Cognition Exam3
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Visual Imagery
seeing in the absence of a visual stimulus
another way of thinking, adds a dimension to verbal techniques
Mental Imagery
experiencing a sensory impression in the absence of a sensory input
Wundt
consciousness = sensations, feelings, and images
imageless thought debate that the cognitive rev revitalized
Imageless Thought Debate
Aristotle - not possible to think wo imagining
Dalton - it is possible
is imagery visual perception or language based?
Pavio
1963, 1965
mem for words that evoke mental images is better than for words that do not (tree vs. truth)
Conceptual peg hypothesis
inferred cognitive from behavioral memory data
Conceptual Peg Hypothesis
images that words can “hang on to” - easier to remember words that are easily associated with a large number of things
boat-hat: hat can be many places, associates easily with other words
Shepard & Metzler
1971, mental chronometry
RT method for mental rotation - polygon shapes, have to mentally rotate them to see if they match another shape
quantitative method of imagery study → perception and imagery share a mechanism
Mental Chronometry
amt of time needed to carry out a task
Perception and Imagery Mechanism?
spatial representation of stim corresponds btwn imagery and perception
mental scanning, Kosslyn
Mental Scanning
participants create mental images then scan them in their minds
Kosslyn 1973
memorize a picture then create an image of it
in image move from one part to another, push button after
took longer for mental movement of longer distances in the picture
evidence for imagery being spatial
Lea 1975
alternative explanation to imagery being spatial: attentional
more distractions/interesting things encountered in a mental scan lead to a longer RT
rebuttal to Kosslyn 1973
Kosslyn et al., 1978
response to Lea, same implications as first study
island with 7 locations, did 21 trips, still took longer for greater distances
visual imagery is spatial
Pylyshyn 1973
spatial representation is an epiphenomenon
imagery is propositional - represented as abstract symbols
Epiphenomenon
something that accompanies a real mechanism but is not actually a part of it - 3rd variable
Viewing Distance
how far away you are from an object changes what it looks like
if the object fills the visual field → details become harder to observe
if the object is far away → details are lost
Kosslyn 1978
imagine a rabbit and an elephant with the elephant filling the space
or a flea and a rabbit similarly
easier to give details about the rabbit with the flea by RT
mental walk - had to move closer to smaller animals to provide details
evidence that viewing distance effects imagery → imagery is spatial
Perky 1910
imagery and perception mix
low brightness projection on wall (participants could not see)
participants mistook the actual projection (picture) as their own mental image
Brain Imaging
Kosslyn 1995 - topographic map, image sizes
Grannis 2004 - overlap in frontal, differences in the back of the brain
Kosslyn et al. 1995
topographic map - activate specific locations on brain structure
size of mental images - smaller images to back of temporal
larger images activate a larger area of the brain
Granis et al. 2004
imagine studied images when hearing a tone
tell if object of imagining is wide or tall
overlaps for seeing image/imagining in front (frontal lobe), differences in the back
perceptual vs. imagery differences in the brain
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
decreases brain functioning in a particular area of the brain for a short time (highly magnetic wand)
if behavior is disrupted - that brain region is responsible for the behavior
TMS Perception vs. Imagery
view (perception) or imagine (imagery) bars and judge their lengths
TMS on visual cortex slowed RT for both
Visual Cortex Damage - removed right occipital
from MGS results of mental walk task
decreases the size of the visual field
15 ft → 35 ft away from a horse for it to fill the full visual field
Dissociations
evidence for independence of perception and imagery
CK vs. RM double dissociation
CK
visual agnosia - inabil to name images of objects even own drawings
could draw objects with great detail from memory
imagery intact, perceptual damaged
RM
occipital and parietal lobe damage
could draw accurate picture of objects in front of him
could not draw accurate pictures of objects from memory
had perceptual, did not have imagery
Perceptual vs. Imagery Conclusions
separate mechanisms but some shared mechanism
different in experience
perception is automatic and stable
imagery takes effort, is fragile, and faces difficulties with ambiguous swaps (rabbitduck)
Spatial Imagery
abil to visualize spatial relations
PFT - paper folding test
Object Imagery
ability to visualize details, features, and objects
VVIQ - vividness of visual imagery questionnaire
Individual Differences in Visual Imagery
spatial and object imagery ted to trade off
Aphantasia
inability to generate mental images voluntarily, 4% of the population
difficulty with WM tests w visual components
impairs visual search
Communication
system by which info can be exchanged
nonverbal/behavioral/pheronomal/verbal
Language
sys of communication using sounds or symbols, human specific
components combine to form larger units
Phonemes
letter symbols, smallest units of distinct sounds
Syllabaries
syllable symbols
Logographics
whole words and bound morphemes
un in unhappiness = morpheme
morpheme = smallest units that carry meaning
Alphabet
standardized list of symbols representing phonemes
Nature of Languages
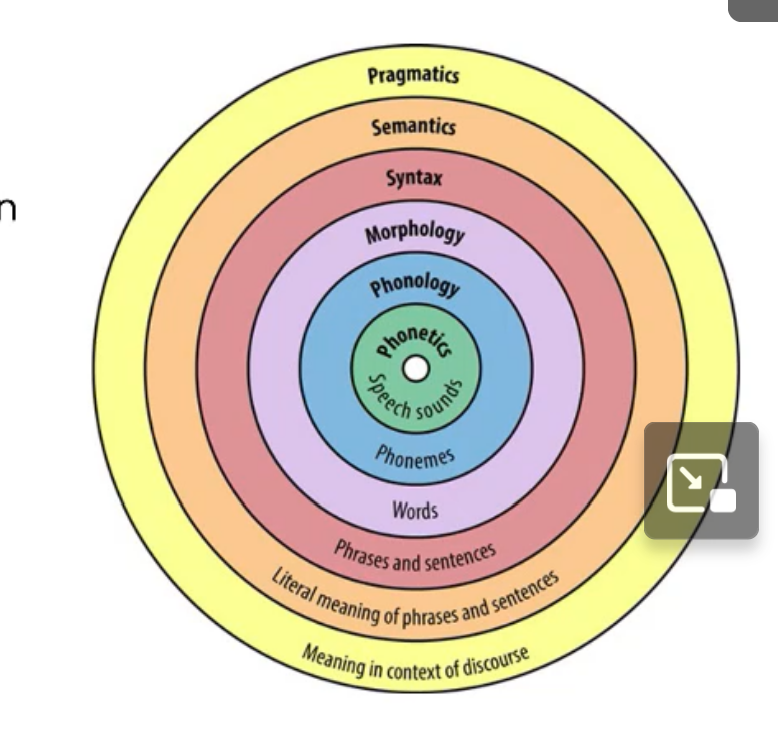
Hierarchical - consists of a series of small components that can be combined to form larger units
Rule Based Nature - specify permissible ways for arranging words and phrases
Universality of Language
deaf children with invent their own sign language (one lang mastery is important to reach cognitive potential)
all humans with normal capacity develop a lang and learn its rules
lang is universal across cultures
lang dev is sim across cultures
coo → babble → 1st words → multiwords
lang are unique - dif words, sounds, and rules
but the same - nouns, verbs, negatives, questions, and past/present tense
Imagery - Vision and Language
both routes to imagination
aphantasia - lack of imagination, use lang to compensate
Internal dialouge
Lack of Internal Dialogue
deficit in creative achievement
originality during divergent thinking
lack of diverse responses
compensate using visual imagery
Nature vs. Nurture Lang 1957
BF Skinner - nurture, language learned through reinforcement, Verbal Behavior
Noam Chomsky - nature, Syntactic Structures, human lang coded in genes, similar underlying basis of all lang, children produce sentences they have never heard before (never been reinforced)
Psycholinguistics
discovery of psychological process by which humans acquire and process lang
Comprehension - understand
Representation - cognitive activation/grouping/connection
Speech Production - physical process
Acquisition - learning
Lexicon
all the words a person understands
Semantics
meaning of a language, literal
Lexical semantics
meaning of words, each has 1+
Word Frequency Effect
respond to common words faster than uncommon
Rayner and Duffy 1986 - eye tracking, more time to access low frequency words
Complications in Understanding Words
variable word pronunciation
speech segmentation - perception of individual words even tho there are no true silences btwn spoken words through contect, stat learning, meaning, and frequency
Understanding Ambiguous Words
lexical ambiguity - words have multiple meaning
Tanenhaus 1979 - lexical priming, name a known category after a sentence is shown, speed boast if item of category (as itself or the verb) is given (rose → flower) → access all word meanings at brief delay
Lexical priming
people briefly access all meanings of a word before relying on context to determine accurate meaning
Meaning Dominance
when one meaning is used more frequently than the others
biased dominance = one dominant meaning, slower response to nondom word
balanced dominance = all meanings on same level, slower response
Understanding Sentences
semantics, syntax, parsingS
yntax
rules for combining words into sentences
Parsing
mentally groups words into phrases
helps listener create meaning
Garden Path Sentences
begin by appearing to mean one thing → end up meaning another
temporary ambiguity - one meaning adopted before error causes shift to correct meaning
from late closure
Parsing Model
use heuristics - simplest syntactic structure
late closure - parser assumes each new word is part of the current phrase
Constraint Based Parsing
info, word meaning, and context used to make predictions about parsing
memory load/prior lang experience - infrequent in english, object relative construction
Object Relative Construction
requires holding of early part of sentence in mind to understand the full sentence
Tanenhaus and Truesnell 1995
scene context, visual world paradigm - respond to spec instructions in a scene and process info
eye tracker - place the apple | on the towel | in the box
measured erroneous eye mvmt
Coherence
rep of text in ones mind that creates clear relations
inferences help maintain coherence btwn text and with the stories plot
Inference
readers create info during reading that is not explicitly stated
anaphoric = connecting obj/people
instrument = tools or methods something was done with
causal = events in one clause caused by events in prev sentence
Situation Model
mental rep of the topic of the text
represent events as if experiencing the situation, protag POV
slow downs occur from mismatch btwn mental rep and the sentence
Brain Imaging - Reading
unexpected words incongruent with the situation create a larger N400 response
situations simulate properties of objects, related concepts and motor movements
Given-New Contract
speaker constructs sentences so they include given and new information
sentences are easier to understand when they do not require inferences
Common Ground
some idea of what the other person knowns
Entrainment
synchrony btwn two convo partners
Syntactic Coordination
using sim grammatical constructions
Syntactic Priming
production of a specific grammatical construction by 1 person increases the chances the other person will use that construction
reduces comprehensional load in conversation
Conversation Skills
Theory of Mind
Prosody
Turn taking - when to enter convo
Theory of Mind
being able to understand what others feel, think, or believe
nonverbal communication - being able to interpret and react to a persons gestures, facial expressions, tones of voice, and other cues to meaning
prosody
Prosody
pattern of intonation and rhythm in spoken language, creates emotion
limited in text
Bilingualism Benefits
cognitive reserve - protection from age related decline, stim neuroplasticity
metalinguistic awareness - compare linguistic features cross lang
code switching - cognitive flexibility
attentional control - selectively attend and inhibit distractions
Bilingualism Drawbacks
tip-of-the-tongue states - impede comm
slower lexicon access speed
language attrition - less used lang may decline
mixing/blending during lang processing
Problem
obstacle btwn present state and a goal without an immediately obvious solution
difficult to solve
Gestalt Approach
based on how you represent a problem in the mind
restructuring, Kohler’s circle problem
Restructuring
changing the problems representation
Insight
sudden realization of a problem solution, often requires restructuring
Metealfe and Weibe
Metealfe and Wiebe 1987
triangle of dots - move 3 to make it face the other way
chain problem - 4 chains of 3 links, can open and close 3, make a loop
asked warm/cold every 15 seconds
rapid solving of insight problems after cold for a while, gradual solving of algebra problems
Fixation
focus on spec chars of a problem that keep one from arriving at a solution
Functional Fixation
restricting the use of an obj to its familiar functions
candle problem, 2 string problem - Maier 1931
Maier 1931
candle problem - candles, matchbox, tacks - get candle on wall in a way that doesn’t drip wax everywhere
2 string problem - 2 strings attached to ceiling too far apart to reach them both at once, have pliers and metal chair - must tie them together
Mental Set
preconceived notion about how to approach a problem based on past experiences with the problem
Luchins water jug
Information Processing Approach
initial state - conditions at beginning of problem
goal state - problem solution
Intermediate state - conditions after each step made towards solution
Operators - actions that take the problem from one state to another
Means-end Analysis - reduce dif btwn initial and goal state
Subgoals - small goals that help create intermediate states that are closer to the goal
Tower of Hanoi
information processing approach
discs moved one at a time, only the top disc can be moved
larger discs cannot be placed on top of smaller discs
Multilated Checkerboard Problem
importance of how a problem is stated - think aloud protocol helps
2 corners removed, can 31 dominos still cover the checkerboard
blank, colored, color names, or bread & butter boards
bread and butter worked the best
Analogies
making comparison in order to show similarities btwn 2 different things
Analogical Transfer
transfer from 1 problem to another (source → target problem)
lock and key → checkerboard
Gick & Holyia
analogical problem solving
noticing a relationship
mapping an overlap btwn source and target
applying the mapping to create a parallel solution
Dunker’s Radiation Problem
analogue problem solving
inoperable deadly tumor, strong ray can destroy tumor and healthy tissue, weaker ray will not penetrate the brain
Analogy: fortress attack, mines on roads that small groups can travel over, divide up troops over many roads
Analogical Encoding
process by which 3 problems are compared and the similarities btwn them are determined
Negotiation strategy
trade off - you get x if I get y
contingency - if x happens you get y
Analogical Paradox
can be dif to apply analogies in the lab but used frequently irl
3-15/hr bio-immunologist, 1/5min engineers
naturalistic setting of research → dif isolating variables and understanding the process of where such thinking emerges
Expert
person who, by devoting a large amount of time to learning about a field and practicing and applying that knowledge has become acknowledged as being extremely knowledgeable or skilled in that field
chess board set up, grouping of physics problems
only advantaged in their field, spend longer analyzing problems, less likely to be open to new ways of looking at problems - Dunning-Kreguar effect
Creativity
anything made by people that is in some way novel and has potential value or utility
poor for arts/theatre description
fitness indicator - more creative are better mates
divergent thinking - open ended, large # of potential solutions
Generating Ideas
examples reduce creativity - functional fitness
group brainstorming - share whatever ideas come to mind wo criticism, fewer ideas shared than individual, some dominate the convo
Creative Cognition
technique to train people to think creatively
randomly pick 3 obj, spend 1 min making project
preinventive forms - ideas that precede creation of the finished creative project
Chi and Snyder 2012
draw 4 lines through dots wo lifting the pen
deactivated left anterior temporal lobe causing people to think outside the box (inc to 40% of people solve)
Kounios et al. 2006
the prepared mind
EEG on compound remote → association problems
frontal lobe activity inc before insight solutions
occipital lobe activity inc before non-insight solutions
Incubation
facil by mindwandering, getting ideas after taking a time out
assoc w default mode network (active brain areas during rest)
inc functional connectivity btwn executive control network and DMN → creative people