hgap AP units 1-2
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PLEASE 5!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Friction of distance
It suggests that interaction tends to decline with increasing distance. It encompasses not only geographic distance but also costs
Geographic Information System (GIS)
for mapping, analyzing, and managing spatial data. It is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, manage, and analyze spatial or geographic data.
Perceptual/ vernacular region
an area defined by people's feelings and attitudes towards it, rather than by strictly defined boundaries.
Reference maps
are used to show the locations of various features and provide a general overview of the geography of an area.
Remote sensing
the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact, typically through satellite or aerial imagery.
Satellite imagery
captured images of the Earth's surface taken from satellites, used in remote sensing to analyze and monitor environmental conditions.
Satellite navigation system (GPS)
A system that uses satellites to determine the precise location of a receiver on Earth by triangulating signals.
Aerial Photography
the taking of photographs from an aircraft or drone, often used in remote sensing to collect data about the Earth's surface and monitor changes in the environment.
Thematic maps
maps that emphasize a specific subject or theme, often used to visualize spatial data related to certain factors such as population, climate, or land use.
Time-distance decay
refers to the principle that the interaction between two places decreases as the distance between them increases, affecting how spatial phenomena spread.
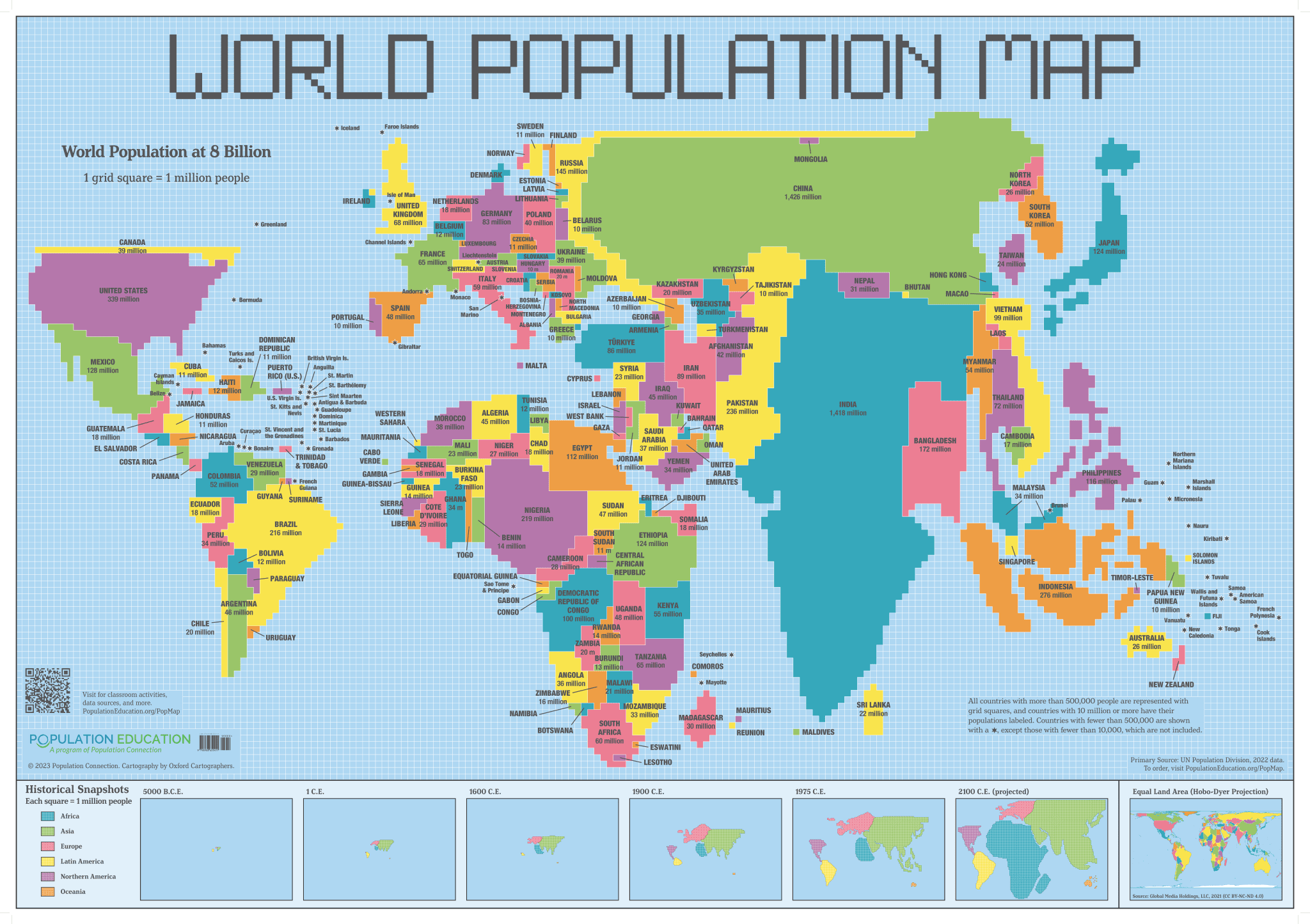
Distorts the size of places to represent a value
Cartogram map
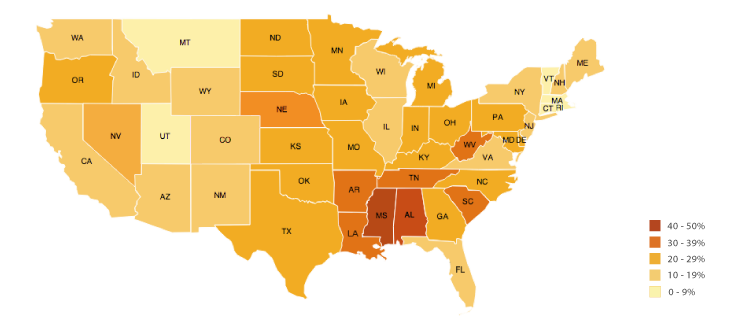
Uses different shades or colors to show data values across areas.
Choropleth map
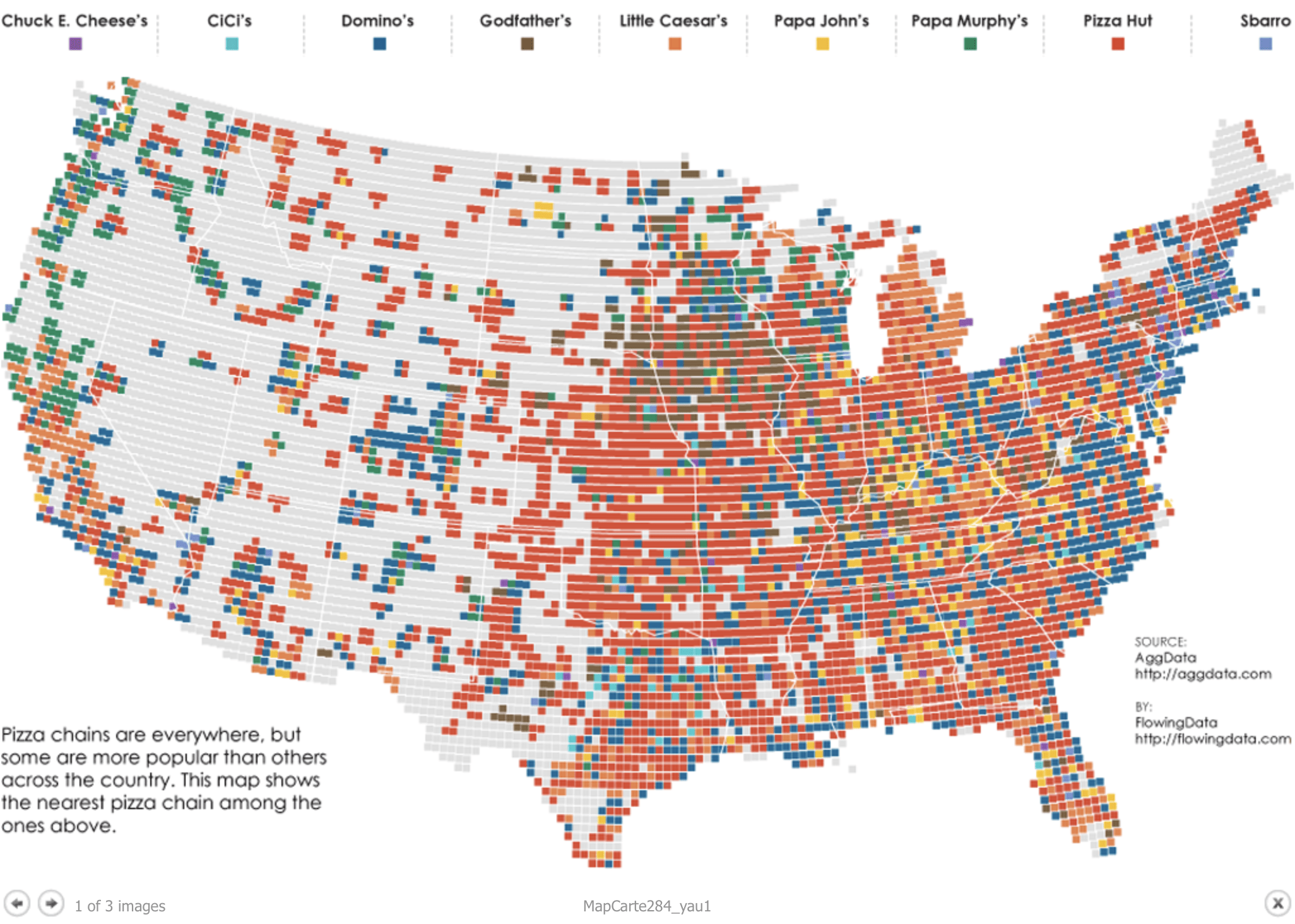
Uses dots to show frequency of a feature
Dot Density map
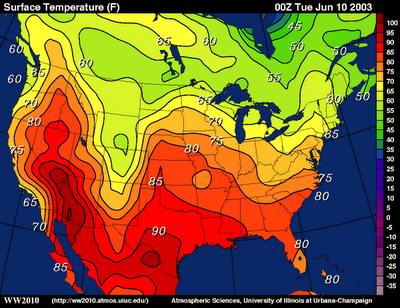
Uses lines to connect points of equal value, like elevation or temperature.
Isoline map
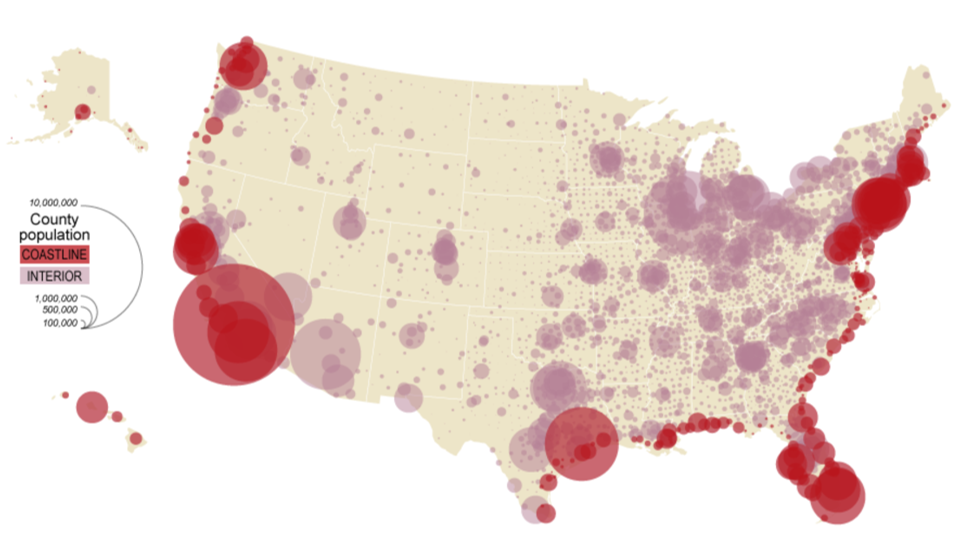
Uses different-sized symbols (like circles) to show how much of something is in a place.
Proportional Symbol Map
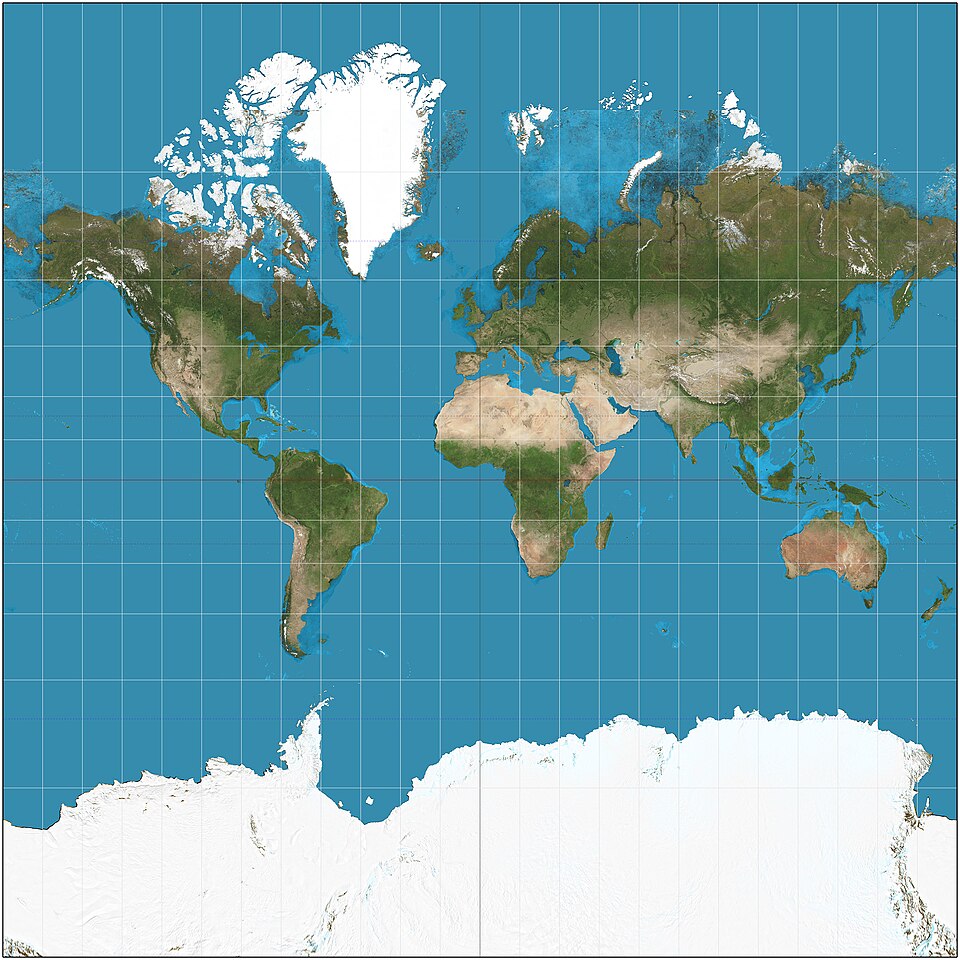
Preserves shape and direction, useful for navigation. Distorts size, especially near the poles
Mercator map
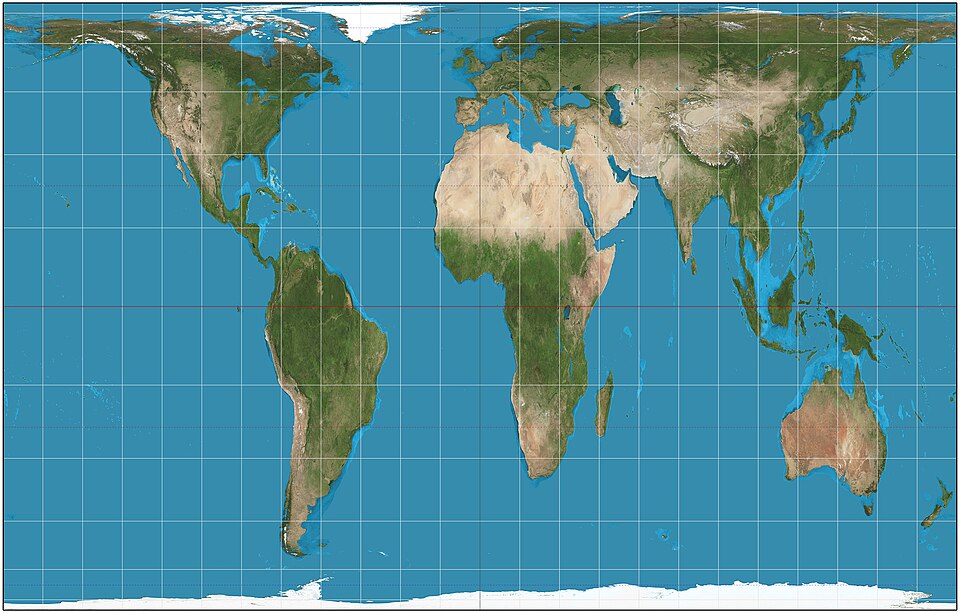
Preserves area, so all countries are shown in correct size. Shapes look stretched, especially near the equator and poles.
Galls Peters map
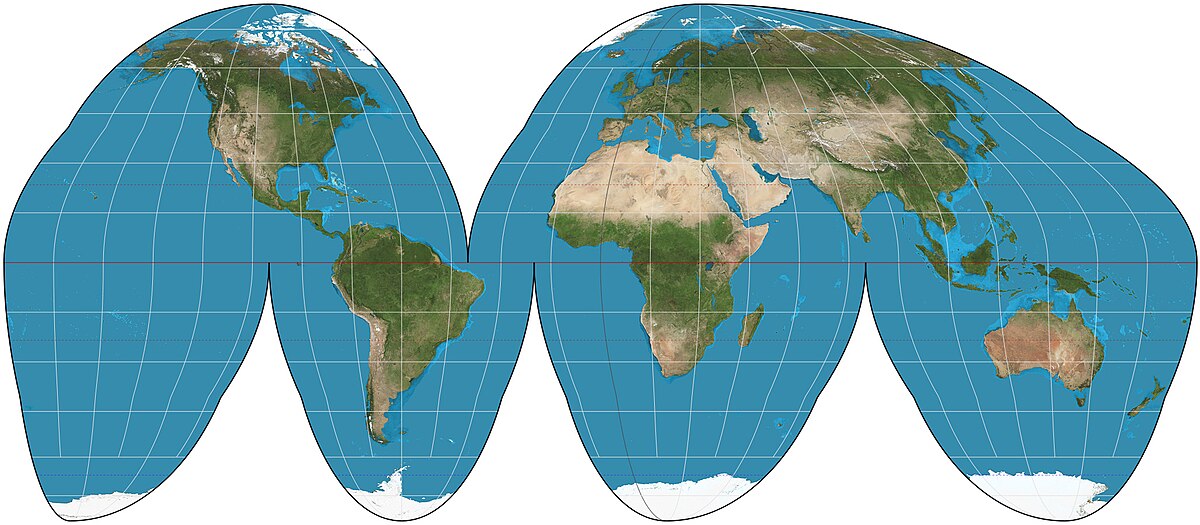
Reduces distortion in land size by “cutting” oceans. Good for land-focused maps
Goode map
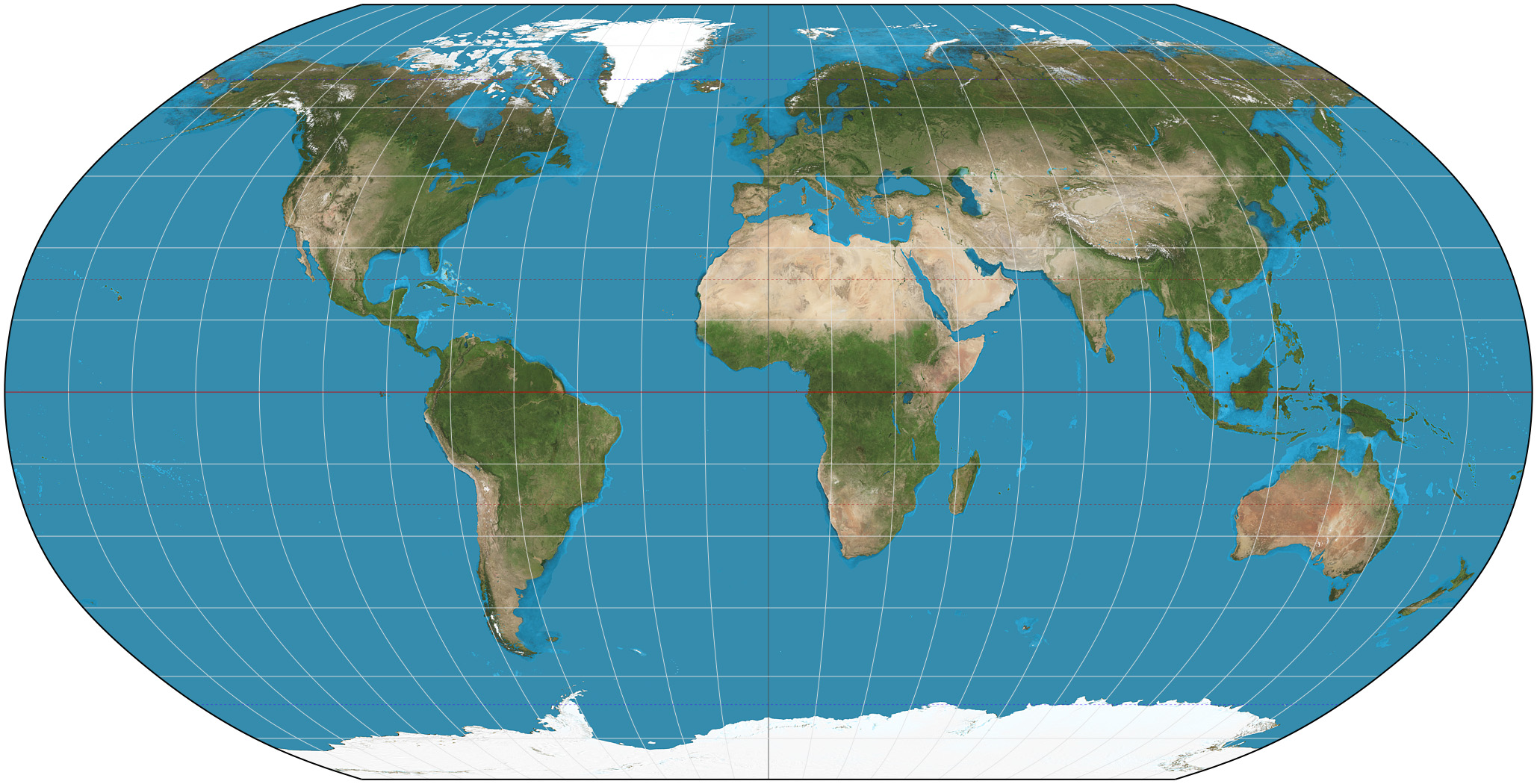
Keeps the curvature of the Earth. Everything is distorted in small areas.
Robinson map
Counterurbanization
The demographic trend of people moving from urban areas to rural areas, often seeking a better quality of life or lower cost of living.
Cyclic movement
A type of migration that involves repeated movement between locations, often for seasonal employment or migration patterns.
Ecumene
The permanently inhabited areas of the Earth, focusing on regions where humans have established a sustained presence and live regularly.
Ehrlich Theory
The theory proposed by Paul R. Ehrlich that suggests population growth will outpace food production, leading to widespread famine and resource depletion. (like Mathusian theory!)
Eugenic Population Policies
Policies aimed at controlling the reproduction of individuals considered to be 'desirable' or 'undesirable' to improve the genetic quality of a population.
Internal migration
The movement of people within a country, often from rural to urban areas, in search of better employment opportunities and living conditions.
International migration
Interregional migration
The movement of people between different regions within a country, often driven by factors such as economic opportunities, lifestyle changes, or environmental conditions.
Intraregional migration
The movement of people within the same region, typically from one city or town to another, often influenced by factors like housing availability and local job markets.
Remittances
Monetary transfers sent by migrants to their home country, typically to support family members or communities.
Transhumance
The seasonal movement of people and their livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures, typically practiced in mountainous regions.
Transnational migration
The movement of individuals across national boundaries, often for reasons such as employment, education, or escaping conflict, while maintaining ties to their home country.