GMS 200 Final Exam Notes
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
competitive advantage
what you do that gives you an edge: cost of production, access to resources, even gov. policy (provides license to monopolize)
sustainable competitive advantage
an approach that is different for competitors to replicate
strategy
something that will provide a competitive advantage
what are characterisitcs of an oligopolu
few players directly competing against each other
long term competitive advantage in defined market segment
what are characteristics of hypercompetition
several players directly competing
competitive advantage is temporary
strategy formulation
the process of creating a strategy; assessing existing strategies, organization, and environment to develop new strategies and strategic plans capable of delivering future competitive advantage.
strategic questions for strategy formulation
what is the business mission?
who are our customers?
what do customers consider value?
what have been our results?
what is our plan?
what is a mission statement
identifies customers, products/services, location and underlying philosophy
explains why the business exists
who are the 2 players when it comes to electric vehicle charging
flo
sun country highway
who will battery makers replace?
oil giants
how have lithium batteries grown in popularity?
R&D has resulted in a decrease in the cost of battery production
what does one need to take into account to assess their macro environment?
technology
government
social/demographic structures
global economy
natural environment
what does one need to take into account to assess their industry environment?
resource suppliers
competitors
customers
what are web based business models
brokerage models
advertising model
merchant model
subscription model
infomediary model
community model
characteristics of a competitive advantage
cost + quality
knowledge and speed
barriers to entry
financial resources
what are porter’s generic strategies
focuses on scope and competitive advantages depending on cost and differentiation; differentiations strategy, cost leadership, focused cost leadership, and focused differentiation
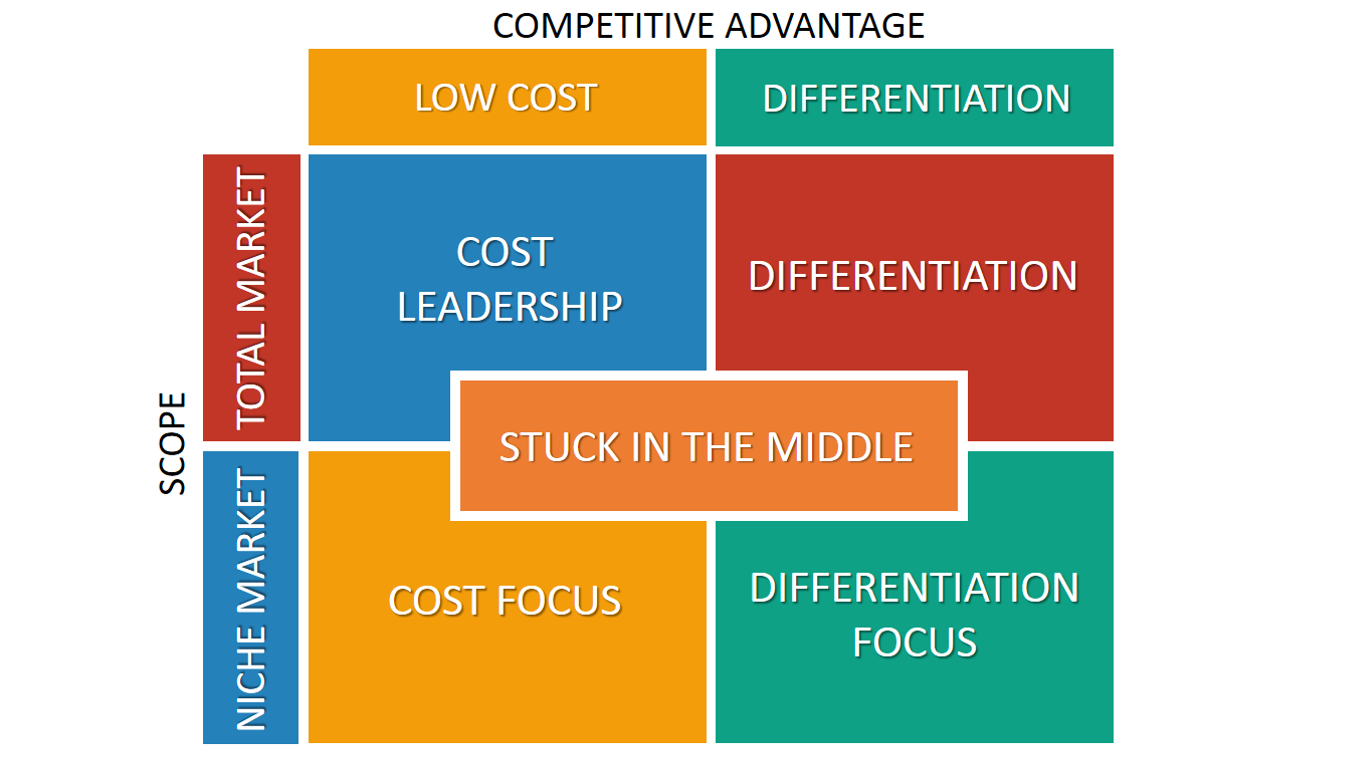
portfolio planning approach
a way to evaluate and manage different products or investments to make the best use of resources and align with the company's goals.
BCG Matrix
A strategic framework used to evaluate business units or product lines based on their market growth and market share, categorizing them into four quadrants: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs.
types of adaptive strategies
prospector strategy
defender strategy
analyzer strategy
reactor strategy
prospector strategy
pursuing innovation in face of risk for growth
defender strategy
protecting market share by emphasizing products without seeking growth
analyzer strategy
maintaining existing operations and keeping efficiency, adopt successful innovations from competitors
reactor strategy
merely responding to competition to keep afloat
failure of substance
inadequate attention to major strategic planning elements
failure of process
lack of participation, goal displacement error
critical tasks of strategic leadership
guardian of trade-offs
create a sense of urgency
everyone understands strategy
teacher / be inspiring
be a great communicator
corporate strategy
what busiinesses are we in
business strategy
how do we compete in each of our major businesses
functional strategy
how do we best support each of our business strategies; finance, hr, marketing
types of growth strategies
concentration strategy, diversification strategies
what is vertical integration
owning the supply chain
retrenchment
the reduction of costs or spending in response to economic difficulty
what are key activities in retrenchment
correcting weaknesses of operations
liquidation
restructure
downsizing/rightsizing
divesting - moving resources from businesses
multidomestic strategy
polycentrism (adapting product), for instance, nestle
transnational strategy
standardized but try to incorporate some local values, mcdonalds, balance efficiencies in global operations and responsiveness to local markets
what are the 2 sources of managerial power
position power - power based on authority and hierarchy
personal power - based on other’s perception
what are the 3 position powers?
reward power - reward of x if y
coercive power - if no x i will punish you
legitimate power - bcs i am boss
what are the 2 personal powers?
expert power - a source of special knowledge
referent power - others likely to identify with this
blake and moutons leadership
a grid representing an x axis of concern for production and y axis for concern for people, with numbers on each axis indicating appropriate concerns. helps leaders understand their own leadership style and improve.
what are the 3 classic leadership styles
autocratic - tasks over pppl, authority, control, keeps information, acts in a uniletal command-and-control fashion
laissez-faire - little concern, lets group make decisions, do the best you can, don’t bother me
democratic - sharing information, encouraging, helping
what does fidler’s contingency model demonstrate?
good leadership depends on match between leadership and situational demand, there's an understanding that good leadership is dependent on personality
what does the hershey-blanchard situational leadership model show
a leadership theory that suggests there is no single "best" style of leadership. Instead, effective leadership depends on the readiness or maturity level of the team being led.
what are the 4 types of leadership styles the hershey blanchard model proposes
telling - high task focus, low relationship focus; specific instructions + supervision, for low competence and committed
selling - high task focus, high relationship focus; direction, supportive, engaged behaviour. low commitment and competence
participating - low task focus, high relationship focus; share decision-making, relationship building, for high competence low commitment
delegating - low task focus, low relationship focus; minimal guidance, for high competence high commitment
what is house’s path goal leadership theory?
effective leadership deals with the paths through which followers can achieve goals, leaders adapt their style to needs of employees. leadership influences employee satisfaction, motivation, and performance
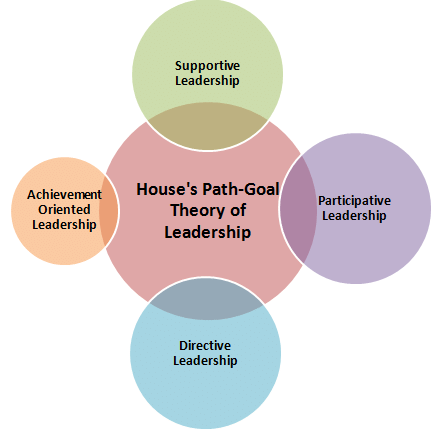
what is the vroom-jago leader-participation theory?
decision-making tool that helps leaders select the best approach to making decisions in a given situation; depends on nature of problem/situation to decide how to lead
what are characteristics of transformational leaders?
vision
charisma
symbolism
empowerment
intellectual stimulation
integrity
what are characteristics of entrepreneurship?
internal locus of control; contingence, whatever you do is beyond you
high energy level
need for achievement
self-confidence
tolerance for ambiguity
passion and action-oriented
self-reliance
flexible
what is personal agency belief?
it is entrepreneurship! which consists of self efficacy * locus of control
what is the typical background of entrepreneurs?
parents were entrepreneurship or self-employed
families encouraged responsibility, initiative, and independence
have tried more than one business venture
relevant career/personal experience
strong interests in creative production and enterprise control
seek independence and sense of mastery
kirner’s theory of entrepreneurship
no such thing as equilibrium, BUT we have equilibrium tendencies, when you discover opportunities > arbitrage (selling stuff cheap for high), you don’t need money to be an entrepreneurship you need to have an idea, entrepreneurship is error correction
schumpeter theory of entrepreneurship
entrepreneurship process is about creating and destructing,
harper’s cornerstone hypothesis
the value of focusing on critical, interconnected components rather than viewing a system’s parts as equally influential
baumd’s theories on entrepreneurship
there is such thing as productive and unproductive entrepreneurship, societies can make ppl unproductive bcs that is how they make money > need some ppl with the low paying jobs not innovating
facts about entrepreneurs
entrepreneurs are made not born
entrepreneurs take calculated risks they are not gamblers
ideas > money
you don’t need to be young
you don’t need a degree
characteristics of a small business
<100 employees
independently owned + operated
50% of labour force works in small businesses
entrepreneurship + the internet
intl. business entrepreneurship
family business
reasons for failure of small bsuinesses
no leadership
poor planning
unexpected accelerated growth
bad strategy
ethical failure > quantity over quality
insufficient commitment
no experience
life cycle of a venture
birth - establishment, getting customers, finding money; fighting for survival
breakthrough - working on finances, becoming profitable, growth; coping with growth
maturity - refining strategy, continuing growth, managing success; investing and staying flexible
forms of legal ownership
sole proprietorship
partnership
corporation
LLC
PLC
general partnership
equal liability and rights to decision process
limited partnership
different roles in management, proportionate to investment, different limits of liability
limited liability partnership
provides limited liability to all partners; protection
financing ventures
debt financing, equity financing, venture capitalists, initial public offerings, angel investors
debt financing
borrowing money, loans, pay back regardless of financial performance
equity financing
typical investment, take equity of business and receive dividends which can be diluted, no obligation to pay dividends
venture capitalist
big private equity investment focusing on start-ups/small companies with long term
initial public offerings
organization enters stock exchange
angel investors
well-off individuals who invest in small companies
promoting entrepreneurship in large corporations
intrapreneurship
skunkworks - a group within an organization given a high degree of autonomy and unhampered by bureaucracy, with the task of working on advanced or secret projects
promoting entrepreneurship
business incubators, small business development centers
functional structures
similar skills + tasks grouped together
ppl work in areas of expertise
not limited to business
works well from smaller organizations
divisional structures
groups of ppl who have the same tasks, customers, location
common in complex organizations
avoids problems encountered with functional structures
matrix structure
combines functional and divisional
horizontal structures
organization focus on processes not functions
ppl in charge of core processes
more teams less hierarchy
empowerment to increase performance
use IT
multiskilling and multi competencies
openness, collaboration, performance commitment
boundaryless organizational structure
a combination of team and network structures with addition of temporariness
absence of hierarchy
empowerment of members
use of technology
acceptance of impermanence
network structures
a central core linked through networks with outside contractors and suppliers of essential services
own only core components and use strategic alliances/outsourcing for other resources
problems with outsourcing
outsourcing activities part of core
outsourcing to untrustworthy vendors
no contracts
overlooking impact on existing employees
losing control to vendors
overlooking costs
failing to anticipate the need to change vendors
organizing trends
shorter chains of command
less unity of command
more delegation
more empowerment
centralization mixed with decentralization
reduced use of staff