Exoenzymes and Toxins & Respiratory Infections
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
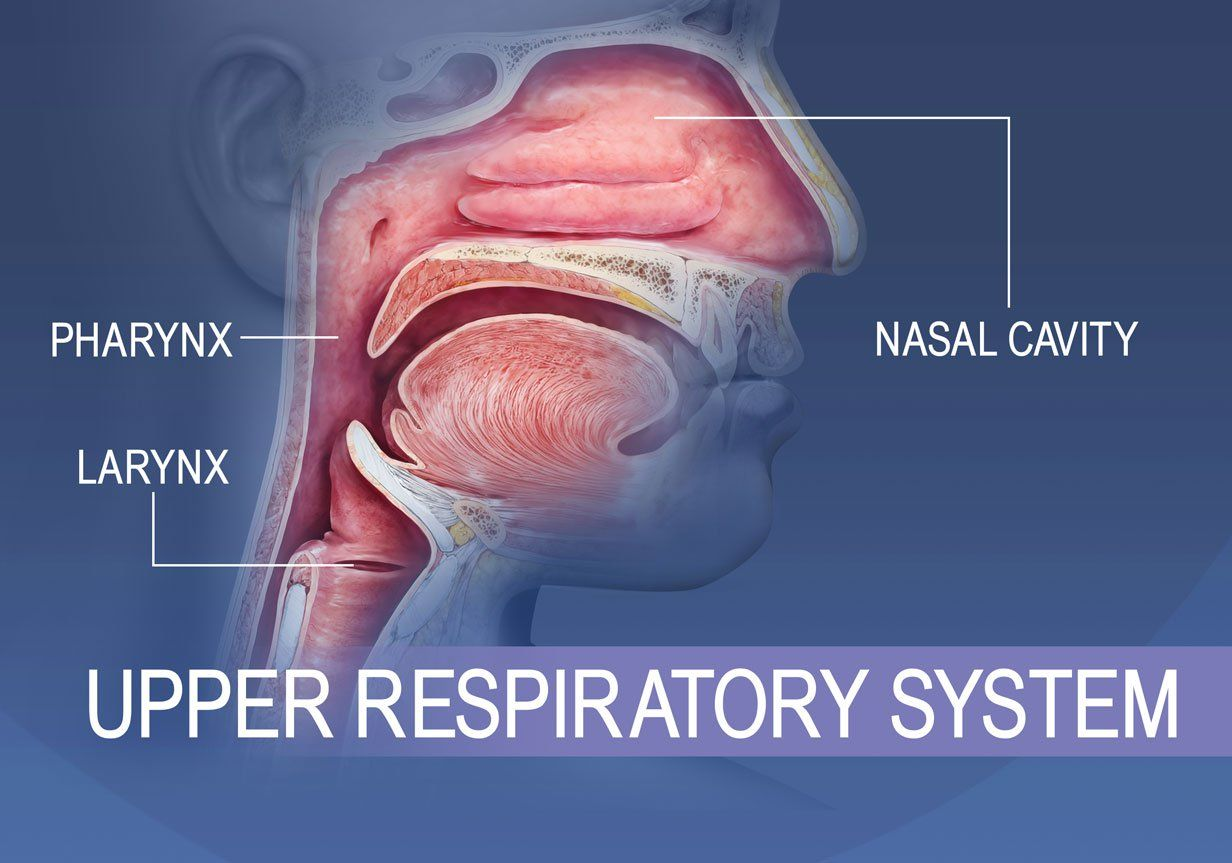
Respiratory System
Upper Respiratory Tract (URT)
Lower Respiratory Tract (LRT)
Upper Respiratory Tract (URT)
paranasal sinuses
nasopharynx
oropharynx
epiglottis
larynx
lined with normal bacterial flora or indigenous microbiota
normal bacterial flora or indigenous microbiota
protect body from potential pathogens
In a normal person in the community, what normal flora are found in their URT?
staphylococcus sp.
streptococcus sp.
streptococcus pneumoniae
viridans streptococcus
haemophilus sp.
anaerobes
In a normal person in the hospital or LTC, what normal flora are found in their URT?
staphylococcus spp.
anaerobes
Enterobacteriaceae
e. coli
klebsiella spp.
candida spp.
pseudomonas spp.
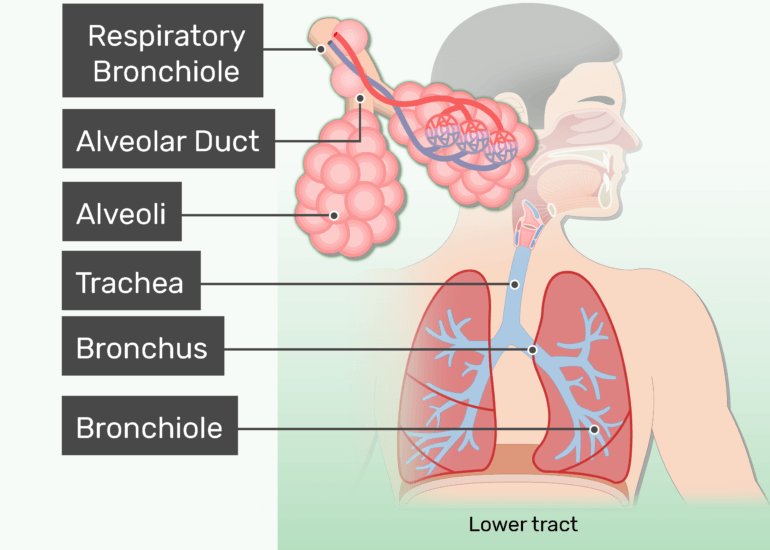
Lower Respiratory Tract (LRT)
trachea
bronchial tubes
alveoli of the lungs
sterile, no microbiota/normal flora
Opportunistic infections
may be caused by indigenous microbiota of the URT of the respiratory system
Normal Flora of Nares (nostrils)
staphylococcus epidermis
corynebacteria
staphylococcus pneumoniae
Neisseria sp.
haemophilus sp.
streptococcus pneumoniae
Normal Flora of Nasopharynx (URT)
non-hemolytic streptococci
alpha-hemolytic streptococci
Neisseria sp.
streptococcus pneumoniae
streptococcus pyogenes
haemophilus influenzae
Neisseria meningitidis
LRT Infections
most common cause of death from infectious diseases in US and globally
most common and most deadly communicable diseases (pneumonia and influenza)
numbers dropping since 1980 for 5-14 and 5-24 age groups
rise in non-communicable diseases like COPD
more chronic diseases
longer lifespans = living longer = more likely to develop chronic disease and die from it
COVID and Influenza
type of infection
deaths
compared to total infectious disease deaths
LRT infections
Covid-19
7 million deaths from 704,500,000 cases
Flu/Pneumonia:
11 million deaths
more than 34 million deaths from infectious diseases overall
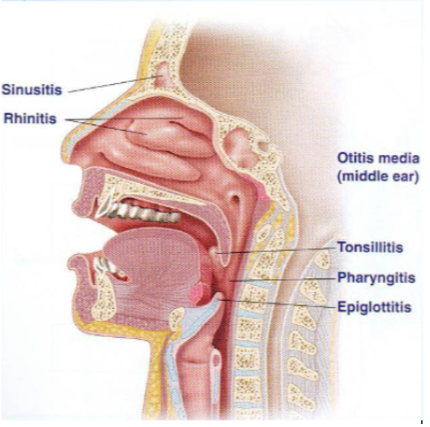
Syndromes associated with URT
sinusitis
rhinitis
otitis media (middle ear)
tonsilitis
pharyngitis
epiglottitis
Syndromes associated with LRT
bronchitis
bronchiolitis
pneumonia
Epiglottitis
inflammation of epiglottis (flap of skin covering larynx)
swelling → respiratory blockage
we see this complication in children with swollen epiglottis → obstruction of airway and breathing
frequent bacterial causes:
haemophilus influenzae
streptococcus pyogenes
Tonsilitis
infection of tonsils
Sinusitis
inflammation of sinuses → filling with fluid and infection
Acute rhinitis
commonly seen with common cold
swelling and inflammation of nasal mucus membranes
Laryngitis
inflammation of mucus membranes of voice box (larynx)
pharyngitis
infection of pharynx → sore throat, potentially strep throat
streptococcus pyogenes causes bacterial pharyngitis
sore throat (not strep): viral
most cases are caused by viruses and not s. pyogenes
streptococcal pharyngitis
streptococcal pharyngitis
reservoirs: infected humans
transmission: person to person, direct contact (hands, droplets/secretions, carriers)
hospitalized patient care
standard precautions
droplet precautions for infants/young children
viruses that infect the URT
rhinovirus - most common
coronavirus - not just covid/SARS
influenza virus
parainfluenza virus
respiratory syncytial virus
herpesvirus
adenovirus
bocavirus
coxsackievirus
enterovirus
RSV
RSV
high-risk populations:
premature babies in first year of life
infants under 6 months
children with asthma
patients of an age with a weakened immune system or underlying lung or heart problems
older people
leading cause of infant hospitalization in the US
almost all children under 2 will get RSV
common respiratory virus that causes mild, cold-like symptoms
immunizations can protect infants, some young children, and at-risk or older adults
Current RSV, flu, and Covid rates
RSV and flu hospitalization rates are low
Covid hospitalization peaking (sept./oct.) and then we will likely see another peak (jan./feb.)
right now, ~3 hospitalizations per 100,000 people
morbidity/incidence rate (number of people with new infection of covid/flu/RSV)
2025: <1% of deaths were associated with Covid
correlation between hospitalization and deaths caused by these diseases
viruses that infect the LRT
influenza virus
parainfluenza virus
respiratory syncytial virus
adenovirus
bocavirus
metapneumovirus
Flu Viruses
Type A
Type B
47-82 million flu illnesses last flu season (last fall - last april)
increased numbers last year
virulence factors present
H Spike
N Spike
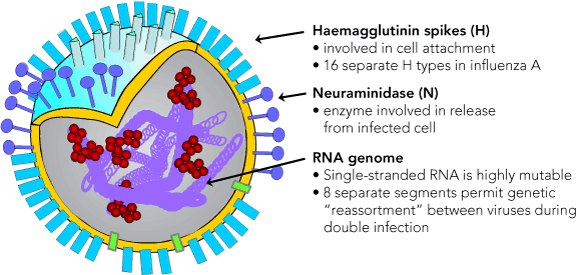
Flu H Spike
Hemagglutinin Protein (HA) is an adhesin that recognizes and attaches to receptors, or integrins, present on respiratory cells
for the H spike, Hemagglutinin helps virion attach and penetrate host cells
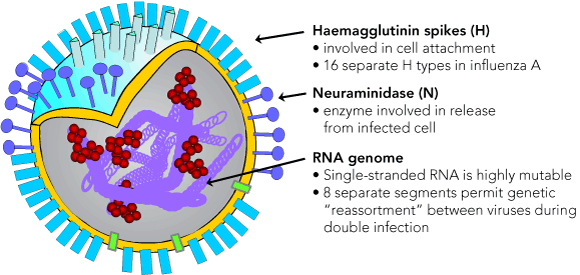
Flu N Spike
Neuraminidase (NA) helps release virions from the host cell after replication and assembly
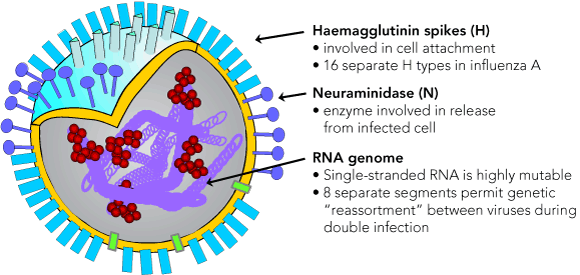
Why do we need a new flu vaccine every year?
H and N spikes are constantly changing and mutating
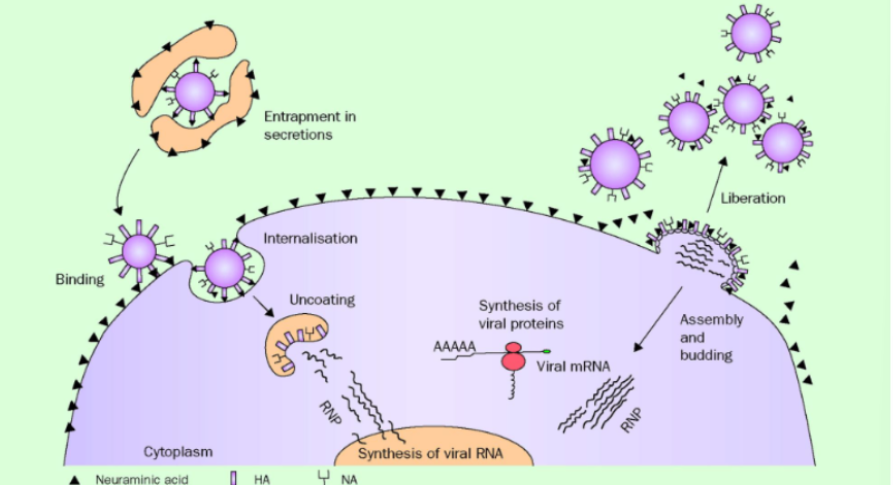
Flu virus infecting cell process
Major mechanisms (most important virulence factors) by which pathogens cause disease
exoenzymes or toxins the pathogens produce
some pathogens produce both
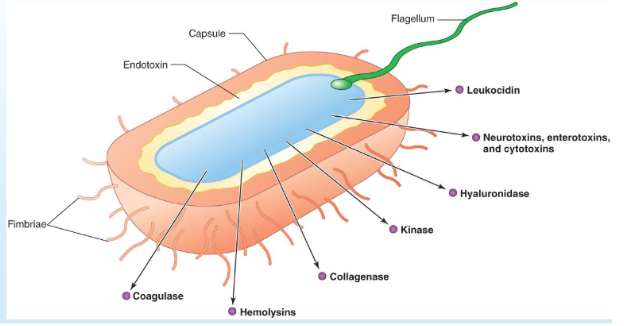
Exoenzymes
enzymes that act outside the cell that produces them
examples of exoenzymes released by bacteria:
necrotizing enzymes: cause destruction of cells and tissues
necrotizing fascilitis
coagulase: causes clot formation around cells, protecting bacteria from phagocytosis and other cell defenses
kinase: bacteria later produce to dissolve clot and release bacteria
streptokinase (SK): bacterial protein produced by B-hemolytic streptococci
Acts indirectly by forming plasminogen-streptokinase complex (activator complex) which converts inactive plasminogen into active plasmin
SK is non-fibrin specific
Can degrade fibrin clots as well as fibrinogen and other plasma proteins
hyaluronidase
collagenase
hemolysins
lecithinase
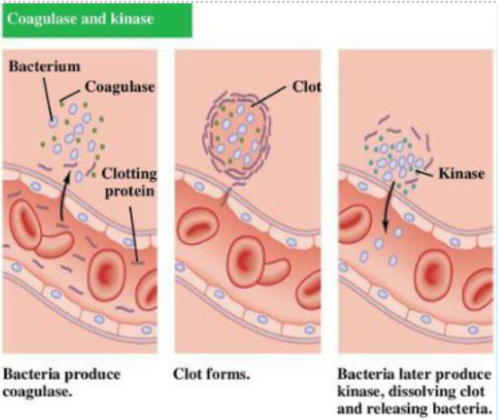
Toxins
poisonous substances released by various pathogens to damage host tissues and cause disease
endotoxins
exotoxins
Endotoxins
part of cell wall structure of gram-negative bacteria
Released from cell walls of bacteria
can cause serious, adverse physiologic effects such as fever and shock
Toxin = pyrogenic (causes fever)
Liberated when bacteria die and cell wall breaks apart
Lipopolysaccharides act throughout the body
Fever, weakness, aching, septic shock
Typhoid fever and meningitis
gram-negative
Exotoxins
Produced within cell, then released
Examples: neurotoxins, enterotoxins (GI), exfoliative toxin, erythrogenic toxin (causes redness), leukocidins (destroy WBCs)
gram-positive
act at specific sites
produce characteristic diseases
Diphtheria, Tetanus
Neurotoxins
most potent exotoxins
Clostridium tetani: spastic, rigid muscle contraction
Enterotoxins
exotoxins
C. diff
causes Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC)
Erythrogenic Toxin
exotoxin
Scarlet Fever
caused by strep pyogenes
Staph. Aureus TSST-1
exotoxin
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Exfoliative Toxin
exotoxin
scalded skin syndrome
produced by S. aureus
gram-positive vs. gram-negative
impacted by peptidoglycans
crystal violet penetrates cell and stains peptidoglycan layer(s), decolorizer is added to stained cells
stain remains purple on gram-positive (thick peptidoglycan layer): exotoxins
stain becomes pink on gram-negative (thin peptidoglycan layer): endotoxins
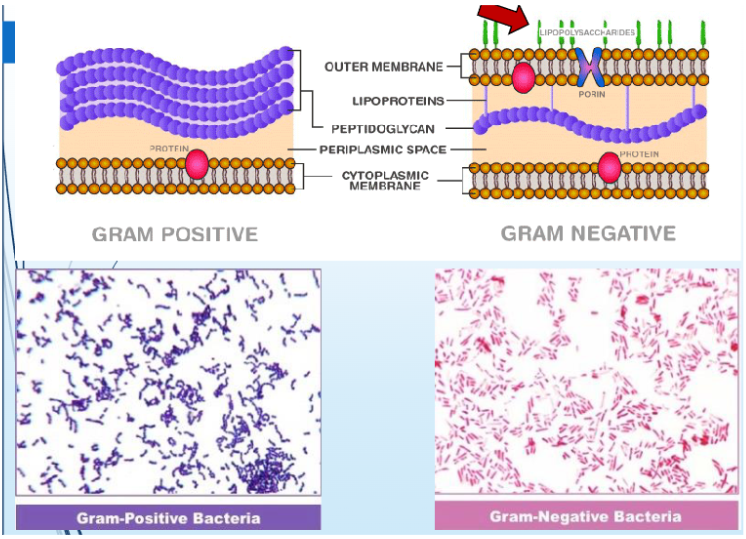
Virulence Factors Diagram