Astronomy Midterm Exam Review
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Solar System
The Sun plus everything gravitationally bound to it, including 8 planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and more.
Dwarf Planets
Smaller planetary bodies, including Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres.
Asteroids
Rocky/metallic bodies mostly found in the asteroid belt, ranging in size from millimeters to hundreds of kilometers.
Comets
Icy celestial bodies that develop comae and tails when near the Sun, originating from the outer solar system.
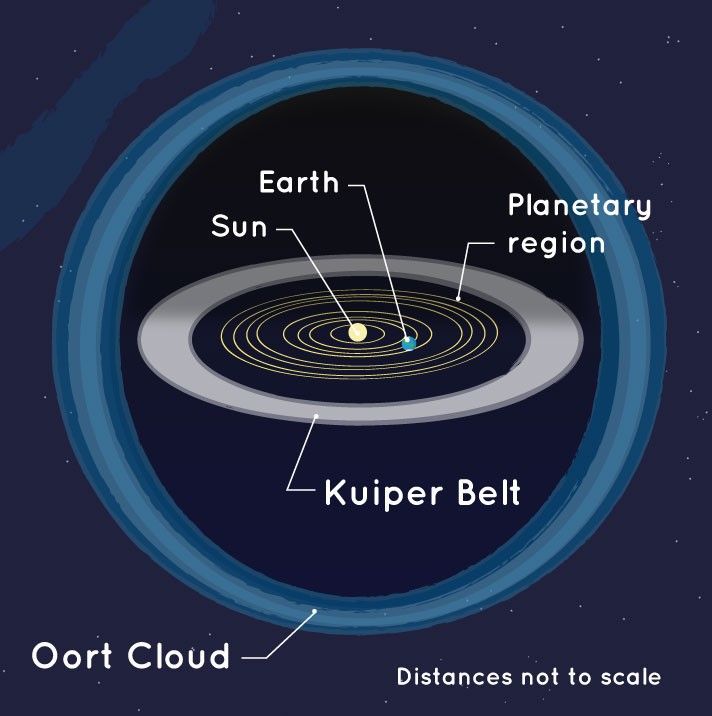
Kuiper Belt
A disk-shaped region beyond Neptune, containing icy bodies and the source of short-period comets.
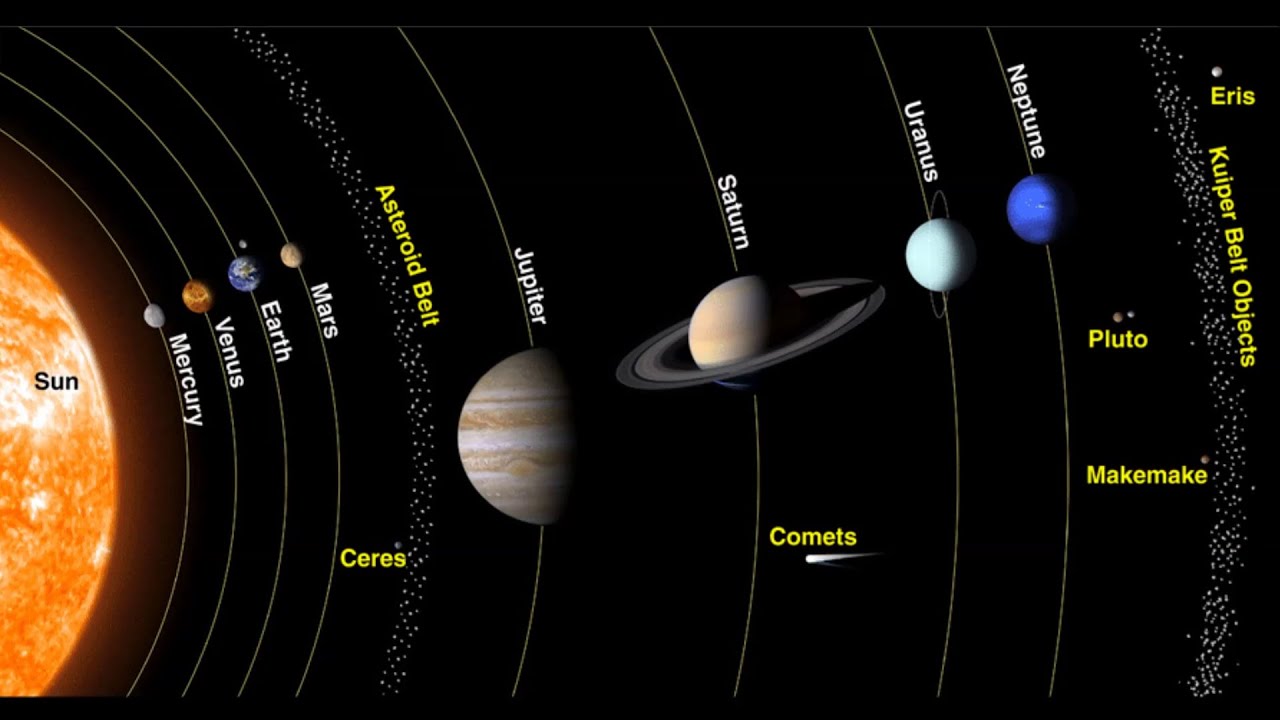
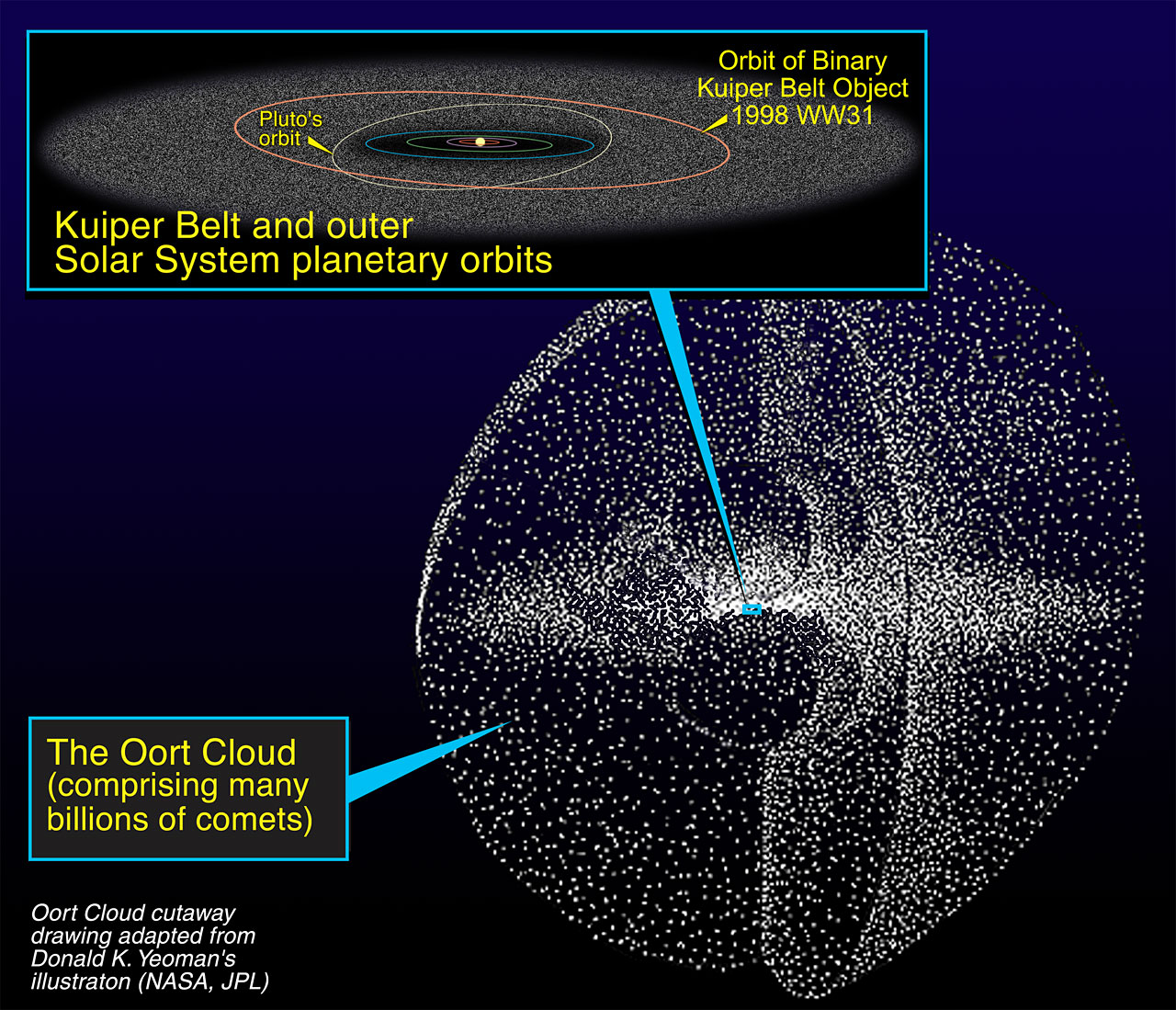
Oort Cloud
A hypothesized spherical region far beyond the Kuiper Belt, thought to be a reservoir of long-period comets.
Interplanetary matter
All solid and gaseous material that exists in the space between planets in the solar system. (basically everything that’s not a planet, moon, or large object in the interplanetary medium.)
Example:
Astroids (rocky and bigger than meteriods
Meteoroids (rocky)
Icy Objects
Comets (Icy with some rock and dust)
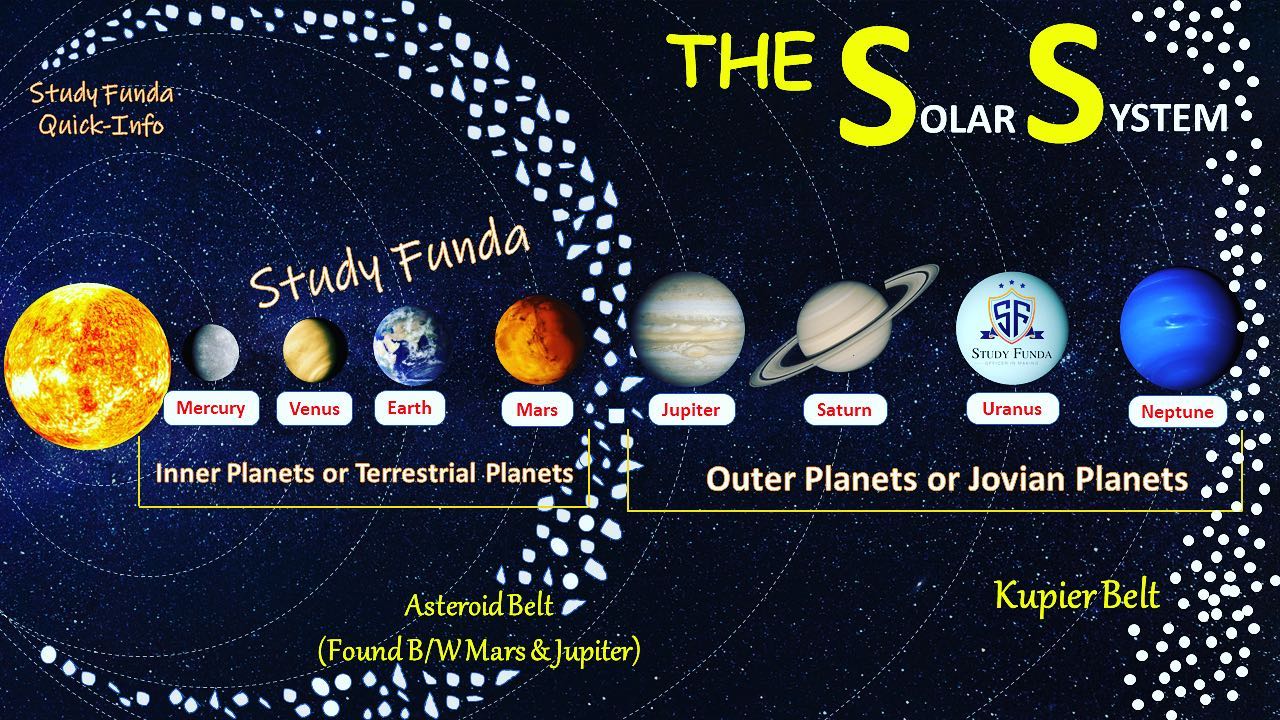
Terrestrial Planets
INNER Rocky, solid planets closer to the Sun with higher densities; includes Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
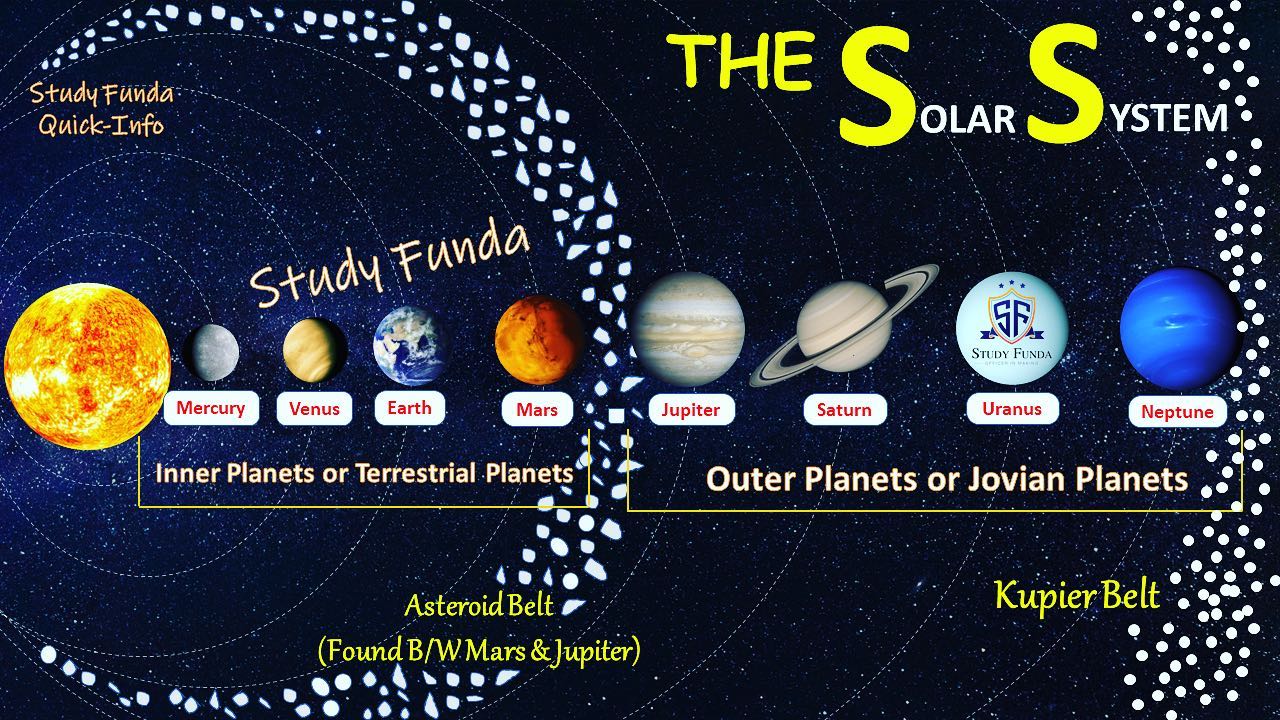
Jovian Planets
OUTER Large, low-density planets with thick atmospheres; includes Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Asteroids vs Comets
Asteroids are rocky; comets are icy, and they behave differently when near the Sun.
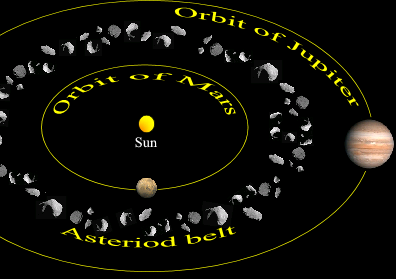
Asteroid Belt
belt closest to the sun
objects found in Astroid Belt:
Asteroids, meteoroids, dwarf planets
Kuiper Belt vs Oort Cloud
Kuiper Belt is near the solar system's edge with frozen bodies; Oort Cloud is a distant spherical region.
Solar Nebula
The cloud of gas and dust that collapsed under gravity to form our solar system about 4.6 billion years ago. after spinning faster it flattened into a disk
Gravity Assist (slingshot)
Using a planet’s motion & gravity to change a spacecraft’s speed and direction relative to the Sun without using extra fuel.
Crust (Earth)
The outer layer of Earth, comprising continental and oceanic regions.
Mantle (Earth)
The layer beneath the crust that is solid but can flow slowly over time.
Outer Core
The liquid layer of Earth's core responsible for its magnetic field.
Inner Core
The solid, metallic center of Earth, primarily composed of iron and nickel.
Troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, where weather occurs and temperature decreases with altitude.
Greenhouse Effect
The trapping of heat in a planet's atmosphere by greenhouse gases, warming the surface.
P-waves
Primary seismic waves that compress and can travel through both solids and liquids.
S-waves
Secondary seismic waves that shear and can only travel through solids.
Shadow Zones
Areas where seismic waves do not arrive due to their path being blocked by Earth's core.
Divergent Boundaries
Where tectonic plates move apart, creating new crust.
Convergent Boundaries
Where tectonic plates collide, causing subduction or mountain building.
transform boundries
Where tectonic plates slide past one another, like the San Andreas Fault.
Auroras
Natural light displays in Earth's polar regions caused by solar wind interacting with the magnetosphere.
Tides
The rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun.
Impact Craters
Depressions on a planetary surface caused by collisions with asteroids or comets.
Giant-impact Hypothesis
Theory explaining the formation of Earth's Moon through a collision with a Mars-sized body called Theia
Lunar Maria
Dark, basaltic plains on the Moon formed by ancient volcanic activity.
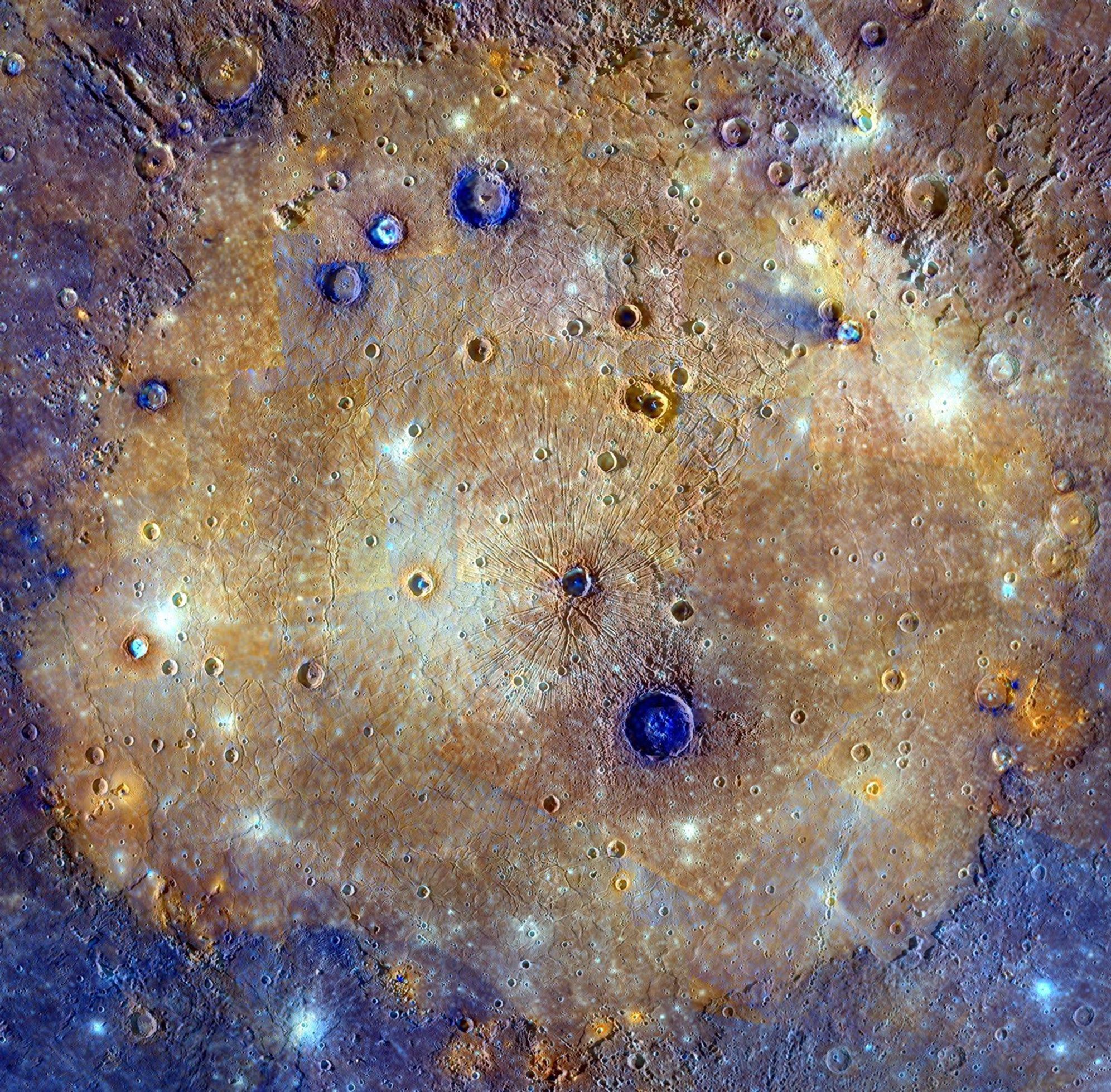
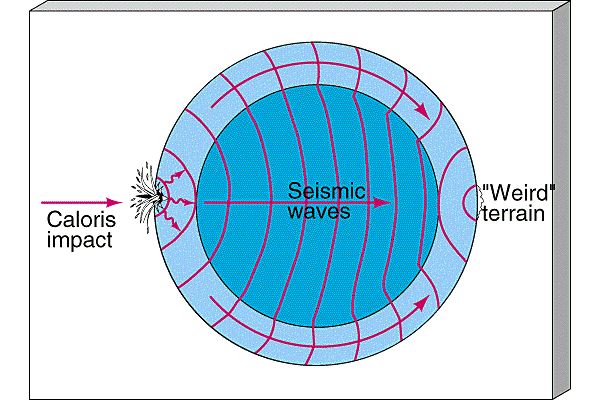
Caloris Basin
Mercurys most prominent/visable land feature.
A multi-ring crater/basin
Ringed by mountain ranges
Impact caused seismic waves inside mercury to create weird terrain on the other side
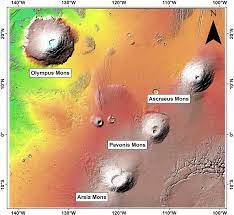
Mars' Tharsis Region
An immense volcanic plateau on Mars, home to the tallest volcano in the solar system (Olympus Mons)
Curiosity Rover
Mars rover that found evidence for ancient habitable conditions.
Seismic Evidence
Data from seismic waves used to infer the internal structure of celestial bodies.
Radiometric Dating
A method to determine the age of materials by measuring the decay of isotopes.
Mercury's Interior
Features a large core and a thin mantle, suggesting unique geological history.
Venus' Atmosphere
Characterized by a dense composition primarily of CO₂, creating extreme surface temperatures.
Past Water on Mars
Evidence found in the form of channels, deltas, and minerals indicating historical presence of water.
Polar Ice Caps on Mars
Layered deposits of water and CO₂ ice that change with seasonal cycles.
Life Potential on Mars
No confirmed life, but potential for habitability in the past or subsurface.
Seismic Wave Propagation
How P and S waves travel through Earth to reveal its layered structure.
Weird Terrain
Unusual hilly texture on Mercury
Created by seismic waves traveling inside mercury that resulted from the impact of the Caloris basin/crater
Scarps
(cliffs) formed when the planets crust cooled and shrank early in mercurys history and caused creases on the surface
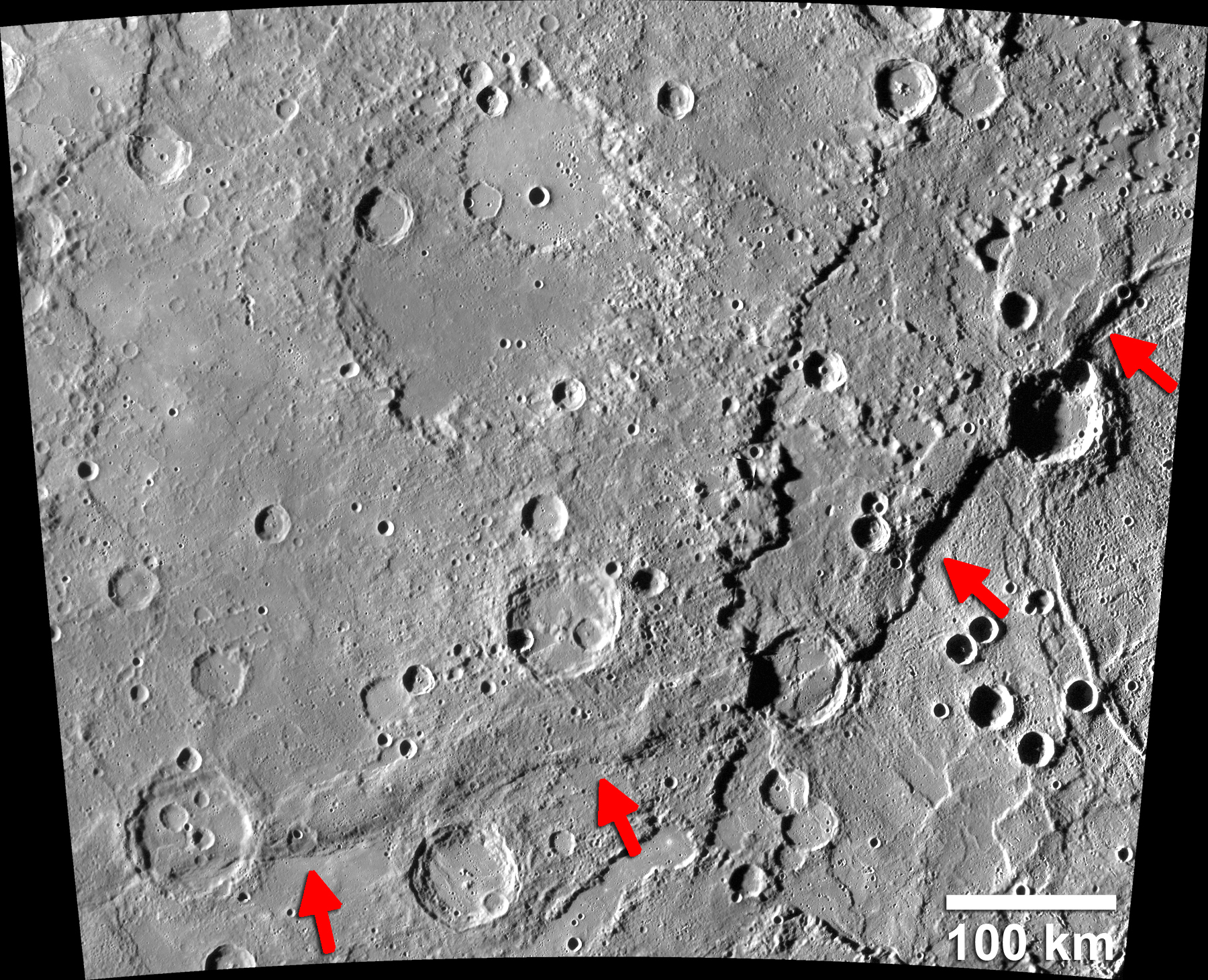

Hollows
look like small white textured spots on Mercurys surface
land features not found anywhere else
caused by sublimation (solid→ gas change)

Moon interior
Regolith
Thick layer of dust left behind from meteorite impacts

Formation of the Solar system
Nebula/solar nebula (cloud of gas and dust) forms
Nebular Contraction- gravity causesNebula/solar nebula (cloud of gas and dust) to collapse on itself
Disk Formation- flattens into spinning disk
Sun forms- most material moves to center to create the sun
Accretion- condensation causes gasses in the disk to cool and condese into solid particles (dust, rock, ice).
Planetesimals- are formed by acretion
Planets are made- more accretion happens by using planetesimals to create planets
phases of Venus
Retrograde Motion
Venusian atmosphere,
polar vortex,
Volcanoes, lava domes
Ishtar Terra
Aphrodite Terra
Mars topography
Olympus Mons
Valles Marineris
, Hellas Basin
Viking, Pathfinder, Spirit,
Opportunity, Curiosity
,
Perseverance, Ingenuity,
Phoenix
, MRO
evidence of water on Mars?
runoff channels,
teardrop shaped islands
deltas, gullies
liquid impact crater ejecta
Martian polar ice caps
Swiss cheese terrain
Martian atmosphere, dust devils, frost
, dust storms
Magnetosphere