Paleo 200: Chapter 1 - Appearances and Anatomy
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
what is palaeontology?
study of all prehistoric life.
primarily coming from fossils.
what is a fossil?
preserved evidence left behind by prehistoric organisms.
literally means “dug up”.
what are bones made of?
minerals which do not decay as easily as flesh and other soft tissues.
what are adaptations?
traits that have evolved because they serve specific functions.
what are the four major functions of bones?
passively resist gravity to maintain form.
provide ridged framework for muscle attachment.
provide protection and can be major components of horns and other weapons.
store mineral reserves.
how can animals get minerals from bones?
storage of calcium by growing bone deposit and increasing density of already existing bone.
what are vertebrates?
animals that have two special kinds of skeletal adaptations: skull and vertebrae.
group where dinosaurs belong to.
what are vertebrae?
structures made primarily of bone.
cartilage that surround portion of spinal nerve cord.
what do vertebrae interlock with each other to form?
vertebral column.
what are animals that lack vertebrae called?
invertebrates.
what can a skull provide?
give palaeontologist great insight into dinosaur’s life.
what is the brain case?
hollow chamber formed by multiple skull bones that houses the brain.
what pass through small openings that connect to brain?
nerves.
what provide clues to dinosaur’s mental capabilities?
the size and shape of brain case.
what are nares?
pair of openings for nostrils.
what are orbits?
pair of openings for eyes.
what are fenestrae?
additional skull openings.
what is the laterotemporal fenestrae?
fenestrae on lateral sides of skulls.
what is supratemporal fenestrae?
fenestrae on top of the skull.
what is the antorbital fenestrae?
located between each orbit and naris.
may have made skull lighter or houses large sinus cavities.
what is the centrum?
spool or disk shaped body of vertebra.
what covers the neural canal above the centrum?
neural arch.
what is the opening in each vertebra?
neural canal.
what are the vertebral processes?
provide attachment surfaces for muscles and sometimes provide articulation surfaces for ribs.
what are the two types of vertebral processes?
transverse process and spinous process.
what is a transverse process?
extend from the lateral sides of vertebrae.
what is the spinous process?
extends upwards from neural arch.
what is the cervical vertebrae?
extra large openings for blood and nerve channels to support animals’s head.
located in the neck.
what is the dorsal vertebrae?
located in the back.
tall spinous process and large rib articulation surfaces.
what is the sacral vertebrae?
located in the hips.
solid anchors for powerful leg muscles.
what happens when sacral vertebrae fuse with one another?
sacrum is formed.
what is the caudal vertebrae?
located in the tail.
what is underneath the caudal vertebrae bones?
chevrons.
what purpose do chevrons serve?
protect large blood and nerve channels.
support tail muscles.
what are gastralia?
smal ribs positioned across dino’s underbelly, underneath the ribcage.
what do dinosaurs, mammals, reptiles and amphibians belong to?
tetrapods.
what are tetrapods?
animals that evolve from ancient ancestors with four feet and limbs.
how are limbs of tetrapods connected to rest of skeleton?
limb girdles.
what do forelimbs connect to?
pectoral girdle.
what is the largest bone on each side of the pectoral girdle?
scapula.
what are hindlimbs connected to?
pelvic girdle.
what are the three bones that the pelvic girdle is composed of?
ilium, ischium and pubis.
what is the ilium?
upper hip bone where sacral vertebrae are fused.
what is the pubis?
below ilium, positioned in front of the ischium.
what is the ischium?
positioned behind pubis nearer the tail.
what is the acetabulum?
depression or hole in pelvic girdle where hind limb articulates.
what is the largest bone in the forearm?
humerus.
what are the bones between elbow and wrist?
radius and ulna.
what are bones in the wrist?
carpals.
what are the bones between wrist and fingers?
metacarpals.
what are finger bones called?
phalanges.
what is the largest bone in hindlimbs?
femur.
what are the bones between the ankles and toes?
metatarsals.
what are the bones in the toes called?
phalanges.
what impacts how the tetrapod moves?
limb proportions, or limb postures.
what happened when dinos walked?
only their toes touched the ground.
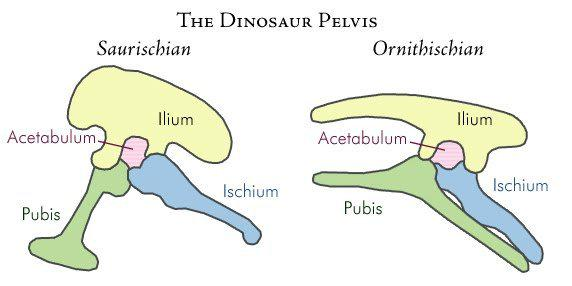
what are the two major groups of dinos?
saurischians and ornithischians.
what are saurischians?
pubis downward and forward towards ribcage.
lizard hipped.
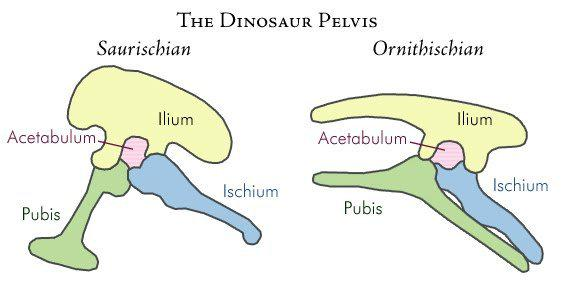
what are ornithischians?
special beak forming bone.
pubis extended downwards and backwards towards tail.
bird hipped.
what are the two groups of saurischians?
sauropodomorph and theropods.
what are sauromodomorphs?
large herbivores with elongated necks and small heads.

what was the early group of sauromodomorphs?
prosauropods.
what are prosaurpods?
first group of large bodied dinosaurs to evolve.
what are the later group of sauropodomorphs?
sauropods.
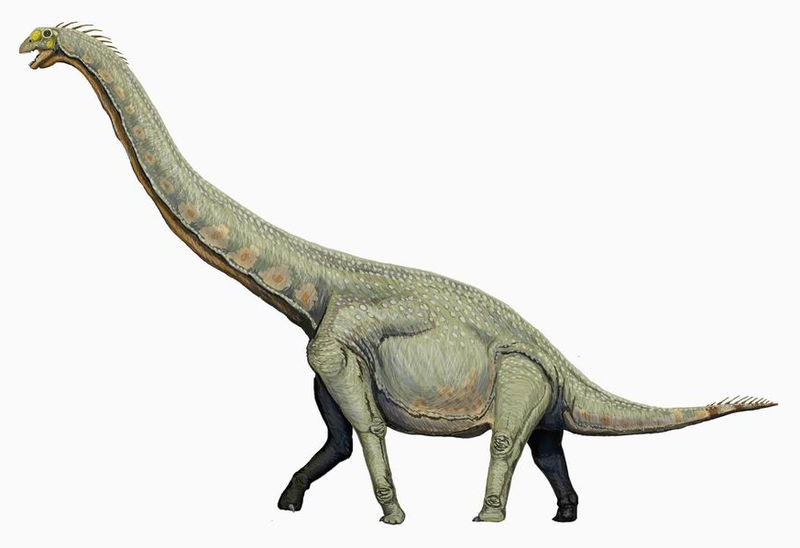
what are sauropods?
largest animals to ever walk the earth.
column like legs.
vertebrae: filled with complex air sacks which reduced weight.
teeth: simple and peg like.

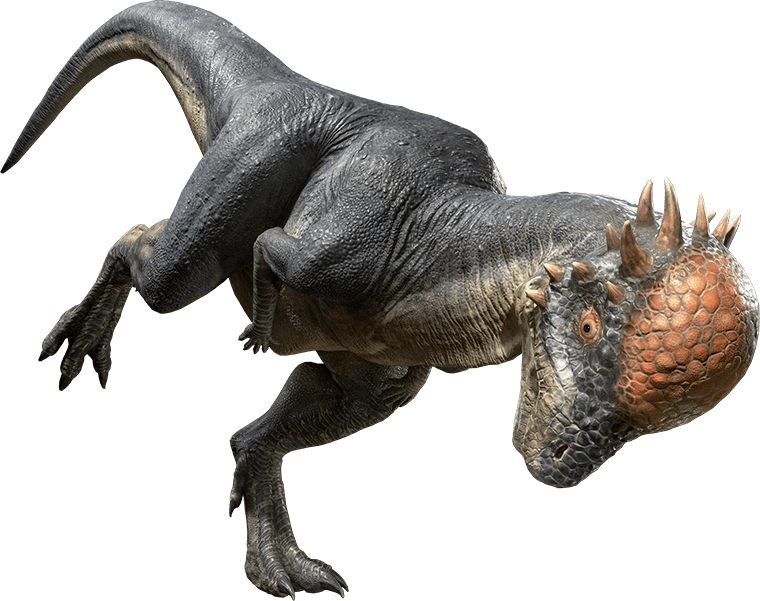
what are theropods?
bipedal carnivorous saurischians.
teeth: serrated and blade like and sharp hooked claws.
why do ornithischians have backwards pe
what do all ornithischians possess?
beaks: herbivorous adaptation that helped chop off large mouthfuls of vegetation.
what are the five major groups of ornithischians?
ornithopods, pachycephalosaurs,
what are ornithopods?
lacked armour and walked bipedally or assumed bidepal stance.
ex. small antelope sized dinos.
what are the sub groups of ornithopods?
iguanodonts and hadrosaurs.
what are iguanadonts?
large ornithopods with spike shaped claw on each hand.

what are hadrosaurs?
duck billed dinos.
elaborate boney crests, large beaks in front of their mouth.
dental batteries that are dense and tighly packed (side to side and backward and forward).
what are pachycephalosaurs?
bipedal with short arms, stout and strong tails, armoured skull.
thick, domed skull roofs and backwards pointing horns.

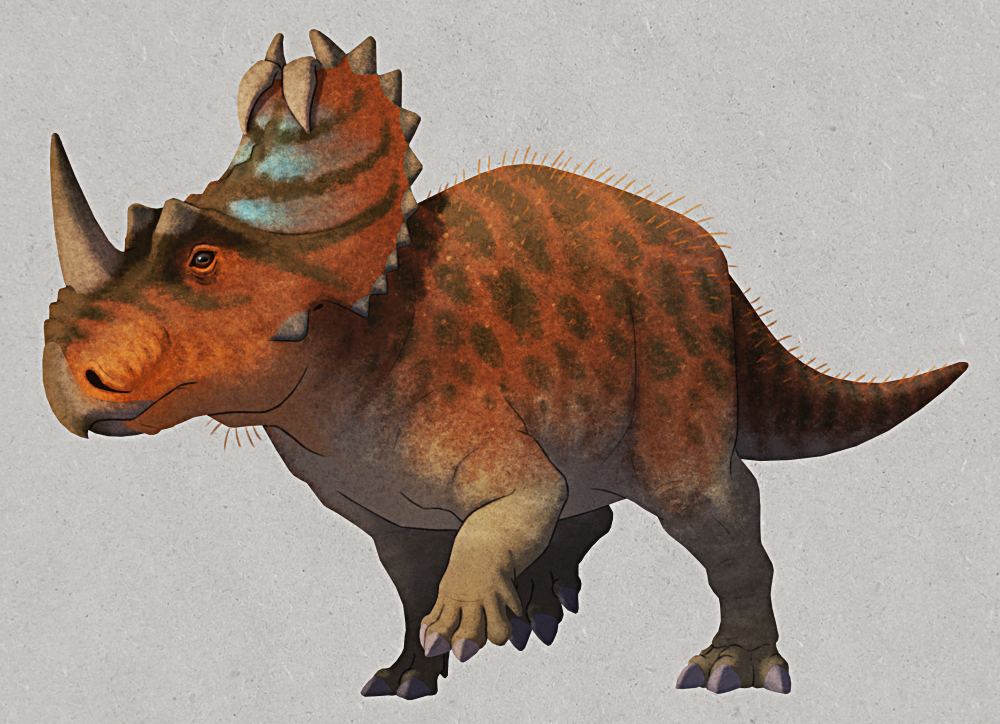
what are ceratopsians?
large parrot like beaks and skulls that expanded in the rear.
large bony frill or neck shield and large horns and dental batteries.
quadrupedal and short tails.

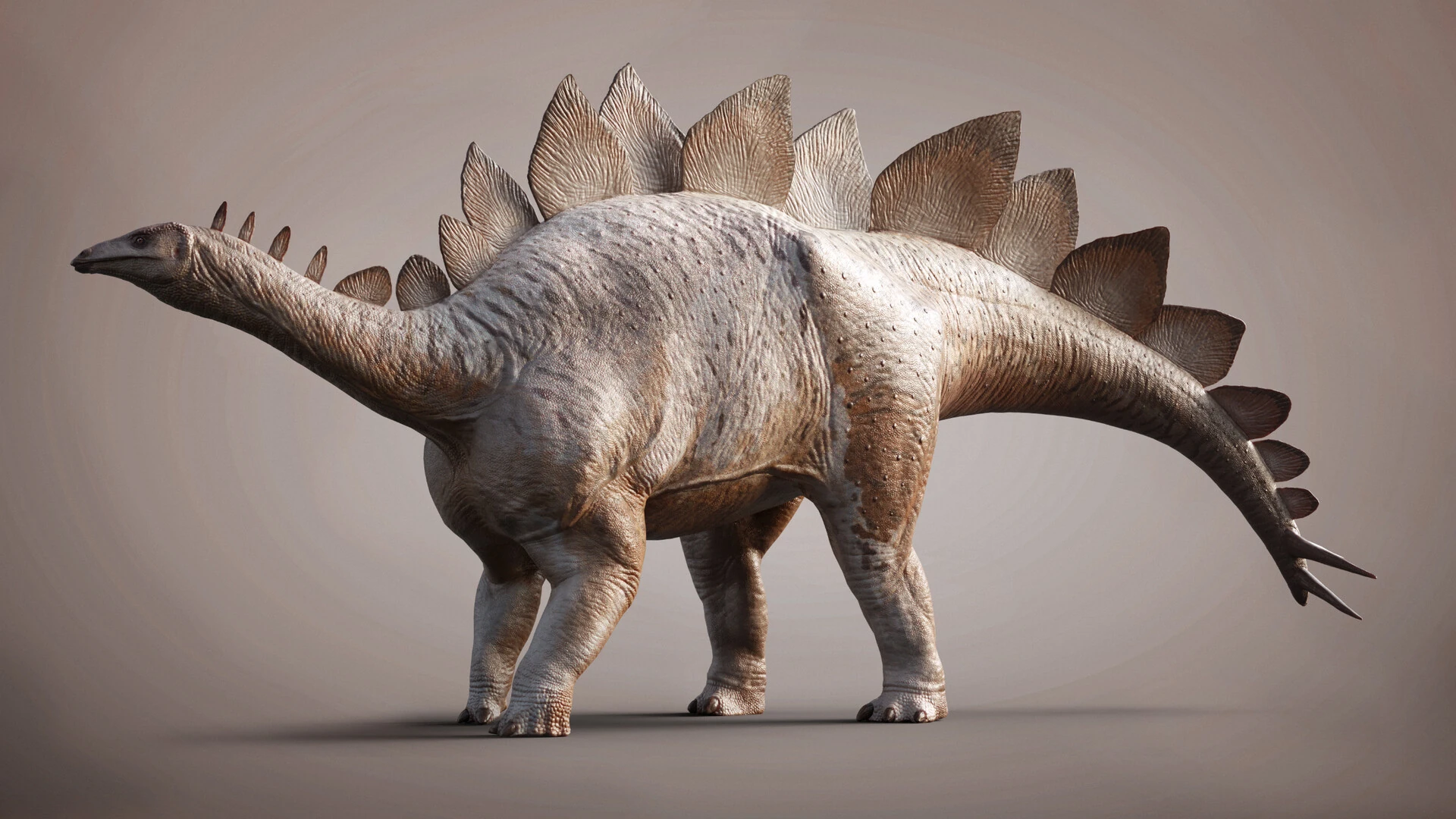
what are stegosaurs?
quadrupedal dinosaurs with rows of projecting osteoderm plates down back and tail.
front legs shorter than back, enabled them to stand on hind legs.

what are osteoderms?
bones that develop with skin and common component of animal armour.
what is an anklyosaur?
most heavily armoured dinosaur.
quadrupedal with short legs and wide ribcages.
spikey back and club at end of tail.

what is an integument?
body covering.
what is the first mummified dinosaur?
hadrosaur.
what is keratin?
tough but flexible material composes hair, feathers, fingernails, claws, beaks and horns.
what is the small theropod specimen with fossil feathers called?
sinosauropteryx.
what dino was first reported to have feathers?
yutyrannus: largest known feathered dino.
what dinosaur had feathers and filamentous integument?
theropod dinosaurs.
what features did ceratopsians psittacosaurus have?
long, stiff bristle like structures on tail.
what was the feature of tianyulong ceratopsian?
covered in long filaments over most its body.
what was the features of kulindadromeus?
bristle like filaments but branching, feather like structures.
what kind of osteoderms did anklylosaurs have?
armour and tail club ends.
what kind of osteoderms did stegosaurs have?
plates an spikes along back.
what kind of osteoderms with sauropods have?
mineral reserves.
what are melanosomes?
pigament cells within feather.
influence shape and arrangment.
what do black and gray melanosomes result from?
long and narrow melanosomes.
what do brown and reddish melanosomes result from?
short and wide melanosomes.
what do white feathers indicate?
no melanosomes.
what do shiny black and blue feathers indicate?
narrow melanosomes, aligned in same direction.
what is a scipionyx?
preserves mineralized remains of trachea, throat and intestines.