Gametogenesis and spermatogenesis 12 and 13
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the main purpose of spermatogenesis?
To produce spermatozoa for fertilisation and sexual reproduction
sections of spermatogenesis
development and maturation of spermatozoa and process continues throughout life
Structure: Seminiferous tubules

Lined with cells called spermatogonia

Location of seminiferous tubules
Inside testis
What type of cells are spermatogonia?
Parent sperm cells are diploid cells
Function: epididymis
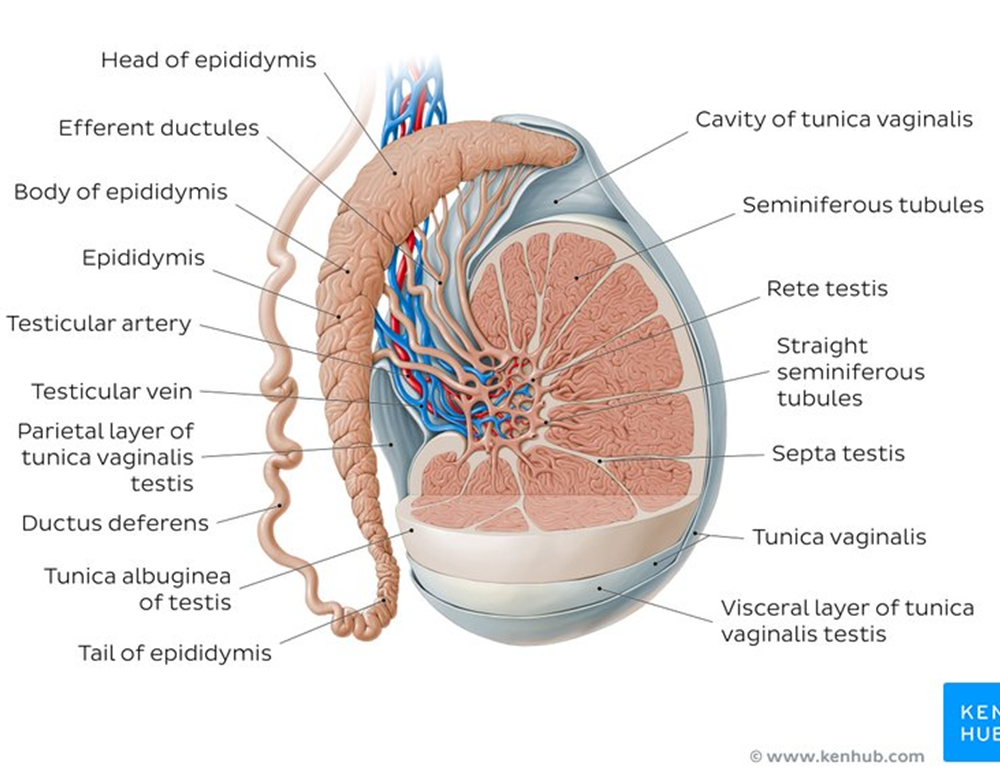
stores and matures spermatozoa
How do the spermatogonia provide a continous source of cells?
They undergo mitosis
What is a primary spermatocyte?
One of the daughter cells that were pushed inwards and enlarged
When does mitotic division begin? sperm
At puberty
How long to undergo all steps?
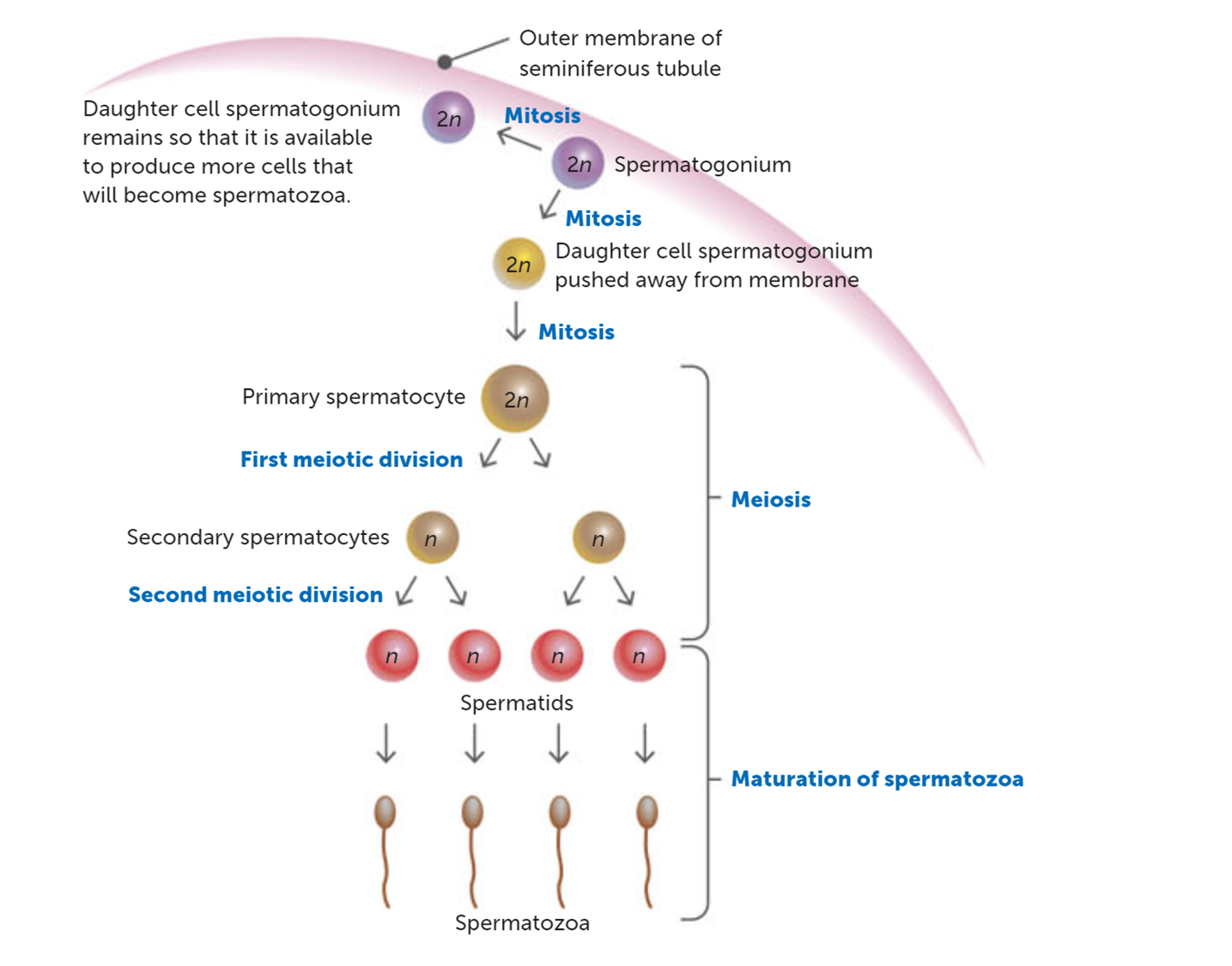
72 hours
How is a secondary spermatocyte produced?
When the primary spermatocytes (diploid cells) undergo the first stage of meiosis
What type of cells are secondary spermatocytes and how many are produced during meiosis?
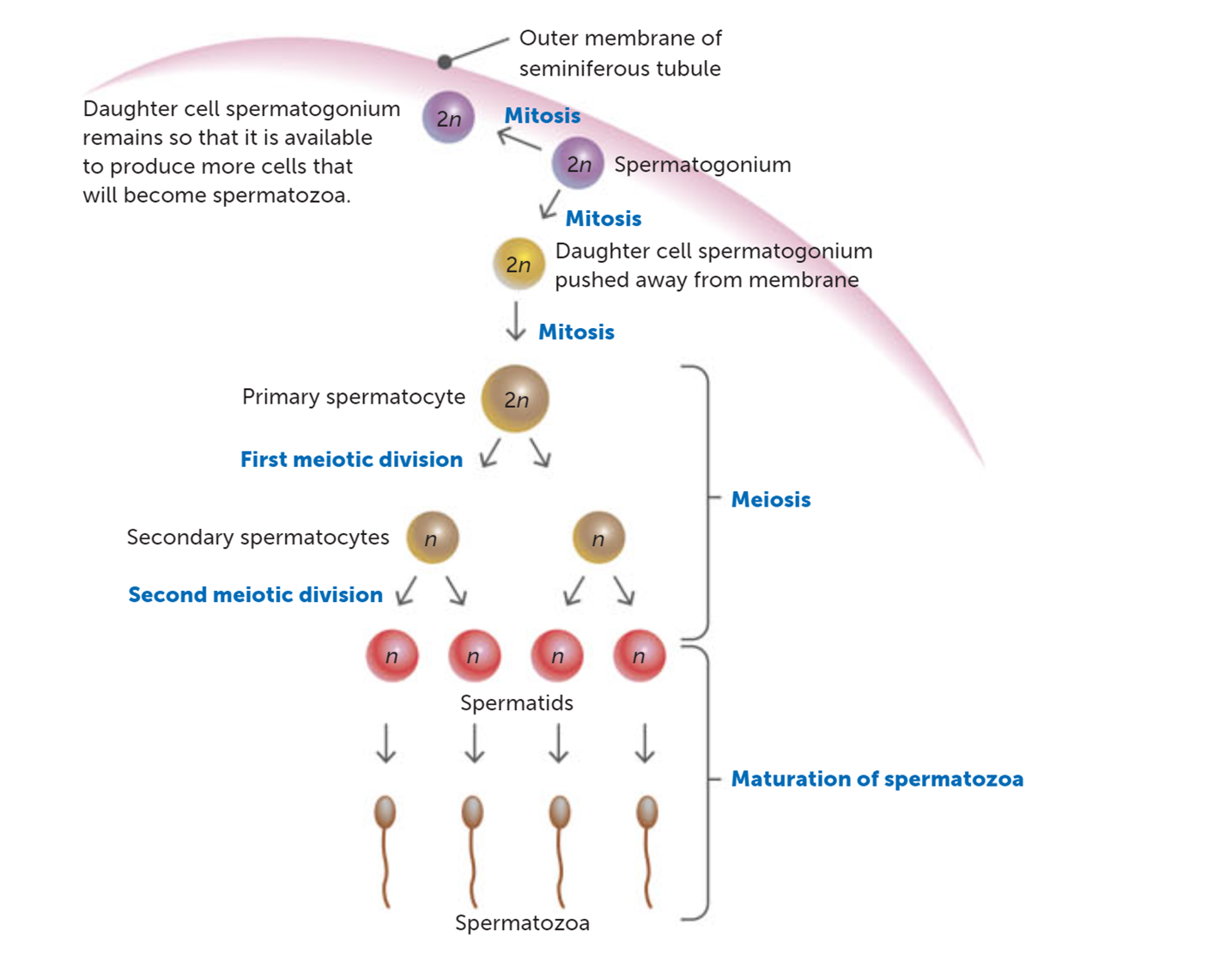
Haploid cells and two
What happens during the second stage of meiosis?
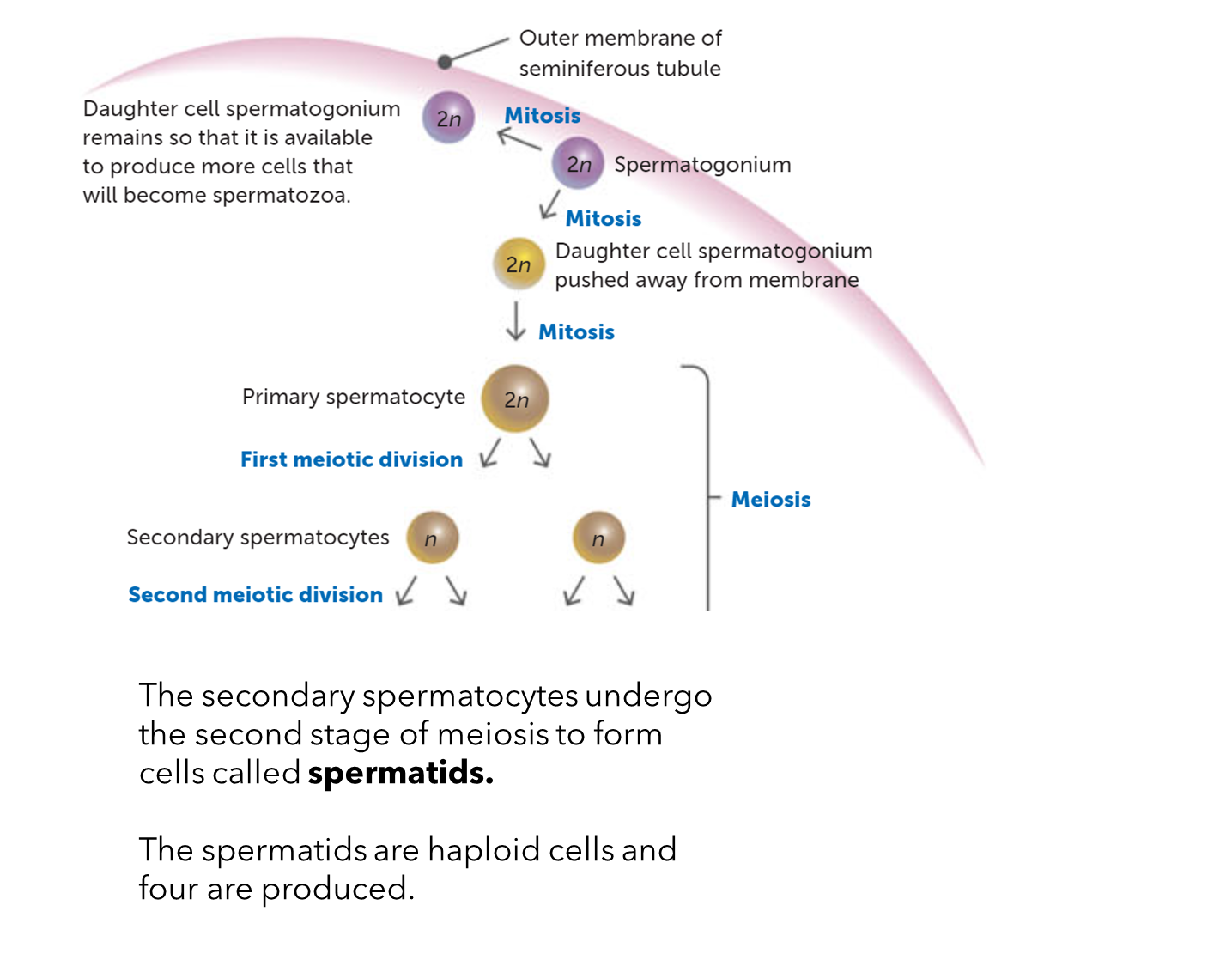
When secondary spermatocytes undergo it to form cells called spermatids
What are spermatids and how many are produced?
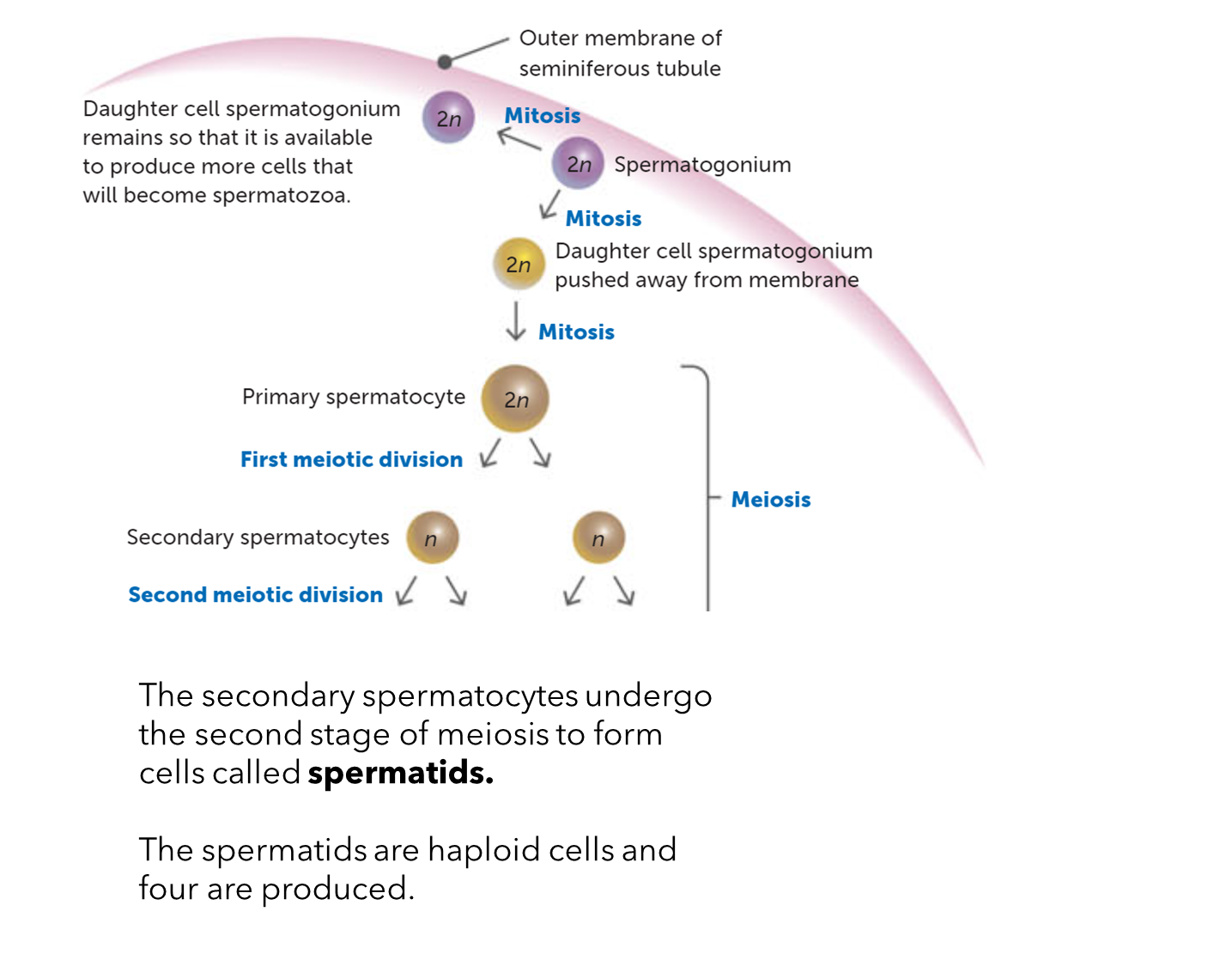
Haploid cells and four are produced
What is the name of the final stage and where does it occur?
Maturation, occurs in epididymis
What happens during maturation?
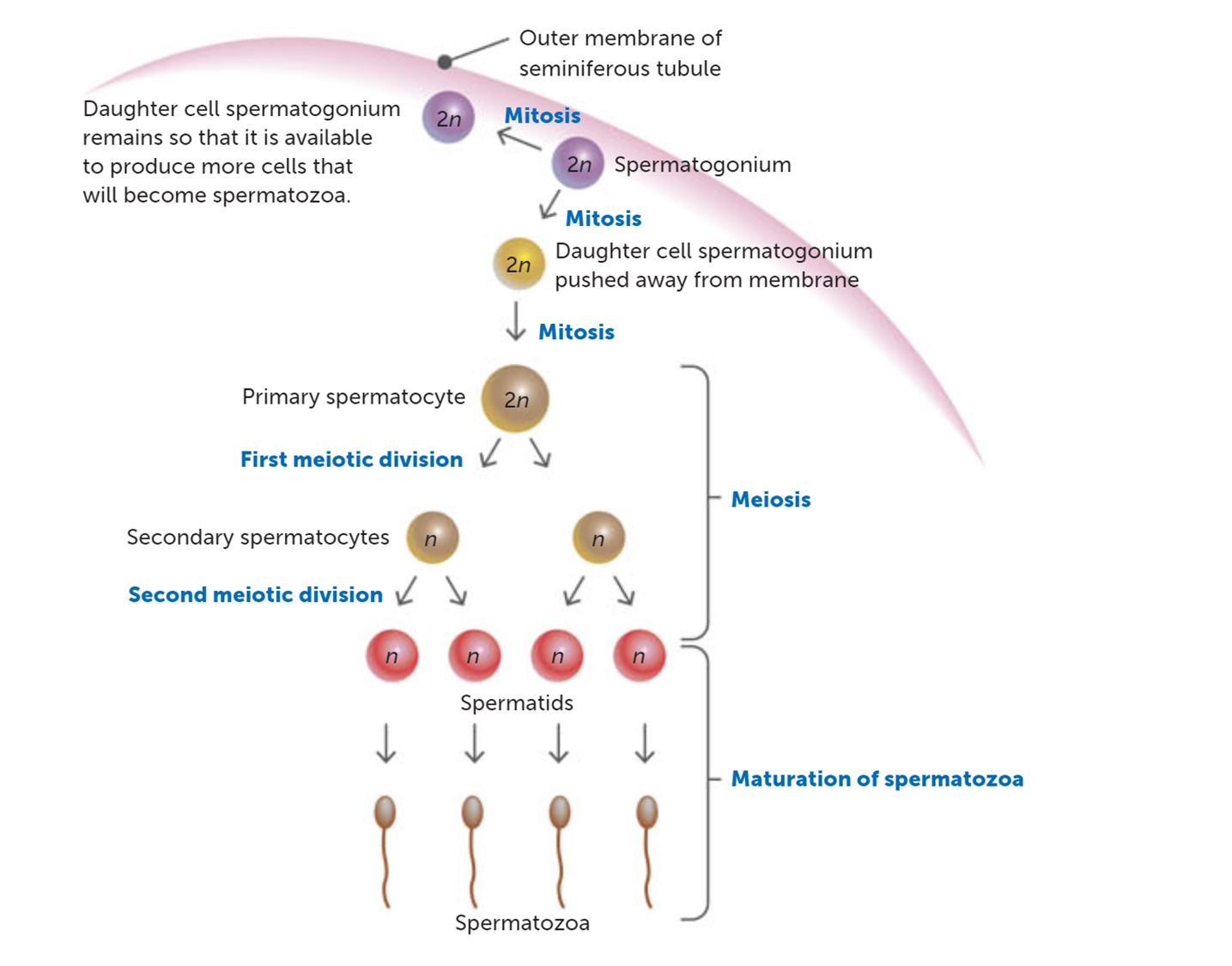
The spermatids lose most of their cytoplasm and form a tail of contractile materials and are now spermatozoa
What type of cells are oogonia?
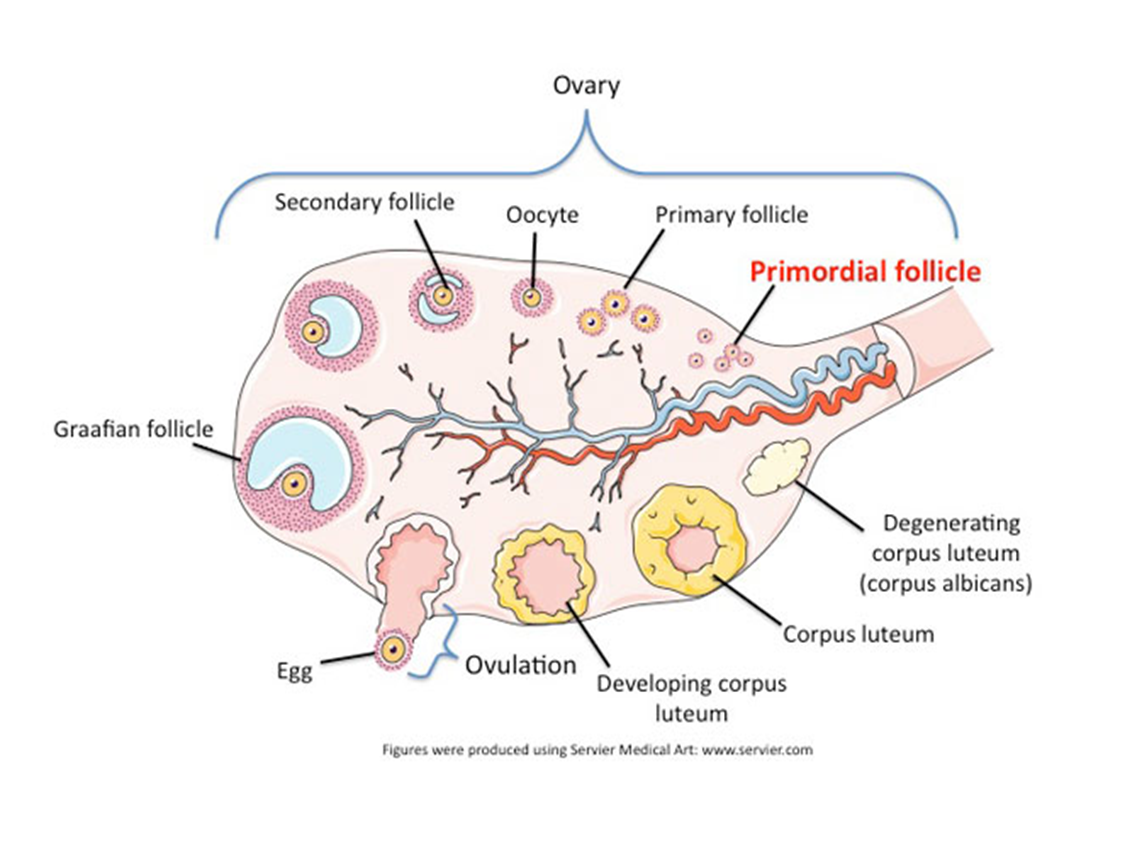
mother (parent) cells, diploid cells
Where does oogenesis occur?
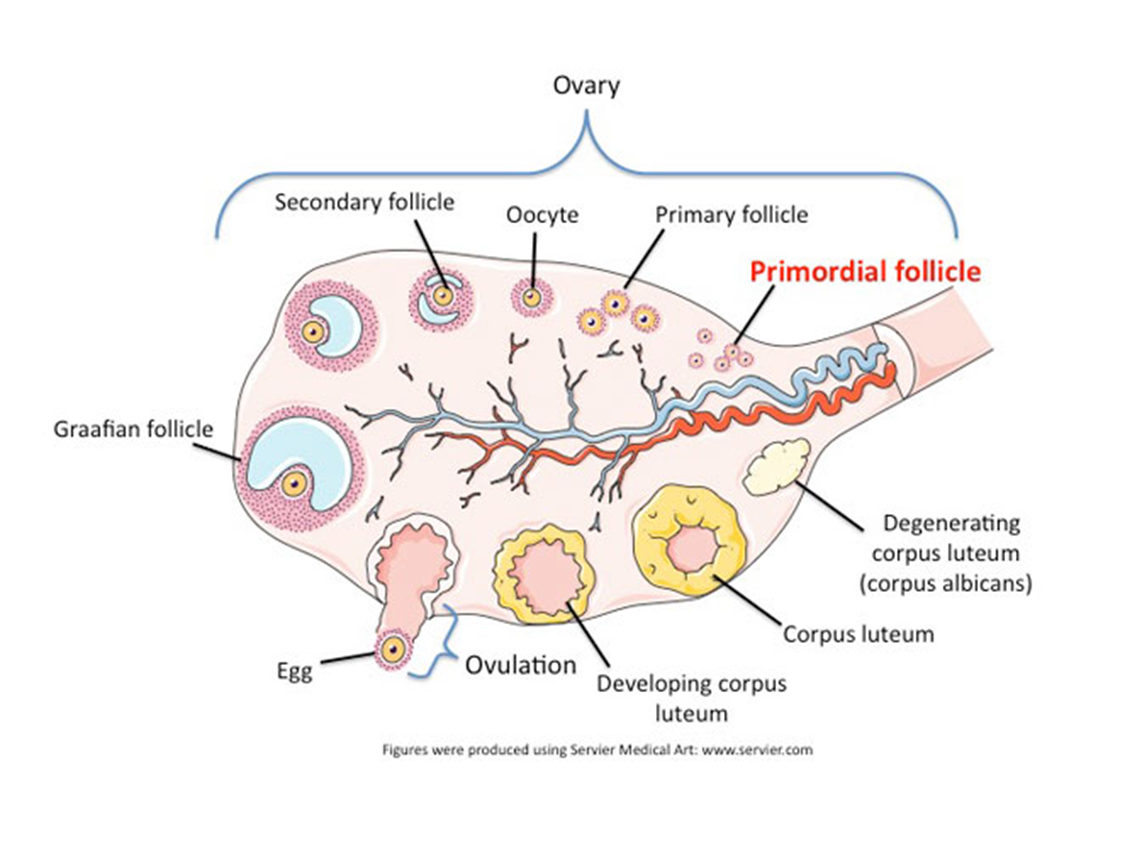
Inside the ovaries
Structure: Wat do primary follicles contain and why?
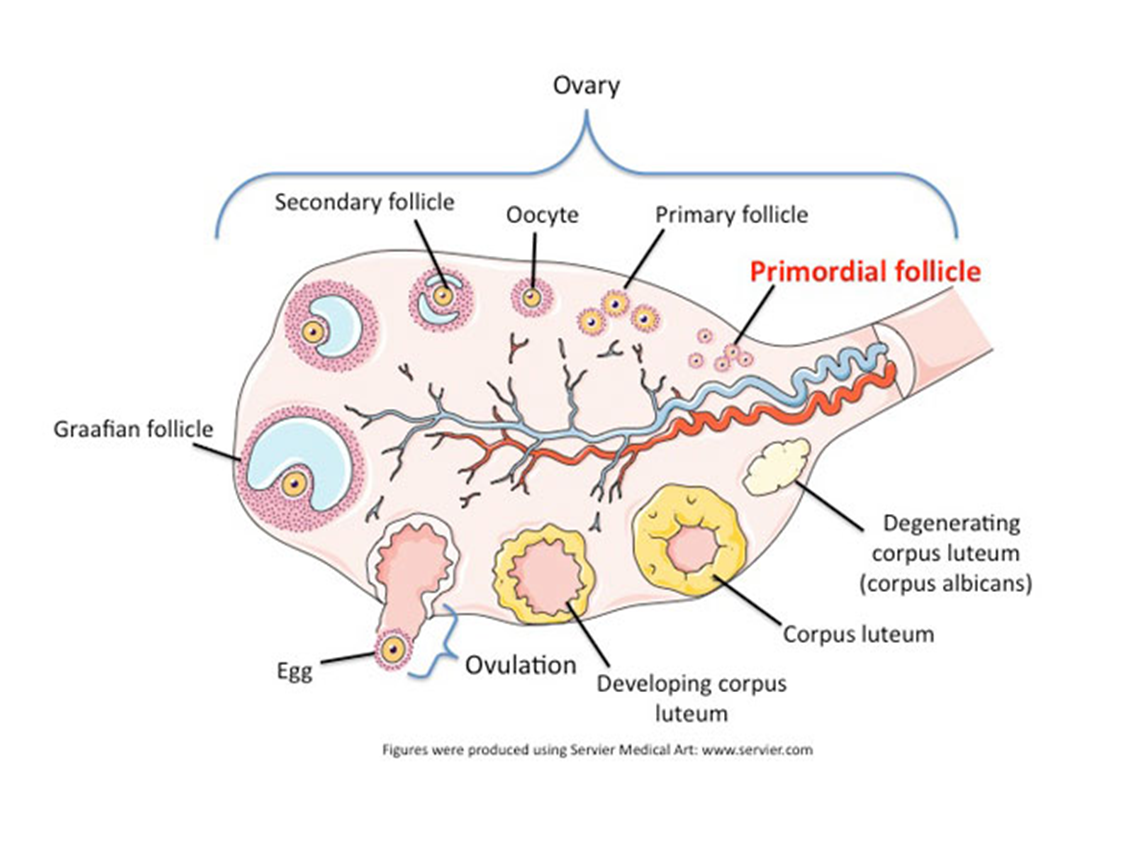
They contain the ova and Granulose cells for nourishment of the oocyte.
When does the primary follicle grow and mature?
At puberty
How does a primordial follicle become a primary follicle?
Activation
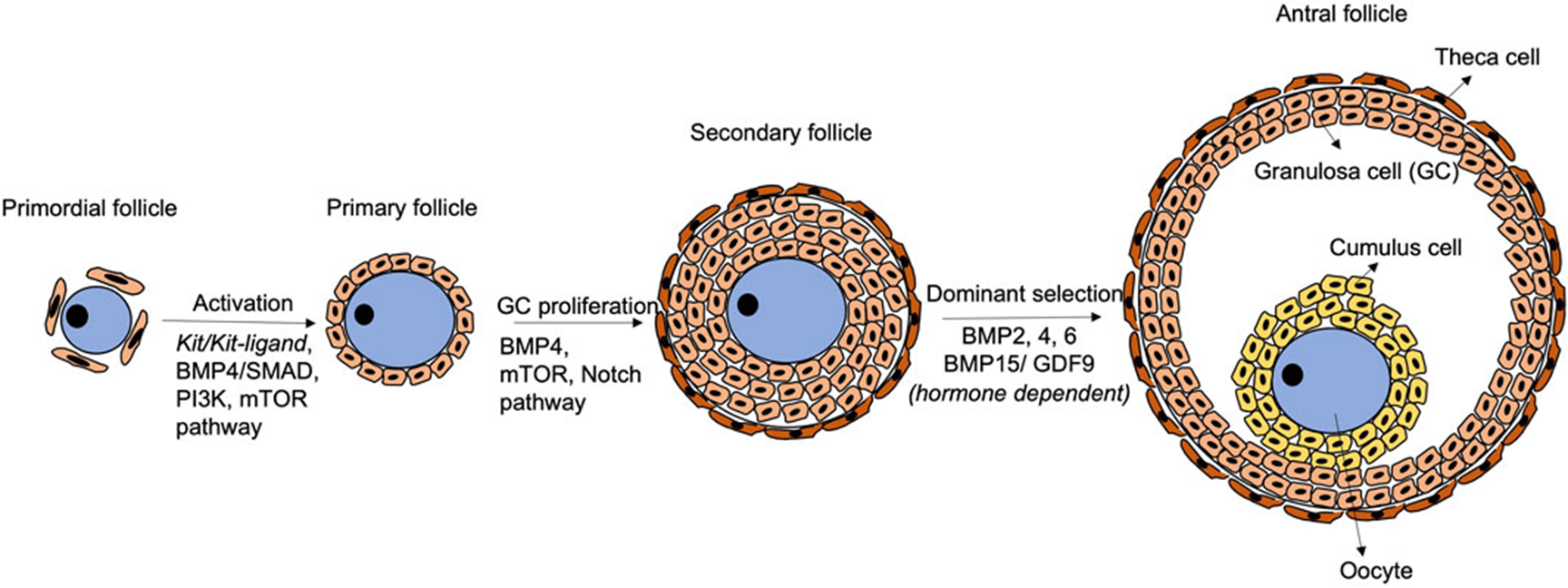
Primary follicle → secondary follicle
GC profileration
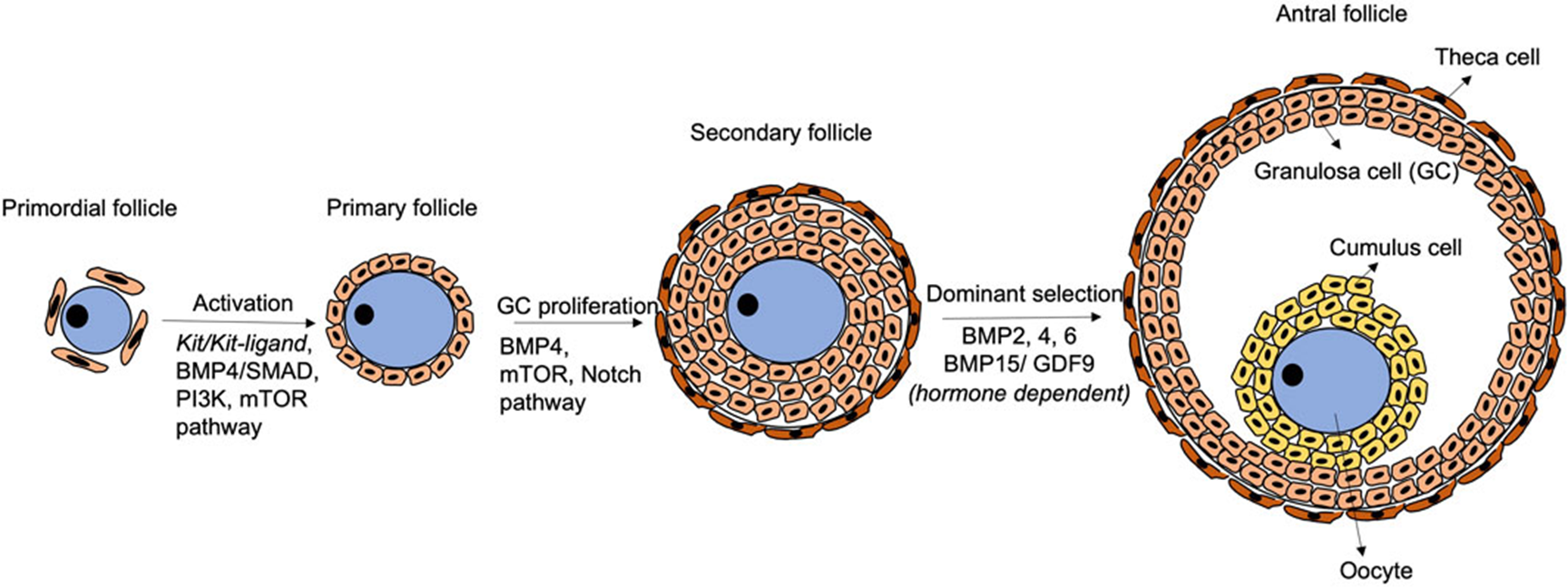
Secondary follicle → Antral follicle
Dominant selection
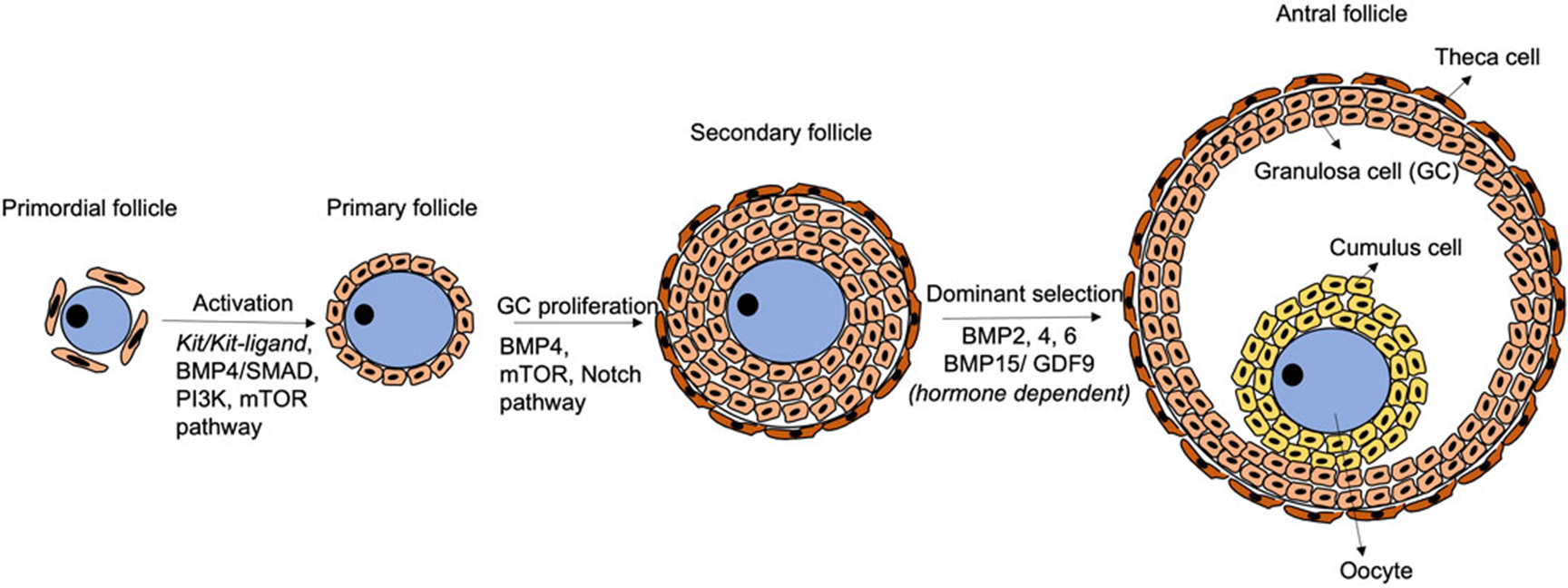
All parts of an antral follicle:
Theca cells, granulosa cell, cumulus cell, antrum, oocyte
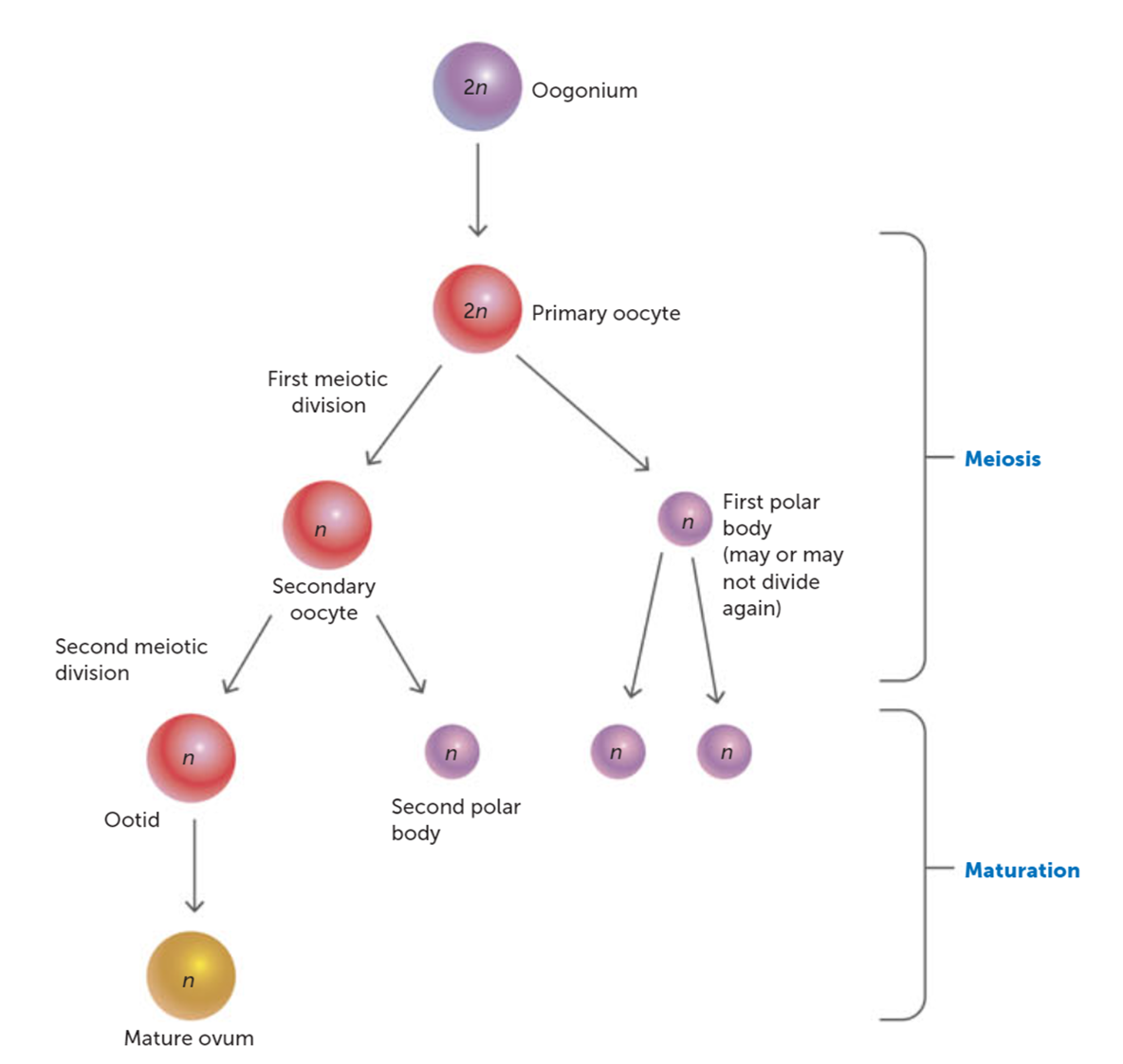
Oogenesis products star to end with DNA:
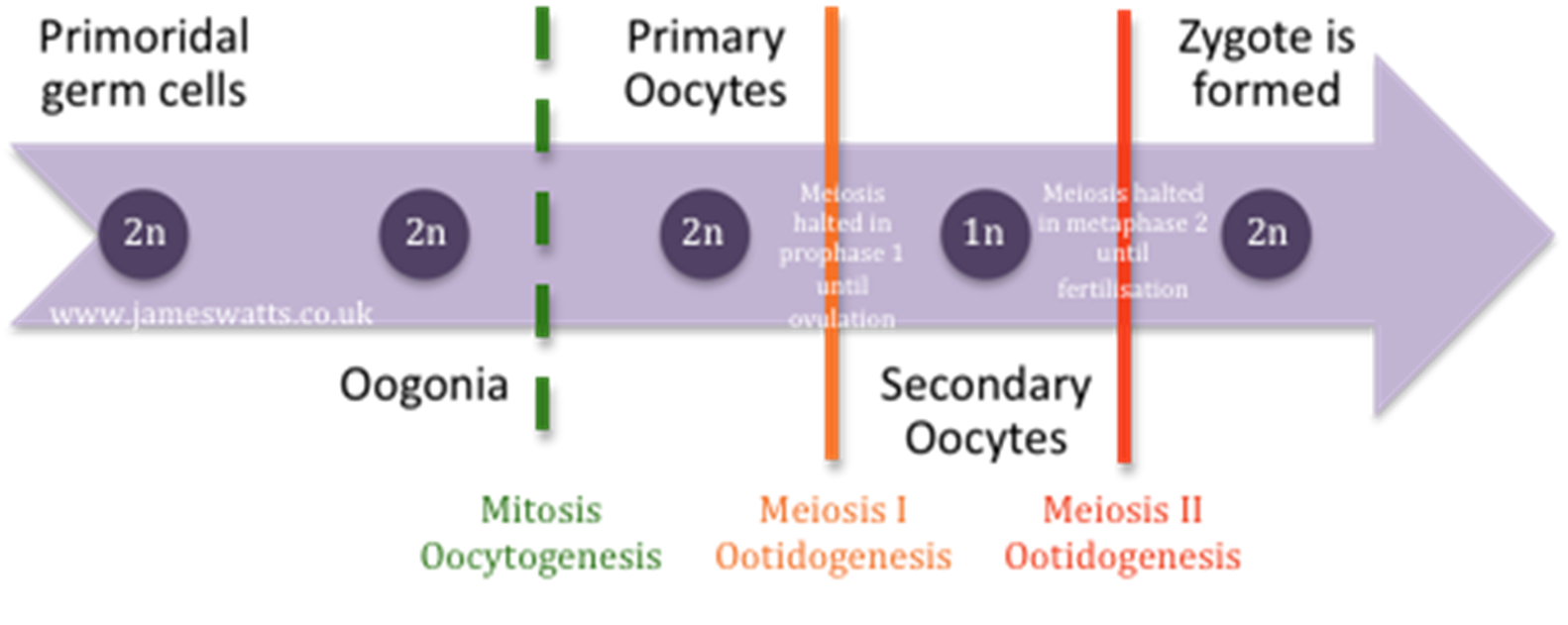
Primoridal germ cells (2n), oogonia (2n), mitosis oocytogenesis, primary oocytes (2n) meiosis halted in prophase 1 until ovulation, meiosis 1 ootidogenesis, secondary oocytes (1n) meiosis halted in interphase 2 until fertilisation, meiosis 2 ootidogenesis, zygote is formed (2n)
Where and when are oogonia/oogonium
In ovaries from birth
What type of cells are oognia and what process do they undergo?
Diploid, mitosis
What happens once oogonia have gone thru mitosis?
They will go through a growth phase and become a primary oocyte
When do oogonia begin meiosis 1?
before birth but are arrested at prophase 1
What surrounds the primary oocyte at the arrested stage?
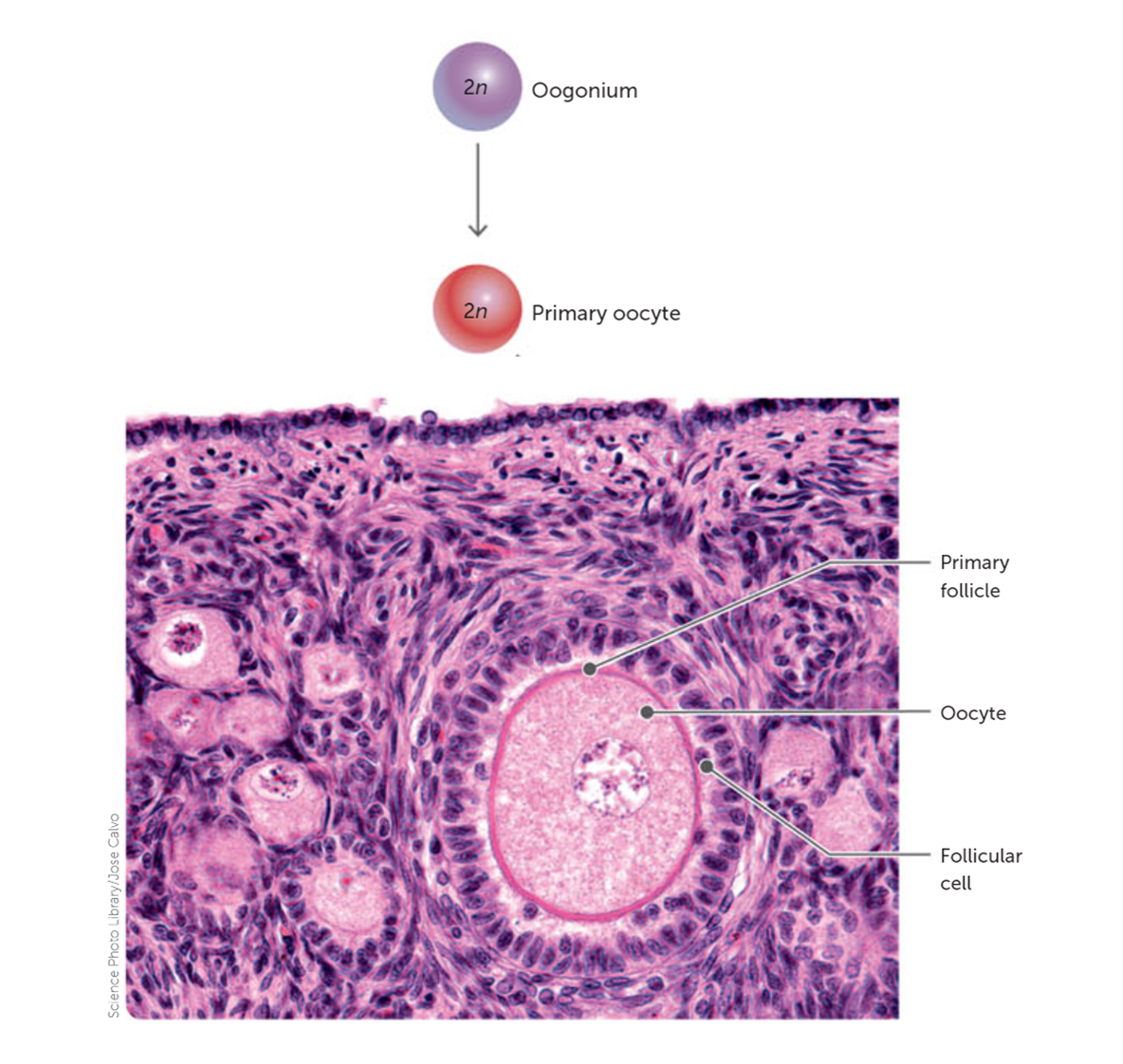
It is surrounded by granulosa cells, forming a primary follicle
When does meiosis 1 begin in oogenesis and what happens to it?
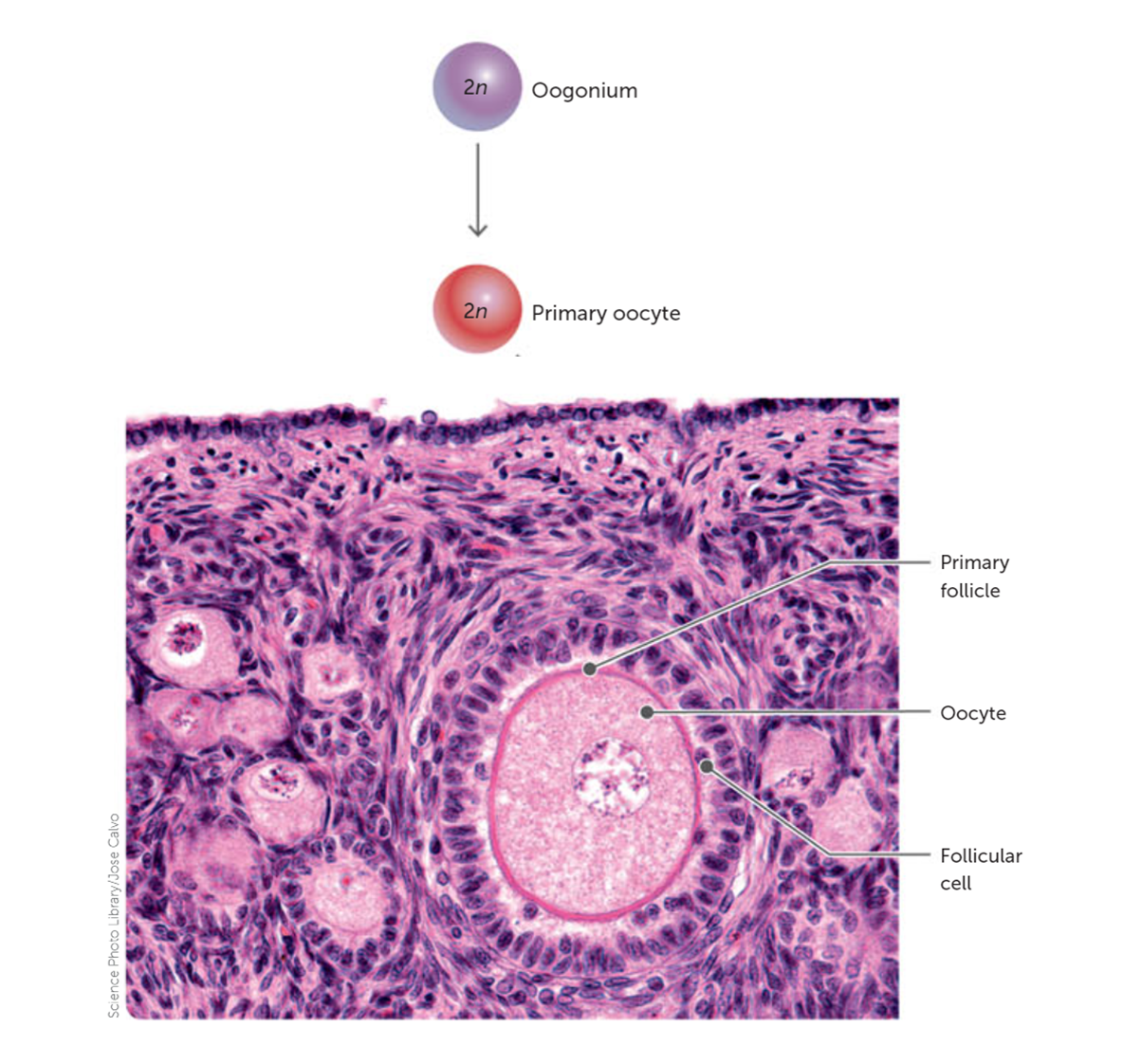
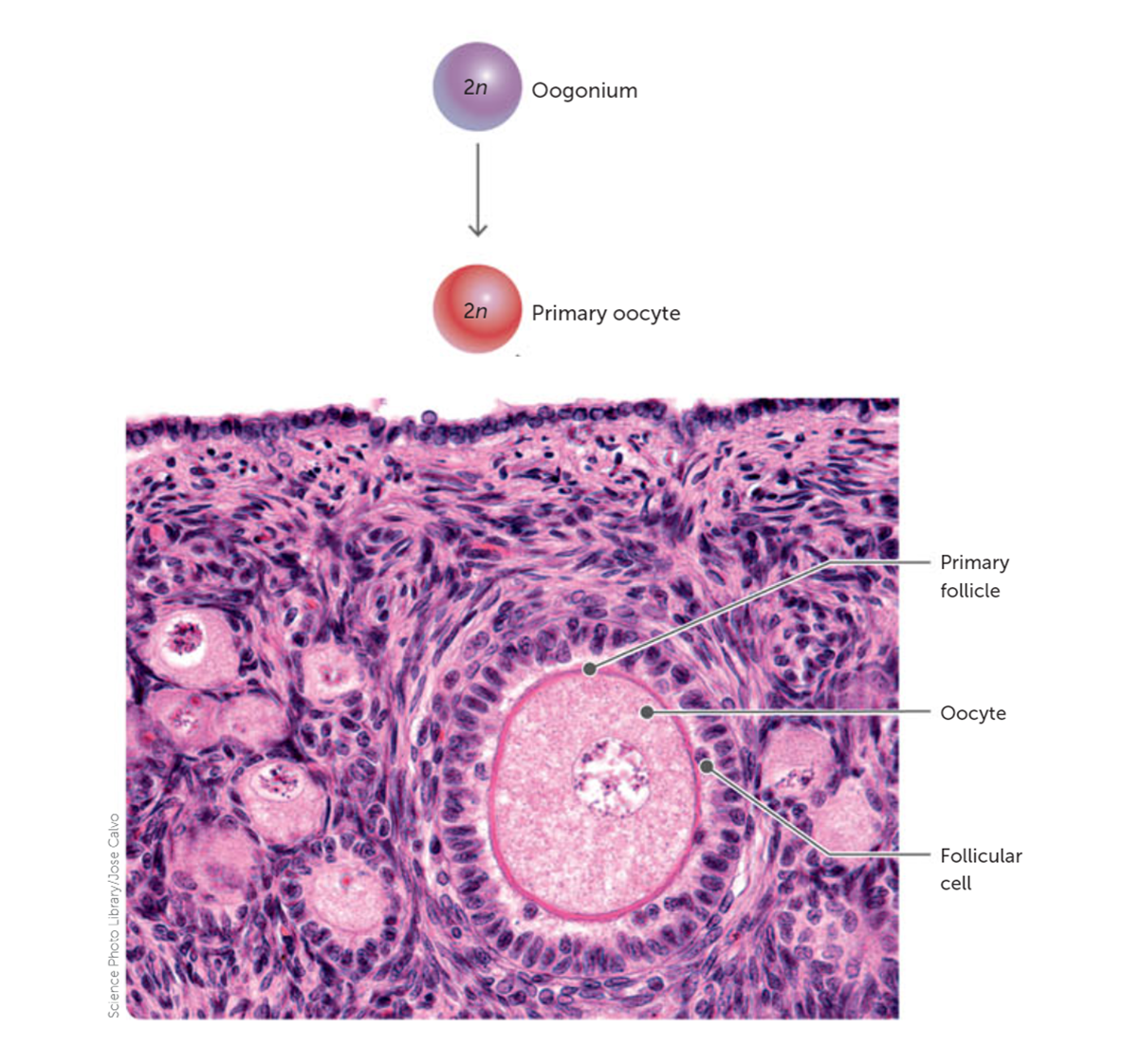
Meiosis I begins before birth, but is arrested at Prophase I
What happens to the primary follicle at puberty?
It grows and matures in preparation for ovulation
What does the primary oocyte do during puberty?
It competes the first meiotic division, forming a secondary oocyte and the first polar body
What are the products of the first meiotic division of the primary oocyte?
Secondary oocyte receives most of the cytoplasm and polar body
What is the chromosome number of the secondary oocyte and the polar body?
Both contain 23 chromosomes and are haploid (n).
What happens to the secondary oocyte after meiosis 1?
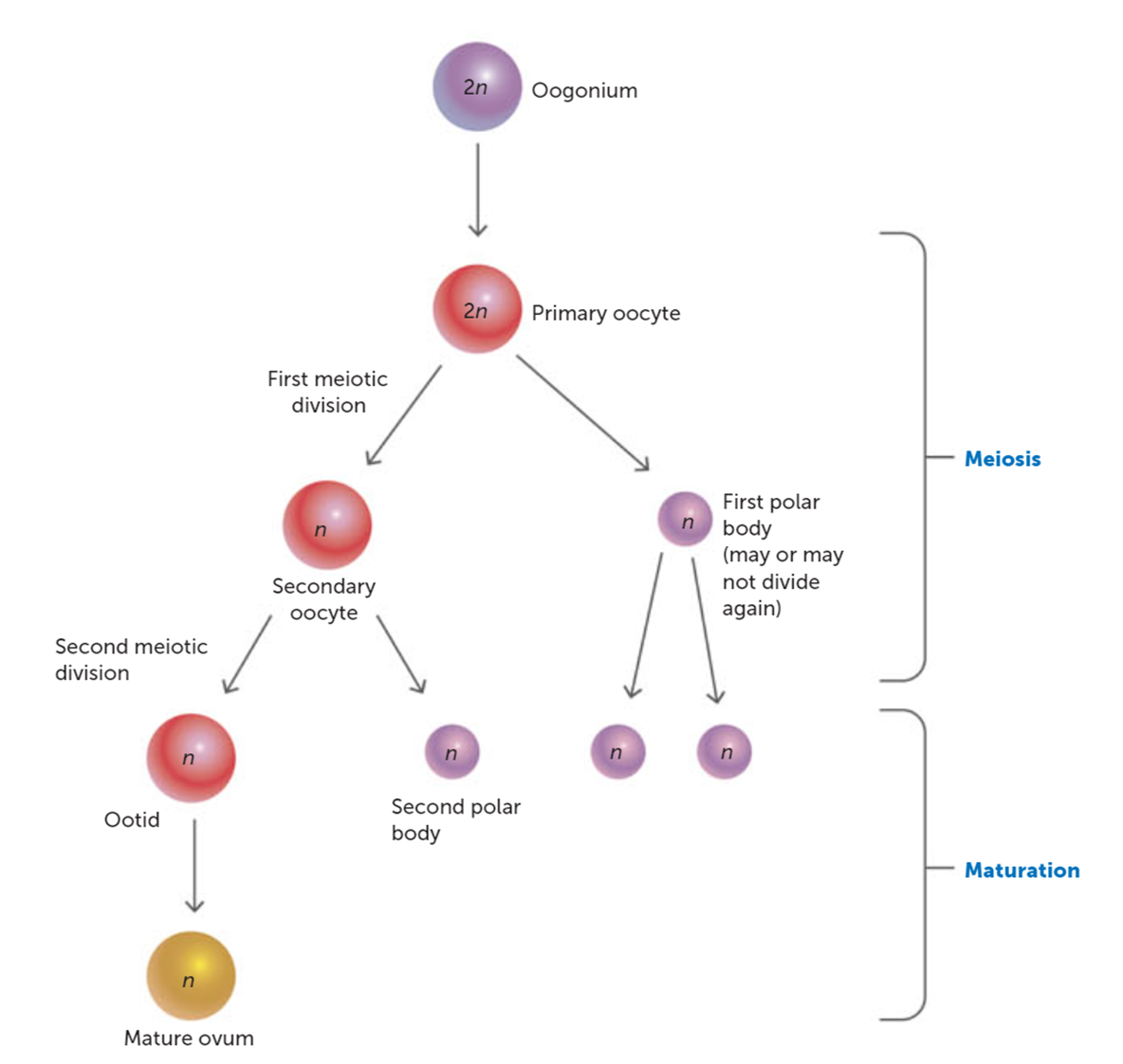
It begins meiosis 2 but gets arrested at metaphase 2 until fertilisation occurs, this is the point where ovulation occurs
At what stage of oogenesis does ovulation occur?
Ovulation occurs when the secondary oocyte is arrested at Metaphase 2 of Meiosis 2
What is released from the follicle during ovulation?
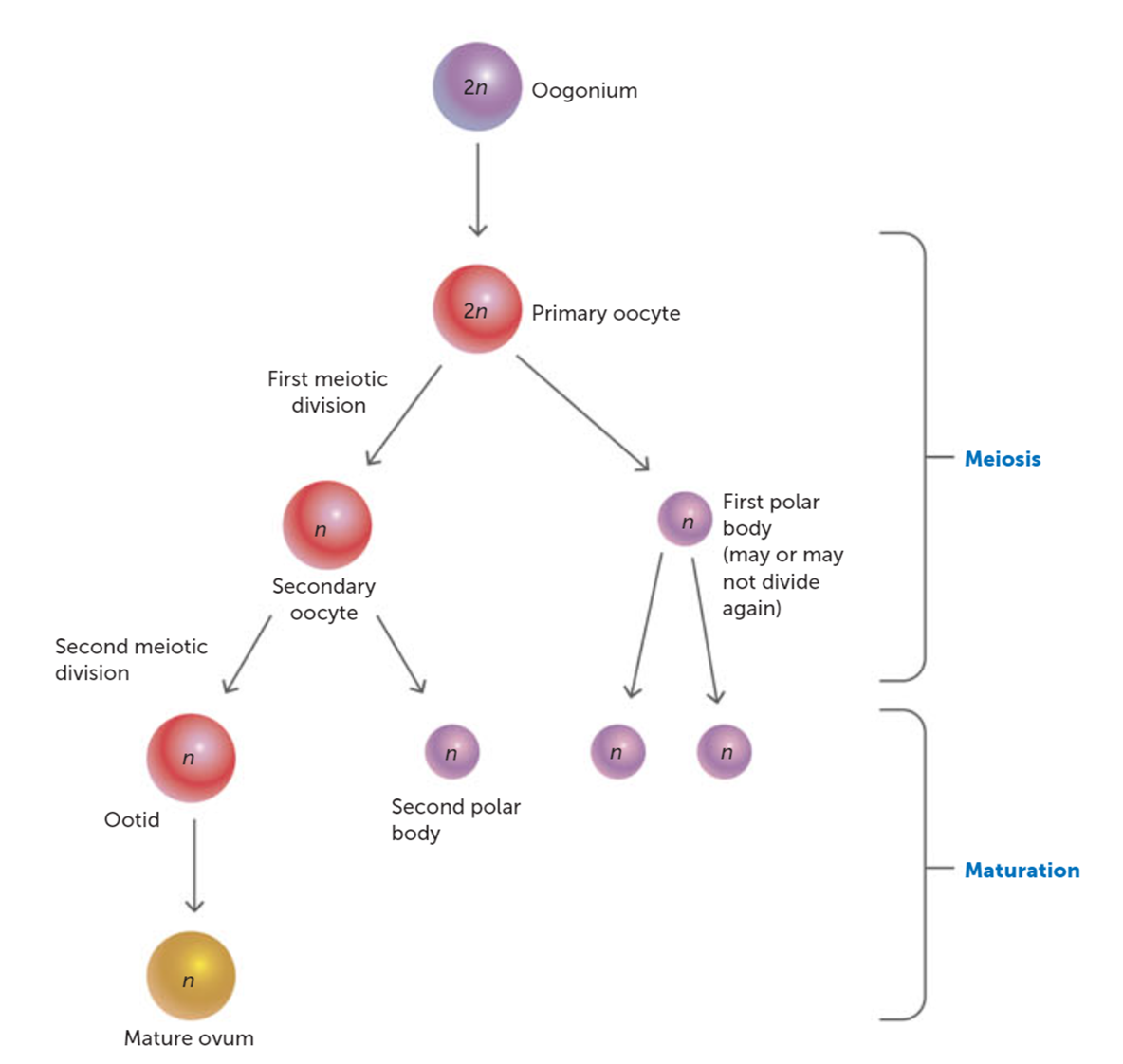
: The secondary oocyte (arrested at Metaphase 2) and the first polar body are released from the mature follicle into the fallopian tube.
What triggers the secondary oocyte to complete Meiosis II?
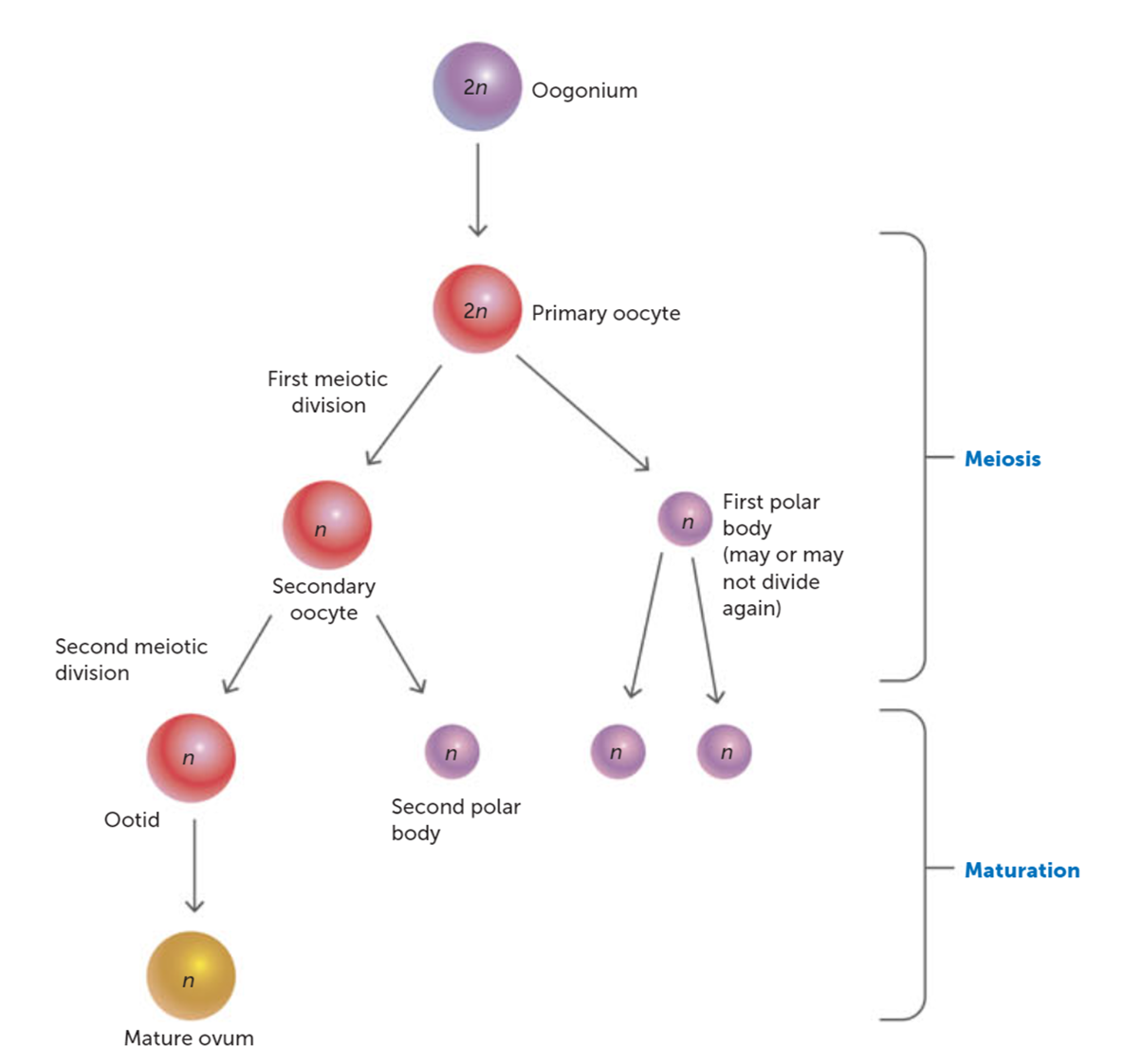
Penetration by a spermatozoon (fertilization).
What are the products when the secondary oocyte completes Meiosis II?
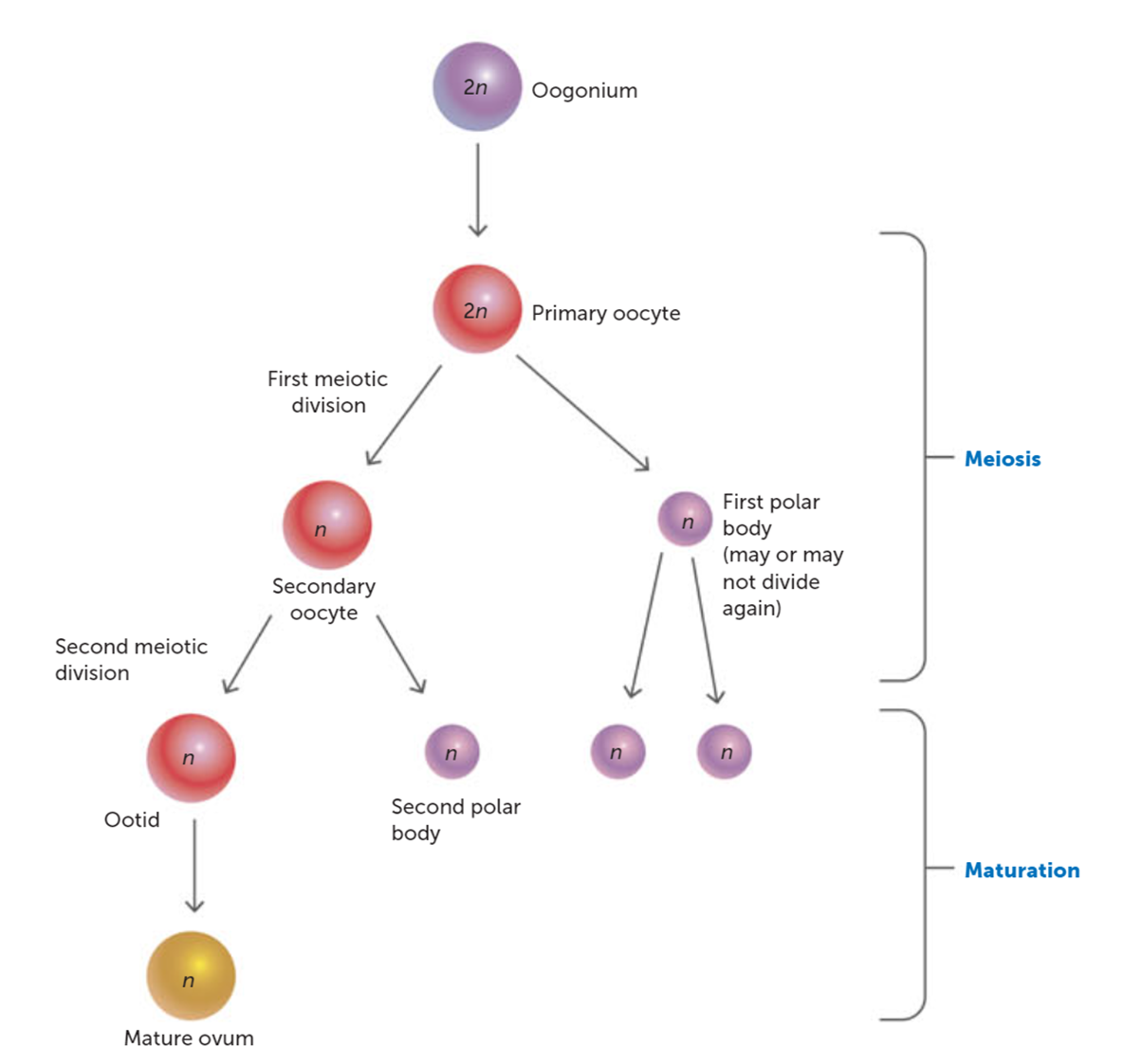
Two cells, an ovum and a second polar body.
Which cell is larger after Meiosis II and why?
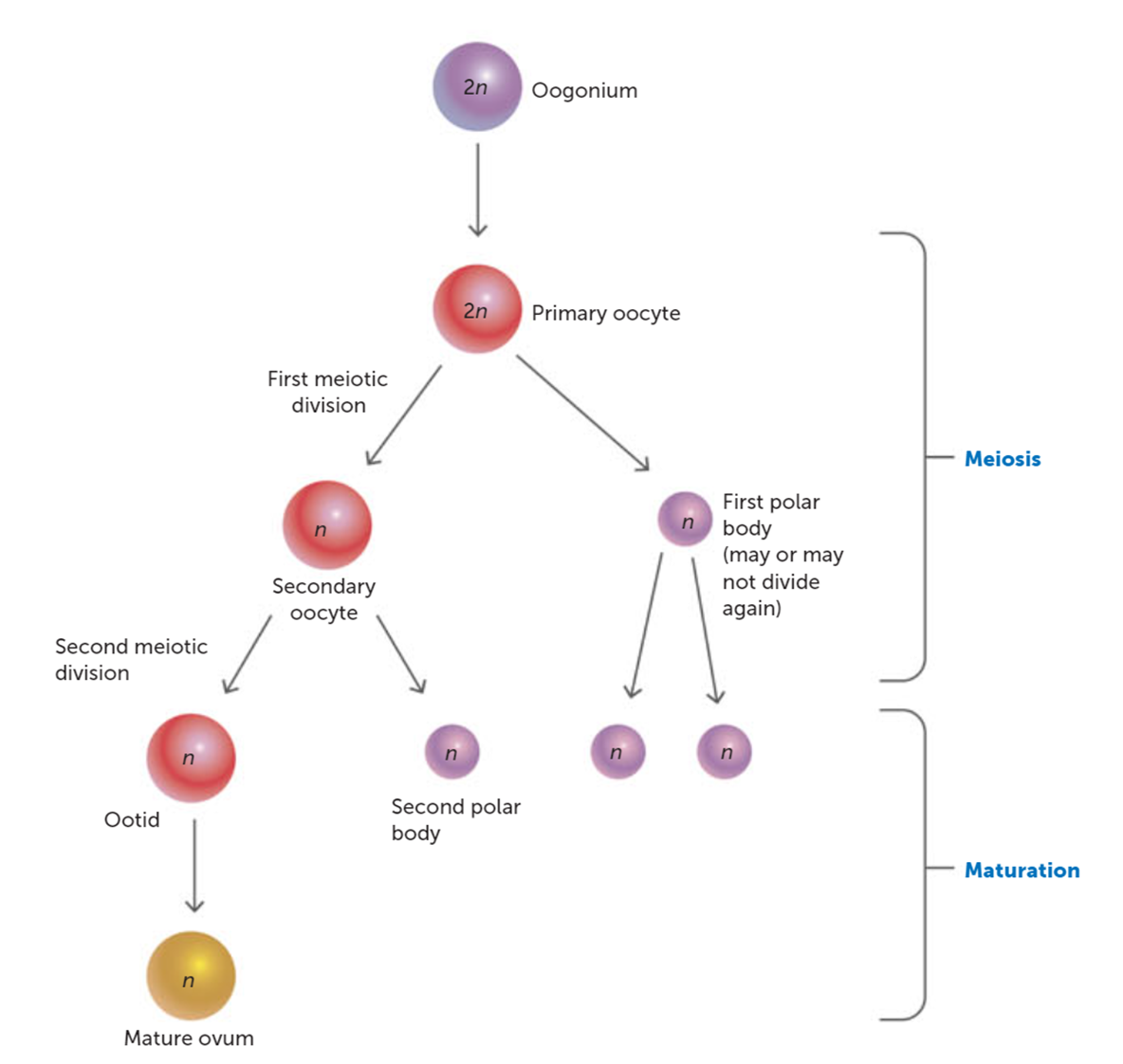
The ovum, it retains most of the cytoplasm to support early development.
What happens to the secondary oocyte if it is not penetrated by a spermatozoon?
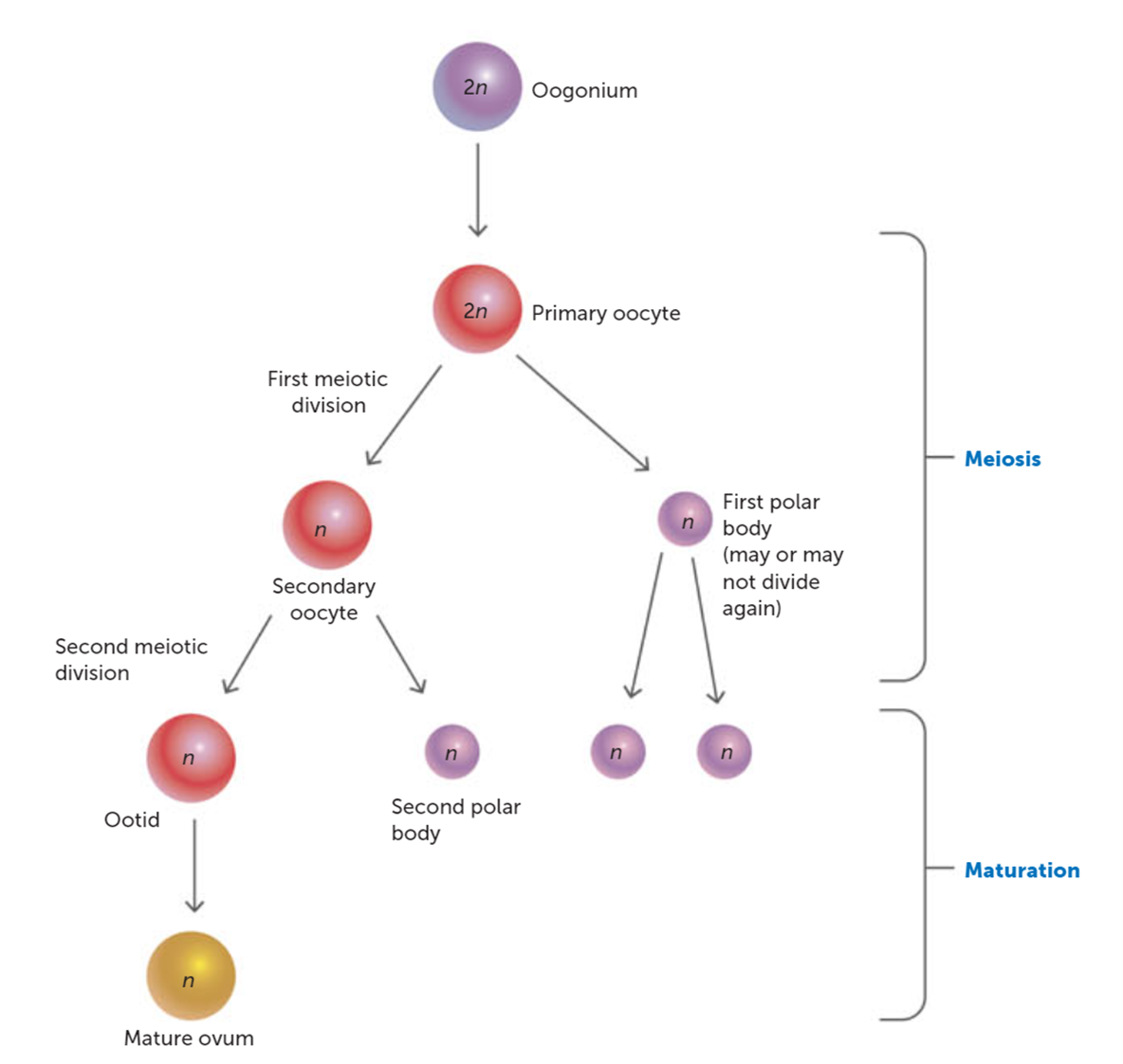
It does not complete Meiosis II and is shed from the body during menstruation.
How is an unfertilized secondary oocyte removed from the body?
It degenerates and is released along with the uterine lining during menstruation
What is menopause and age?
Wen ovulation ceases to occur in women due to the reduction of the number of mature ova, 45 - 60 years
What is the result of meiosis 1 in oogenesis?
One secondary oocyte and one polar body
At what stage of meiosis are primary oocytes arrested in until puberty?
Prophase 1
How many functional ova are produced from one primary oocyte?
One
Two things that are different about spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Division and sizes