U3 AOS 2: Human Resource Management
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
How can HR management help meet business objectives?
HR management ensures staff are appropriately trained and motivated to pursue objectives for the business
e.g. good training and regular performance appraisals
better customer service
more profits
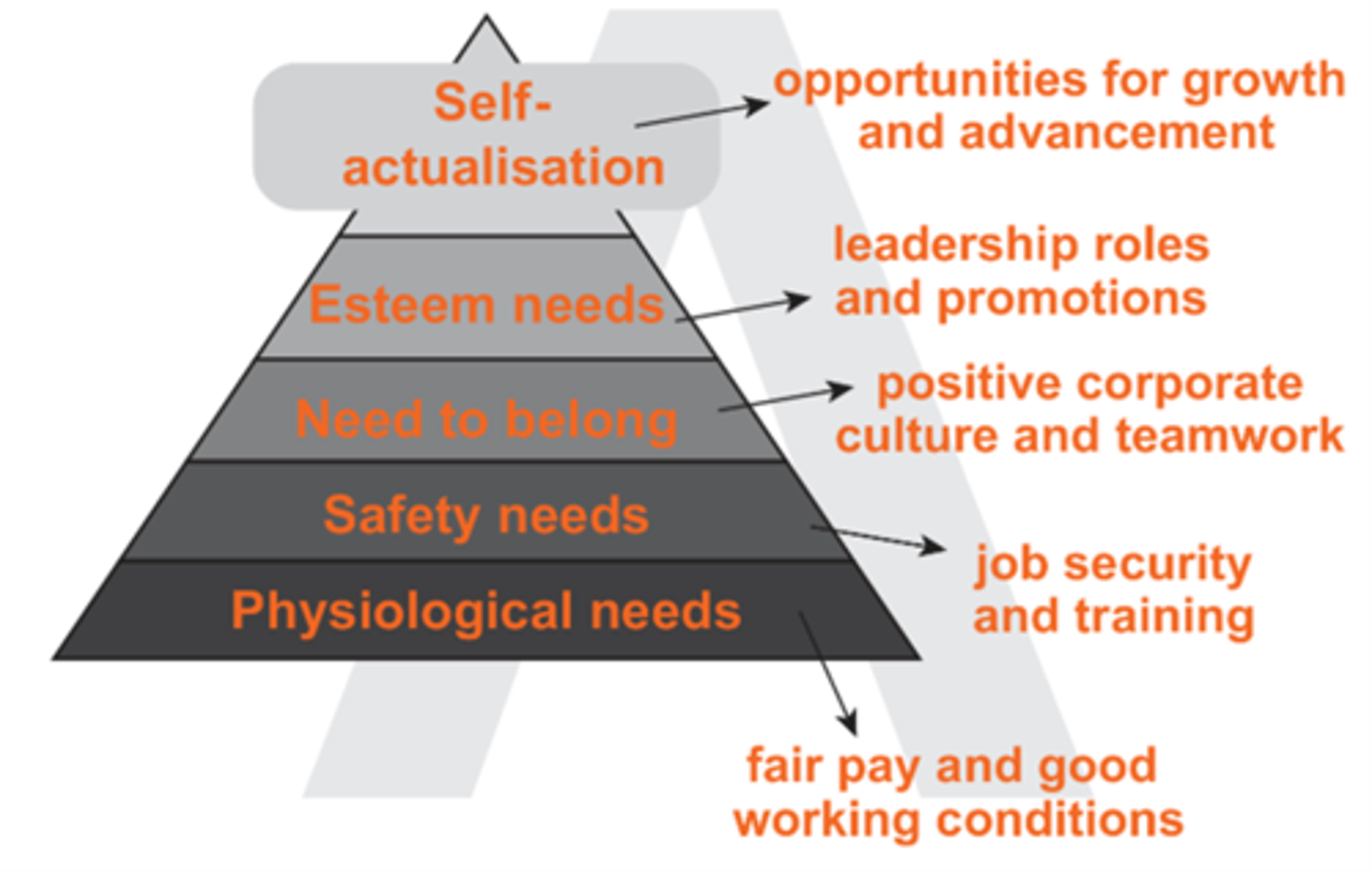
What are the 5 levels in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, and how can a business support each one?
What are the requirements for motivating goals according to Locke and Latham’s Goal Setting Theory?
· Specific, clear, and explicit
(e.g. ‘increase sales by 5% this quarter’)
· Challenging but not overwhelming
(e.g. increase sales by 5% not %500!)
· Set up by employees and employers together
(i.e. not determined autocratically with no employee input)
· Accompanied by advice and feedback from management
(i.e. ongoing support and recognition of achievement)
What are the components of Lawrence and Nohria’s Four Drive Theory, and how can each of them be met by a business?
1. Acquire: drive to obtain material goods/status met through performance-based promotions
2. Bond: drive to connect with others, met through good interpersonal management and fostering positive employee relationships
3. Learn: drive to become more skilled, smart or creative, met through varied, challenging opportunities and rewarding upskilling
4. Defend: drive to protect self/others from threats or change, met by maintaining supporting environment and open communication
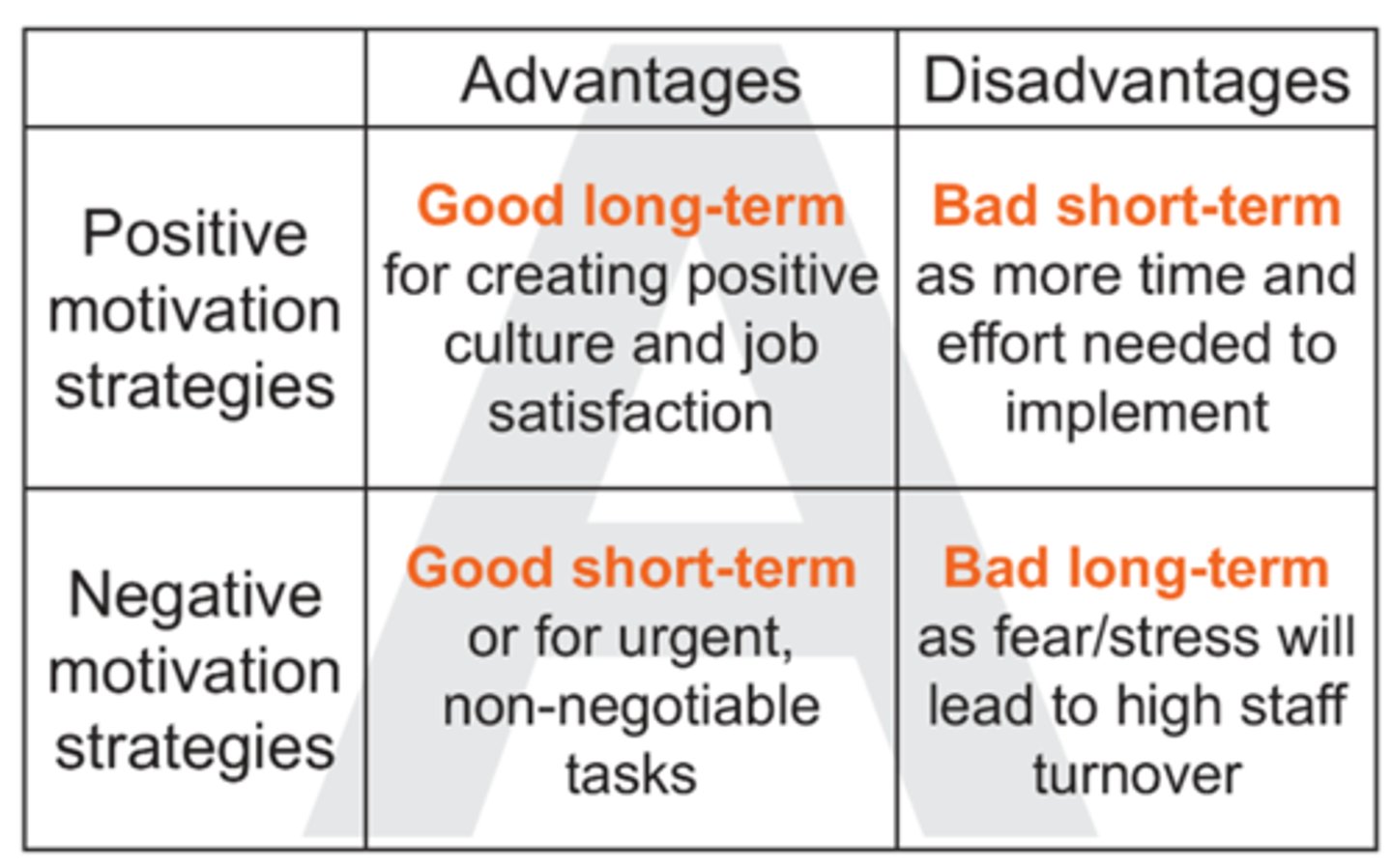
Name the 5 motivation strategies and explain their long-term positive effects.
1. Performance related pay: drive to obtain material goods/status met through performance-based promotions
2. Career advancement: drive to connect with others, met through good interpersonal management and fostering positive employee relationships
3. Investment in training: drive to become more skilled, smart or creative, met through varied, challenging opportunities and rewarding upskilling
4. Support strategies: drive to protect self/others from threats or change, met by maintaining supporting environment and open communication
Evaluate motivation strategies
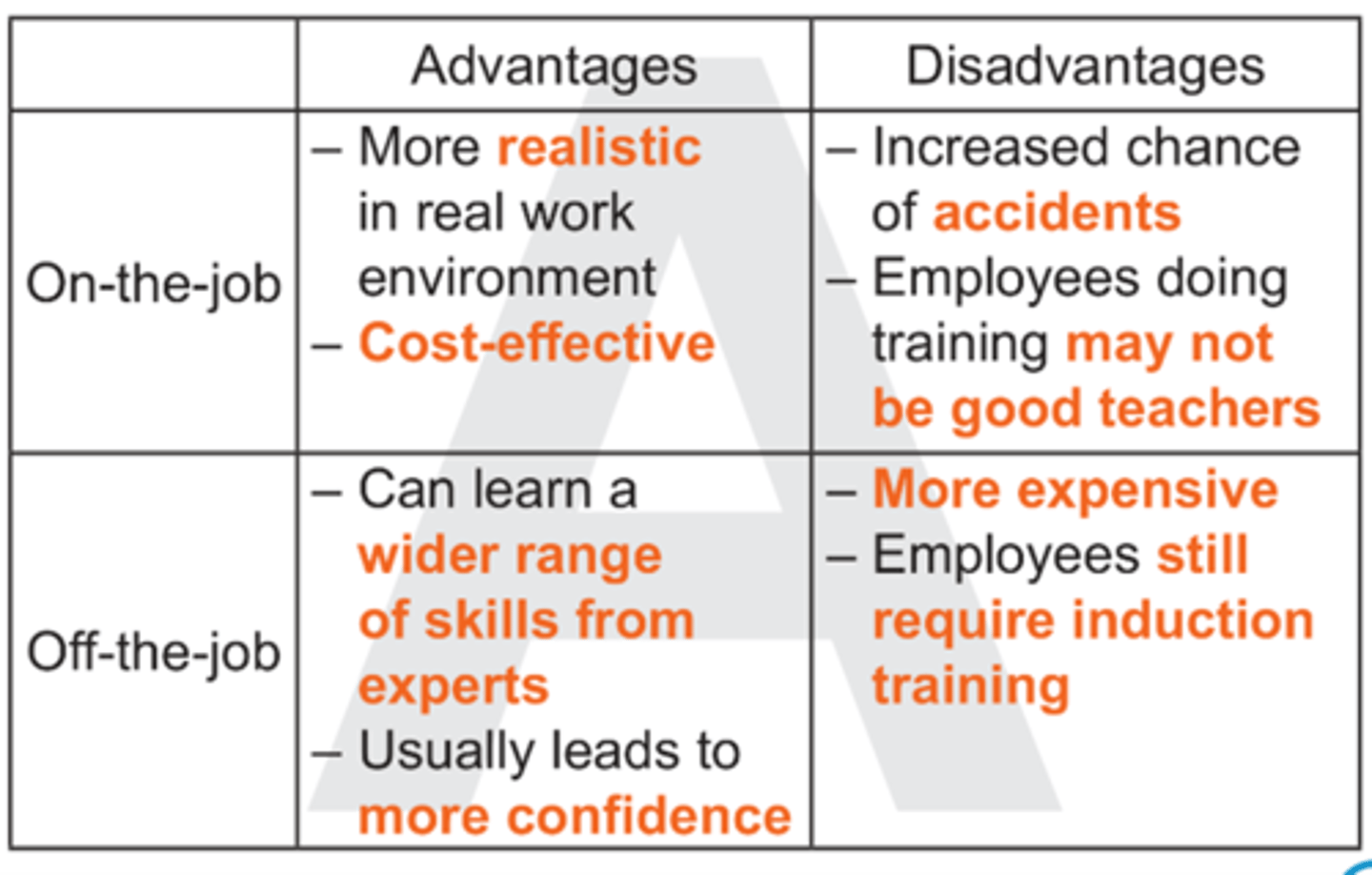
Evaluate on-the-job and off-the-job training options.
What are the 4 performance management strategies that HR managers can use?
1. Management by objectives: create, agree to, and monitor goals with employees
2. Appraisals: formal assessment of performance to give feedback and identify areas of improvement
3. Self-evaluation: employee rates their performance to compare with manager’s assessment
4. Employee observation: manager discreetly watches employee’s work habits
What are the different types of voluntary and involuntary termination?
Voluntary: retirement, resignation, nomination (e.g. if business is downsizing, an employee may volunteer)
Involuntary: dismissal, redundancy
How does the role of unions differ from that of HR managers in the workplace?
Unions = represent employees, campaigning on their behalf for better conditions and pay, ensuring employers abide by agreements
HR managers = represent the business, negotiating disputes and agreements between employees and employers
What requirement do awards and workplace agreements have to adhere to?
· Must meet the 10 National Employment Standards set by the Fair Work Act 2009
· Must pass the no disadvantage test
· Negotiations must be in good faith
What is the difference between industry-wide awards, collective agreements, and individual contracts?
Industry-wide awards = legally enforceable conditions of employment (e.g. pay, length of shifts)
Collective agreements = negotiation between employees/unions and an employer
Individual contracts = agreement between an employer and a single employee
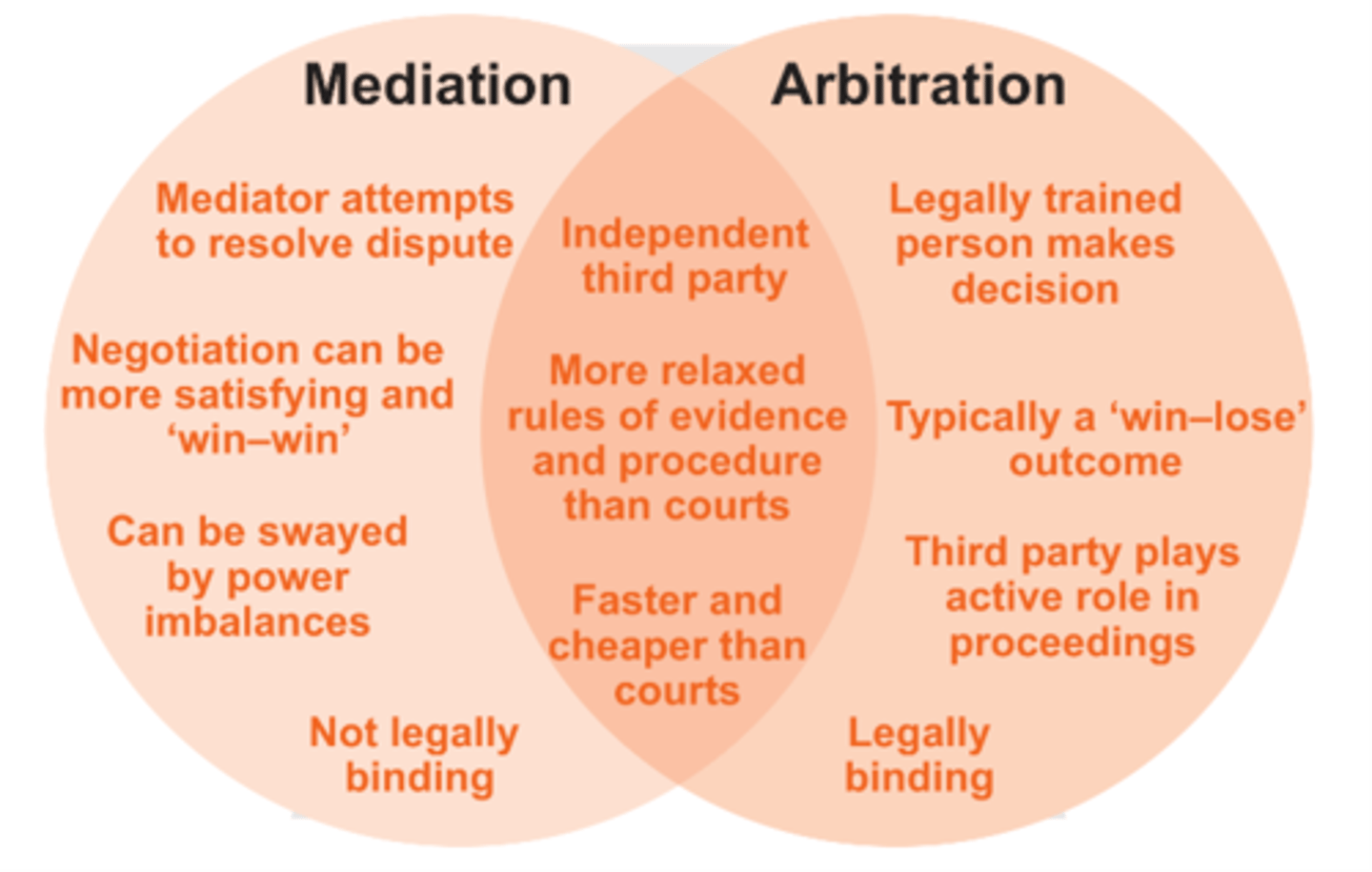
Compare and contrast mediation and arbitration as dispute resolution methods.
appraisal
the formal assessment of how efficiently and effectively an employee is performing their role in the business
arbitration
a means of dispute resolution involving an independent third party hearing both both arguments in a dispute and determining the outcome
award
a legally binding document determined by the Fair Work Commission that sets out minimum wages and conditions for whole industries or occupations
career advancement
the assignment of more responsibilities/authority to employees - or the promotion of employees to positions that bring rewards such as increased salary, increased responsibilities
collective bargaining
a process that occurs when a third party participates in the resolution of a dispute and attempts to resolve the differences through discussion
development
the process of preparing employees to take on more responsibilities in the future, acquiring better knowledge and skills, and gaining more experience
dismissal
occurs when the behaviour of an employee is unacceptable and a business terminates their employment
dispute
a result of disagreements or dissatisfaction between individuals and/or groups
employee observation
a strategy where a variety of opinions on the performance of employees is sought with the aim of arriving at a more comprehensive picture of past and current performance
enterprise agreement
an agreement about pay and conditions made at workplace/enterprise level and negotiated between groups of employees (or represented by their union) and employees
entitlement considerations
the rights to benefits that employees have when leaving the workplace, either on a voluntary or an involuntary basis
Fair Work Commission
Australia's national workplace relations tribunal. Its role is to assist employees and employers to maintain fair and productive workplaces. The FWC is an independent body that operates under the Fair Work Act 2009.
Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's sequence of human needs in order of their importance
Human Resource Management
the effective management of the formal relationship between the employer and employees
Human Resource Manager
coordinates all the activities involved in acquiring, developing, maintaining and terminating employees from a business's human resources
investment in training
the direction of finances, or resources such as time, into the teaching of skills to employees
lockout
occurs when employers close the workplace for a period of time as a means of applying pressure to employees during a period of industrial conflict
Management by Objectives
a process by which management and employees agree on a set of goals for each employee, with these goals all contributing to the objectives of the business as a whole
mediation
The confidential discussion of issues in a non-threatening environment, in the presence of a neutral, objective third party who helps the parties in dispute to work towards an agreement, but does not offer suggestions or advice
motivation
the individual internal process that energizes, directs, and sustains behavior; the personal "force" that causes you or me to behave in a particular way
need
a personal requirement
negotiation
a method of resolving disputes whereby discussions between the parties result in a compromise and a formal or informal agreement about a dispute
off-the-job training
occurs when employees learn skills in a location away from the workplace. It usually involves sending individuals or groups of employees to a particular specialised training institution (such as a university or TAFE college).
on-the-job training
occurs when employees learn a specific set of skills to perform particular tasks within the workplace. This training usually occurs in the working environment, and uses the equipment, machinery and documents that are present in that workplace.
penalty rates
additional wages paid to employees who work outside of normal working hours
performance management
a focus on improving both business and individual performance through relating business performance objectives to individual employee performance objectives
performance related pay
the monetary compensation provided to employees relative to how their performance is assessed according to set standards
productivity
a measure of performance that indicates how many inputs it takes to produce or create an output
redundancy
occurs when a person's job no longer exists, usually due to technological changes, a business restructure or a merger or acquisition
renumeration
payments made to employees for work or a service performed
resignation
the voluntary ending of employment by the employee 'quitting' their job
retirement
occurs when a person decides to give up full-time or part-time work and no longer be part of the labour force
sanction
a form of penalty of discipline imposed on an employee for poor performance
self-evaluation
a process whereby employees carry out a process of self-assessment, based on a set of agreed criteria
strike
occurs when employees withdraw their labour for a period of time in pursuit of improvements in their employment conditions
support
the assistance or services (such as counselling and mentoring) provided by the business to help employees cope with difficulties that may impede their work performance
termination
the ending of the employment of an employee
trade unions
organisations formed by employees in an industry, trade or occupation to represent them in efforts to improve wages and the working conditions of their members
training
the process of teaching staff how to do their job more efficiently and effectively by boosting their knowledge and skills
transition considerations
issues relating to the process of changing from one job to another or from one set of circumstances to another
unfair dismissal
when an employee is dismissed because the employer has discriminated against them in some way, such as firing someone because she is pregnant
workplace relations
the interactions between employers and employees, or their representatives, to achieve a set of working conditions that will meet the needs of employees, as well as allowing the business to achieve its objectives