Anatomy & Physiology (LAB 2a) - Microscope; Nervous & Muscle Tissue
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Head of microscope
Houses ocular & objective lenses
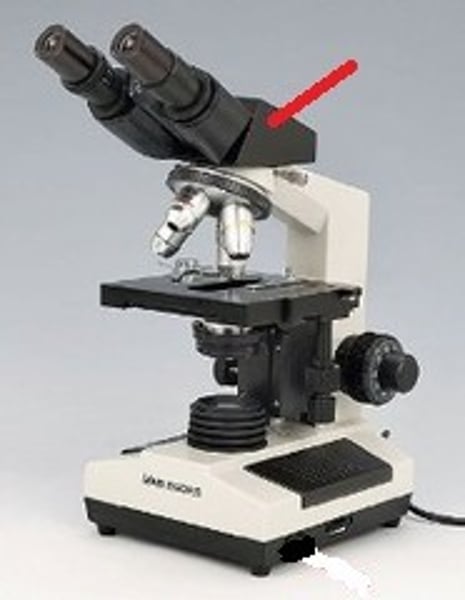

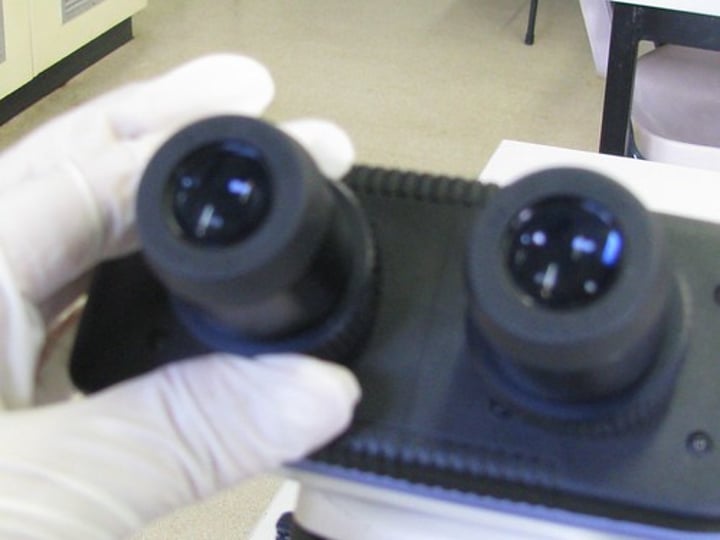
Binocular
eyepiece of microscope

Revolving nosepiece
holds the objective lenses
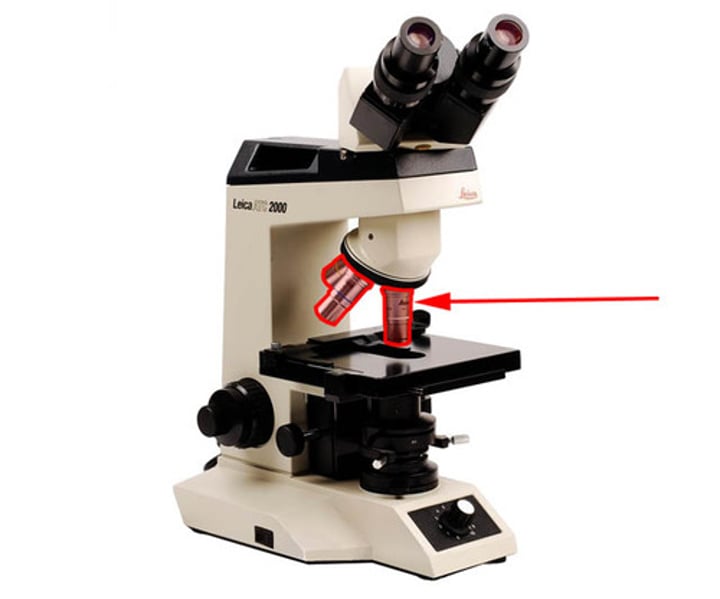
Objective lenses
magnify at a power of 4x, 10x, 40x, & 100x
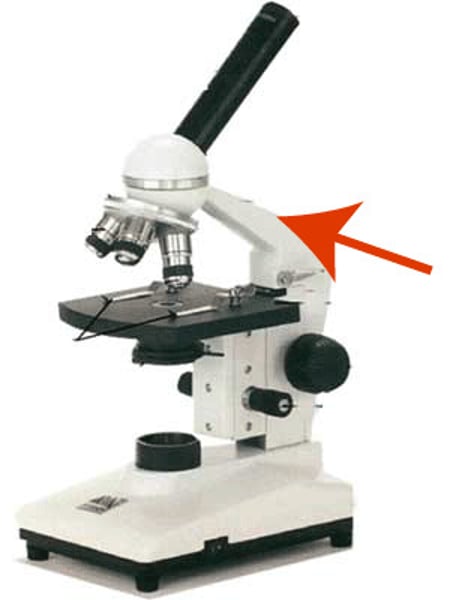
Arm of microscope
handle; connects head to base
On/Off switch
turns the microscope on or off
Rheostat
Dimmer knob, controls brightness (light intensity)
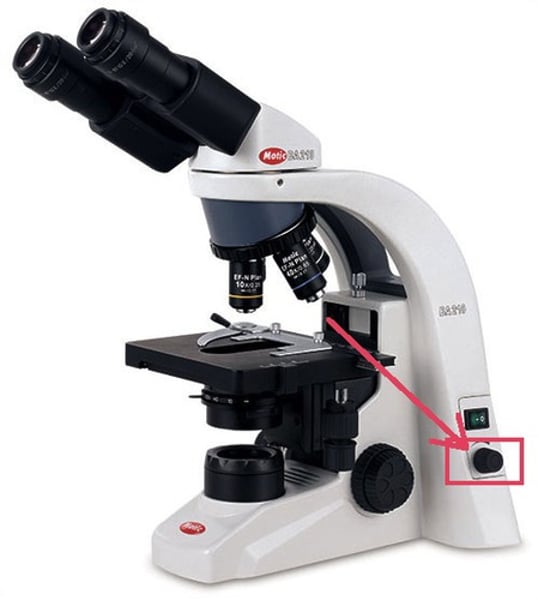
Stage of microscope
holds the microscope slide in position
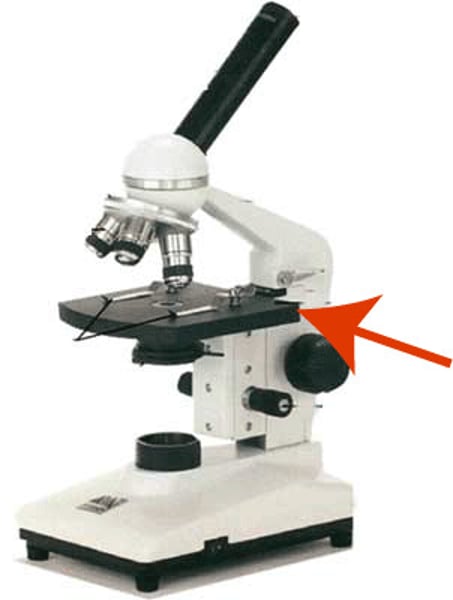
Mechanical stage
holds the slide in position for viewing and has two adjustable knobs that control the precise movement of the slide
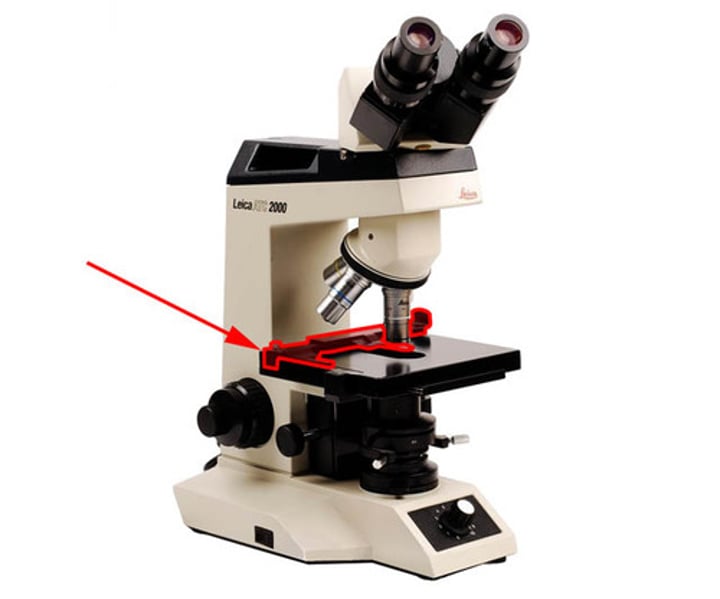
Condenser lense
focuses light onto the specimen
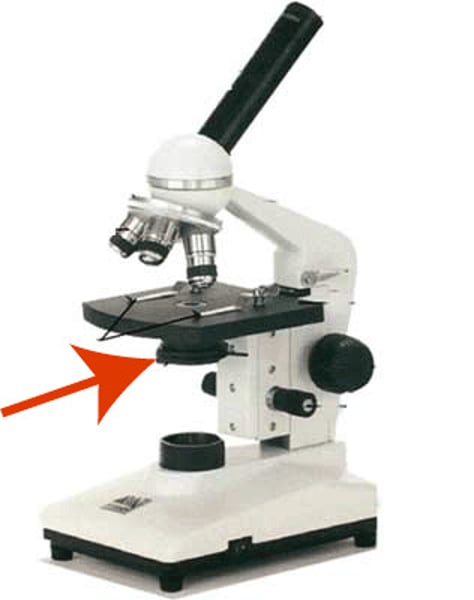
Z-axis stage knob
forward and back
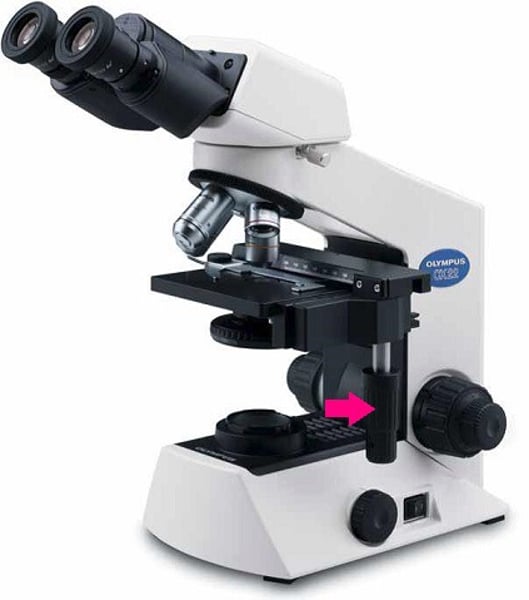

X-axis stage knob
moves side to side
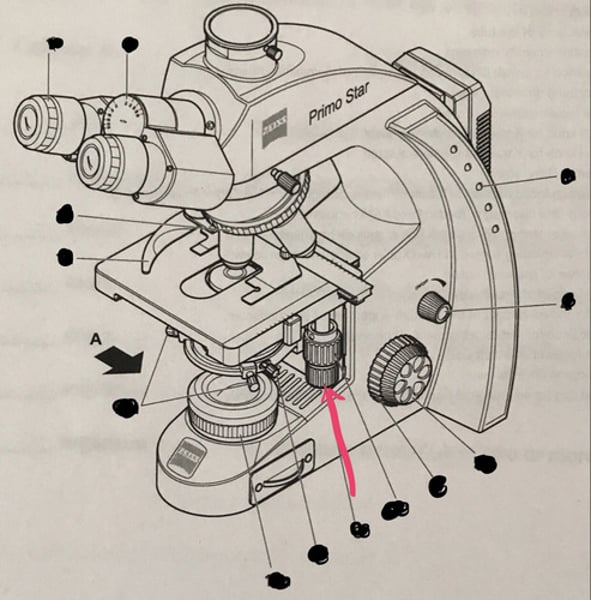
Iris diaphragm
reduces the amount of light by opening or closing
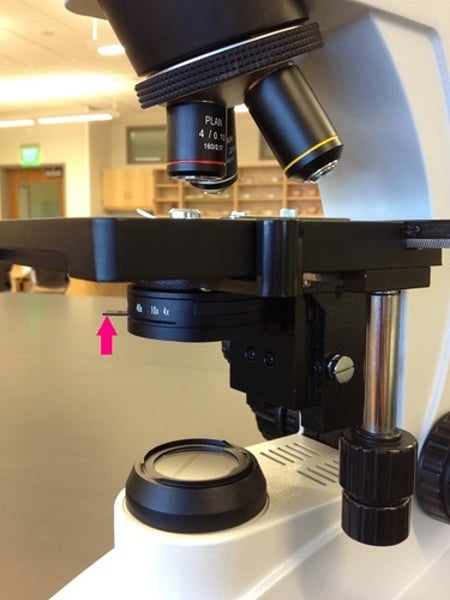

Sub stage light
a light within the base providing the light source for illumination of the specimen
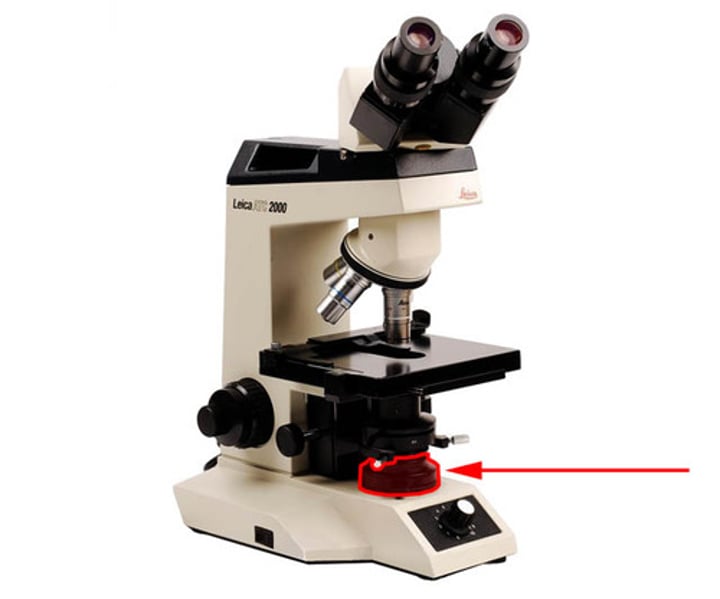
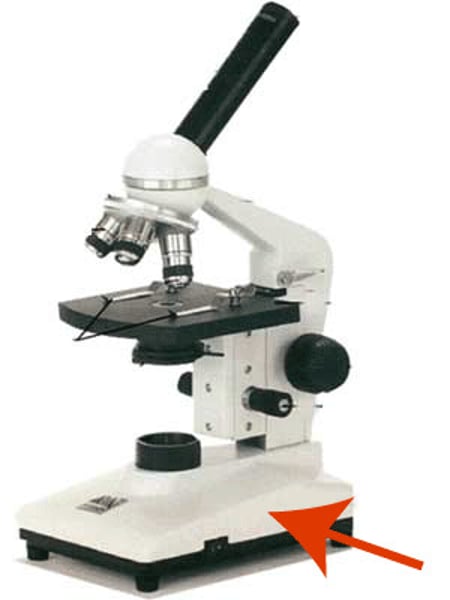
Base of microscope
bottom of the microscope

Coarse adjustment
large knob used with 4x & 10x ONLY
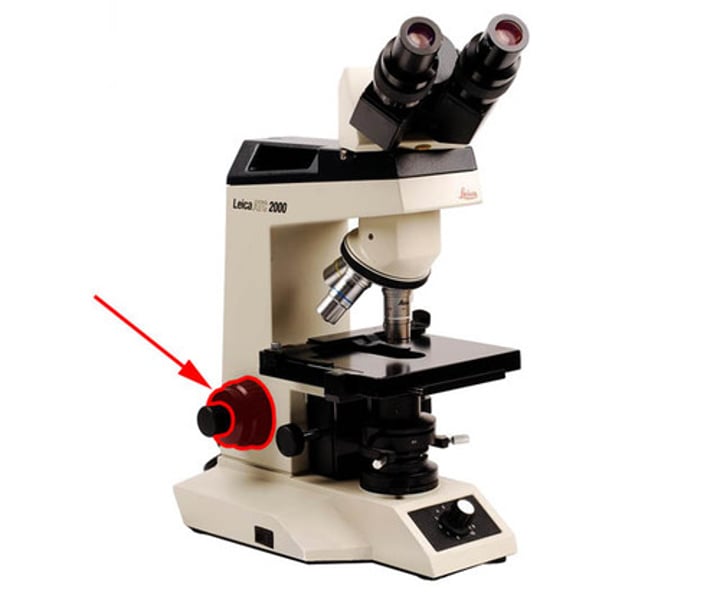
Fine adjustment
small knob used in 40x & 100x
Real image
projected by the objective lens to the ocular lens
Virtual image
seen by the eyes
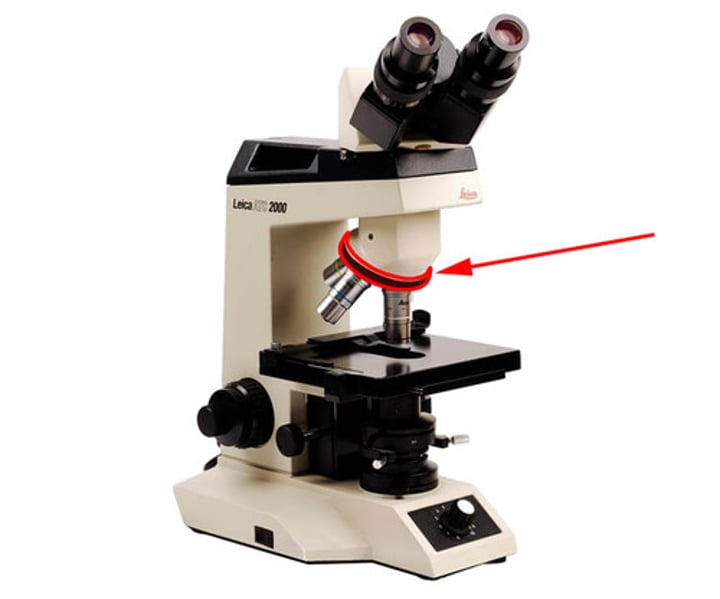
Tension adjustment ring
lies behind the coarse adjustment knob
Histology
study of tissues
Nervous tissue
control, communication, & coordination
- located in brain, spinal cord, & nerves
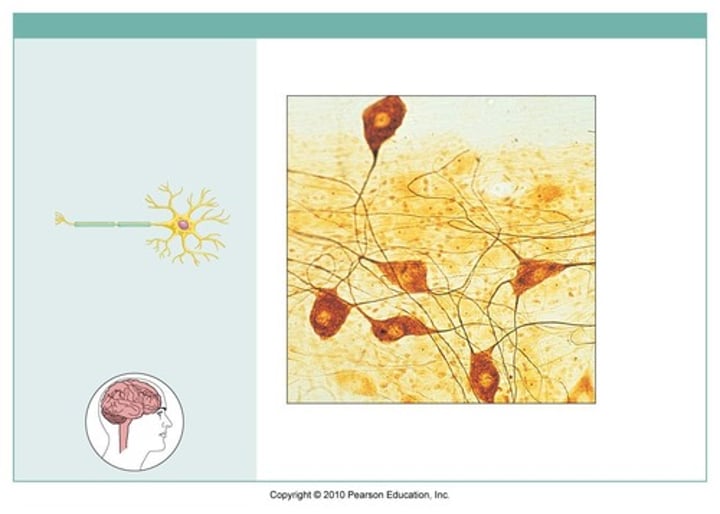
Neurons
nerve cells; generate, receive, & transmit AP nerve impulses
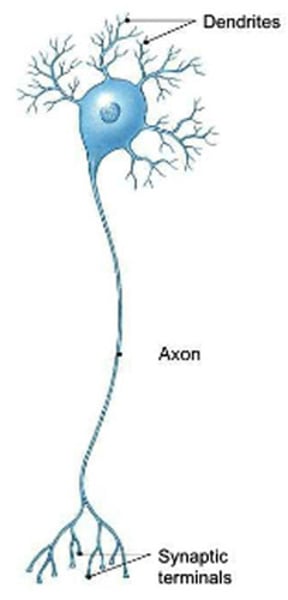
Muscle tissue
contract, excitable, highly cellular, actin & myosin fibers, & well vascularized
- smooth muscle
- cardiac muscle
- skeletal muscle
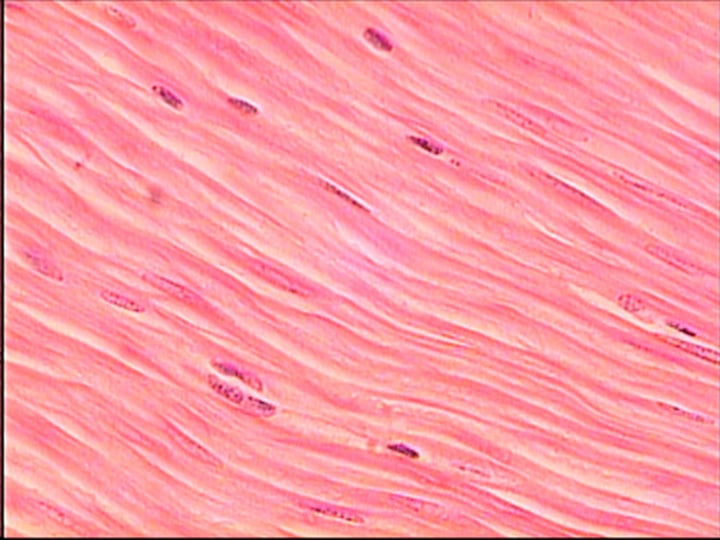
Smooth muscle tissue
- NO striations
- spindle-shaped
- single nucleus
- involuntary control
- line walls of hollow organs
- found in digestive, urinary organs, uterus, airways, blood vessels
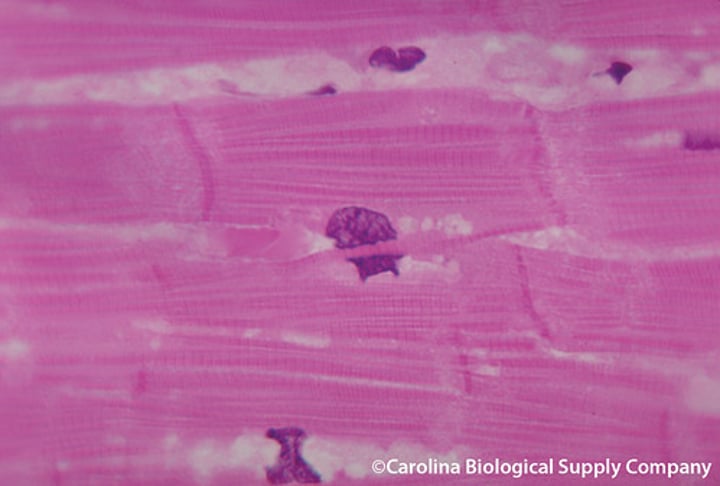
Cardiac muscle tissue
- slight striations
- contracts to propel blood thru vascular system
- irregular & branched
- unicleated
- involuntary control
- found within heart wall & septum
Intercalated discs
unique transverse-thickened junctions which aid in contraction
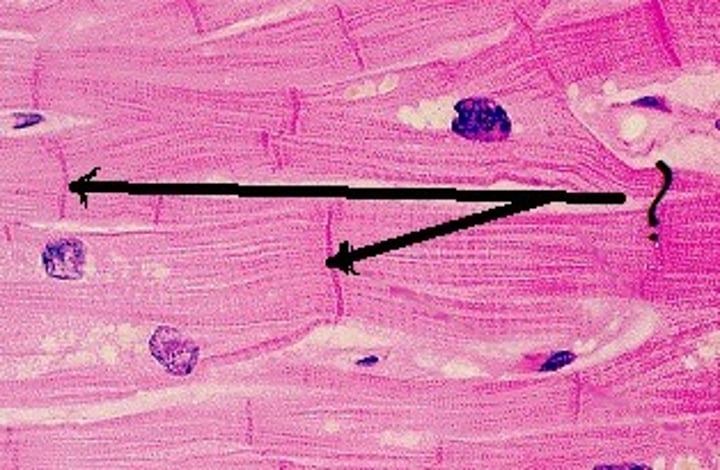
Desmosomes (anchor junctions)
strengthen & prevent separation of cells during contractions
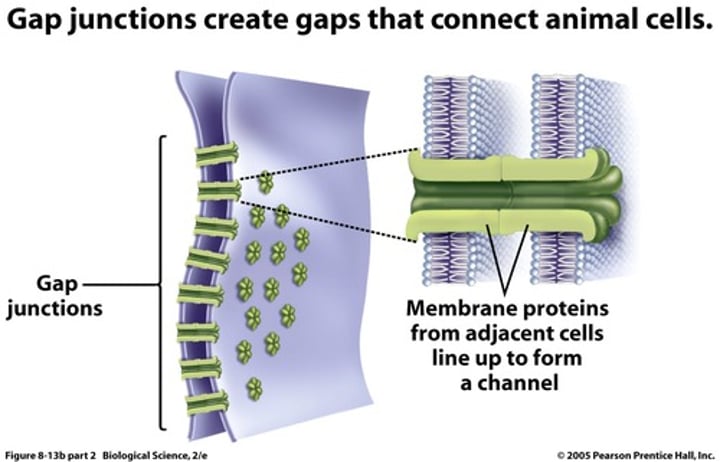
Gap junctions
allow quick passage of action potentials
Skeletal muscle tissue
- obvious striations
- long & cylindrical
- voluntary movement
- long cylindrical cells = muscle fibers
- multinucleated
- found attached to bone

You are looking at muscle tissue thru the microscope & you see striped branching cells that connect with one another. What type of cell are you looking at?
Cardiac muscle cells