Understanding Product Life Cycle and Marketing Strategies
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Product
Goods and services provided by a firm.
Product Portfolio
Range of products a business controls.
Brand
Identity distinguishing a business's products.
Unique Selling Point (USP)
Feature making a product stand out.
Differentiation
Making a product distinct from competitors.
Product Life Cycle
Stages a product goes through from launch.
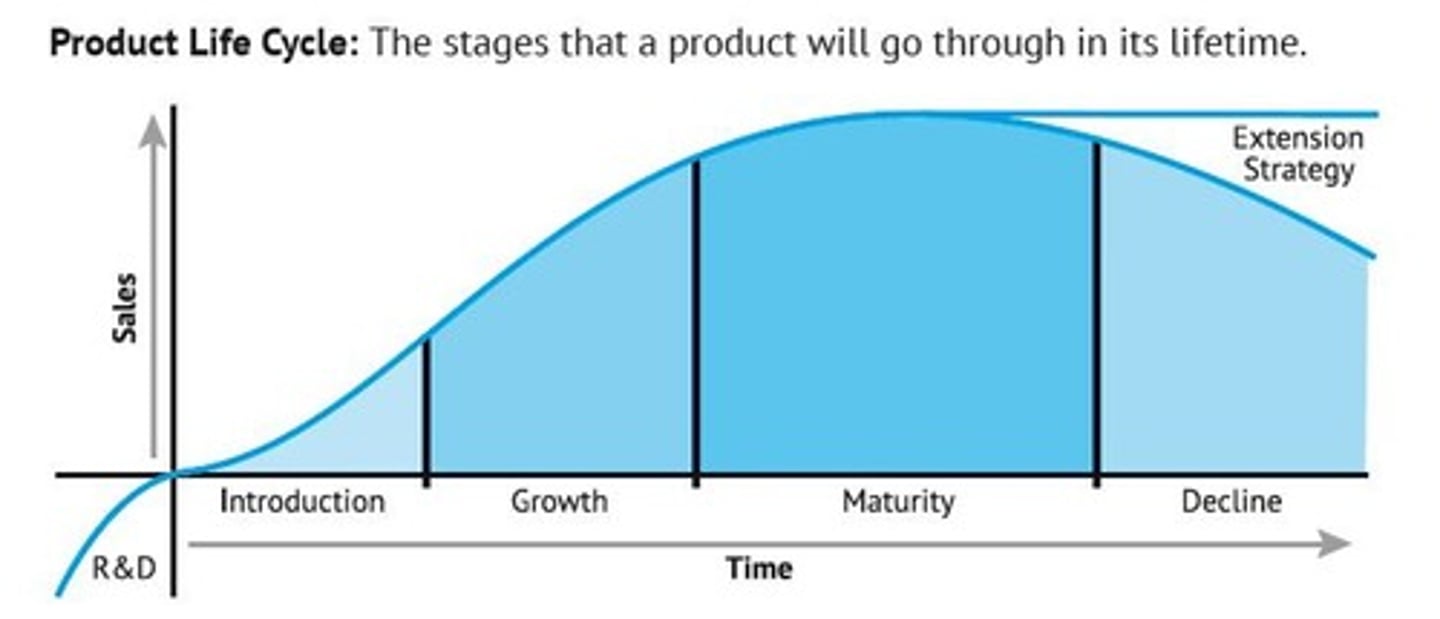
Extension Strategy
Tactics to prolong a product's market life.
Cash Flow
Movement of money in and out of business.
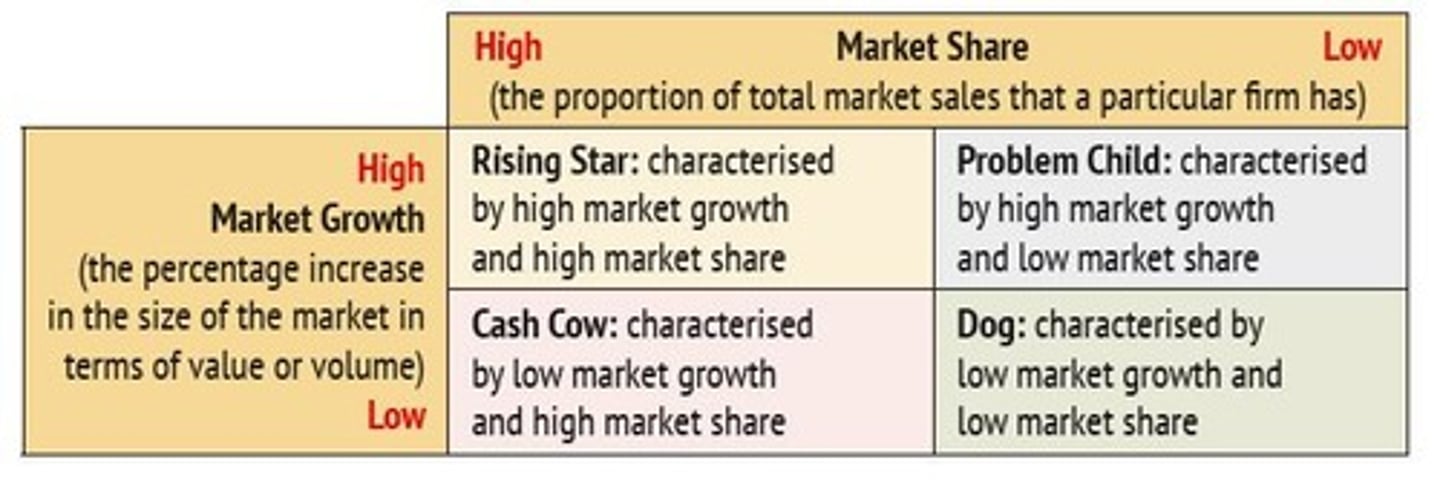
Boston Matrix
Tool for managing product portfolio effectively.
Brand Loyalty
Customer commitment to repurchase a brand.
Corporate Branding
Creating a perception associated with a company.
Geographical Branding
Branding representing a region's identity.
Brand Recognition
Consumer's ability to identify a brand.
Physical Goods
Tangible products like cars or televisions.
Intangible Services
Non-physical offerings like consultancy or teaching.
Product Analysis
Evaluating product positioning in the market.
Consumer Behavior
How consumers decide to purchase products.
Brand Promise
Expectation set by a brand to consumers.
Pricing Strategies
Methods to set product prices competitively.
Advertising
Promotional activity to influence consumer perceptions.
Market Positioning
How a product is perceived relative to competitors.
Stakeholders
Individuals or groups affected by business decisions.
Product Features
Attributes that influence consumer purchasing decisions.
Customer Needs
Ability to meet customer expectations effectively.
Brand Image
Perception of a brand in the consumer's mind.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Distinct feature that differentiates a product.
Product Life Cycle
Stages a product goes through from launch to decline.
Development Stage
Negative cash flow due to R&D before sales.
Introduction Stage
High production and promotion costs after launch.
Growth Stage
Increasing sales revenue with economies of scale.
Maturity Stage
Sales stabilize; product acts as a cash cow.
Decline Stage
Sales begin to decrease over time.
Extension Strategy
Methods to prolong a product's market presence.
Changing the Product
Modifying features or flavors to attract customers.
Increasing Promotion
Enhancing marketing efforts to boost sales.
Cash Cow
High market share in a low growth market.
Rising Star
High market share in a high growth market.
Problem Child
Low market share in a high growth market.
Dog
Low market share in a low growth market.
Sales Revenue
Income generated from selling products or services.
Market Share
Percentage of total sales in a market.
Market Growth
Increase in market demand over time.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages due to increased production.
Cash Inflows
Money received from sales or investments.
Cash Outflows
Money spent on expenses or investments.
Product Portfolio Analysis
Evaluating a company's range of products.
Cash Cow
Product generating steady profits for funding others.
Rising Star
High market share in a rapidly growing market.
Boston Matrix
Framework for analyzing product portfolio performance.
Market Growth
Rate at which a market expands over time.
Market Share
Percentage of total sales in a market held by a product.
Promotional Spending
Investment in marketing to increase product visibility.
Negative Cash Flow
Outflow exceeds inflow, common in rising stars.
Product Life Cycle
Stages a product goes through from introduction to decline.
Extension Strategy
Methods to prolong a product's life cycle.
Unique Selling Point (USP)
Feature that differentiates a product from competitors.
Differentiation
Process of distinguishing a product from others.
Fierce Competition
Intense rivalry among firms in a market.
Capital Investment
Funds invested to enhance production capacity.
Nurturing
Supporting a product to help it grow and succeed.
Discontinue
To stop production or sale of a product.
Product Portfolio
Collection of all products offered by a business.
Cross Subsidisation
Using profits from one product to support another.
Market Scope
Potential for future profits in a specific market.
Sales Increase Opportunity
Potential for higher profits through increased sales.
Personal Style Products
Items purchased to showcase individual style or wealth.
Product Portfolio
The mix of products a business offers.
Fixed Costs Spreading
Distributing fixed costs across multiple products.
Market Targeting
Focusing on specific customer segments for sales.
Risk Reduction
Minimizing potential losses through product variety.
Sales Smoothing
Evening out sales fluctuations over time.
Growth Opportunities
Chances for business expansion through product diversity.
Product Breadth
Number of different product lines offered.
Product Depth
Varieties within each product line offered.
Proctor and Gamble
Company with over 20 brands in its portfolio.
Brand Definition
A name that differentiates a product from others.
Consumer Reliance
Trust in a brand for quality and value.
Distinctive Identity
Unique characteristics that consumers associate with a brand.
Brand Recognition
Ease of identifying a product by its brand.
Brand Value
Perceived worth of a brand in the market.
Consumer Loyalty
Repeat purchases driven by brand attachment.
Price Inelasticity
Demand remains stable despite price changes.
Advertising Costs
Expenses incurred to maintain brand visibility.
Brand Competition
Rivalry from similar product brands.
Dyson Vacuum Cleaners
Market leader known for bagless technology.
Technological Advantage
Superior technology that enhances product appeal.
Dyson
Market leader with bagless system and colors.
USP
Unique Selling Proposition; product's distinguishing feature.
Product Differentiation
Making products distinct from competitors.
Methods of Promotion
Creating a product personality through marketing.
Eco-packaging
Environmentally friendly packaging for products.
Form
Physical appearance differing from competitors' products.
Add-ons
Additional features enhancing product value, e.g., warranties.
Quality and Reliability
Emphasizing product durability and performance.
Customer Loyalty
Consumer commitment to a brand over time.
Pricing Strategies
Approaches to setting product prices based on market.
Introduction Stage
Product is new; low awareness and high costs.
Growth Stage
Increasing awareness; profits begin but advertising costs high.
Maturity Stage
Peak sales; competition increases; profits high.
Saturation Stage
Market full; few new customers; profits decline.