Renal Final 2.1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
what does an increased RBF cause in the kidneys? what is the compensation?
inc. RBF → inc. GFR + inc. O2 delivery → inc. Na load + RA → inc. O2 demand → m. hypoxia
inc. EPO + dec. RBF (to conserve energy)
why does an increase in Na RA result in a depletion of renal O2 levels?
inc. Na RA @ mTAL → inc. Na/K ATPase → inc. O2 demand in hypoxic m.
mTAL → site for ischemic injury
what would a partial loss of nephrons cause?
hypertrophy of remaining nephron
inc. GFR per nephron
inc. Na RA
inc. O2 demand
inc. risk of AKI + ischemia
why is the inner medulla hypoxic? how does this contribute to concentrated urine?
countercurrent XC: (+ low RBF → osmotic gradient)
O2 out of desc. c. → into asc. c. (doesn’t reach deeper tissue)
loses H2O + gains solute desc. → loses solute + gains H2O asc. (from TDL (from IS) + CD) (traps solute)
hypoosmotic in TAL → hyperosmotic in CD → conc. urine
via H2O RA (AQP, ADH, VR)
how does a high Na filtered load cause medullary hypoxia?
high Na at PCT → more O2 consumption at cortex → less O2 at medulla
high Na in filtrate still after PCT → higher demand on mTAL
high NaCl at medulla → TGF → VC AA (dec. O2 supply)
what factors control RBF levels?
myogenic autoregulation: inc. stretch/BP → AA constriction (opp. true too)
tubulo glomerular feedback: MD @ end of TAL sense NaCl
vasoconstrictors + dilators
what is the difference of vasodilator and vasoconstrictor effect on RBF?
dilators → inc. O2 supply + dec. O2 demand
constrictors → inc. O2 demand + dec. O2 supply
what are the vasodilator stimuli?
NO
adenosine (A2AR)
PG
what is the effect of NO on RBF? what occurs of NO synthase is inhibited?
higher in medulla
dec. NKCC2 @TAL (dec. Na RA) + CD → dec. O2 demand
NO synthase inhibition → dec. perfusion → dec. mPO2 (+ inc. NKCC2) → ischemia
what are the vasoconstrictor stimuli?
Ang. II (AT1)
adenosine (A1AR)
endothelins
NE
vasopressin (ADH)
what is the effect of Ang II on RBF?
VC EA → inc. GFR BUT dec RBF @ cortex
inc. Na RA → inc. O2 demand
@ high conc. also VC AA → dec. GFR
indirect VD via inc. PG + NO @ medulla
balance of VD + VC prevents ischemic injury
what is the relationship between adenosine and RBF?
high NKCC2 (via high NaCl) → ATP cons. inc. = inc. adenosine by MD
TGF response (dec. GFR) → VC AA + inhibits renin
stimulates Na RA @ c. PCT (reduce load) but inhibit @ m. TAL (conserve O2)
what is the difference between adenosine (A1AR) and (A2AR)?
A1AR: (superficial)
AA constrict via high NaCl→ dec. GFR + dec. RBF
inc. Na RA @cPCT
A2AR: (jxtmed)
dilates EA → inc. RBF BUT dec. GFR
dec. Na RA @mTAL
what effects the regional pO2?
rate of O2 delivery
rate of O2 consumption
rate of O2 removal → via O2 shunting → hypoxia if dec. RBF
what can increase O2 consumption/regional pO2?
inc. GFR → inc. O2 cons.
inc. diet Na/diuretic (acetazolamide) → inc. O2 demand @ TAL
inc. glucose filtered load (via DM) → inc. RA → inc. O2 demand
what changes in blood property can effect pO2?
alkalosis → inc. Hb affinity + dec. O2 dissociation
fibrosis → dec. O2 diffusion
how does pregnancy cause dysregulation? what factors can cause ischemia?
inc. VD (relaxin + progesterone) → inc. GFR + RBF → inc. O2 demand
ischemia: → proteinuria + dec. RBF
vol. depletion
preeclampsia (HTN + endothelial swelling)
HELLP (hemolysis, ele. liver enzyme, low platelet) → renal insuff.
how does strenuous exercise cause dysregulation?
compound hypovolemia (via sweating) → act. SNS
VC (via NE) → blood shunt to muscle → dec. RBF
act. RAAS → VC, Na retention, inc. fluid vol. (HTN)
inc. Na RA → inc. O2 demand
how does high altitude cause dysregulation?
acute:
resp. alk. → diuresis (HCO3, H2O, Na sec.) → blood conc. → inc. Hb (dec. O2 diss.) + dec. RBF
chronic:
inc. NE → VC (dec. RBF → dec. GFR → dec. O2 cons.)
inc. EPO (inc. Hb → thicker blood) → fluid retention → inc. Na RA
how does blood glucose cause dysregulation? what occurs if there are SGLT2 inhibitors?
diabetes → inc. Na RA @ PCT via SGLT2 → hypertrophy (Na backflow → inc. mTAL load) + inc. O2 demand → AKI
SGLT2 inhibitor → glycosuria + natriuresis (dec. Na RA @ PCT)
inc. Na to MD → TFG → VC AA → dec. RBF (dec. O2 demand)
how do NSAIDs cause dysregulation?
inhibit COX → dec. PG (VD)
inc. unopposed VC → dec. RBF → ischemia @ mTAL
how do diuretics (acetazolamide + furosemide) cause dysregulation?
acetazolamide (CA inhibitor) → inhibit cPCT Na RA (via NHE3) → inc. Na to mTAL → inc. O2 demand → AKI
furosemide (loop diuretic) → dec. Na RA @ mTAL (via NKCC2)→ protection (inc. Na @ MD → AA constrict → dec. GFR → dec. O2 demand)
how does low-dose dopamine cause dysregulation? what does a higher dose cause?
lower dose (acts on DA-1 R) → inc. perfusion
AE VD → inc. RBF
inhibits NHE3 (dec. Na RA @ PCT) → natriuresis/inc. load → inc. O2
high dose → VC → dec. RBF
what is the multi hit for dysregulation? what does it cause?
dec. perfusion
diabetes
risky procedures
tubulo interstitial disease
cause → VC, tub. toxicity, oxidative stress
what increases RBF post surgery?
ANP → VD AA /VC EA + dec. RAAS → inc. RBF + natriuresis
DA-1 agonist (VD)
furosemide → block NKCC2 → VD AA
ACE inhibition → dec. Ang II (VC)
corrective VC via adrenergic agonists → dec. RBF + inc. O2
what is renal clearance defined as?
rate at which plasma volume is cleared of a substance
(urine conc. x urine vol.)/plasma conc.
what is GFR equivalent to?
renal clearance
Kf (SA+ perm) x NFP
UxV/P
what substances are eliminated only via glomerular filtration and can assess GFR? Describe both?
inulin → exactly, freely filtered + NO degradation/sec./RA
creatinine → almost equal, secreted (so less accurate)
what decreases creatinine clearance?
age
dec. muscle mass
sclerosis → dec. RBF → dec. GFR
low cardiac output
when does clearance of creatinine increase? how is this different from inulin?
inc. GFR (dec. P conc.) → sec. inc. → inc. Cr Cl
inulin NOT impacted by P conc. (only filtered)
how do GFR changes impact plasma creatinine?
if GFR compromised → inc. creatinine in plasma
inc. GFR → inc. clearance → dec. creatinine in plasma
how to calculate free water clearance? what do the values indicate?
CH2O = U (urine flow rate L/day) x (1 -(Uosm/Posm)) (clearance of osmoles)
gain/loss of H2O via excretion of dilute/conc. urine
(-) → urine hypertonic/hyperosmolar (conc.)
(+) → urine hypotonic (e.g diabetes) (dilute)
what is the filtration fraction (FF)?
portion of RPF that is filtered via glomerular filtration (20%)
GFR/RPF
how does PAH calculate RPF? what is the reasoning behind the actual RPF value?
effective RPF → CPAH
actual RPF → CPAH/0.9 (renal clearance of PAH is 90% of RPF since PCT secretes PAH)
what can cause inaccurate readings of RPF using PAH?
metabolic alkalosis: PAH clearance overestimates RPF
diabetic KA: ketones compete w/ PAH for BL OAT into filtrate + H neutralizes PAH → lower clearance → underestimates RPF
high PAH → transport saturation =dec. PAH extraction ratio
how to calculate RBF?
RBF = RPF/(1-hematocrit)
what is filtered load? what occurs if filtered load exceeds urinary excretion? what occurs if urinary excretion exceeds filtered load?
GFR x P conc.
FL > UE → RA
FL < UE → excretion
what is the difference of transport max for reabsorption and secretion?
Tm for RA → (GFRxP) - (UxV)
filtered load (larger)- urinary excretion
Tm for secretion → (UxV) - (GFRxP)
urinary excretion (larger) - filtered load
what is renal threshold? what is the threshold?
plasma conc. at which fully RA substance starts to appear in urine
renal threshold > plasma conc. → substance RA
renal threshold < plasma conc. → substance excreted
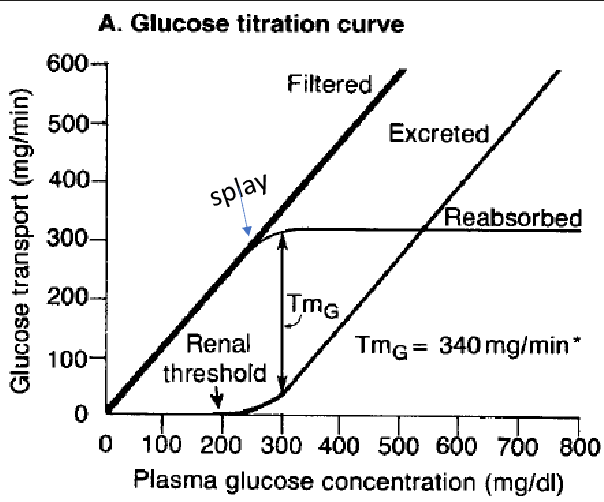
what does the titration curve of glucose show?
renal threshold → P conc. @ which fully RA substance appears in urine
Tm splay starts → no more RA + inc. excretion (since it’s appearing in urine)
filtration is proportional to P conc
glucose RA @ PCT (if SLGT2 inhibited → excreted)
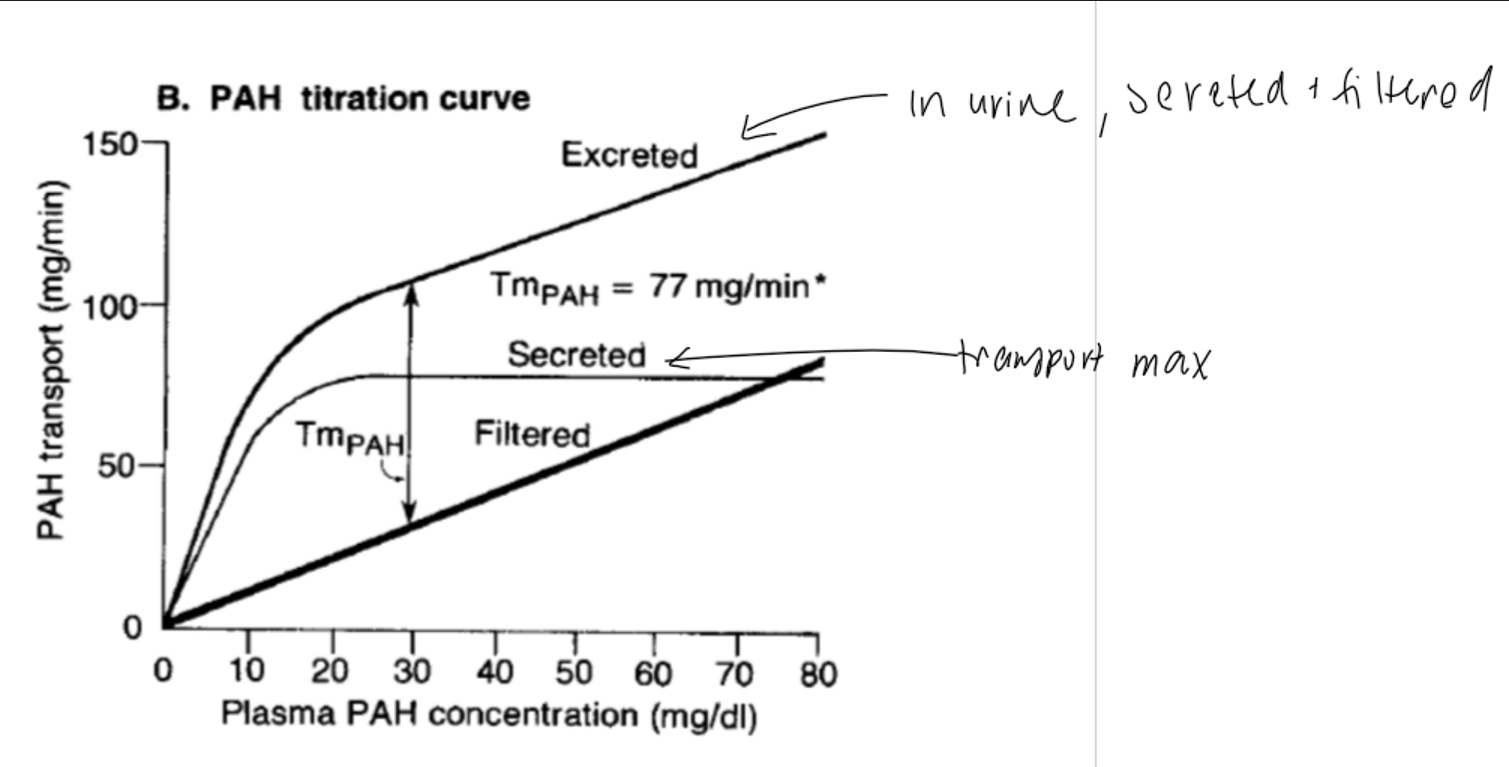
what does the titration curve of PAH show?
Tm via saturation → excretion inc. (filtration + secretion) BUT at lower rate
secretion plateaus @ Tm
inc. P conc. → inc. filtered amount
PAH sec. @ PCT
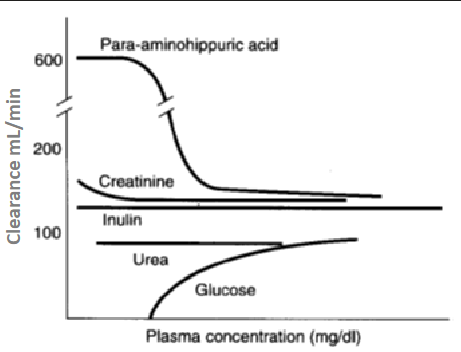
what does this graph describe about the relationship between plasma concentration (mg/dL) and clearance (mL/min) of the following substances?
PAH: secreted, high clearance @ low P conc. → OAT saturate @ high P conc.
creatinine: filtered + slight sec., slightly higher clearance @ low P conc. (slightly overestimates clearance/GFR)
inulin: filtered, NOT sec./RA; clearance constant
urea: filtered, slight RA; low clearance (depends on hydration)
glucose: completely RA; 0 clearance @ low P conc. (clearance inc. in diabetes)
how is urea recirculated? what is its importance?
liver protein metabolism
freely filtered → RA @ PCT → sec. @ TDL
maintains high solute conc. in medulla (med. osm)
UT-A1 (apical) + UT-A3 (BL) (via ADH)→ urea RA @ CD
RA H2O @ CD
what does it mean if there is increased BUN in the blood? decreased BUN?
inc. BUN
dehydration → inc. UT-A T (via inc. ADH) → inc. urea RA @ CD → urine conc. (via H2O RA following urea)
renal failure → dec. filtration + clearance
dec. BUN
low protein met.→ less urea → can’t conc. urine
what is FA oxidation? what is it the main source of energy for?
FA broken down for energy
main energy source for segments w/ high ATP demand + high O2 supply (PCT)
medulla less FAO → via low O2 tension
what is glycolysis? what is it the main source of energy for?
glucose → pyruvate
main energy source for high energy demand + low O2 supply (m. TAL + m. CD)
medulla
what is gluconeogenesis? what are the precursors? where is the localization?
glucose from non-carb precursors (@ c. PCT)
lactate > glutamine > glycerol > alanine
localization: mit., cytosol, ER in liver > kidney > SI
what is the process of lactate metabolism in GNG? what occurs when lactate is the substrate?
lactate → pyruvate → oxaloacetate → PEP → F-1,6BP → F-6P → G-6P → glucose
cytosolic NADH/NAD high → (OAA → PEP) via PEPCK-M @ mit. → PEP diffuse to cytosol
what is the process of glutamine metabolism in GNG? what does glutamine metabolism generate?
glutamine uptake (SNAT)→ glutamate →
a-KG → OAA → malate → pyruvate + HCO3
a-KG → OAA → PEP → glucose
HCO3 + NH3 (ammonia genesis)→ counteract met. acidosis
what is the process of glycerol metabolism in GNG?
triglyceride → glycerol → glycerol 3-P → DHAP → F1,6 BP → F-6P → G-6P → glucose
what is aa metabolism in GNG? what happens when alanine is the substrate?
alanine + a-KG→ pyruvate + glutamate via ALT
low c. NADH/NAD → forms malate to transport OAA from mit. to c. → PEPCK (OAA → PEP)
aspartate + a-KG → OAA + glutamate via AST
how does EtOH metabolism disrupt GNG?
high NADH, lactate, & malate + low glucose production
via pyruvate → lactate ; OAA → malate
dec. pyruvate + dec. OAA → no GNG → hypoglycemia + lactic acidosis
what is the function of pyruvate carboxylase? what is its cofactor? what is an allosteric activator?
pyruvate → OAA (glycolysis → GNG)
biotin → avidin in raw egg white inhibits it
Acetyl CoA → ADP inhibits it
what is the function of PEPCK? what is it stimulated + inhibited by? what does it use as an energy source?
OAA → PEP
stim: glucocorticoids, glucagon, epinephrine during fasting to sustain GNG
inhibit: insulin during eating, dec. glucose prod.
GTP
what is the function of F1,6- bisphosphatase?
F 1,6-BP → F 6-P
what is the function of PFK-1? what is it inhibited + activated by?
F6-P → F1,6-BP backwards
inhibit: citrate + ATP
act. : AMP + F2,6 BP (most potent)
inc. F2,6 BP → inc. glycolysis + dec. GNG (via inhibition of F2,6 BP)
what is the function of G 6-phosphatase?
G 6-P → glucose
in ER
what is the function of pyruvate kinase (PK) and pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) in glycolysis and GNG?
both glycolysis enzymes need to be INACTIVATED for GNG to progress
inhibited in fasting states
PK: PEP → pyruvate
inhibited via ATP, NADH, acetyl coa
PDH: links glycolysis to TCA cycle
inhibited by ATP, alanine, glucagon, NE