Final Animal Nutrition
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Active Transport
This is the passage of nutrients across a membrane against a concentration gradient using a Transporter and ATP
Leptin
This hormone is produced by adipose tissue and reduces appetite
Nutrition
Numerous chemical reaction & physiological processes which transform food into body tissue & activities
Zymogen
This is an enzyme that is released in an inactive form that will become activated at a different location/time
Catabolism
This is a metabolic process by which complex structures within the animal are broken into simpler, smaller structures
Papillae
These small finger-like protrusions increase surface area in the rumen
Somatostatin
This hormone is produced in the duodenum & inhibits the release of gastrin, secretin and CCK
Allosteric Modifiers
These compounds alter the activity of the enzyme by binding to the enzyme away from the active site to increase or decrease activity
Ventriculus
The muscular compartment of the chicken digestive tract assists with mechanical digestion and is also called the gizzard
Proventriculus
This is the “true” gastric stomach in avians
Type of absorption that takes molecules from a High concentration to a Low concentration that requires a Carrier protein and No use of ATP:
Facilitated Diffusion
Which of the following is typically Not a function of the gastric stomach?
Microbial Breakdown
Which of the following is one of the major paired salivary glands discussed din class:
Parotid
Which animal will produce the greatest quantities of saliva?
Dairy Cow
Mucin is not produced by what region(s) of the stomach?
Esophageal
Absorption in the small intestine occurs primarily in the:
Jejunum
List the 6 classes of nutrients and indicate which ones may be used for energy
Water - most limiting
Protein - cost-effective but produce energy
Carbohydrates - produce energy
Fats - produce energy
Minerals - no energy production
Vitamins - no energy production
Name four compartments of the ruminant stomach & describe the primary function(s) od each section
Reticulum - Mechanical digestion: pacemaker/contractions
Rumen - Fermentation
Omasum - Filters food and enzymatic digestion
Abomasum - “True” stomach and chemical digestion
What is the importance of Nutrition?
it involves every aspect of life
It accounts for over ½ production cost per animal
Extra credit: Primary source of energy for the brain?
Glucose
Extra credit: Stuff about Dr. Engle
No
What is the importance of nutrition?
It involves every aspect of life
It accounts for ½ of production cost per animal
Describe the steps of the rumination process, what the purpose of rumination is, and how this process may be stimulated by the type of diet being fed.
Rumination: breaks down molecules and increases surface area
Purpose: increase surface area or reduce particle size.
Diet: Feed larger particle sizes like roughages
Regurgitation - anti-peristalsis of cud/food from the stomach back to the mouth
Remastication - rechewing cud/food in the mouth
Resalivation - aids in remastication cud to break down food particles more
Redeglutition - re swallowing cud/food, peristalsis
Describe the importance of enzymes and how they function. Include in your discussion what happens if the enzyme is exposed to all allosteric activators.
Enzymes are used in almost all body functions
if an enzyme is exposed to an allosteric activator, there will be no reaction, the reaction will speed up, lowering the activation energy, and not all of the activation energy will be used so it can be unfilled over again multiple times
no reaction
speed up the reaction by lowing activation energy
not all AE is used up in the process, so it will be used over and over again
Describe the major benefits and disadvantages associated with ruminant digestion of feeds discussed in class
Benefits
acts as own personal space heaters
no competition, readily available food
digest use feeds other animals can’t
Disadvantages
can result in bloat
gas production
List all the sites where significant microbial fermentation will occur in a ruminant animal. As a result of this fermentation, bloat can occur. Please also describe the 2 types of bloat typically seen and indicate which would be effectively treated using a compound such as “bloat guard” or mineral oil.
Both produce bloat
Hindgut fermentors - in the stomach
Pregastric fermentors - in the rumen and large intestine
Bloat
Free-gas bloat - gas in the abdomen that builds up and can’t be released
Frothy bloat - production of bubbles that cause frothy gas/bloat —> treated with bloat guard or mineral oil
Name the 3 major types of microorganisms found in the rumen and identify which group of microorganisms is present in the greatest number
Bacteria = greatest numbers present
Fungi
Microbes
The slide before is not letting place Protozoa instead of microbes
Describe the 3 physical factors of water that allow it to effectively cool the body. Additionally, name 2 sources of water other than drinking water
Physical factors
high heat capacity/specific heat
requires a lot of calories to heat up
high thermal conductivity
distribute heat throughout the body
high heat of vaporization
sweating/panting release heat
Water sources
H2O in feed
Metabolic H2O
Describe what an enzyme cofactor is and give examples of both types of cofactors
An enzyme cofactor is a catalyst to an enzyme. It aids in a reaction.
Metal cofactor —> breakdown chemical configuration —> zinc copper
coenzymes/organic cofactor —> hydrogen
Describe the effects of the following digestive regulators and where they are secreted from
Gastrin - pyloric region/antrum; on switch and increases gastric juices
Secretin - duodenum mucosa; increased secretion from the pancreas
Name the regions of gastric stomach and describe unique characteristics associated with each region
esophageal - non grandular
cardiac - produce mucin
fundic - produce mucin and secretion of HCL
pyloric - produce mucin
Glycogen
This pancreatic hormone will stimulate an increase in blood glucose and lipolysis
Glycosuria
This is a condition where there is excess sugar present in the urine
Cortisol
This hormone is produced by adrenal glands and will stimulate an increase in blood glucose and lipolysis
Lipolysis
This is the process where tissue lipase frees fatty acids from the lipid droplet for subsequent beta-oxidation
Caprophagy
This is the practice of an animal consuming its own feces. Rabbits practice a speizlized form called cecotrophy.
Chylomicron
This compound lipid transports triglycerides and other lipid compounds through the lymphatics to the thoracic duct of the left subclavian vein in non-ruminants
Unsaturated fatty acids
This is a type of fatty acid with double bonds between the carbons
Bile salt stim. lipase
This zymogen is activated by bile salts and is produced by mammary glands. It cleaves fatty acids from triglycerides
Chyrmotrypsin
This proteolytic zymogen is produced in the pancreas and is activated by trypsin in the duodenum
Ketosis
Disease that results during the catabolism of fat when not enough oxaloacetate is available to utilize Acetyl CoA produced for energy production
Pepsinogen
This proteolytic zymogen is secreted from the fundic region of the stomach and is activated by hydrochloric acid
Lysine
This amino acid tends to be the 1st limiting amino acid for swine fed a typical corn/soybean meal ration
Sucrose
This disaccharide is made from glucose and fructose
Which of the following transports lipids from the intestinal cell through the lymphatics to the bloodstream in ruminants?
Very Low Density Lipoproteins
What are the primary end product(s) of urea catabolism by urease
CO2 and Ammonia
Lipid metabolism is regulated just as carbohydrate metabolism was regulated. Which hormone(s) increase lipogenesis?
Insulin
GLobular proteins tent to…
Be easily digested
Which type of diabetes is called “Insulin Dependent” (is treated with insulin)
Type 1
Which of the following are essential fatty acids for mammals
Linolenic (18:3 N-3) and Linoleic (18:2 N-6)
What conditions predispose a female to gestational diabetes?
All of the above: obesity, improper diet, multiparous
Describe the 2 mechanisms by which N may be removed from amino acids
Deamination - removes free ammonia
Transamination - N group is moved to other cytoskeleton
Name this fatty acid. Use the N-system, also circle the double bond that would have been added by the delta-6 desaturase
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH
18:3n^-6
Name the 10 common essential amino acids
PVT. TIM HALL
Phenylalanine
Valine
Tryptophan
Threonine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Histidine
Arginine
Leucine
Lysine
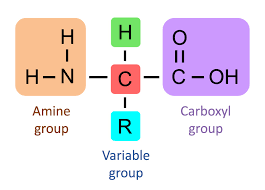
Draw the structure of a generalized amino acid and describe how this structure helps it to act as a buffer
This structure has an acid and base which helps it act like a buffer
NH3+ - Amine group
R - Side Chain
COOH - Carboxyl group
Name the three primary volatile fatty acids and indicate which one(s) are gluconeogenic
Acetate
Propronate - gluconeogenic
Butylate
Name 2 of the 3 primary ketone bodies describe 2 groups of animals that are particularly prone to ketoacidosis (species and physiological state) and what can be done to alleviate the disease
acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate
high producing dairy cows —> after birth
Ewes with twins in 3rd trimester —> before birth
We can increase blood glucose by using a blood IV dextrose drip. This will help alleviate the disease
Describe the Lipolysis and Beta-oxidation of triglycerides. Be sure to include the location within the cell and which processes produce ATP.
Lipolysis: hormone-sensitive lipase removes fatty acids from tryglycerides
in the cytosol of the fat wall
Beta-oxidation: transforms fatty acids to make acetyl-CoA. Each acetyl-CoA goes through a TCA cycle and produces ATP (al well as NADH+ FADH+)
in the mitochondria of the cell
Free Radical
This compound is characterized by having an unpaired electron and is extremely reactive and may cause damage to the body
Fresh cow vs Dry cow
Fresh - this is a term in the dairy industry to describe a cow that has just given birth and started lactation
Dry - no longer produces milk
Degradable intake protein - DIP
This protein in the diet can be digested in the rumen by the microbes to be incorporated into microbial protein
Vitamin A
The active form of this vitamin with the greatest biopotency is retinol
Fat soluble
This class of vitamins needs to be supplemented to cattle grazing winter or formant low-quality pastures
Acidosis
This disease is caused by a sudden and rapid fermentation of carbohydrates leading to a sudden decrease in rumen pH
Urinary calculi
This disease is common when an improper Ca:P ratio leads to crystal precipitates in the urethra
This is the maximum dietary fat concentration that a cow fed a high forage diet should consume
5%
Thiomolybdates
This compound is formed when there is too much sulfur and molybdenum in the ration of a ruminant
Organic form
This is the term used to refer to supplements where a mineral is incorporated into another molecule (I.E. Selenomethionine)
Which dietary Ca:P ration would prefer to feed your lactating beef cows?
2:1
Circle the following statement that is true in regards to beef cow nutrition
Most forages do not contain NRC requirements of trace minerals
What macro minerals tend to be limiting in pastures and ca lead to pica?
Phosphorus
What would your 1st choice as an energy supplement be for a pregnant cow in her last 1/3 of gestation fed grass hay as the forage base and assuming the fed rate would be varied on each to deliver the same amount of energy?
Corn
Feeding ura (in small amounts) to cows on pasture:
May increase the digestibility of cellulose
What is the primary reason why you should not want to buy dog food past the expiration date?
The vitamins are likely broken down
Ketosis (Ketoacidosis)
All of the above
is a concern in obese sheep near parturition
is characterized by hypoglycemia and excess ketone production
is a concern in some high-producing dairy cows
may be treated with a dextrose drip of propylene glycol
Which bacteria may proliferate when sheep gorge themselves on grain:
Clostridium perfringens
Which of these feeds would I choose to reduce the DCAD (Dietary cation-anion difference) of my pre-fresh dairy cows?
Brewers grains
What factors can influence vitamin degradation
All of the above
heat
light
moisture
Which product has the greatest concentration of estrogen-like compounds?
Soybean oil
Which of the following may be fed to cattle raised “organically”?
Organically raised and certified alfalfa
Prefresh Dairy cows are fed rations with a low DCAD (Dietary cation-anion difference) for which of the following reasons:
To prevent Milk Fever
Which of the following is not a goal when feeding a dairy cow during the close-up period
To increase the amount of cations in the ration
For a meat product to be labeled “grass-fed” it must be…
Be allowed access to pasture during the growing season
The DCAD (Dietary cation-anion difference) of a prefresh ration can be lowered by which of the following
Feeding cationic salts
The energy balance of fresh cows tend to be reduced because:
The dry matter intake of cows in the last two weeks before calving declines by as much as a third, and maximal fetal growth is occuring
According to the USDA AMS, which products are banned from use in livestock products labeled “natural”
None of the above
Hormone-based implants
sub-therapeutic antibiotics
beta agonist growth promotors
confinement
Extra credit: What vitamin is only provided by digestive microbes or animal products in relatively substantial quantities relative to human requirments?
Vitamin B12
If the gran content of dairy ration get too high:
milk fat will decrease
Net energy requirements for pregnant cows…
increase in the 3rd trimester
You have decided to venture into the sheep business. Your 1st attempt has not fared so well. So far, you have had no animals develop muscle disease (Vitamin E and Selenium), loss of coat color (Copper), a rapid increase in morbidities, anemia (Copper and Iron), and parakeratosis (Zinc). What type of supplement in their diet should you check out? Explain why and what is the similarity in the potential culprits of your problems.
Looking at the symptoms, most have to deal with mineral deficiency. Finding a supplement with copper since there are more cases with copper compared to the other trace minerals.
Name 5 macro minerals discussed in class
Calcium (Ca)
Phosphorus (P)
Magnesium (Mg)
Sodium (Na)
Potassium (K)
Chloride (Cl)
Sulfur (S)
Name the trace minerals
Copper (Cu)
Iron (Fe)
Selenium (Se)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Iodine (I)
Cobalt (Co)