Quiz 1 Bio
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Atomic number 1 atomic mass 1
Hydrogen
Atomic number 2 atomic mass 4
Helium
Atomic number 5 atomic mass 10
Boron
Atomic number 6 Atomic mass 12
carbon
Atomic number 7 atomic mass 14
Nitrogen
Atomic number 8 atomic mass 15
Oxygen
Atomic number 9 Atomic mass 18
Fluorine
Atomic number 11 atomic mass 22
Sodium
Atomic number 19 Atomic mass 39
Potassium
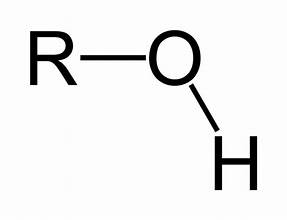
Hydroxyl group, a functional group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, commonly found in alcohols and sugars.
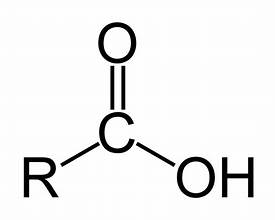
Carboxylgroup, a functional group consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group, important in organic acids.
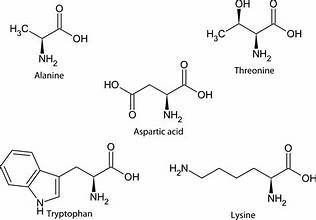
Aminoacid, the building blocks of proteins, containing an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain.
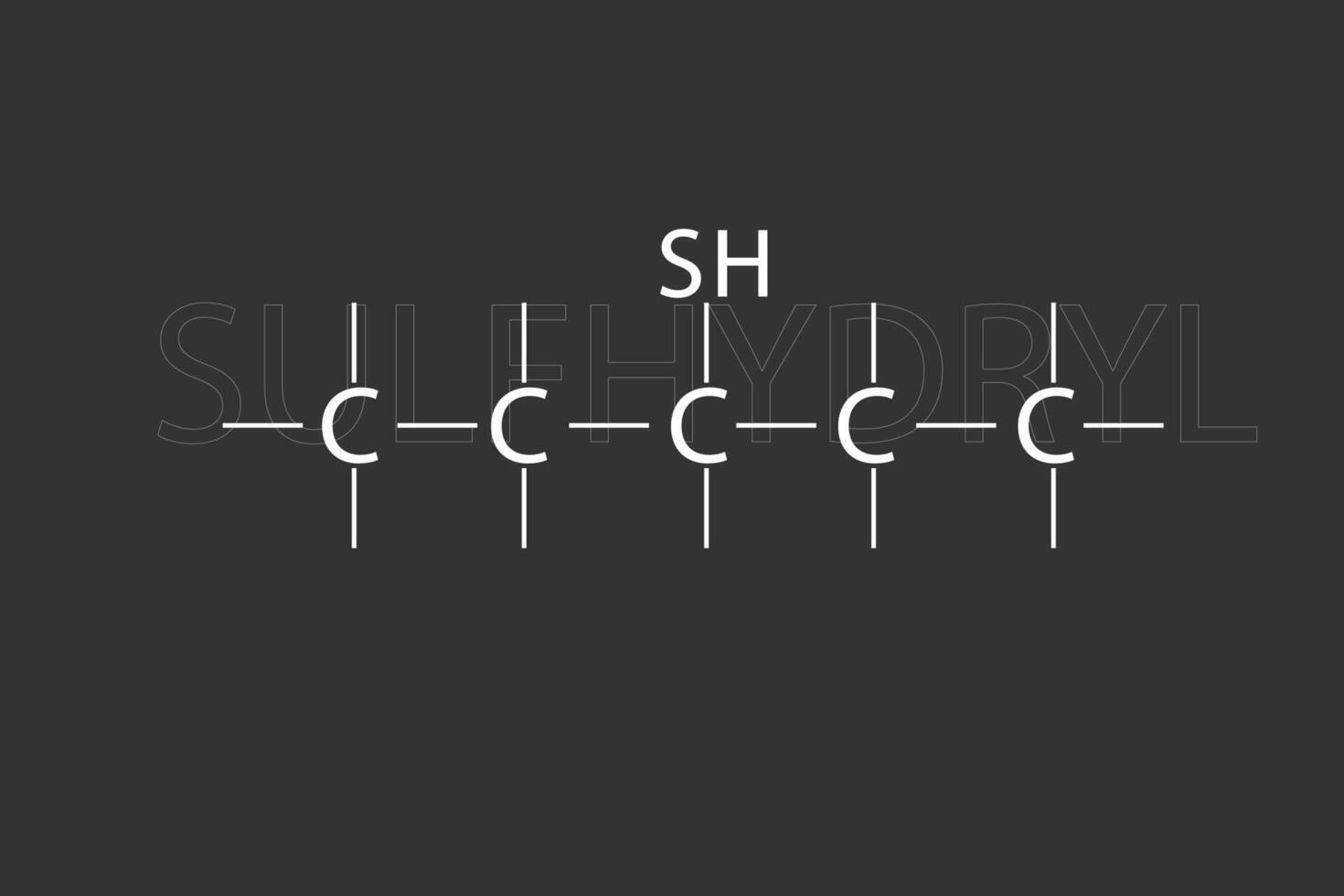
Sulfhydrylgroup, a functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, important in protein structure and function.
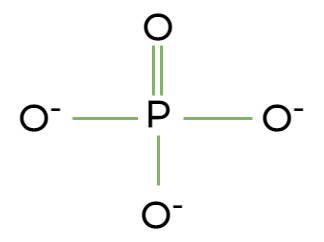
Phosphategroup, a functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, crucial in energy transfer and nucleic acids.