biological molecules
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what do all living things require
movement, respiration, sensitivity, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, excretion and nutrients
what is nutrition
the act of obtaining food for growth and repair
what are the 3 main groups of nutrients
carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
what elements are in carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
what elements are in proteins
hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen
what elements are in lipids
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
what is the basic unit of all carbohydrates
simple sugars
what is an example of a simple sugar
glucose
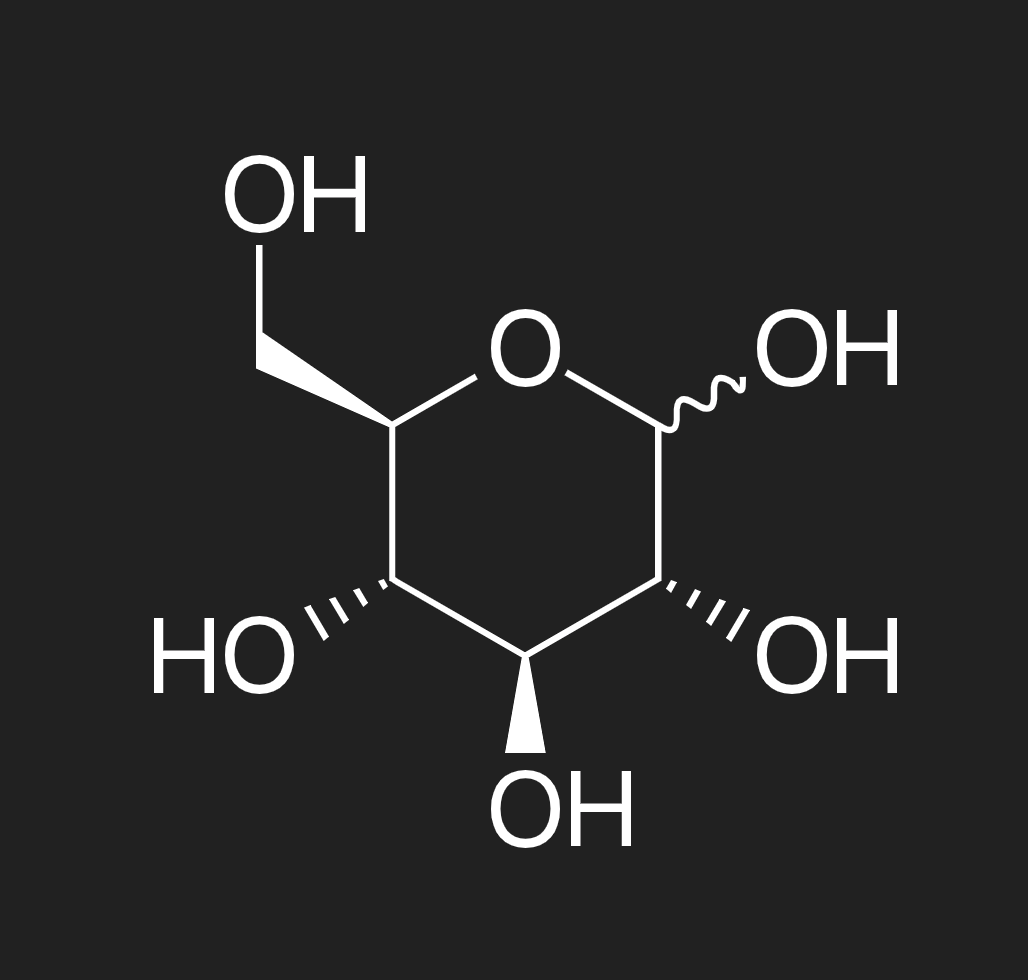
what is the structure of glucose
a monosaccharide
what is a monosaccharide
a single unit of sugar that cannot be broken down further
what is the product of two glucose molecules joining together
a disaccharide and molecule of maltose is formed
what is the produce of lots of glucose molecules joining together
a polysaccharide is formed
give an example of a glucose based polysaccharide
starch
give examples of carbohydrate sources
breads, grains and pasta
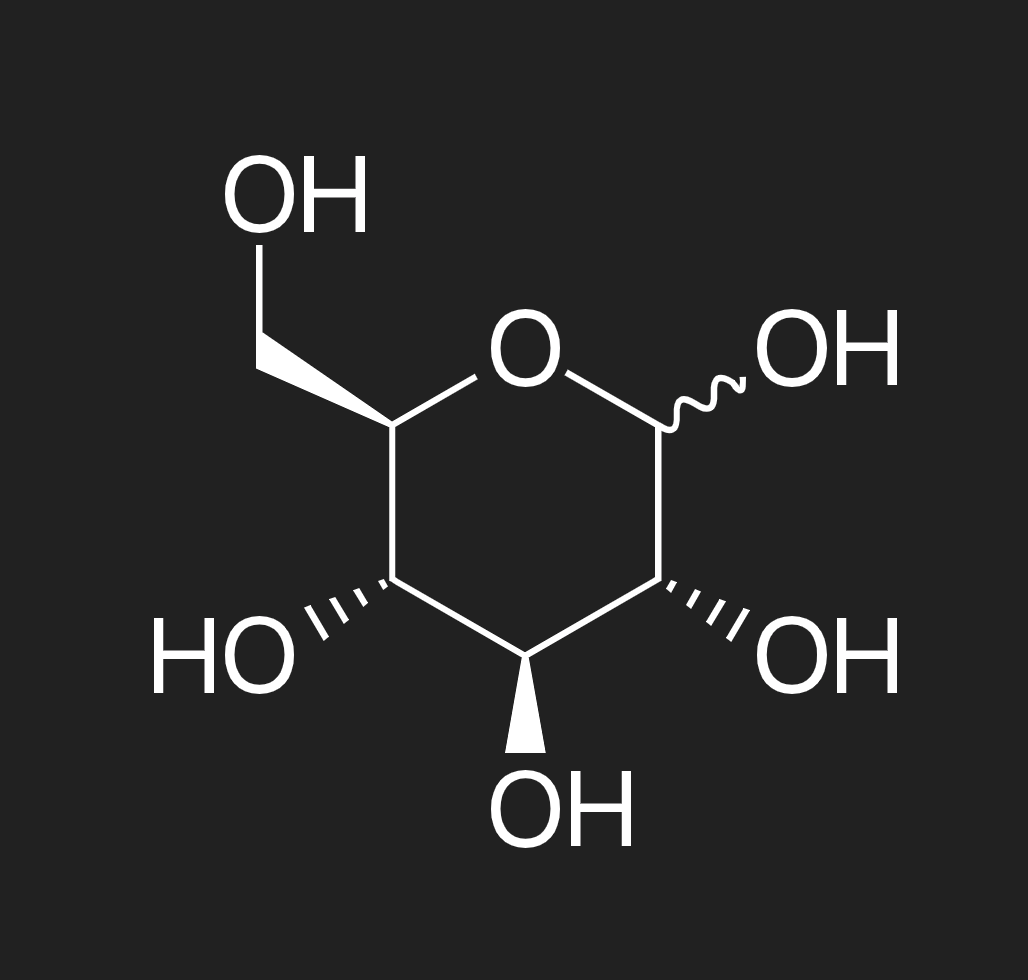
describe the structure of glucose
a six-carbon (hexose) sugar. as a monosaccharide, glucose cannot be broken down any further
what is the basic unit of all protein molecules
amino acids
how many different amino acids are there
20
describe the similarity and differences of the 20 amino acids
they all contain the same basic structure but each amino acid has a different R group (R groups have a variety of sizes and activities)
what happens when amino acids join together
a protein is formed
what happens when two amino acids join together
a dipeptide is formed
what happens when many amino acids join together
a polypeptide is formed
does the order arrangement matter for amino acids
no - even a small change in the sequence of the amino acids can cause a big change in the shape of a protein being formed
what are good sources of protein
fish, meats and eggs
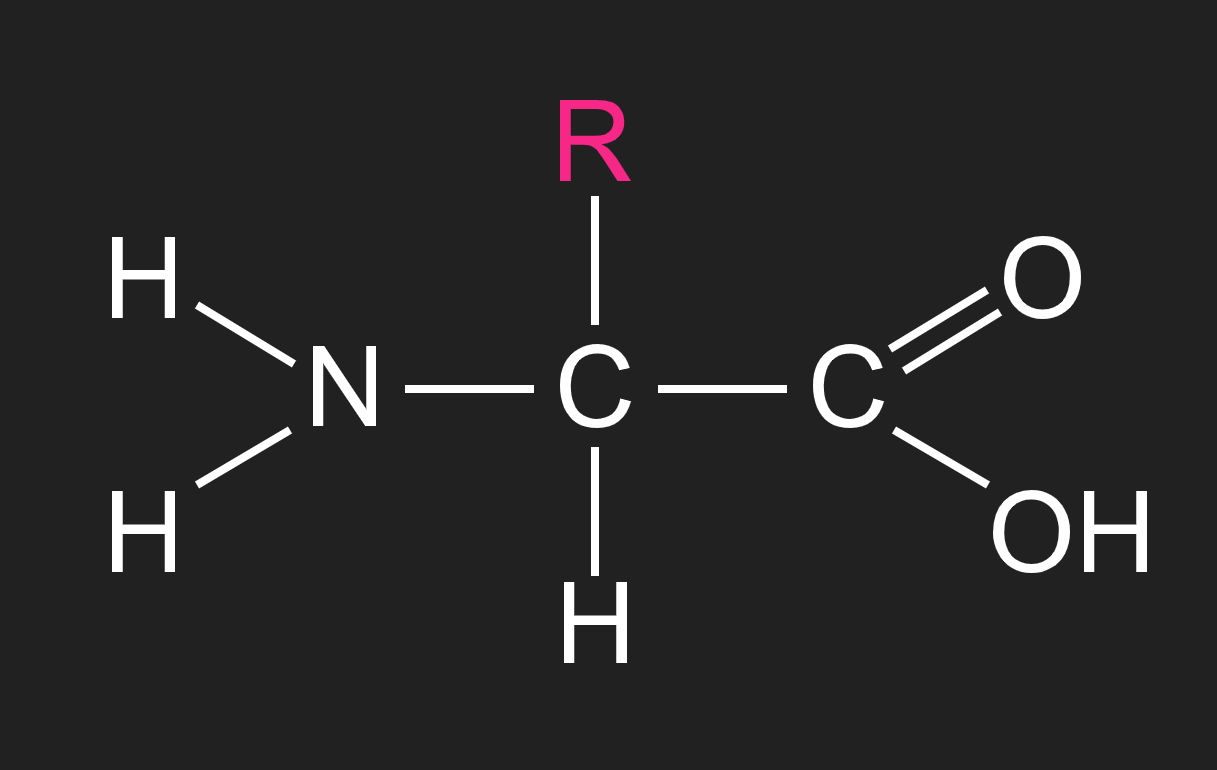
describe the basic structure of an amino acid
there are 20 different R groups across the 20 amino acids
what are sources of lipids
fats and oils
what is the state of fats in room temperature
solid
what is the state of oil in room temperature
liquid
what are the main group of lipids found in foods called
triglycerides
what are triglycerides
triglycerides are a combination of glycerol and three fatty acids
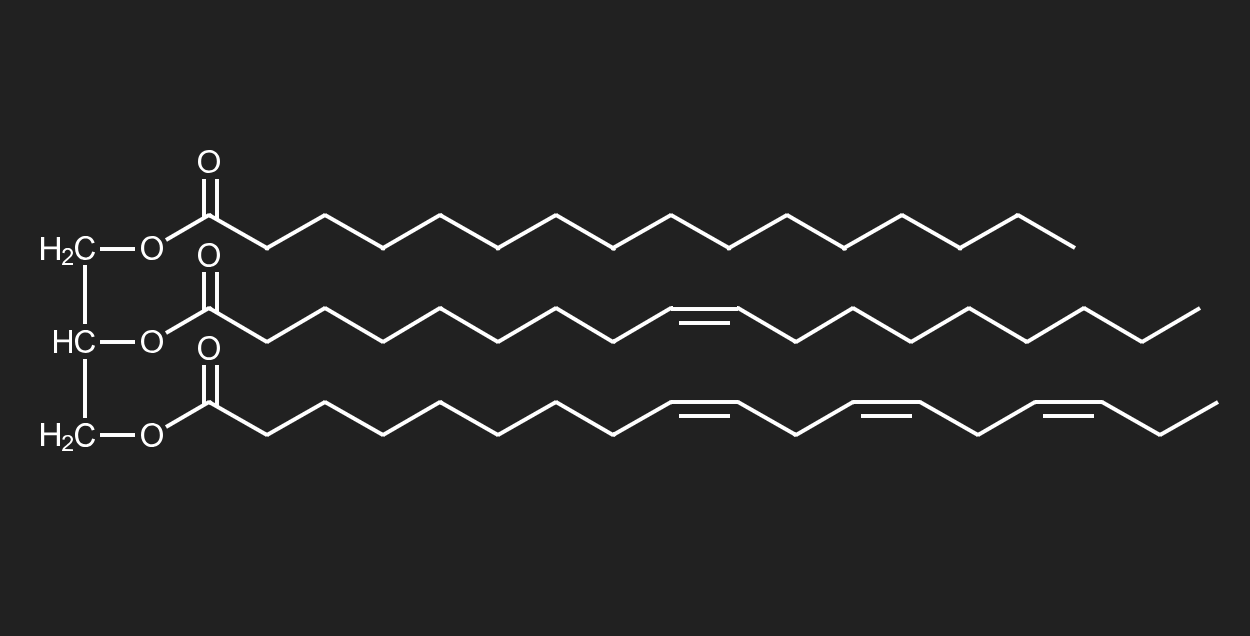
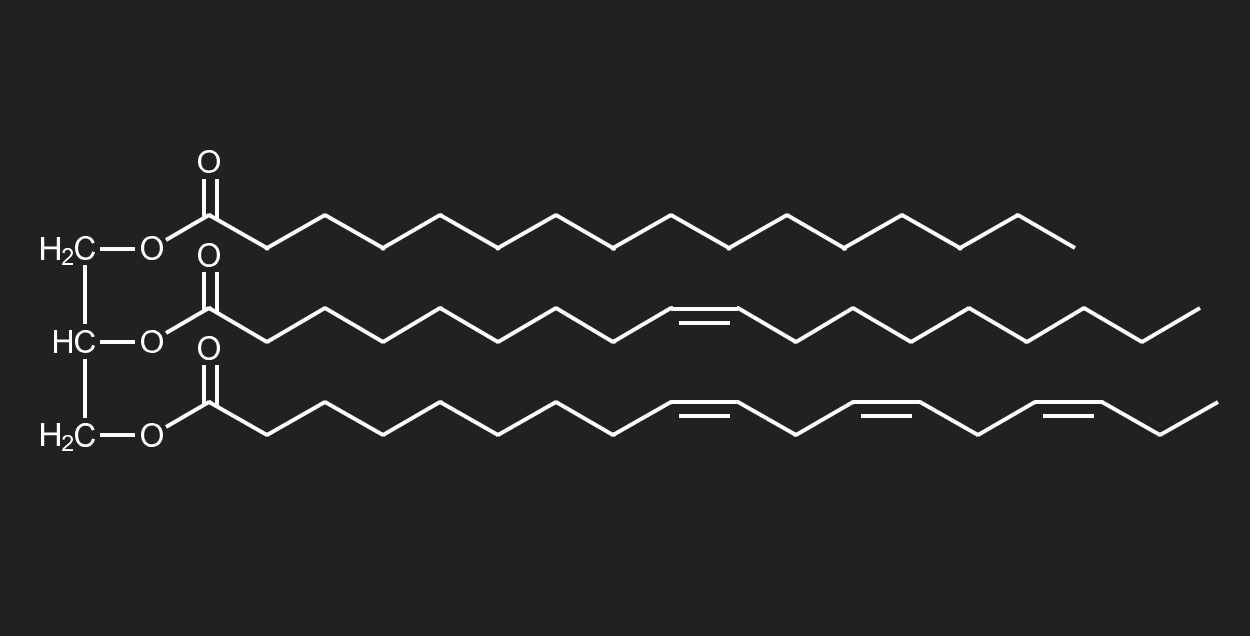
describe the structure of a triglyceride
a triglyceride consists of a glycerol head and three fatty acid tails
what is this?
the structure of a triglyceride
what is this?
the structure of glucose
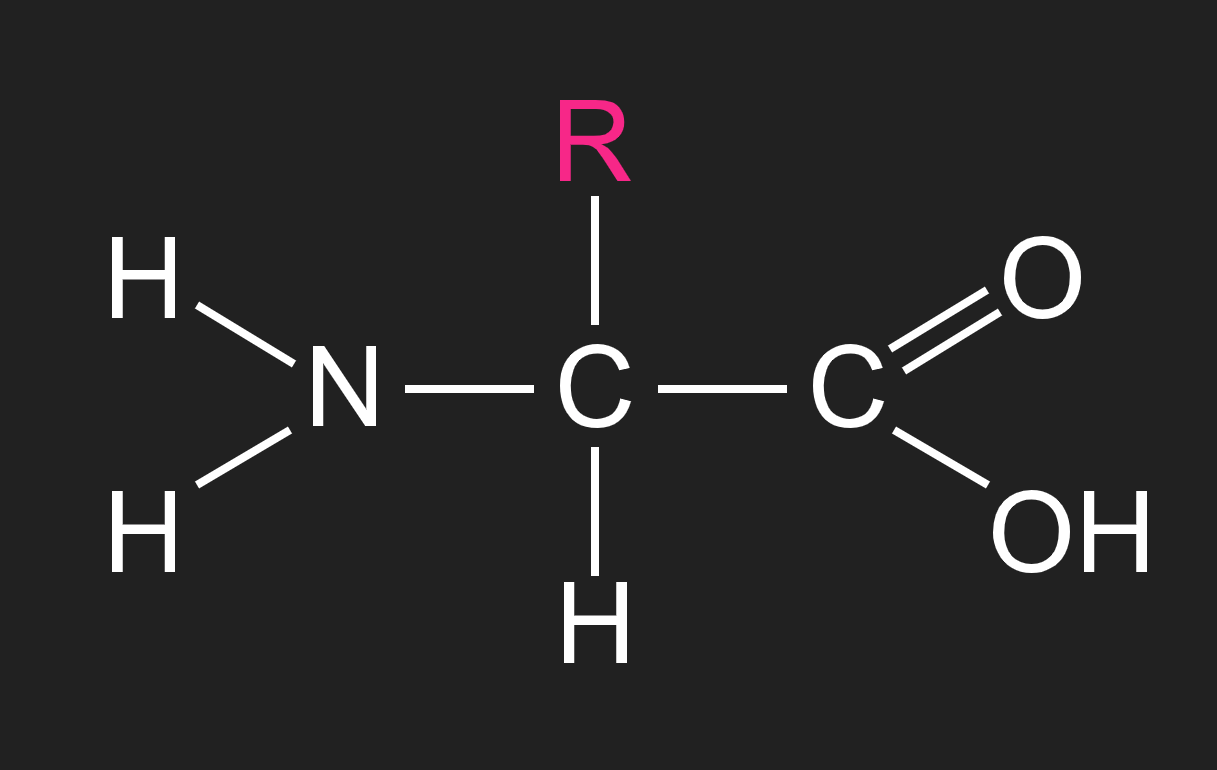
what is this?
the basic structure of an amino acid