CNS Synapses and long term plasticity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the types of memory?
declarative - explicit
conscious aware, what where and when
non declarative - implicit
not conscious, procedural
associative - priming
associative - simple classic conditioning
non associative - habituation, sensitisation
skills
Tests of declarative memory:
word list, delay 15 seconds, try to recall
object recognition - visual
object placement - spatial
Location of declarative memory and what blood flow increases
hippocampus - declarative memory
if the hippocampus is removed then there is declarative memory loss but not procedural
increase in cerebral blood flow following object recall
how was the first observation of LTP conducted? terje lomo experiment
activation of perforant path input to dentate gyrus
synaptic transmission monitored at <0.1Hz - low frequency stimulation of perforant path
brief high frequency 100Hz stimulus applied to same input - tetanus
return to LFS (<0.1Hz)
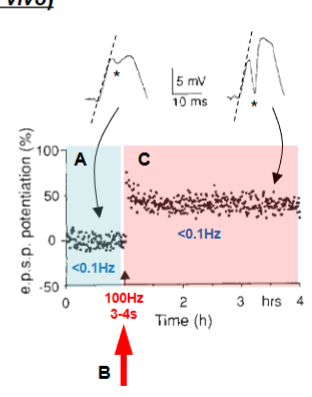
outcomes from the terje lomo experiment?
steeper rise time of the EPSP
increase in number of cells firing action potentials
lasts for several hours
Which synapses is LTP seen for in vitro?
LTP at CA3→ CA1 synapses
Experimental set up for LTP at CA3 → CA1 synapses
examples of 2 types of experiment to demonstrate LTP is complex - early and late
with single 100hz there is only early LTP which lasts shorter
with four 100Hz there is early and late LTP which lasts longer
What are the component phases of LTP
induction phase - initiation of LTP by HFS 100Hz stimulus
transient or early - reversible early LTP following induction
consolidated or late - permanent changes which maintain late LTP
what is induction process mediated by
NMDA receptors
AP5
NMDA receptor agonist
blocks LTP and LTD during HFS
induction process
postsynaptic rise intracellular calcium
postsynaptic depolarisation
mediated by NMDA receptors
what leads to baseline baseline neurotransmission at LFS
glutamatergic transmission at -80mV
only AMPA receptors are responsible for baseline neurotransmission
does D-AP5 have effect on EPSPs evoked by <0.1Hz
no
what happens during 100Hz stimulation for induction of LTP
temporal summation from activation of pre synaptic terminals, sustained activation, release of neurotransmitter
EPSP at -40mV
After AMPA activation there will be NMDA activation
requires more depolarised membrane potential
Evidence for NMDA-R in declarative memory
morris water maze - for spatial memory
AP5 treated mouse still cannot find the platform
Role of protein kinases during early LTP
No block seen when AP5 applied after induction - shows NMDA receptor activation is independent
dependent upon activation of protein kinase C and or calmodulin dependent protein kinase II
increased phosphorylation of AMPA receptor - both by PKC and CaMKII
what does increased phosphorylation by PKC and CaMKII lead to
allows increased conductance of AMPA receptor ion channels
inc current flow inc EPSC amplitude
EPSP in larger
Role of protein kinases during late LTP
protein kinase A dependent
seen through inhibition of H89. therefore involves increased cAMP
anisomycin - transitional inhibitor
actinomycin d - transcriptional inhibitor
DNA is targeted by activation of PKA
anisomycin
transitional inhibitor
actinomycin d
transcriptional inhibitor
if it is only LTP what happens when all the synapses have undergone LTP
eventually all the synapses would become fully potentiated
ceiling point with no inc in synaptic efficiency
therefore LTD reverses and depresses LTP
experimental setup for LTD in CA3 → CA1 synapses
same at LTP
but only 1Hz - low frequency stimulation instead of 100Hz high frequency
How is LTD and LTP similar mechanistically?
both blocked by AP5
both depend on NMDA-R activation
postsynaptic membrane potential depolarisation
increase in postsynaptic intracellular calcium
How is LTD mechanism different to LTP?
not blocked by protein kinase inhibitors
expression is blocked by FK506 and okadaic acid
protein phosphatase inhibitors instead
Difference in activation threshold for LTD and LTP?
difference in activation threshold for protein phosphatases vs kinase
intracellular calcium determines which is induced
<1μM → LTD (dephosphorylation).
5μM → LTP (phosphorylation).