OCR GCSE Biology Complete
1/674
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
675 Terms
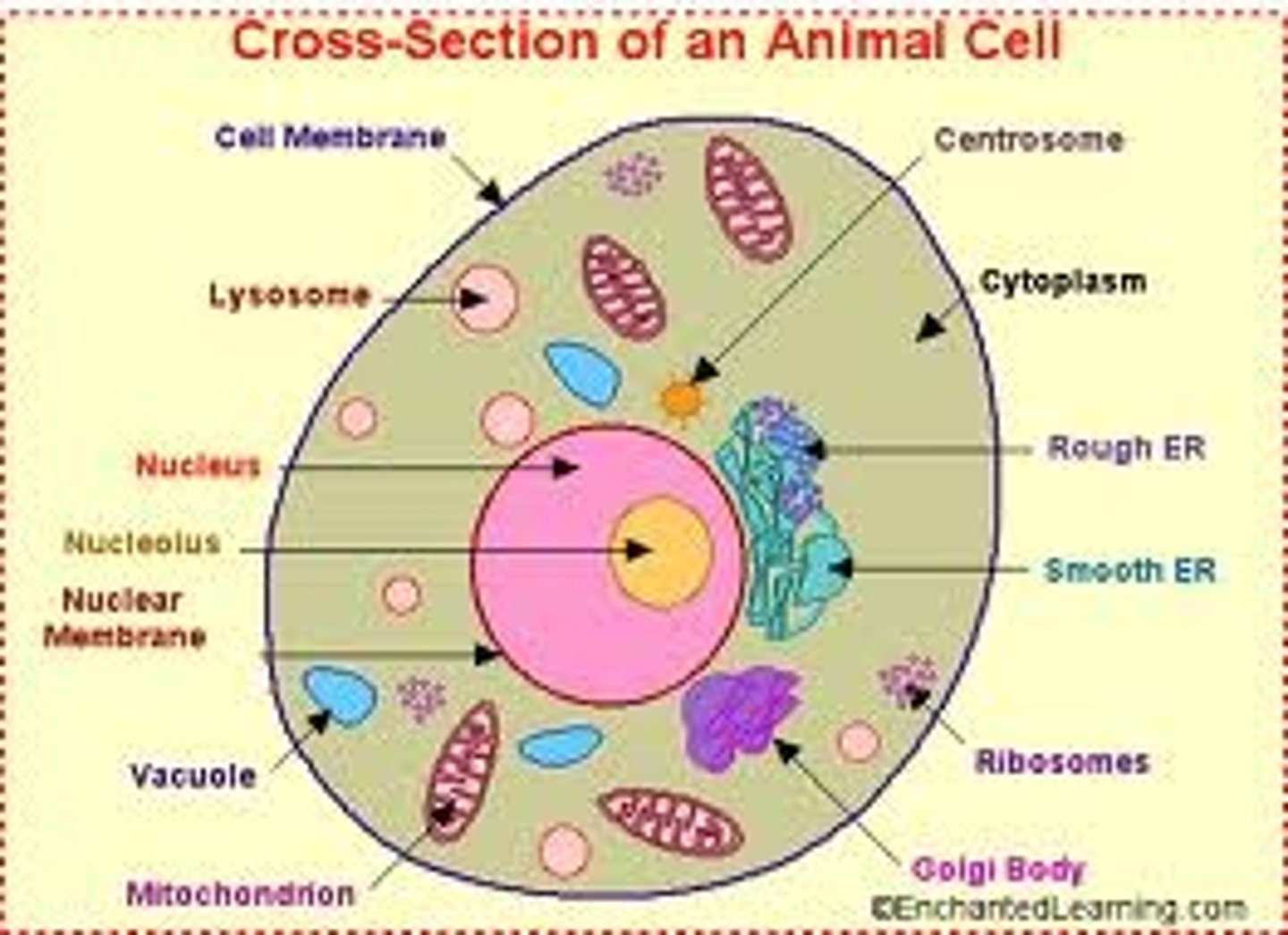
Describe the structure of a typical animal cell
A cell surface membrane surrounding ribosomes, mitochondria, small vacuoles, cytoplasm, and a nucleus with a nuclear membrane.
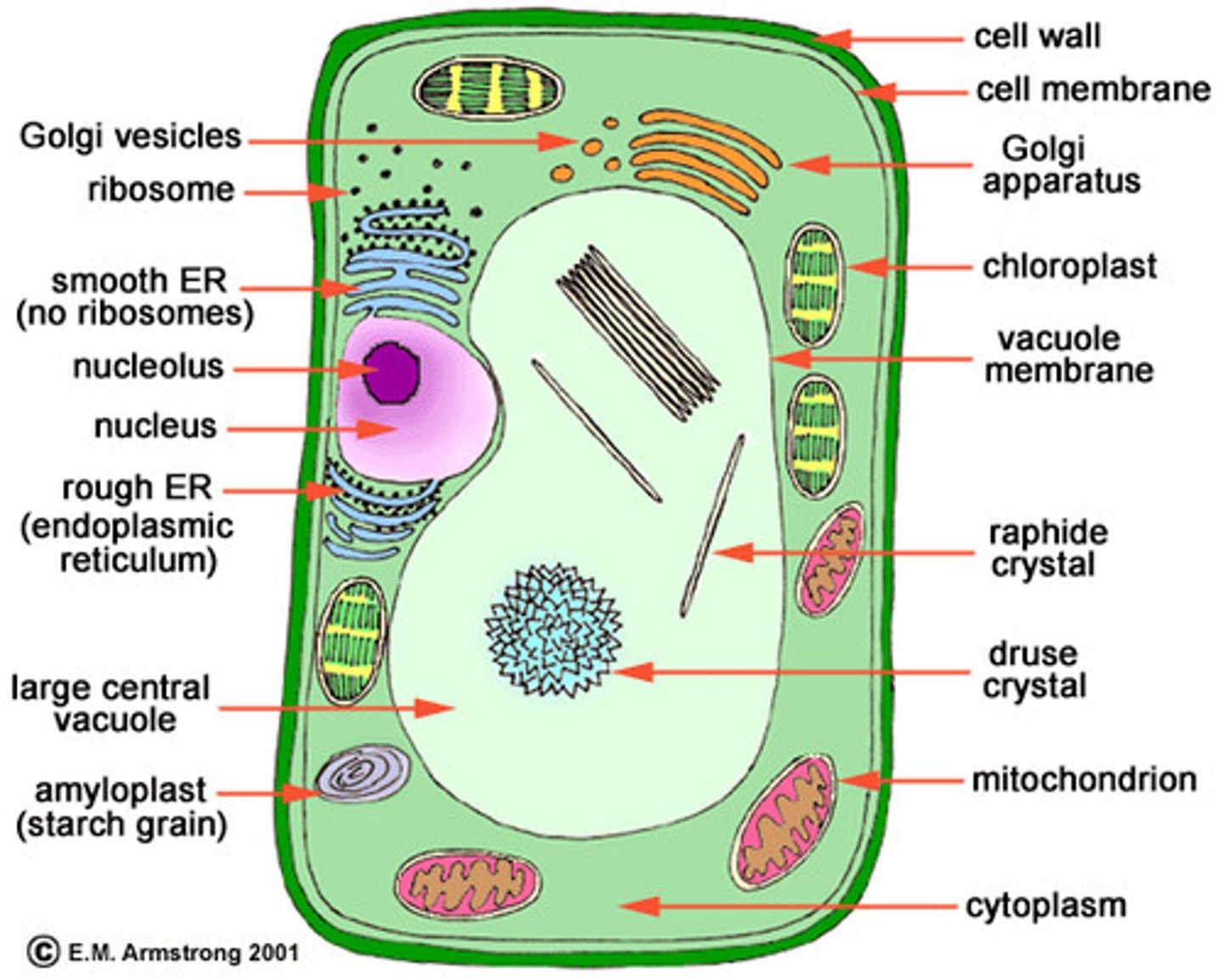
Describe the structure of a typical plant cell
A cell wall and cell surface membrane surrounding membrane-bound vacuoles, chloroplasts with starch grains, large vacuoles containing cell sap, ribosomes, mitochondria, a nucleus with a nuclear membrane, and cytoplasm.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells have no nuclei and no membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells have nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
What types of organisms contain prokaryotic cells?
Bacteria and cyanobacteria
What types of organisms contain eukaryotic cells?
All other kingdoms. Plantae, fungi (including yeast), protoctista, animalia.
What is an organelle?
A part of a cell that plays a specific role.
What is the function of the cell wall?
To give the cell support and shape. It is a tough layer that surrounds some cells.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
To control movement of substances in and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable.
What is the function of the vacuole?
To store food and nutrients.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
They are the sites of cellular respiration for the release of energy.
What is the function of the nucleus?
To control the cell. Also contains DNA.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
A liquid gel where chemical reactions take place.
What is the function of the ribosomes?
The place where protein synthesis takes place.
What is the function of the chloroplasts?
The site of photosynthesis, containing chlorophyll which is a green pigment that absorbs light.
Describe how bacteria work
Bacteria are prokaryotic cells with no membrane-bound organelles. The diameter is 0.5 to 2 micrometers. They have a large surface to area ratio, and food enters through the surface area and quickly reaches all parts of the bacteria. The shapes include rods, spheres, spirals, and commas. Single cells can be in pairs, chains, or clusters.
How does binary fission work?
The cell elongates and DNA is replicated. The cell wall and plasma membrane begin to divide. A cross-wall forms completely around the divided DNA. The cells separate. This occurs every 20 minutes.
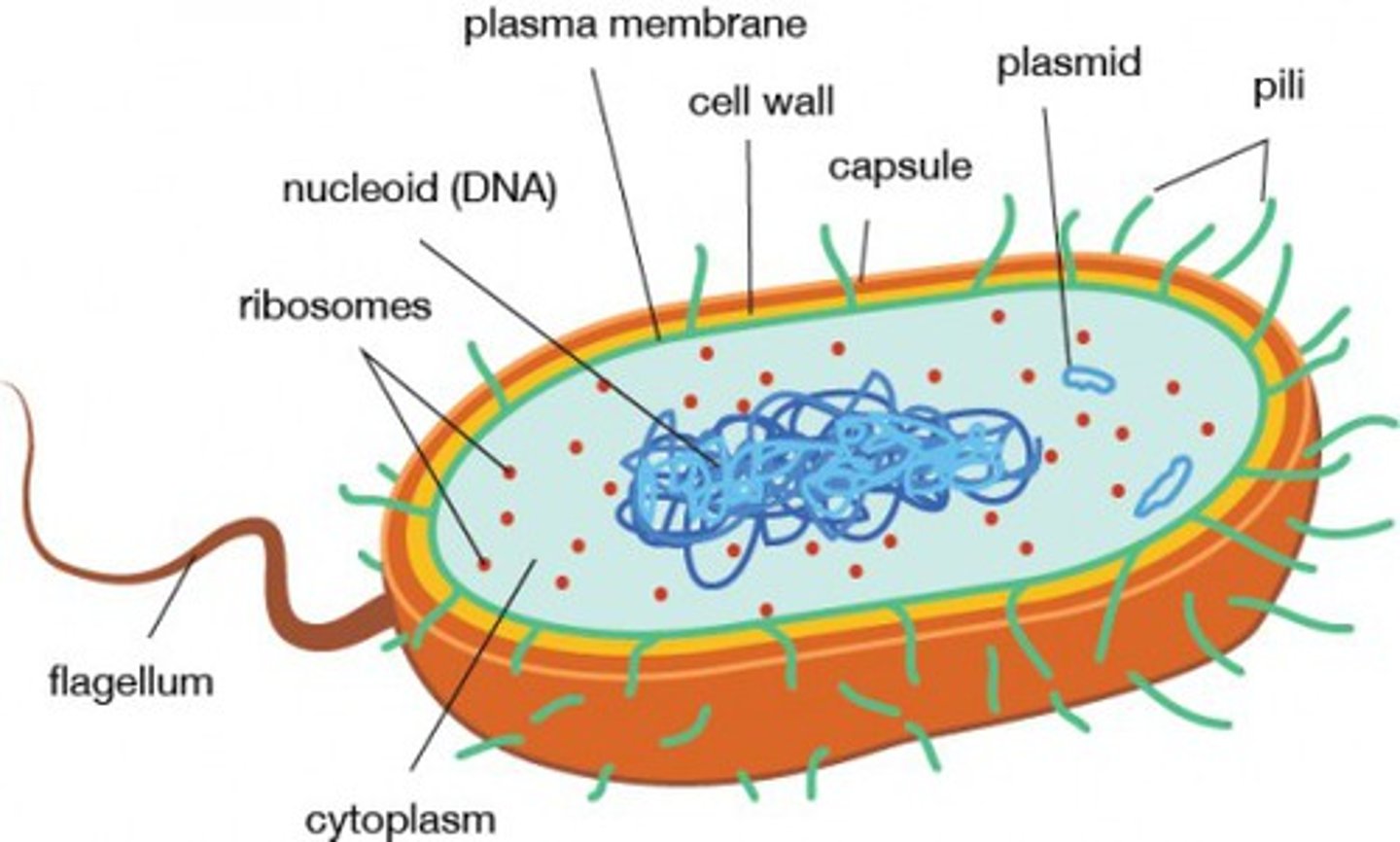
Describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell
A flagellum attached to a capsule (slime layer) which surrounds a cell wall, cell membrane, nucleoid with DNA, plasmids, mesosomes, and ribosomes.
What is the function of the flagellum?
To allow movement. It is whip-like and can rotate.
Which structure allows for cellular respiration?
Mesosomes
What is a plasmid?
A circle of DNA carrying a few genes.
What is the capsule?
A slime layer which helps cells stick together. Slime is a protein.
What are plant cell walls made out of?
Cellulose
What are bacteria cell walls made out of?
Meshworks of murein
What is true about the plasma membrane in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
It has the same structure in both.
What is cyanobacteria?
A phylum of bacteria that obtains energy through photosynthesis, including nostoc, oscillatoria, and gloeocapsa.
Define resolution
The ability to distinguish between two points on an image / how much detail can be seen.
Define focus
Making the image sharper.
Define magnify
Increasing the size of the image.
How do electron microscopes improve from light microscopes?
There is a greater magnification and resolution, allowing for more depth and detail, and you can see cellular organelles.
What are the differences between light and electron microscopes?
Light microscopes use a light source unlike electron microscopes. Electron microscopes can only use dead samples but light microscopes can use dead or alive samples. They fire electrons at samples compared to light travelling through the specimen. Electron microscopes are more expensive and require computers, and can only produce a black and white image.
State the formula for the actual size
Actual size = image size / magnification
State the formula for the total magnification
Total = eyepiece X objective
How many micrometers are in a meter?
1,000,000
How should you draw a scientific drawing?
With no shading, a sharp pencil, no feathering, to scale, include magnification, large, draw what you see, include a scale.
What unit should you use (unless the question says otherwise)?
Micrometers (μm)
What pieces do microscopes contain?
Eyepiece lens, objective lens, slide, stage, mirror, course knob, fine knob.
Describe a method for setting up a stained onion cell for a microscope
Use a scalpel to scrape a thin onion layer. Use a drop of water to stick it onto a slide, and use a drop of iodine to stain the cells. Place under the lens.
What is the role of proteins?
To build and repair muscles and cells
What is the role of lipids?
To develop cell membranes and release energy. Also helps in organ protection and warmth.
What is the role of carbohydrates?
To release energy
What is the role of minerals and vitamins?
Maintaining health and allowing the body to work properly.
What is the role of fibres?
To help food move through the intestine and maintain a clean digestive system.
What is the role of water?
Hydration and help in chemical reactions.
Describe the starch test
Iodine solution turns from brown to blue-black
Describe the sugar test
Benedict's reagent turns from blue to green to orange to orange-red to brick-red.
Describe the protein test
Biuret's reagent turns from blue to purple.
Describe the lipids test
Add ethanol and mix with water. A cloudy liquid indicates the presence of lipids.
How is BMI calculated?
Based on weight and height.
What is BMR?
The energy needed for breathing, circulation, etc without any external work.
Describe the digestive system
Ingested food travels through the throat, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and then the rectum.
What is the role of the oesophagus?
A transport tube that secretes mucus so food can slide down.
What is the role of the stomach?
To produce HCl acid to kill pathogens and denature proteins. To mix food together mechanically. To produce pepsin which breaks down proteins.
What is the role of the small intestine?
To break down, mix, and transport food.
What is the role of the liver?
To produce bile to break fat.
What is the role of the gallbladder?
To store bile
What is the role of the pancreas?
To produce enzymes and secrete glucagon / insulin
What is the role of the large intestine?
To store fecal matter, and absorb the last parts of water and salt
What is the difference between chemical and mechanical digestion?
Chemical uses enzymes whereas mechanical uses muscles
What is the role of bile?
To neutralise HCl in the stomach, to provide optimum pH for amylase, and to emulsify fat so that lipase can work.
What are proteins broken down into by enzymes?
Amino acids
What are carbohydrates broken down into by enzymes?
Simple sugars
What are lipids broken down into by enzymes?
Fatty acids and glycerol
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts - increase the rate of reaction without being used up. Enzymes are proteins (chains of amino acids).
What types of enzymes are there?
Intracellular enzymes and extracellular enzymes (including digestive enzymes)
What are reactions inside cells called?
Metabolic reactions
What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
Catabolism is breaking down large molecules into smaller ones. Anabolism is the synthesis of large molecules from smaller ones. Metabolic reactions are both.
What term describes the relationship between the substrate and active site?
Complementary
What is denaturing?
An irreversible process that changes the shape of the active site, caused by extreme pH or temperature.
What is the optimum temperature of enzymes?
37 degrees celsius
Explain the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity
An increase in substrate concentration causes collisions between the active site and substrate molecules to be more likely, so enzyme activity increases. After a certain substrate concentration, all the active sites are occupied, so enzyme concentration becomes the limiting factor.
State some examples of groups of enzymes and specific enzymes
Groups: protease, lipase, carbohydrase. Specific: pepsin, trypsin, amylase.
Describe the process of breaking down substrates
The substrate molecules bind to the active site. The binding places stress on the polymers, breaking the bonds. When the monomers are released, the enzyme can now bind to other substrates.
What can you measure to check if an enzyme has worked?
pH due to acids, product, time, substrate left.
What are the optimum temperatures for pepsin and amylase?
Pepsin - 2. Amylase - 7.
What are the uses of enzymes?
Biological washing powders, food industry, lactose tolerant milk, soft centred chocolates, slimming foods.
How are enzymes used in biological washing powders?
Proteases break down the coloured, insoluble proteins that cause stains into smaller, colourless soluble polypeptides.
How are enzymes used in the food industry?
Pectinase breaks down in apple cell walls to enable greater juice extraction.
How are enzymes used to make milk for lactose intolerant people?
Lactase breaks down lactose in milk into glucose and glactose.
How are enzymes used in slimming foods?
Fructose is sweeter than glucose, so a smaller amount is needed.
How are enzymes used in soft-centred chocolates?
Invertase creates soft-centred chocolates. The centre initially contains sucrose (can sugar) which is hard.
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + (energy)
What type of reaction is this?
Exothermic, transferring energy to the surroundings by heating.
What are the uses for respiration?
Building proteins from amino acids, muscle contraction, maintaining body temperature, making amino acids from glucose in plants using nitrogen ions in the soil, active transport in root cells.
What do muscles store in case there isn't enough glucose?
Glycogen
How does your body change during exercise?
Sweat, temperature increase, heart and breathing rate increase.
Why does heart rate increase during exercise?
Your respiratory tissues require the heart to pump glucose and water around the body to release energy.
Why does breathing rate increase during exercise?
Your respiratory tissues require oxygen to release energy.
State the formula for the respiratory quotient
Carbon dioxide produced / oxygen consumed
State the formula for cardiac output
Stroke volume X heart rate
When do we respire anaerobically?
When we are exercising hard, and the heart cannot get enough oxygen to the muscles.
Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide + water and more energy. Anaerobic doesn't use oxygen and produces lactic acid and less energy.
What must happen to the lactic acid?
It has to be broken down as it is toxic. Oxygen is needed to break down lactic acid.
What is EPOC?
Excessive post-exercise oxygen consumption - the amount of oxygen needed to oxidise lactic acid to carbon dioxide and water.
What explains why we need to breath deeply and quickly after exercise?
Oxygen debt
How do microorganisms respire?
Fermentation produces ethanol, carbon dioxide, and energy from glucose.
State the equation for fermentation
C6H12O6 → 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO
What can ethanol be in excess?
Toxic to the environment
What are the uses for fermentation?
Wine, beer, baking, hand sanitiser.
What is the role of photosynthesis?
To produce glucose in green plants, which is then used for cellular respiration.
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
Endothermic, absorbing light to start the process.