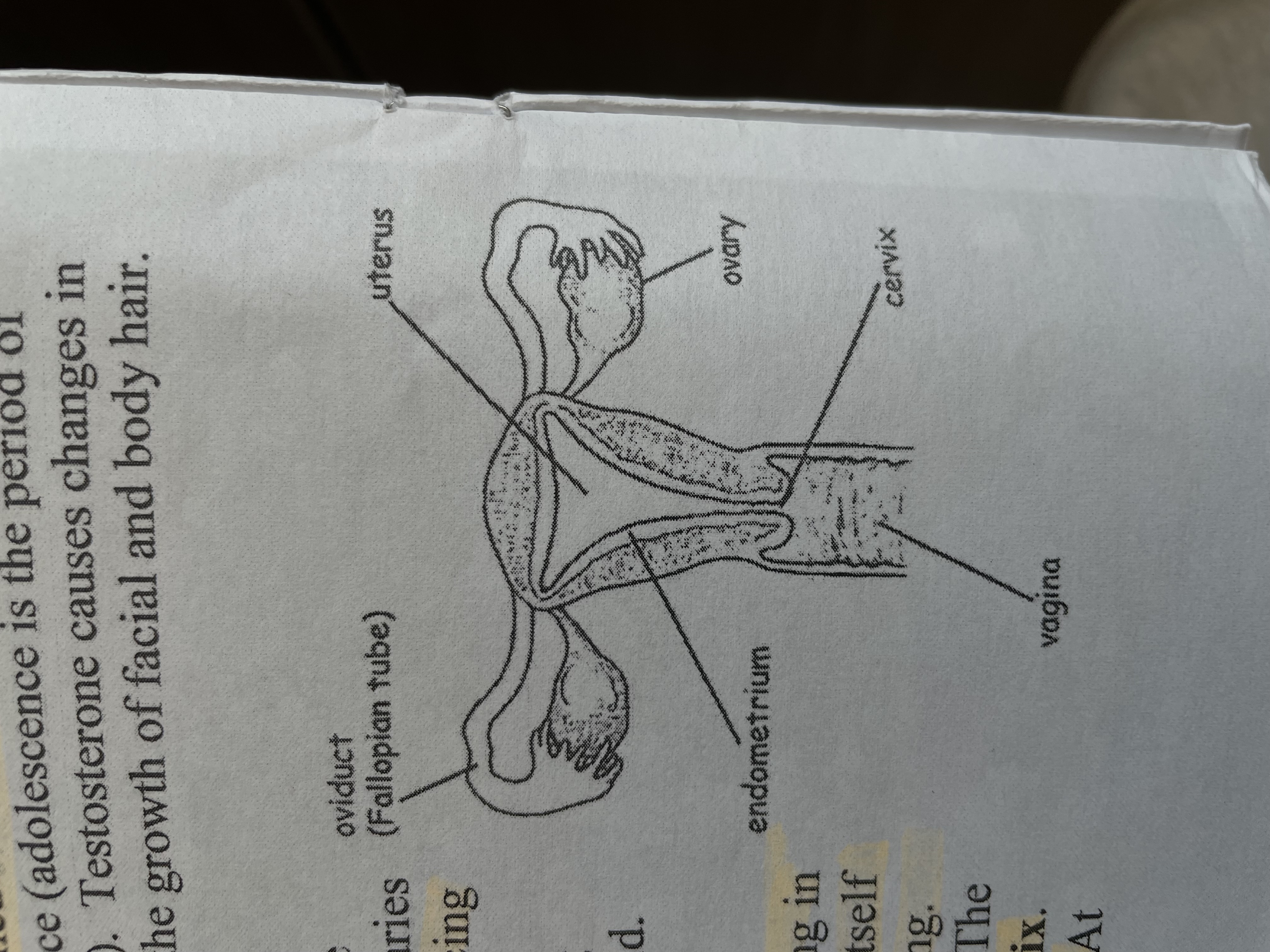
Female reproductive structure
MULTIPLE CHOICE
Sexual reproduction
a form of reproduction where offspring are created by the combination of genetic material from two parents
MULTIPLE CHOICE
Pregnancy
The process of a woman carrying a developing baby (fetus) inside her womb
MULTIPLE CHOICE
chromosomes/sexual reproduction
During meiosis, the # of chromosomes is halved and gametes are produced, each containing a single set of chromosomes
MULTIPLE CHOICE
physical and chemical changes
physical: no new substance is formed
ex: Ice melting
chemical: always causes at least one new substance, with new properties, to be formed
ex: burning paper
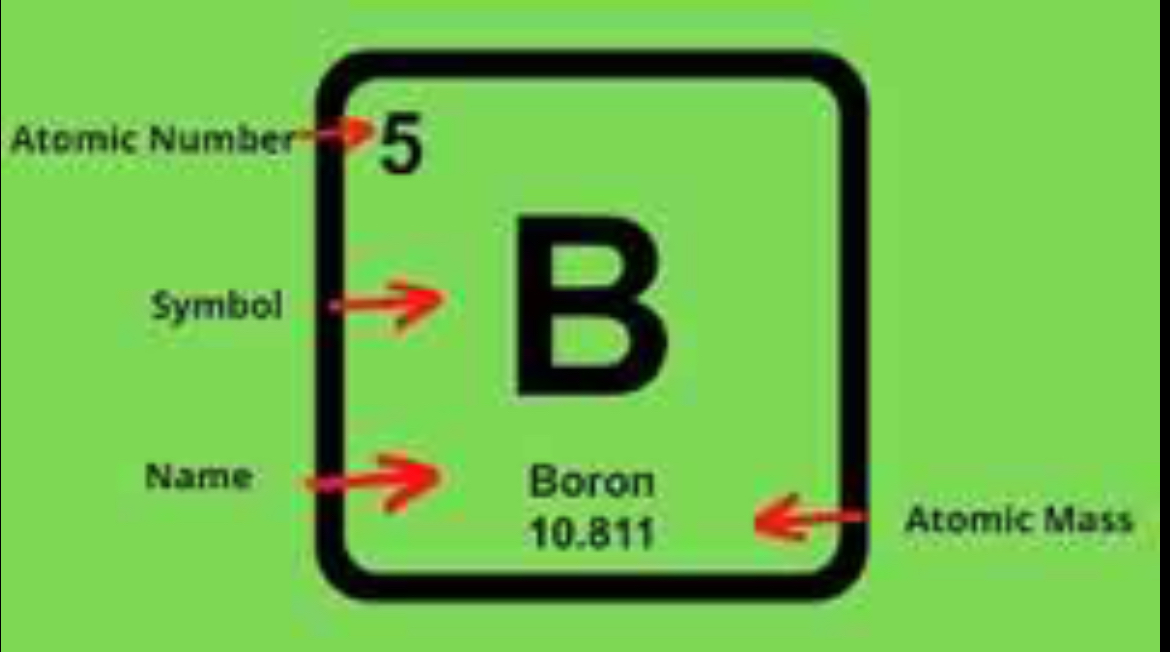
MULTIPLE CHOICE
periodic table of elements and it’s arrangement
What is the relationship between element reactivity and position on the periodic table?
Why are elements categorized in families or groups?
The left side is more reactive than the right side.
Because they have the same # of valence electrons
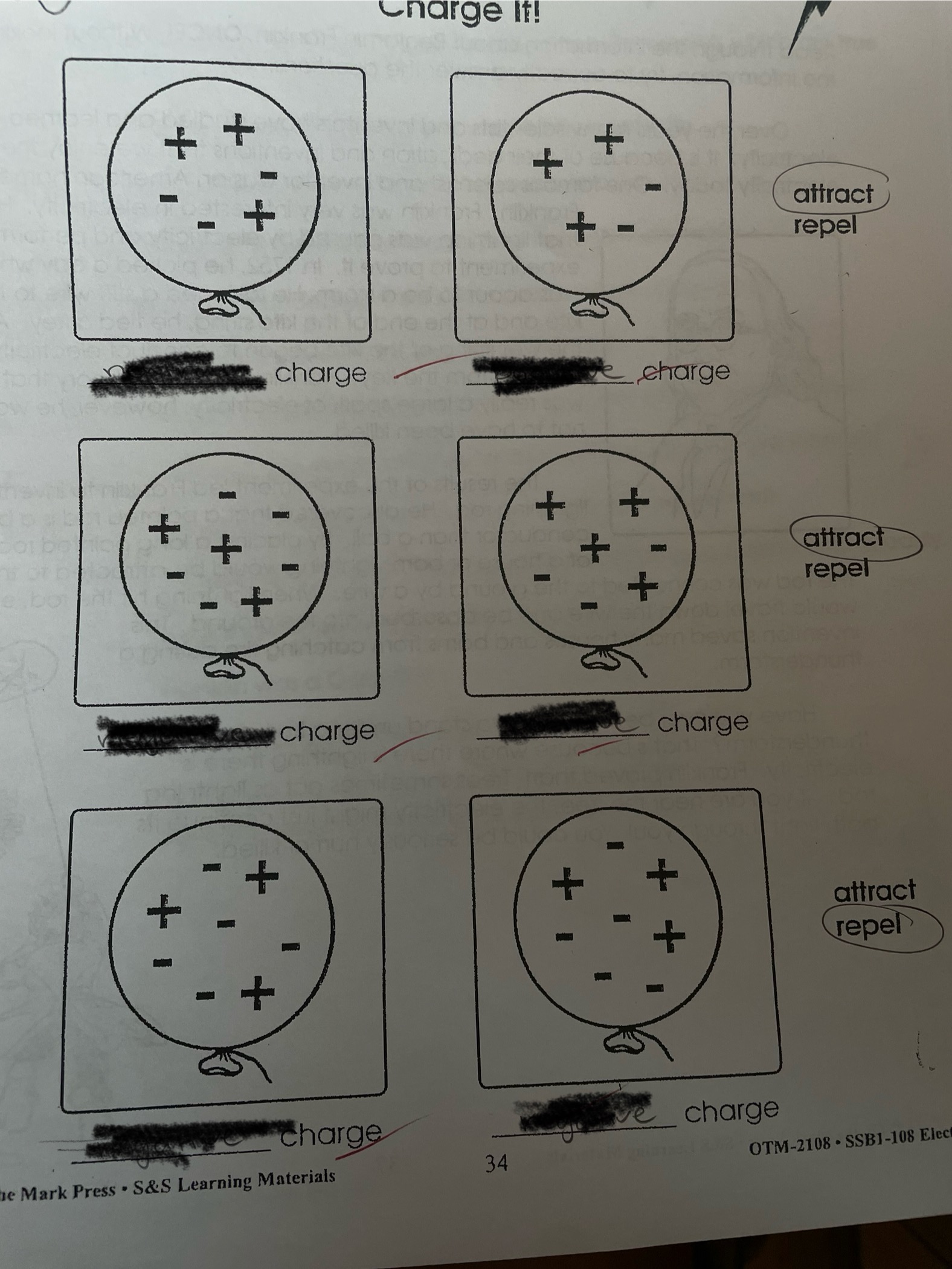
MULTIPLE CHOICE
Electricity and charges and their attractions
(attract/repel/neutral attraction to charged objects)
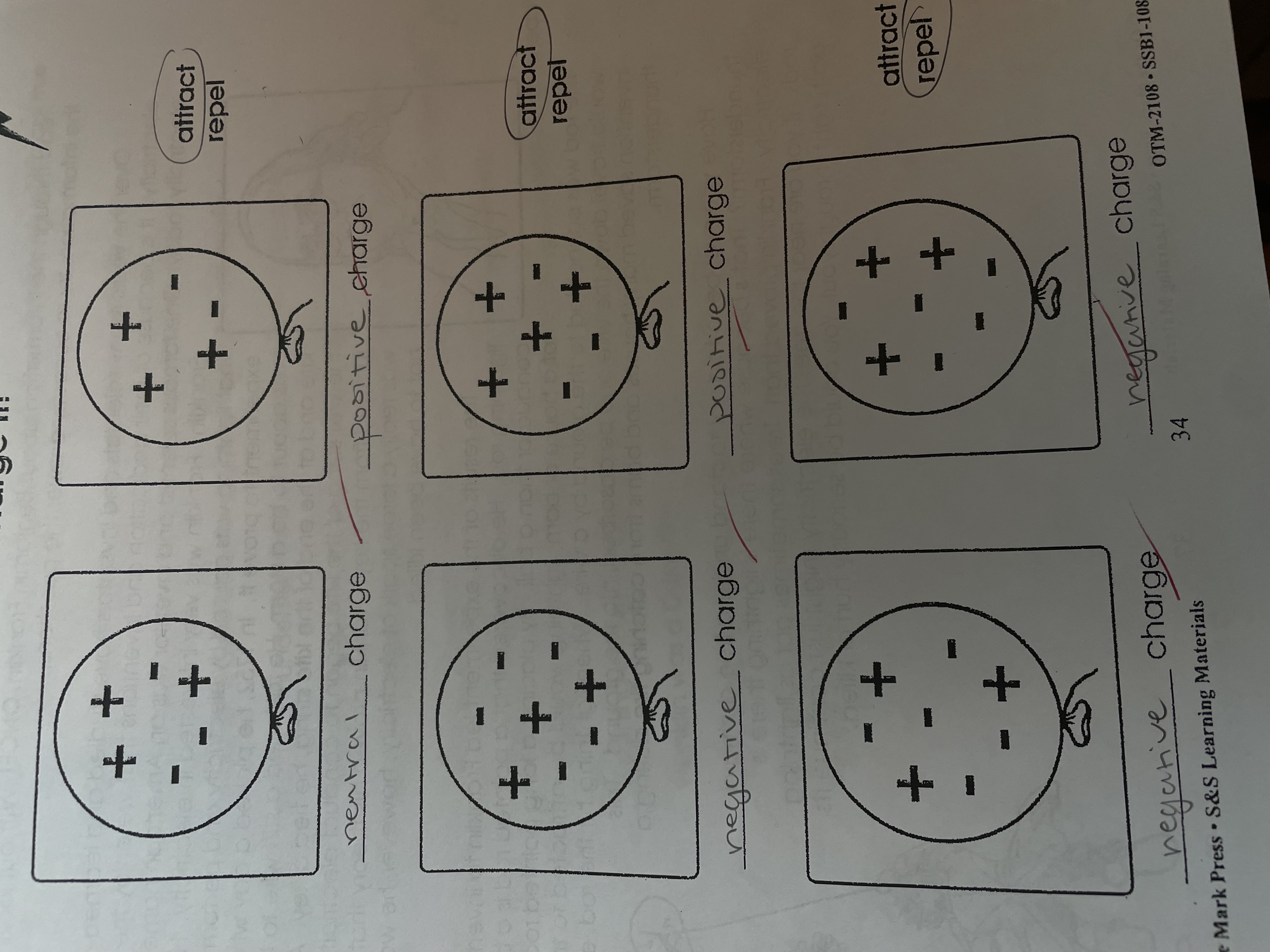
MULTIPLE CHOICE
compounds and ionic bond
Compounds: pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined together
Ionic bond: an electrostatic attraction between two atoms where one atom transfers an electron to the other atom
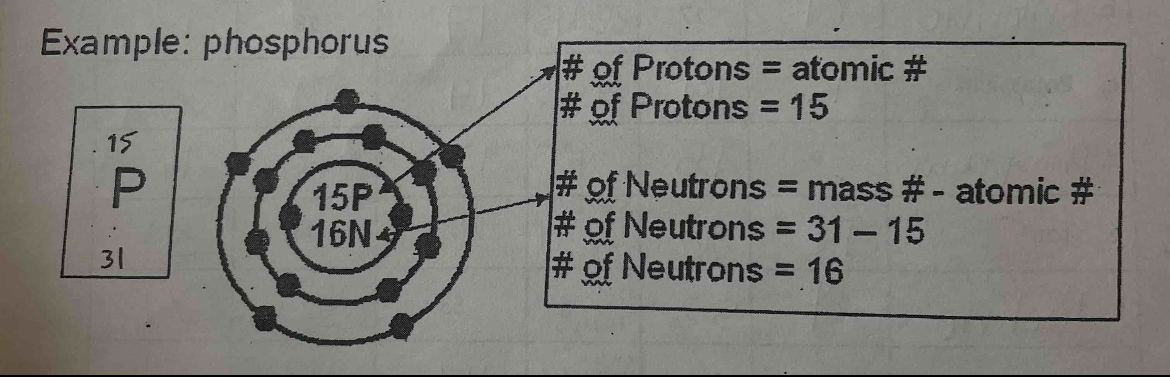
CHEMISTRY
Bohr diagrams of an isotope of a given atom

CHEMISTRY
balancing chemical equations
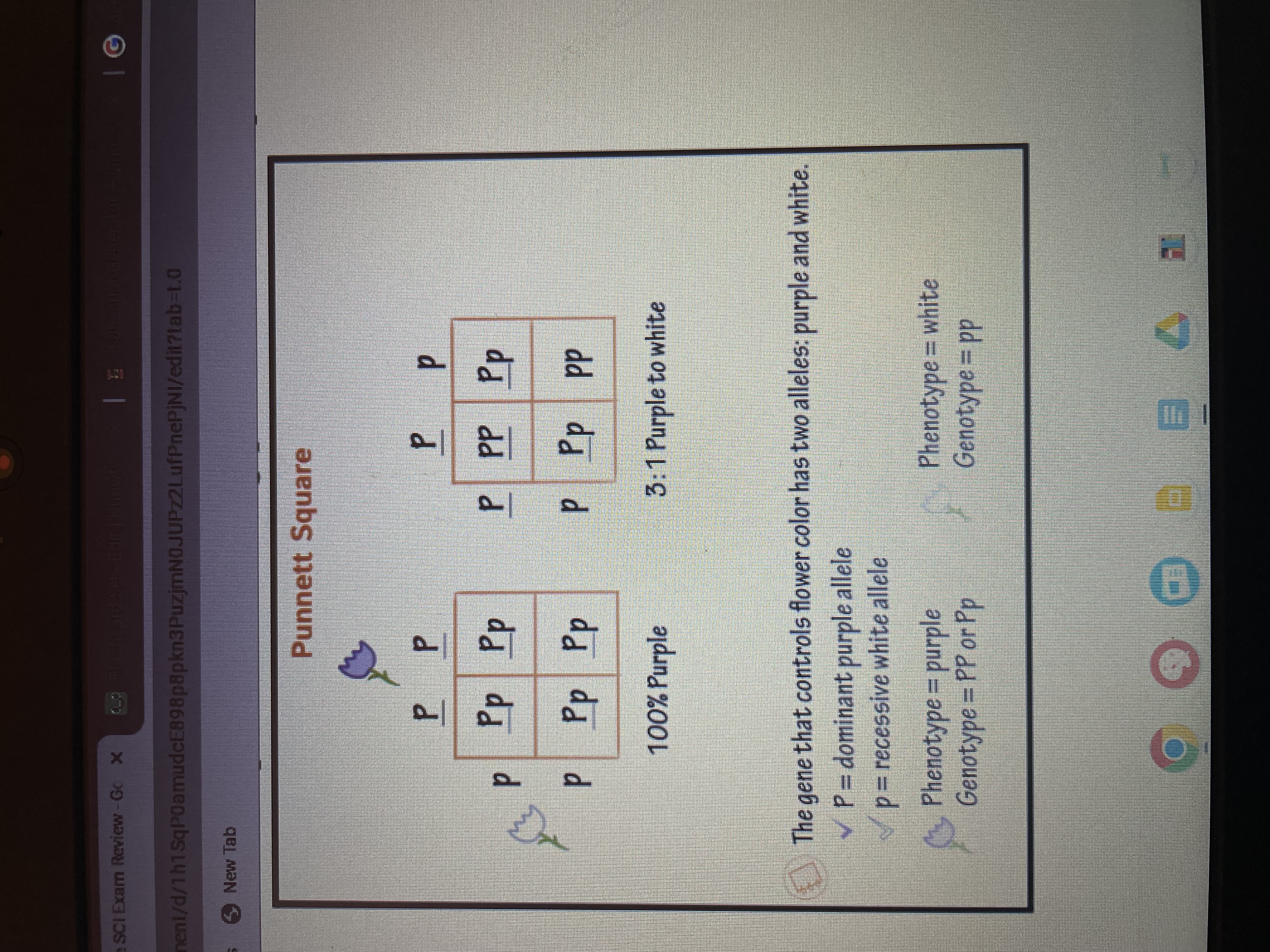
GENETICS
punnett squares