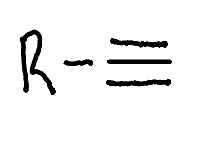How to Know What will be What Mechanism
1/173
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
What Reaction occurs with a 1º carbocation and a strong base and weak nucleophile?
E2
What Reaction occurs with a 1º carbocation and a strong base and Strong nucleophile?
SN2 (80%), & E2 (20%)
What Reaction occurs with a 1º carbocation and a Weak base and Strong nucleophile?
SN2
What Reaction occurs with a 1º carbocation and a Weak base and weak nucleophile?
No Reaction Occurs
What Reaction occurs with a 2º carbocation and a strong base and weak nucleophile?
E2
What Reaction occurs with a 2º carbocation and a strong base and Strong nucleophile?
E2 (80%) & SN2 (20%)
What Reaction occurs with a 2º carbocation and a Weak base and Strong nucleophile?
SN2
What Reaction occurs with a 2º carbocation and a Weak base and weak nucleophile?
No reaction
What Reaction occurs with a 3º carbocation and a strong base and weak nucleophile?
E2
What Reaction occurs with a 3º carbocation and a strong base and Strong nucleophile?
E2
What Reaction occurs with a 3º carbocation and a Weak base and Strong nucleophile?
SN1
What Reaction occurs with a 3º carbocation and a Weak base and weak nucleophile?
SN1 (50%) & E1 (50%)
What type of base is NaH?
Strong Base
What type of base is DBN?
Strong Base
What type of base is DBU?
Strong Base
What type of base is HO-?
Strong Base
What type of base is MeO-?
Strong Base
What type of base is EtO-?
Strong Base
What type of base is I-?
Weak Base
What type of base is Br-?
Weak Base
What type of base is Cl-?
Weak Base
What type of base is RS-?
Weak Base
What type of base is HS-?
Weak Base
What type of base is RSH?
Weak Base
What type of base is H2S?
Weak Base
What type of base is H2O?
Weak Base
What type of base is MeOH?
Weak Base
What type of base is EtOH?
Weak Base
What type of Nucleophile is NaH?
Weak Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is DBN?
Weak Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is DBU?
Weak Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is HO-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is MeO-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is EtO-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is I-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is Br-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is Cl-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is RS-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is HS-?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is RSH?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is H2S?
Strong Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is H2O?
Weak Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is MeOH?
Weak Nucleophile
What type of Nucleophile is EtOH?
Weak Nucleophile
True or false rearrangement (Methyl shift/ hydroshift) can only occur in a markovnikov addition not antimarkovnikov addition.
True
What is the first step of Acid-Catalyzed Hydration?
Protonation of the alkene
What is the Second step of Acid-Catalyzed Hydration?
Nucleophilic attack by water
What is the Third step of Acid-Catalyzed Hydration?
Deprotonation of the oxonium ion
What is the First Step of Oxymercuration Demercuration?
Formation of Mercium Ion through Electrophilic Addition
What is the Second Step of Oxymercuration Demercuration?
Nucleophilic attack by water on the mercuric ion
What is the Third Step of Oxymercuration Demercuration?
Deprotonation of the alcohol
What is the Fourth Step of Oxymercuration Demercuration?
Reduction with NaBH4 to remove Hg(OAC)2
True or False
Rearrangement can occur in Oxymercuration Demercuration.
False; Rearrangement can not occur
What is the first step of Hydroboration-Oxidation?
Hydroboration, which is done three times
What is the second Step of Hydroboration Oxidation?
Oxidation with H2O2 and NaOH
How does the epoxide form in Anti Dihydroxylation?
The alkene attacks the furtherst carbon on mCPBA which then gives its electrons to the adjacent carbon which bonds to the carbonyl group. To prevent a texas carbon the ketone of the carbonyl group attacks the hydrogen connected the the original oxygen which then attacks back to the alkene. This causes a ring to form with the original oxygen and an epoxide.
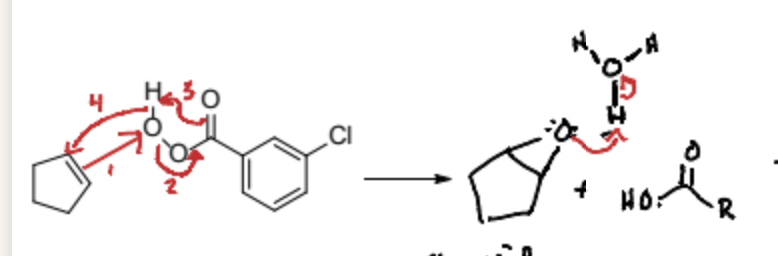
What is the first step of Anti Dihydroxylation?
Formation of an epoxide from an alkene using mCPBA
What is the second step of Anti Dihydroxylation?
The opening of the epoxide ring with water or alcohol, resulting in the formation of a diol.
What is the third step of Anti Dihydroxylation?
Protonation and deprotonation to yield a stable diol.
Is Halogenation Stereospecfic?
Yes, halogenation is stereospecific, typically resulting in anti addition across the double bond.
What is the first step in Halogenation?
The alkene attacks on eof the brominium ions which results in the brominium attacking back. this forms an epoxide like ring.
What is the second step of Halogenation?
The Other bromium Ion not involved in the first step attacks one of the carbons connected in the Brominium Ring resulting in the anti addition of bromine across the double bond.
What is the first step of Halohydrin Formation?
The alkene reacts with a halogen, forming a cyclic halonium ion.
What is the second step of Halohydrin Formation?
The nucleophile, typically water, attacks the more substituted carbon of the halonium ion, leading to the formation of a halohydrin.
What is the first step of Syn Dihydroxylation?
The alkene reacts with a diol reagent, forming a cyclic intermediate.
What is the second step of syn dihydroxylation?
The cyclic intermediate is opened, resulting in the formation of a vicinal diol.
What are the co-oxidants required with syn dihydroxylation?
NMO or Peroxide
What are the reagents of a Oxymercuratio- Demercuration Reaction?
An alkene, mercuric acetate, and sodium borohydride.
What are the reagents for Acid catalyzed Hydration?
An alkene, water, and an acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid.
What are the reactants for Anti dihydroxylation?
An alkene, peroxyacid, and water.
True or False
1º substitued cations favor SN2
True
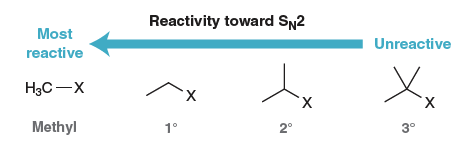
Polar aprotic solvents enhance the rate of an SN2 reaction by
raising the energy of the nucleophile.
What type of solvent is Acetone?
Aprotic
What type of solvent is diethylether?
Aprotic
What type of solvent is THF?
Aprotic
What type of solvent is DMSO?
Aprotic
What type of solvent is DMF?
Aprotic
What type of solvent is H2O?
Protic
What type of solvent is Methanol?
Protic
What type of solvent is Acetic Acid?
Protic
What type of solvent is CCl4?
Nonpolar
What type of solvent is heaxane?
Nonpolar
Does rearrangement occur in Halogenation?
no
Does rearrangement occur in syn Dihydroxylation?
No
Does rearrangement happen in Anti Dihydroxylation?
no
Does rearrangement occur in Acid Catalyzed Reactions?
Yes
Is the halohydrin Reaction anti or regular markovnikov addition?
The halohydrin reaction is an anti-Markovnikov addition, where the halogen and hydroxyl group add to the double bond in an anti fashion.
Does rearrangement occur in Hydroboration Reactions
No
True or False
Elimination reactions can occur in Substitution solvents
True
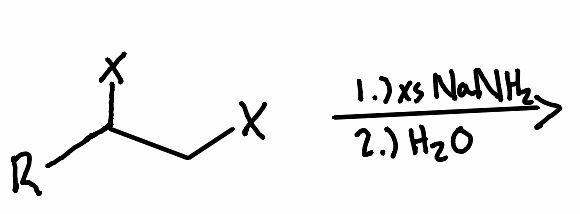
What is the product of the following reaction?
.
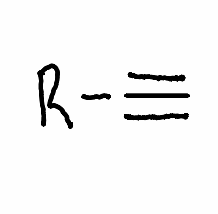

What reactant is needed with the following reaction to perform a vicinal halide elimination to an alkyne?
.
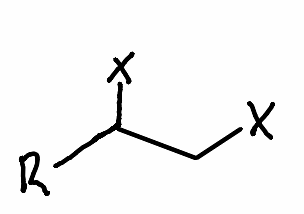
What is the solvent needed to make an alkyne with a geminal halide?
.
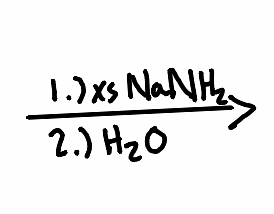
What solvent is needed to make an alkyne with a vicinal halide
.
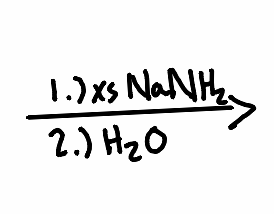
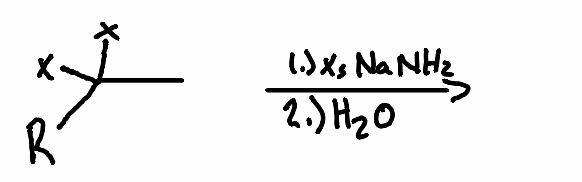
What is the product of the following reaction?
.
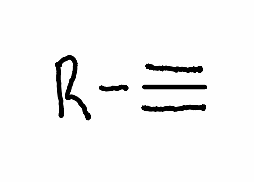

What is the reactant required to get a geminal halide with the following reaction?
.
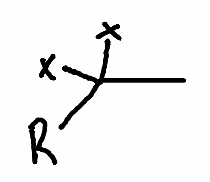
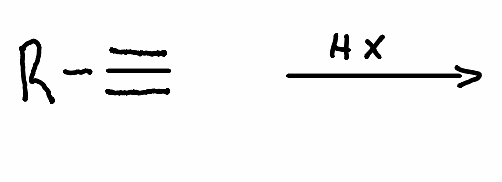
What is the product of this reaction?
.
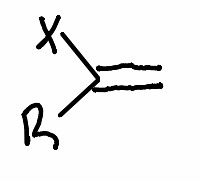
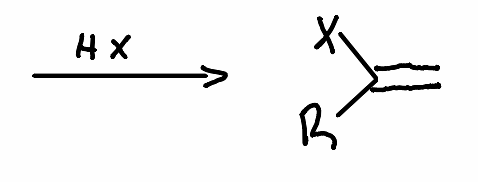
What reactant is used in this reaction?
.
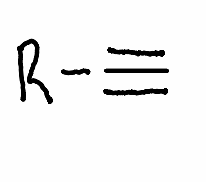
What solvent is required for a hydrohalogenation in one equivalent in an alkyne?
.
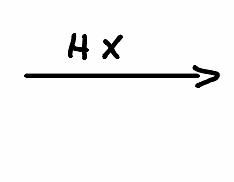
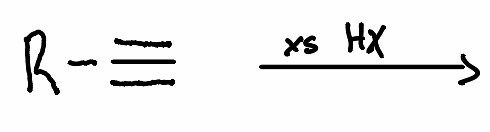
What is the product of the following reaction?
.
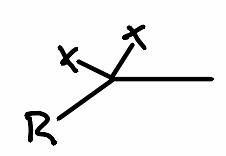
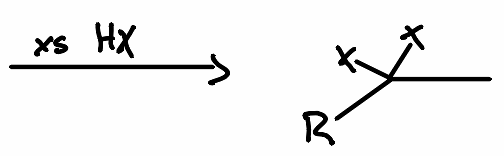
What is the reactant of the following reaction?
.