Exam 7 Anatomy cohort UE Axilla Brachial Plexus
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Axilla
Gateway to the upper limb
Formed by the clavicle, scapula, and upper thoracic wall, humerus, and related muscles
Pyramidal shape
Has an inlet and a base/floor
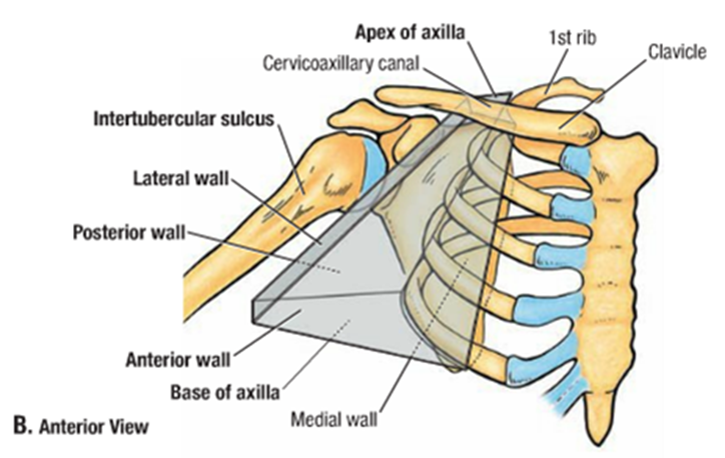
Axillary Inlet
Formed by lateral border of Rib 1, posterior surface of the clavicle, and the superior border of the scapula up to the coracoid process
Axillary artery, vein and brachial plexus; Artery and vein are separated by the anterior scalene muscle
Loocated at the axilla and differentiate at the inlet
Anterior axillary wall muscles
Pectoralis major and minor muscles
Subclavius muscles
Clavipectoral fascia
Pectoralis major
Largest and most superficial muscle of the anterior wall
Its inferior margin underlies the anterior axillary fold
What are the head of pectoralis major?
clavicular: Originate at the median half of the clavicle
Sternocostal head : Origin-medial part of the anterior thoracic wall
Can join the abdominal muscles.
Pectoralis Major
Inserts into the lateral lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
Innervated by the lateral (travels between Pec minor and subclavius) and medial pectoral nerves (pierces through the Pec minor)
Pectolaris major insert
into the lateral lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
What innervate the pectoralis major?
by the lateral (travels between Pec minor and subclavius) and medial pectoral nerves (pierces through the Pec minor)
Pectoralis Minor
Small triangular muscle deep to the pectoralis major
Originates at rib 3, 4, 5 and inserts at the coracoid process of the scapula
Protracts the scapula anteriorly
Innervated by the medial pectoral nerve
Subclavius
Small muscle deep to the pectoralis major
Passes between the clavicle and rib 1
Originates as a tendon from rib 1
Subclavius
inserts as a muscular attachment on the inferior surface of the middle third of the clavicle
Depresses the clavicle and pulls the clavicle medially to stabilize the sternoclavicular joint.
Thick sheet of connective tissue connecting the clavicle to the floor of the axilla
Encloses the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscles
Clavipectoral fascia
Clavipectoral fascia
Cephalic vein, thoraco-acromial artery and the lateral pectoral nerve passes between these muscles.
Medial axillary wall
Serratus Anterior muscle
Upper thoracic wall
Ribs and intercostal tissues
Originates as multiple slips from ribs 1-9
Inserts primarily on the costal surface of the medial border of the scapula
Pulls the scapula forward over the thoracic wall and contributes to scapular rotation
Serratus anterior
Serratus anterior
Innervated by the long thoracic nerve which travels along the surface of the serratus anterior
Passes directly through the medial axillary wall
Supplies the skin on the upper posteromedial side of the arm (part of the T2 dermatome)
Intercostobrachial nerve
Narrow and formed entirely by the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
Lateral Axillary wall
posterior axillary wall
Bone framework is formed by the costal surface of the scapula.
Muscles of the posterior wall
Subscapularis
Distal part Latissimus dorsi
Distal part Teres major
Proximal part of the long head of the triceps brachii
Formed spaces occur in the posterior wall.
Largest component of the posterior wall
Originates from the subscapular fossa
Inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus
Part of the rotator cuff
Subscapularis
Subscapularis
Innervated by the superior and inferior subscapular nerves
Forms inferolateral aspect of the posterior wall
Along with the l. dorsi, mark the posteroinferior border of the axilla
T. major marks the beginning of the brachial artery at its inferior border
Teres major and latissimus dorsi
Teres major and latissimus dorsi
Tendon of the latissimus dorsi also forms inferolateral aspect
Flat tendon curves around the inferior margin of the teres major and inserts on the floor of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus.
Gateways in the posterior wall
Quadrangular space
Triangular space
Triangular interval
Quadrangular space
Axillary nerve, and the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein pass between axilla and the scapular and deltoid regions
Quadrangular space boundaries
Inferior margin of the teres minor muscle
Surgical neck of the humerus
Superior margin of the teres major
Lateral margin of the long head of the triceps brachii.
The circumflex scapular artery and vein pass through from axilla to the scapular region
Triangular space
Medial margin of the long head of the triceps brachii muscle
Superior margin of the teres major muscle
Inferior margin of the teres minor muscle
Triangular space boundaries
Radial nerve passes from the axilla to the posterior compartment of the arm
Triangular interval
Triangular interval Boundaries
Lateral margin of the long head of the triceps brachii muscle
Shaft of the humerus
Inferior margin of the teres major muscle
Floor of the axilla
Formed by fascia and a dome of skin
Anterior fold is more superior than posterior fold
Contents of the axilla
Muscles
Major vessels
Nerves
Lymphatics
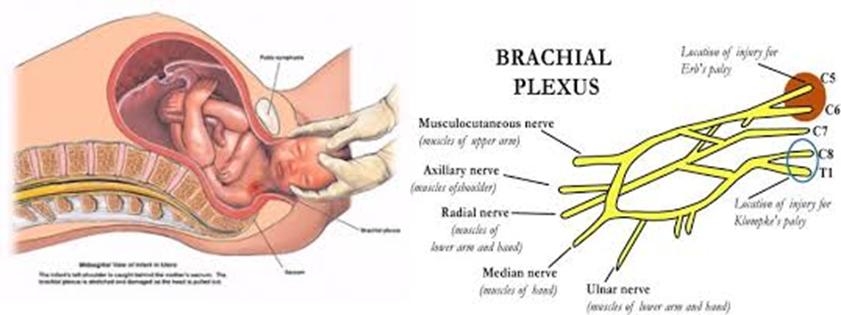
Brachial Plexus
Somatic plexus formed by the anterior rami of C5-C8 and most of the anterior rami of T1
Originates in the neck and passes laterally and inferiorly over rib 1 where it enters the axilla
Innervates the upper limbs
Draw the plexus brachial
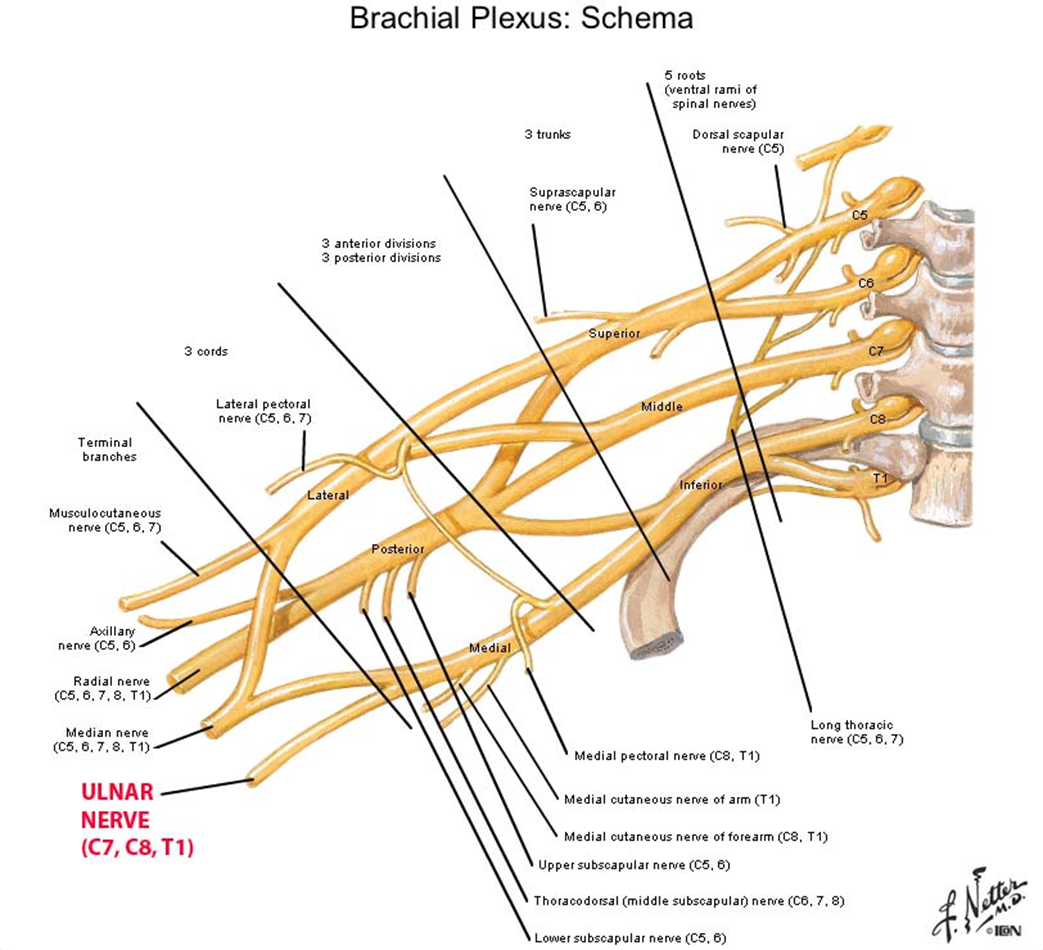
Compositions of plexus brachial
Roots:5
Trunks:3
Divisions3&3:
Cords: 3
Roots of the brachial plexus
Roots are the anterior rami of C5-C8 and T1
Roots enter the posterior triangle of the neck passing between the anterior and middle scalene muscles
Lie superior and posterior to the subclavian artery
Superior trunk
Made from union of C5 and C6 roots
Middle trunk
C7 root
Inferior trunk
C8 and T1 roots
Trunks of the brachial plexus
Each of the three trunks divide to an anterior and posterior division.
Anterior- ultimately give rise to nerves associated with the anterior compartments
Posterior-ultimately give rise to the nerves associated with the posterior compartment
*no peripheral nerves originate directly from the divisions of the brachial plexus
Divisions of the brachial plexus
Cords of the brachial plexus
Three Cords and are related to the second part of the axillary artery and most peripheral nerves of the upper extremity originate from the cords.
Lateral-union of the anterior divisions of the upper/superior and middle trunks and is positioned lateral to the second part of the axillary artery
C5-C7 origin
Medial-medial to the second part of the axillary artery and is a continuation of the anterior division of the inferior trunk
C8-T1
Posterior-posterior to the second part of the axillary artery and is a union of all three posterior divisions
Contains all roots of the brachial plexus
Cords of the brachial plexus
Branches of the roots
C5 contribution to the phrenic nerve
C5-Dorsal scapular nerve
Passes posteriorly usually piercing the middle scalene muscle
Travels along the medial border of the scapula
Innervates the rhomboid major and minor muscles
C5-C6-Nerve to the subclavius muscle
From the superior trunk
Passes anteroinferiorly over the subclavian artery and vein
Innervates the the subclavius muscle
Branches of the roots
C5-C7- long thoracic nerve
Passes vertically down the neck through the axillary inlet and down the medial wall of the axilla
Supplies the serratus anterior muscle
C5-C8 Small segmental branches to the muscles of the neck
Suprascapular nerve
Originates from the superior trunk
Passes laterally through posterior triangle on the neck and the suprascapular foramen to enter the posterior scapular region
Innervates supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
Musculocutaneous nerve-anterior compartment of the arm
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm-sensory to the lateral skin of the arm
Lateral root of the median nerve-anterior forearm and some intrinsic hand muscles
Lateral pectoral nerve-pectoralis major
Branches of the medial cord
Medial pectoral nerve- pectoralis minor
Medial cutaneous nerve of the arm-skin over distal third of the arm
Intercostobrachial nerve-upper part of the medial surface of the arm and the axilla floor
Medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm-skin over the anterior and medial skin of the forearm
Medial root of the median nerve-anterior forearm and some intrinsic hand muscles
Ulnar nerve-all intrinsic muscles of the hand (minus the three thenar muscles and the two lumbrical muscles) also innervates the skin over the little finger and the medial half of the ring finger
All lymphatics of the upper limb drain to the axilla
20-30 axillary nodes divide into groups
Humeral (lateral ) nodes
Pectoral (anterior) nodes
Subscapular (posterior) nodes
Central nodes-receive from the three above
Apical nodes- include cephalic vein area
Axillary lymphatics
Ulnar
Median
Radial
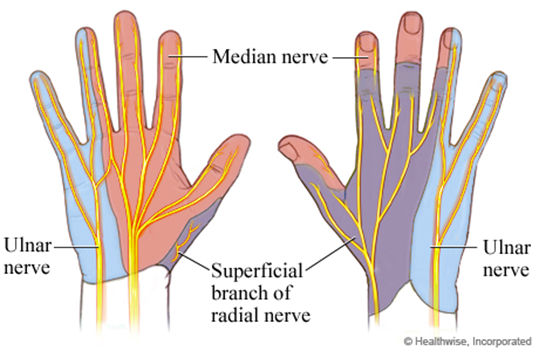
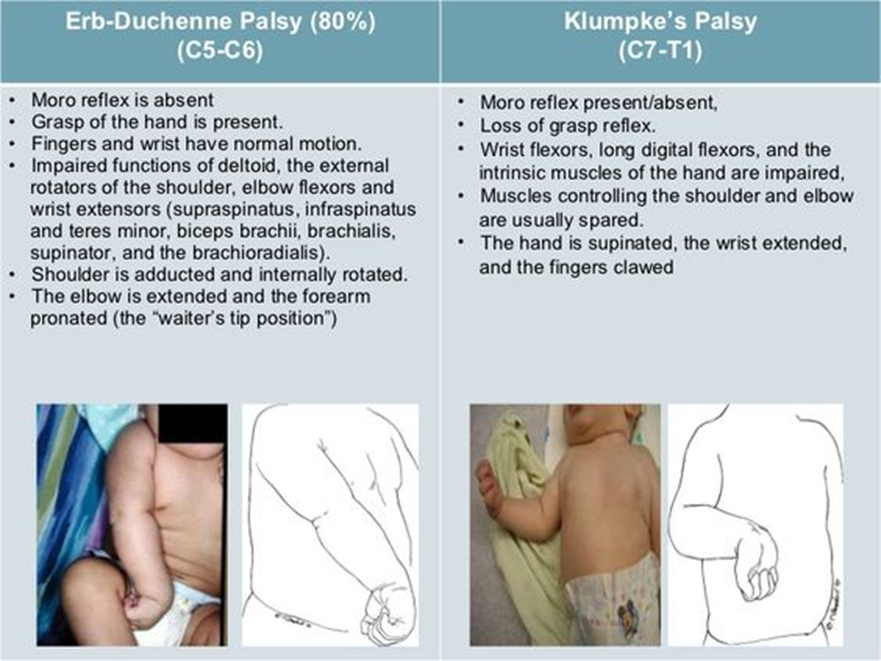
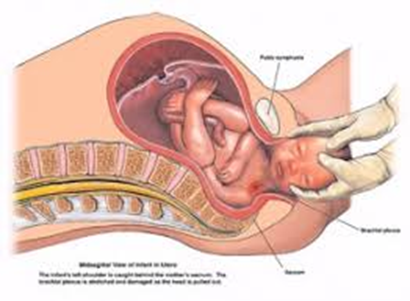
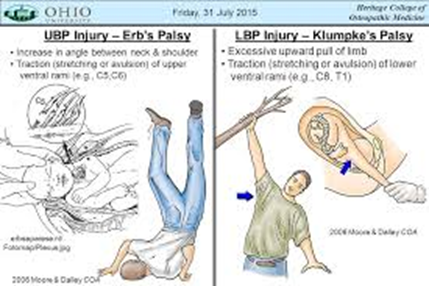
Injury to Brachial Plexus