BIOL*1090: DNA, Mutations, Transcription, Regulation, and Translation
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
histone
A type of protein found in chromosomes that bind to DNA, help give chromosomes their shape, and help control the activity of genes.
scaffold
The chromosome structure consisting entirely of nonhistone proteins remaining after all the DNA and histone proteins have been removed from a chromosome.
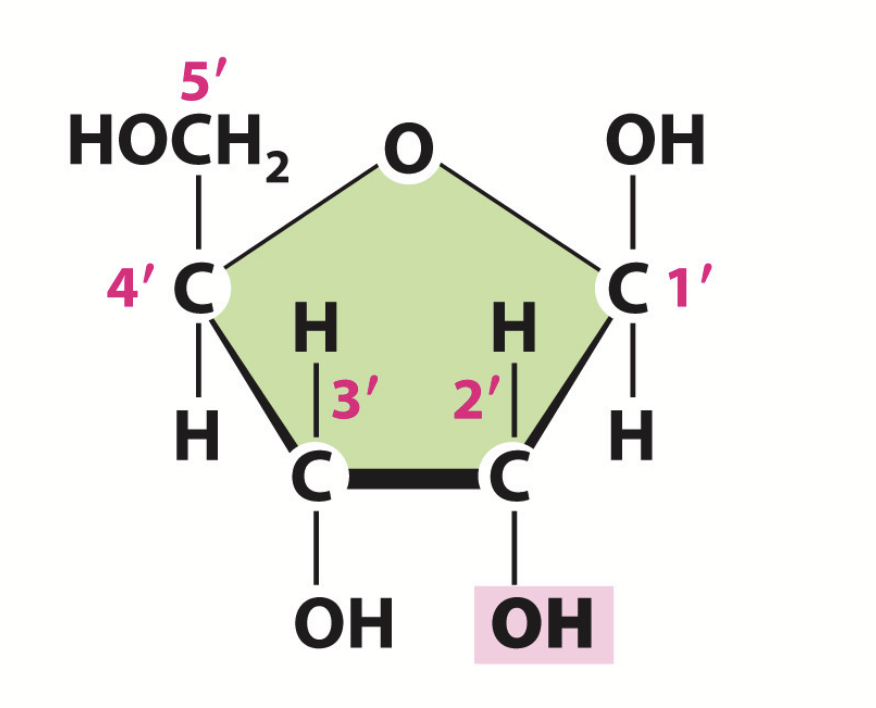
ribose sugar
Sugar found in RNA. Contains hydroxyl groups on the 1’, 2’, and 3’ carbons.
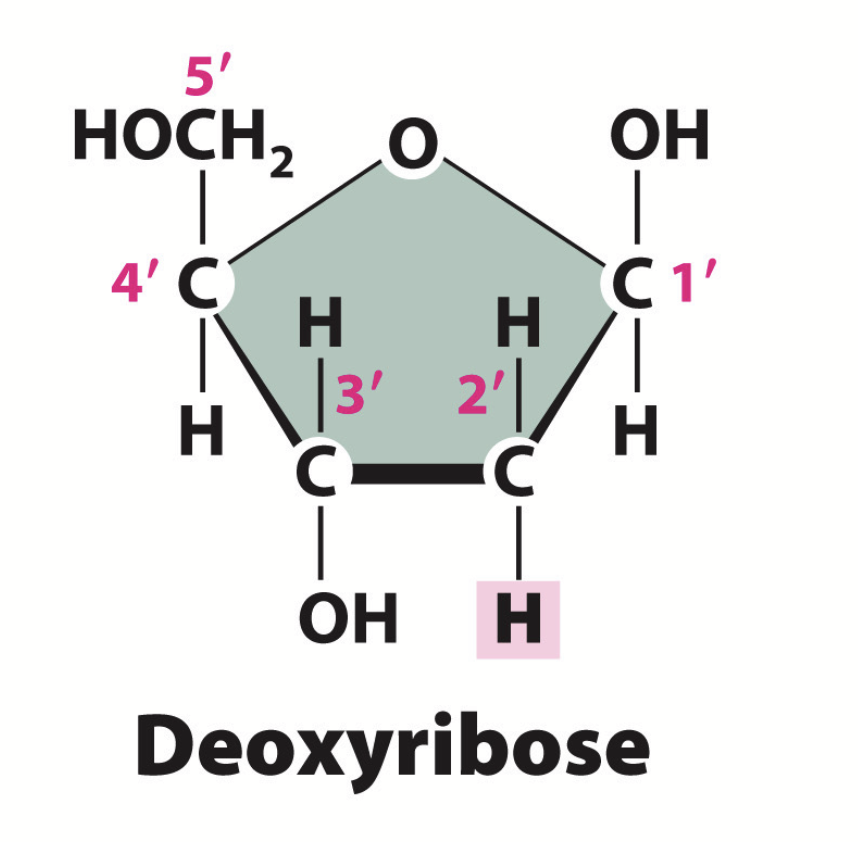
deoxyribose sugar
Sugar found in DNA. Contains hydroxyl groups on the 1’ and 3’ carbons.
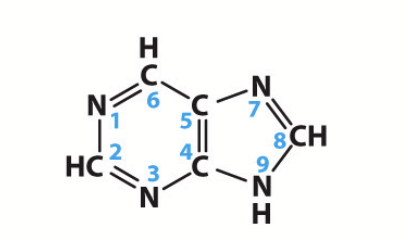
purines
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G); two-carbon nitrogen ring bases.
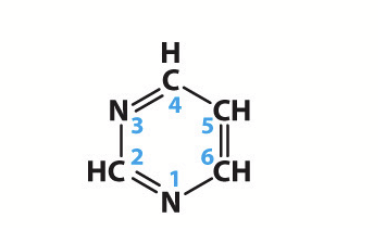
pyrimidines
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U); one-carbon nitrogen ring bases.
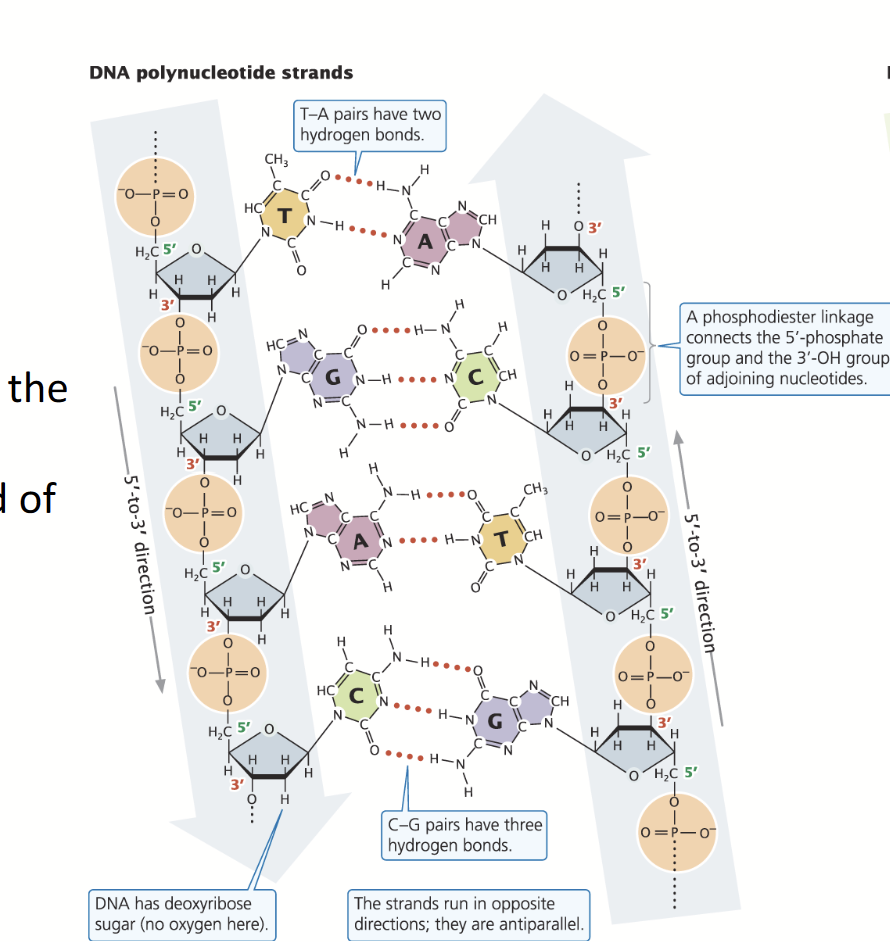
DNA
Consists of two antiparallel strands; phosphodiester bond between the oxygen at the 3’ end and the phosphate at the 5’ end.
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Bases: A, T, C, G
5’ end: Monophosphate
Size: Very large
Strands: Double
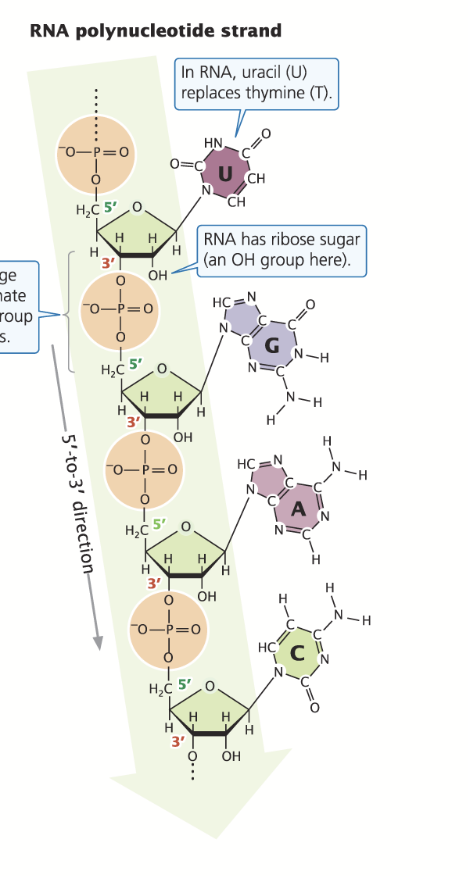
RNA
Consists of one strands; phosphodiester bond between the oxygen at the 3’ end and the phosphate at the 5’ end.
Sugar: RIbose
Bases: A, U, C, G
5’ end: Triphosphate
Size: Smaller
Strands: Single
mutation
Sustainer of life and cause of great suffering. Source of ALL GENETIC VARIATION, which further provides the raw material for evolution. Source of many diseases and disorders.
Useful for probing fundamental biological processes (identifying the function of the gene, etc).
somatic mutation
Mutations that occur in nonreproductive cells and are passed to new cells through MITOSIS, creating a clone of cells having the mutant gene.
germ-line mutation
Mutations that occur in cells that give rise to gametes. Meiosis and sexual reproduction allow these mutations to be passed to approximately half of the members of the next generation, who will carry the mutation in all their cells.
transition mutation
Type of base substitution gene mutation:
Purines changed to purines (A to/from G) or pyrimidines to pyrimidines (T to/from C).
transversion mutation
Type of base substitution gene mutation:
Purines changed to or from pyrimidines.
base substitution
Mutation in which a single codon is altered.
Transition
Transversion
insertion
Addition of a base into a DNA sequence.
deletion
Removal of a base into a DNA sequence.
frameshift mutation
Mutation caused by insertions and deletions, alter the reading frame and may change many codons.
expanding nucleotide repeats
Mutation caused by an increase in the number of a copy of a set of nucleotides.
Hairpin forms on newly synthesized strand, causing part of the template strand to be replicated twice, resulting in a new DNA molecule with additional copies of a certain codon repeat
forward mutation
Wild type → mutant type
reverse mutation
Mutant type → wild type
missense mutation
Amino acid → Different amino acid
nonsense mutation
Sense codon → nonsense codon
silent mutation
Codon → synonymous codon
(code for same amino acid)
neutral mutation
No change in function
(change in amino acid sequence, but NOT function)
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Structural and functional components of the ribosome (Translation).
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In cytoplasm
messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries genetic code for proteins.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In nucleus and cytoplasm
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Helps incorporate amino acids into polypeptide chain (translation).
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
In cytoplasm
template strand
The transcribed strand.
Transcription unit: a promoter, an RNA-coding sequence, and a terminator (end).
Runs from the 3’ → 5’ direction.
terminator
A sequence of nucleotides that signals where transcription is to end. Incorporated into the RNA, so transcription stops only after it has been incorporated into the RNA.
promoter sequence
Located upstream of the transcriptional start site. Contains the -35 and -10 consensus sequences that the RNA recognizes in order to bind with the promoter.
RNA polymerase II
The enzyme responsible for generating the majority of mRNA for making proteins.
RNA strand
Synthesized in the 5’ → 3’ direction; complementary to the template strand. U replaces T.
RNA-coding sequence
The gene coding for protein.
promoter
Tells you when to begin transcription (regulates start).
NOT INCLUDED IN THE TRANSCRIPT!
transcription start site
Between the promoter region and the RNA-coding region. Where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
codon
Group of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid.
regulation
Transcription requires control: regulated by the Promoter/Operator combo. Sometimes must turn Operon on, other times it must be shut down.
negative regulatory proteins
Proteins that inhibit transcription.
positive regulator proteins
Proteins that activate transcription.
inducible operons
When the transcription of the Operon is normally off, and something happens that turns it on.
Usually the case!
repressible operons
When the transcription of the Operon is normally on, and something happens that it needs to be turned off.
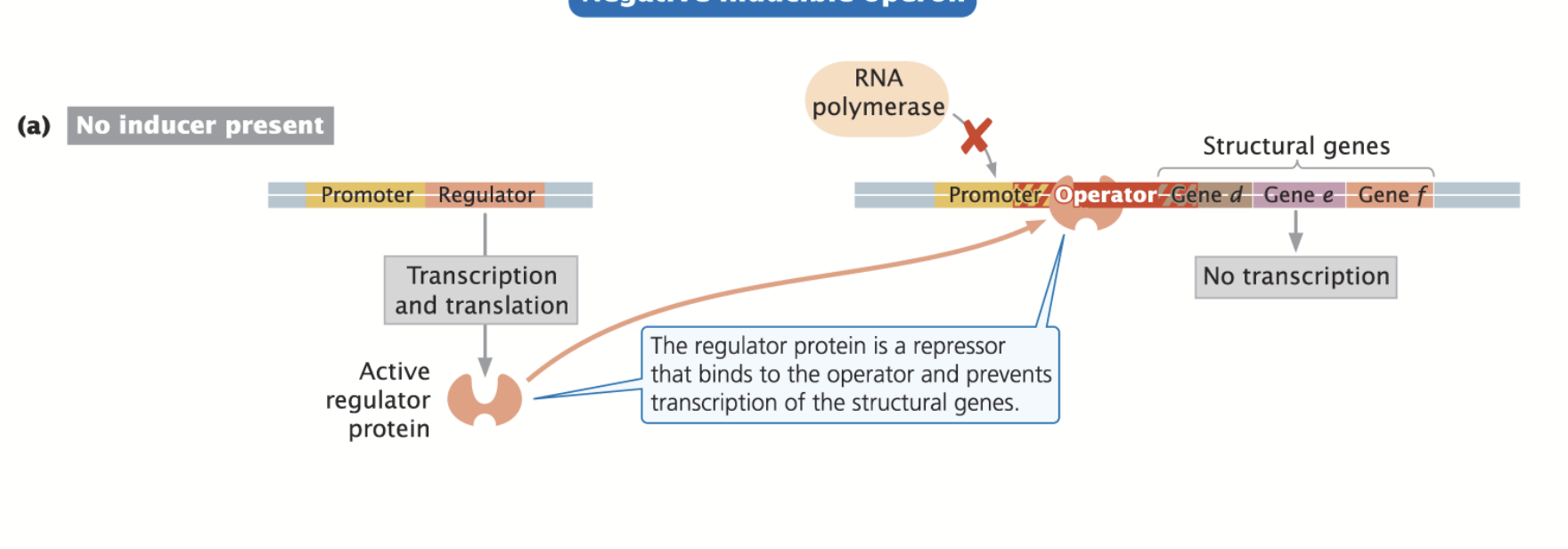
Negative Inducible Operon
Regulator Protein = Repressor: blocks the binding of the RNA polymerase to the promoter, keeping transcription turned off.
Repressor needs to be relieved of its duties in order for transcription to proceed.
An Inducer binds to the inhibitor/repressor and inactivates it. Repressor can no longer bind to DNA and RNA polymerase can activate transcription.
Usually involved in the degradation (metabolism) of molecules!
aminoacyl tRNA synthase
Charge the tRNA by adding amino acids to specific tRNAs.
AUG
start codon; methionine
initiation
Translation: The AUG codon is recognized and Met is established as the first amino acid in the new polypeptide chain.
elongation
Successive amino acids are added one by one to the growing chain (added on the 3’ end).
Ribosomal complex will shift over one, the tRNA goes to the P site and first/longer amino acid chain gets transferred to the single amino acid in the A subunit. The uncharged tRNA is moved into the E site
termination
A stop codon is recognized by a Releasing factor that mimics a tRNA resulting in the completed polypeptide chain being released from the ribosome.
N-terminal
The start of the polypeptide: where Met is.
C-terminal
Last amino acid in the polypeptide.
release factor
Protein that recognizes STOP codon and mimics a tRNA (but doesn’t have an amino acid on it) that pops the ribosome off of the mRNA.