energy changes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
exothermic
reaction which releases energy to the surroundings making temperature increase
eg. combustion of methane: CH4 + O2 → H2O + CO
endothermic
reaction which absorbs energy from the surroundings making the temperature decrease
eg. thermal decomposition of zinc carbonate: ZnCO3 + heat → ZnO + CO2
exothermic reaction notation
change in heat = +285 KJ/mol
endothermic reaction notation
change in heat = -285 KJ/mol
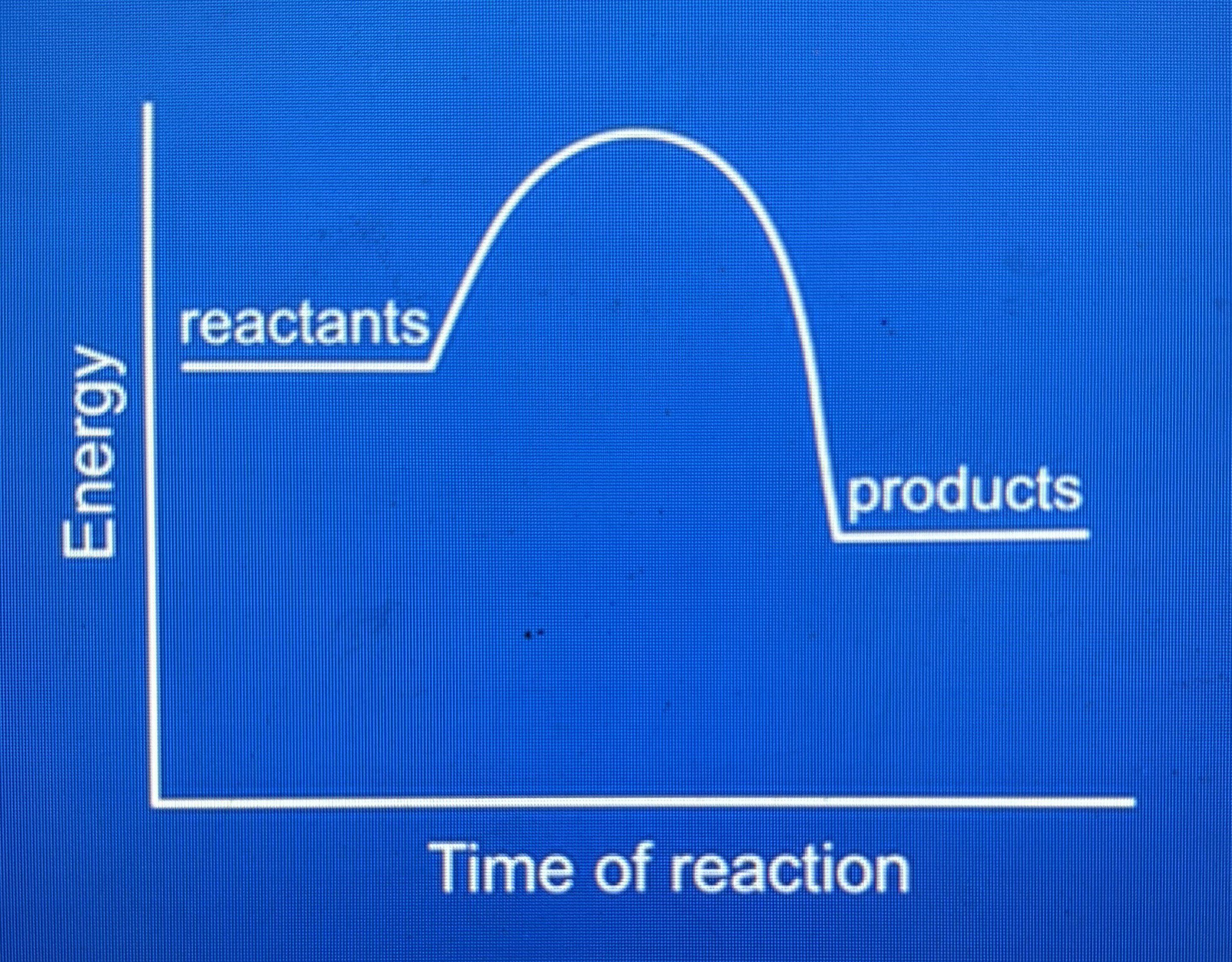
exothermic energy profile diagram
products have less energy than reactants because energy has been transferred to surrounding
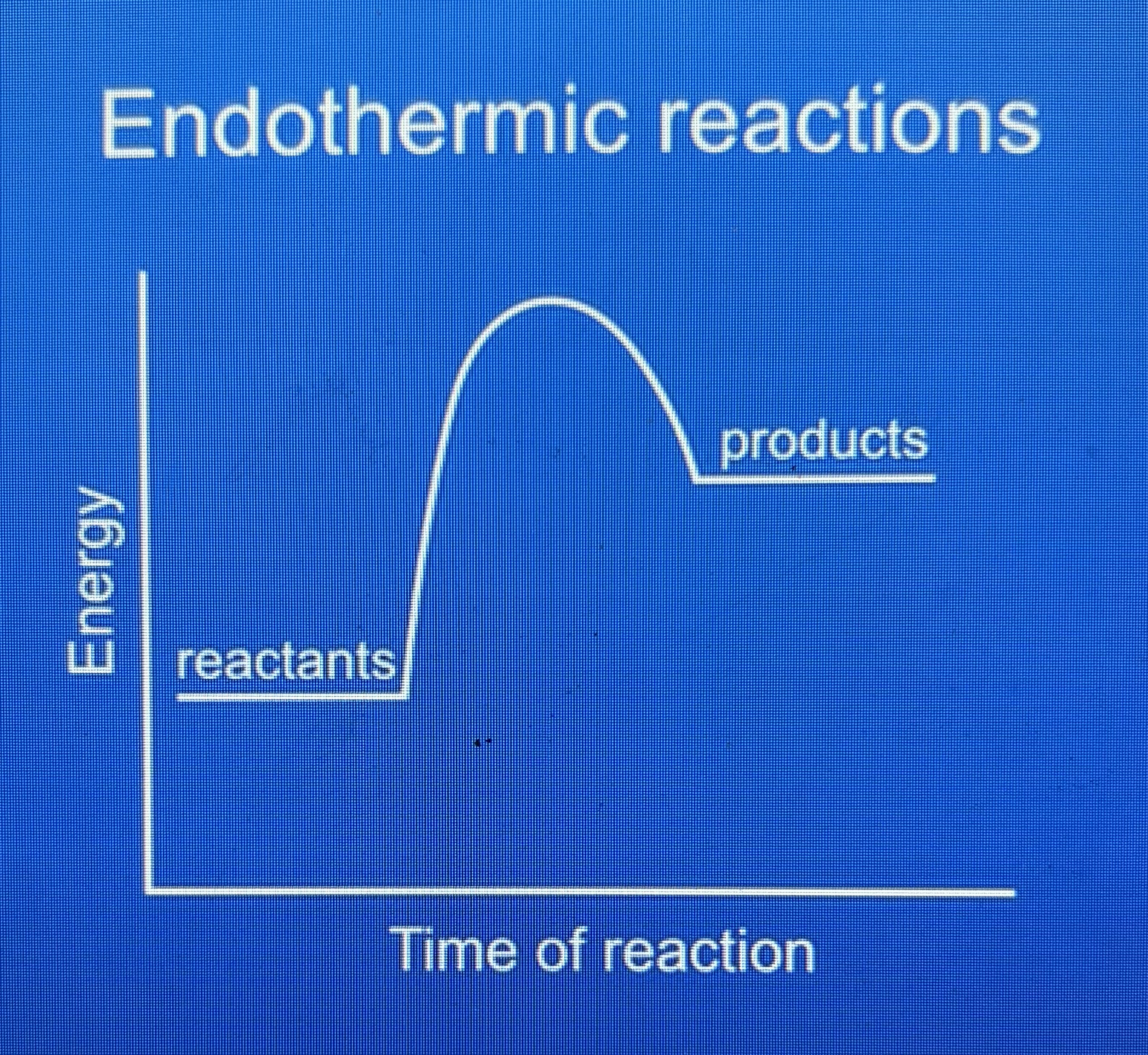
endothermic energy profile diagram
products have more energy than reactants because energy is taken in from the surroundings
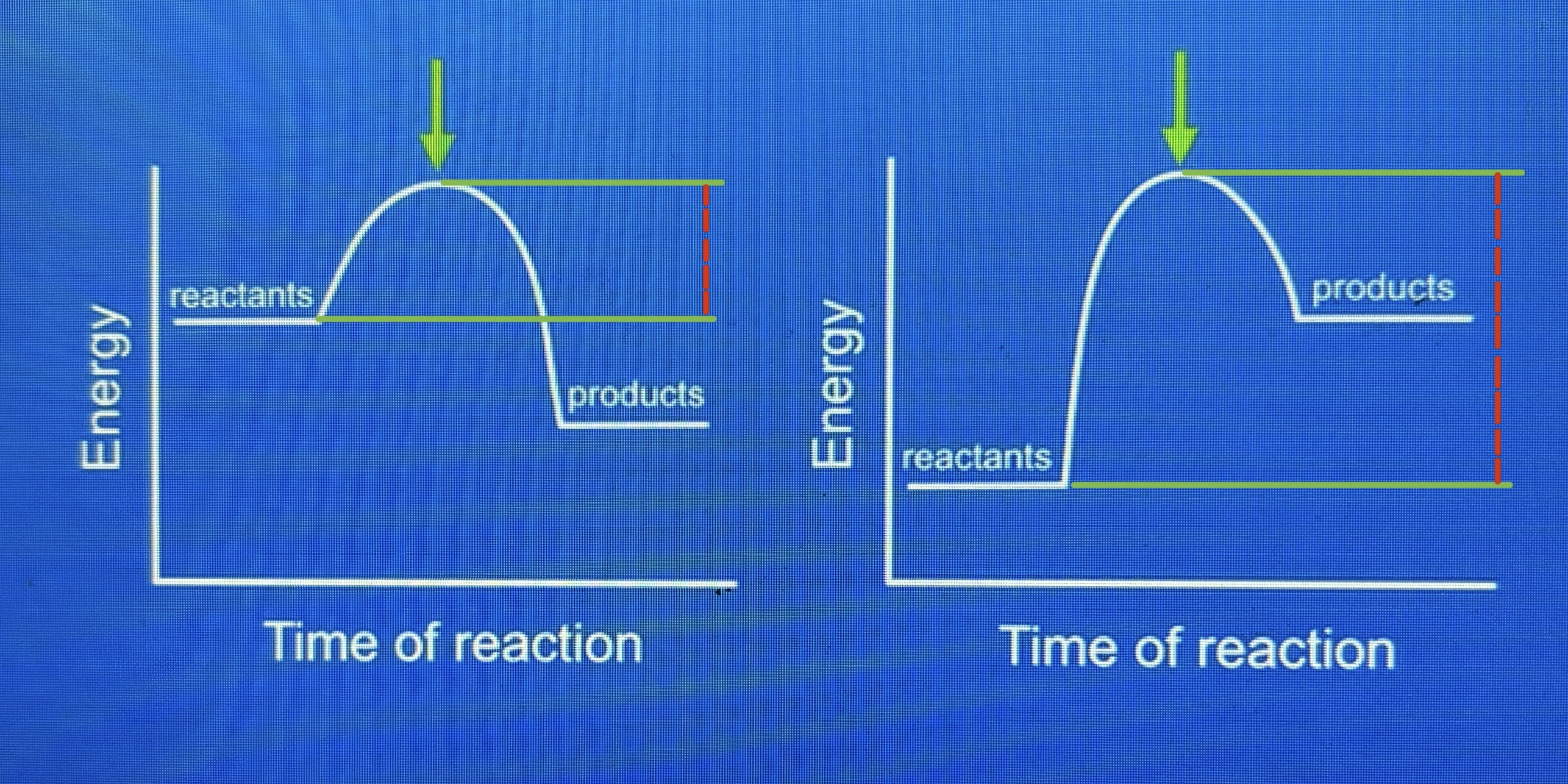
activation energy
the energy required for a chemical reaction to happen; it is the minimum amount of energy colliding particles must have in order to react
cells
two different metals in an electrolyte can produce electricity
→ eventually the chemicals run out and the reaction (electricity) stops
→ cells only produce electricity if the metals used have different reactivities
The greater the different between the reactivity of the metals,
the greater the potential difference produced by the cell.
battery
two or more cells connected in series; produces a greater voltage
alkaline batteries
non rechargeable: at some the point reactants run out
rechargeable batteries
we can reverse the chemical reaction when we apply an electrical current
advantages of rechargeable batteries
no dangerous fuels are required
can produce a higher voltage than a hydrogen fuel cell
disadvantages of rechargeable batteries
run out and need to be recharged
can store less electricity the more charging cycles they go through and eventually must be replaced
fuel cell
react a fuel such as hydrogen with oxygen/air to form a chemical reaction inside the cell and create an electric current
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O : hydrogen is oxidised
negative electrode half equation
2H2 → 4H+ + 4e-
positive electrode half equation
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O
advantages of fuel cells
produce electricity for as long as you provide hydrogen
do not get less efficient the longer they run
can be a source of drinking water
disadvantages of fuel cells
hydrogen is an explosive gas which is difficult to store safely
produce a relatively low voltage so several are needed