Nursing 5 Exam 1 Review: Dysrhythmias and Shock
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
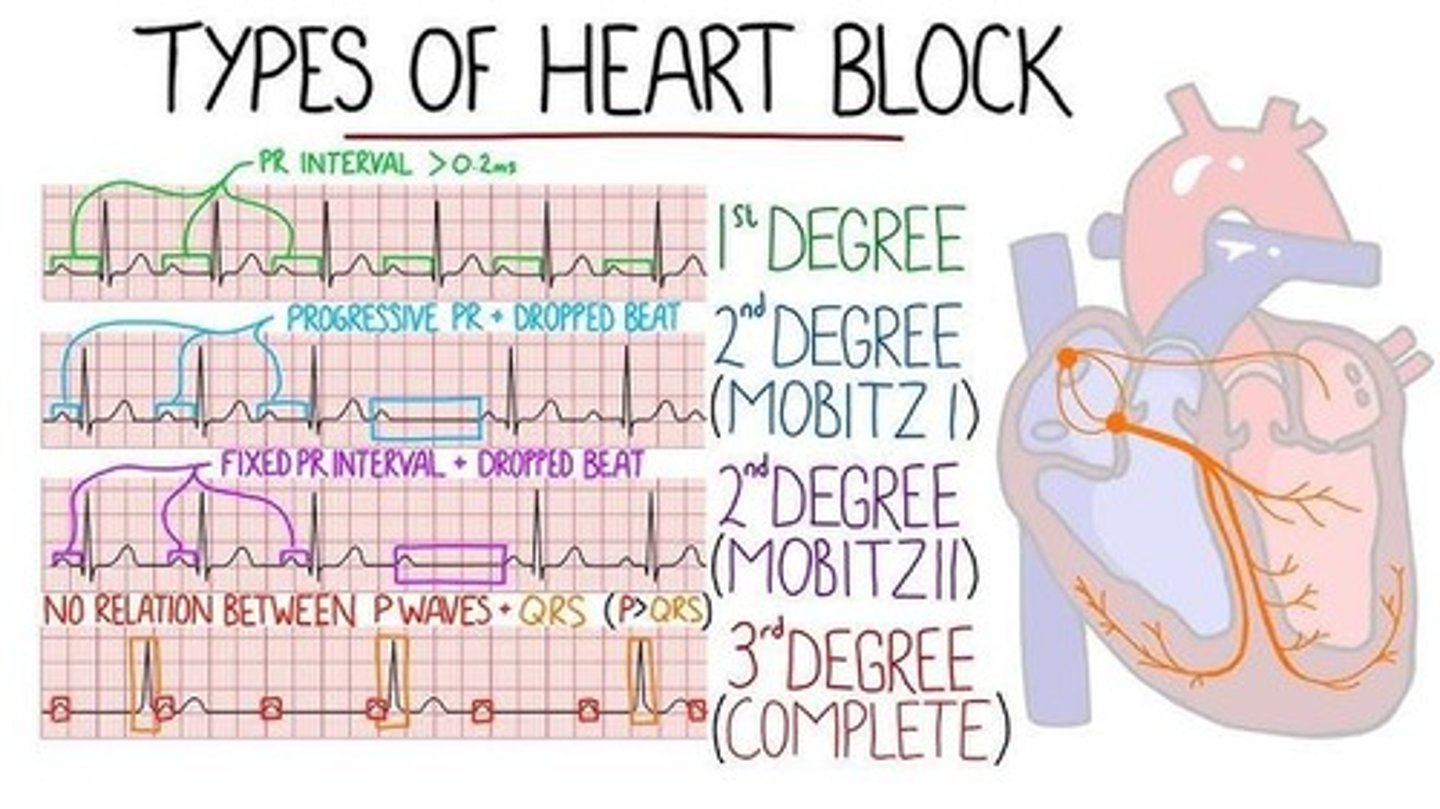
1st Degree Heart Block
PR interval is more than 0.20 seconds, occurs regularly throughout the rhythm (electrical signal is moving slowly down AV node).
Symptoms of 1st Degree Heart Block
Asymptomatic (can really only tell with EKG/heart monitor).
Causes of 1st Degree Heart Block
Can be normal in some patients, MI, or meds (BB, CCB, Digoxin).
Treatment for 1st Degree Heart Block
Continue to monitor, make sure they do not advance to another heart block/abnormal rhythm.
2nd Degree Heart Block Type I (Mobitz 1/Wenckebach)
PR interval will progressively become longer until QRS drops, electrical signal going from atria to ventricles is slowing down until it doesn't stimulate the ventricles to contract.
Symptoms of 2nd Degree Heart Block Type I
Mental status change, weak pulse, HPN, pale, dizzy.
Causes of 2nd Degree Heart Block Type I
MI (especially during an active one), meds (BB, CCB, Digoxin), rheumatic fever, increased vagal tone.
Treatments for 2nd Degree Heart Block Type I
usually no treatment is needed
2nd Degree Heart Block Type 2 (Mobitz 2)
PR interval will remain consistent until QRS drops, electrical conduction system is not sending a steady signal from atria to ventricles.
Symptoms of 2nd Degree Heart Block Type 2
HPN, weak pulse, cold/sweaty, mental status changes.
Causes of 2nd Degree Heart Block Type 2
Active MI (anterior damage), CAD, structural damage, meds (BB, CCB, Digoxin).
Treatment for 2nd Degree Heart Block Type 2
Temporary pacing then placement of temporary pacemaker.
3rd Degree Heart Block (Complete Heart Block)
P waves and QRS complex will not work together, electrical signals from atria is not making it to ventricles.
Symptoms of 3rd Degree Heart Block
Low cardiac output, HPN, weak pulse, mental status changes, cold/clammy.
Causes of 3rd Degree Heart Block
Congenital, heart disease, MI, meds (Digoxin), structural damage, heart valve problem.
Treatment for 3rd Degree Heart Block
Activate emergency response system, atropine, temporary pacemaker then permanent pacemaker.
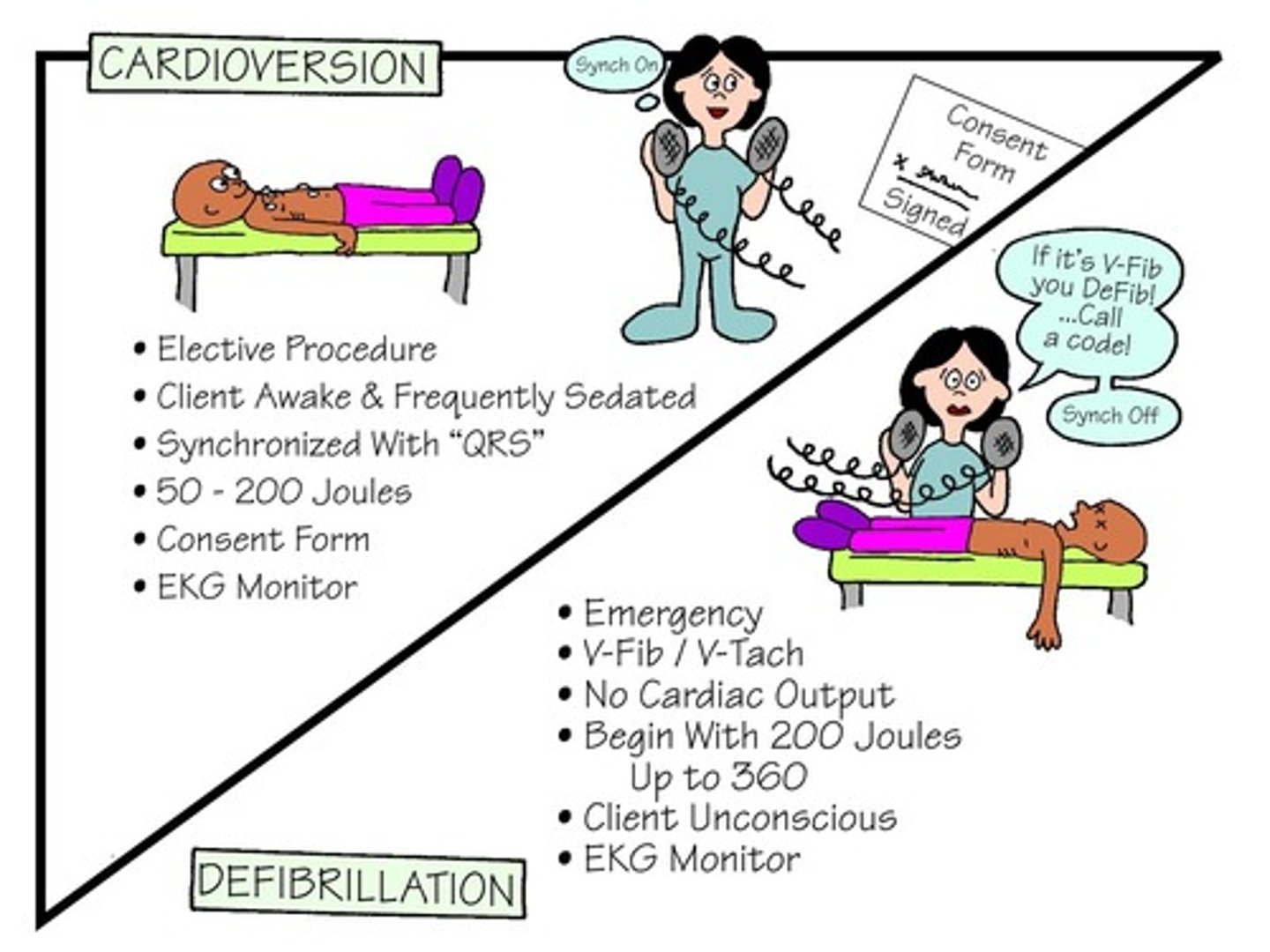
Cardioversion vs Defibrillation
One major difference is the timing of the delivery of electrical current.
Automaticity
Ability of pacemaker cells to spontaneously initiate an electrical impulse. SA node is the predominant pacemaker.
CCB reduce automacy, AV conduction, and myocarduim contractions
Excitability
Ability of myocardial cells to respond to the electrical impulse initiated by the pacemaker cell.
Conductivity
Ability to transmit the impulse from cell to cell.
Calcium Channel Blockers: Diltiazem Verapamil
LOWER SA automaticity, AV conduction, and myocardium contractions
Sodium Channel Blockers - Quinidine, procainamide, Lidocaine
SLOW electrical conduction by blocking NA entry in cells
tx ventricular arrythmias
Refractoriness
The inability of cardiac cells to respond to additional stimuli immediately following depolarization (contraction).
Contractility
The ability of myocardial fibers to shorten in response to a stimulus.
Beta Blockers REDUCE contractility
tx. SVT, A Fib, A Flutter
Dysrhythmias
Result from a disruption in the cardiac conduction system, causing changes in both rate and rhythm, as well as the development of ectopic beats.
Ectopic Beats
Interrupts normal conduction and can cause heart blocks
-abnormal heartbeats “skipped beat” originating outside Sinus Node /SA node
seen in PAC or PAV
caused by BB, Digoxin, coffee, lack of sleep ect.
diagnostic- ECG, Holter Monitor
tx. monitor and treat underlying cause. in severe cases - ablation, K, MG, CA, amiodorone, BB
Bundle branch block
Most common in myocardial infarction (MI). Heart still beats but the timing is off.
Right BBB- right ventricles. Begin. ECG- V1 V2
Left BBB- left ventricle. Serious. ECG notched R waves, I, V5 V6
Sinus arrhythmia risk
Rate varies with respiration, increasing during inspiration and decreasing during expiration; common in the very young/very old.
Causes of sinus arrhythmia
Valve disease, digitalis toxicity/morphine administration.
Significance of sinus arrhythmia
benign
tx. Continue to monitor, look at labs (potassium/magnesium).
Sinus tachycardia
Heart rate will be > 100 BPM due to increased automaticity related to changes in the internal environment.
Symptoms of sinus tachycardia
Rapid pulse, feeling of heart racing, shortness of breath (SOB), dizziness, chest pain.
Consequences of untreated sinus tachycardia
May experience syncope, low blood pressure, or acute pulmonary edema.
Causes of sinus tachycardia
Exercise, excitability, anxiety, fever, pain, hypoxia, hypovolemia, anemia, hyperthyroidism, MI, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, pulmonary embolism, caffeine, drugs (atropine, epinephrine, isoproterenol).
Treatment for sinus tachycardia
Vagal maneuvers, administering beta-blockers (BB), calcium channel blockers (CBB), or adenosine; synchronized cardioversion or possible ablation if unstable.
Torsades de pointes Rhythm
A rare but potentially fatal type of irregular heartbeat that can lead to sudden cardiac death.
Characterization of Torsades de pointes
Wide and narrow alternating - big and small, creating different apical and radial pulses.
Treatment for Torsades de pointes
taking antiarrhythmic drugs
magnesium supplements
pacemaker
implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
Sinus bradycardia
Heart rate will be < 60 BPM, patient may present asymptomatic.
Causes of sinus bradycardia
Increased vagal stimulation or depressed automaticity due to injury or ischemia to the sinus node.
Symptoms of sinus bradycardia
Decreased cardiac output (CO), syncope, hypotension (HPN), patient may be asymptomatic.
Treatments for sinus bradycardia
Management revolves around solving causative factors; transcutaneous pacing may be done until surgical interventions.
Atrial dysrhythmias
These dysrhythmias happen when an action potential is initiated outside the SA node.
Premature atrial contractions (PAC)
An ectopic atrial beat that occurs earlier than the expected next sinus beat.
Causes of PAC
tx
Strong emotions, excessive alcohol/tobacco/caffeine intake; associated with MI, heart failure, other cardiac disorders, hypoxemia, PE, digitalis toxicity, electrolyte/acid-base imbalances.
tx: limit alcohol and caffeine
Symptoms of PAC
Few, sometimes palpitations, or fluttering sensations.
Atrial flutter
Rapid and regular rhythm from an intra-atrial reentry mechanism.
Atria
Contracts at a faster rate than the ventricles due to AV node management of impulses.
Atrial Flutter
Rapid and irregular/disorganized atrial activity, with multiple small reentry circuits.
Atrial Fibrillation
Rapid and irregular/disorganized atrial activity, with multiple small reentry circuits.
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Issues with atria due to an accessory pathway (Bundle of Kent) allowing for a shortcut to ventricles bypassing AV node.
Idioventricular Rhythm
A type of irregular heartbeat where the lower chambers of the heart beat more slowly than normal, characterized by a slow ventricular rate, usually less than 50 beats per minute.
Symptoms of Atrial Flutter
Palpitations, fluttering sensation in chest/throat.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
Decreased CO (HPN, SOB, fatigue, angina) with heart disease - syncope or heart failure.
Symptoms of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Palpitations, dizziness/lightheadedness, SOB, chest pain, fatigue, syncope.
Symptoms of Idioventricular Rhythm
Usually asymptomatic but can require monitoring.
Treatment for Atrial Flutter
Vagal maneuvers/adenosine, antithrombotics, cardioversion if other treatments are unsuccessful.
Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation
Antithrombotics, BB, amiodarone, dofetilide, ibutilide, TEE, and cardioversion if symptomatic.
Treatment for Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Vagal maneuvers, adenosine, BB, antiarrhythmic drugs, cardioversion if other treatments do not work, catheter ablation.
Treatment for Idioventricular Rhythm
Balance electrolytes - usually asymptomatic so keep monitoring.
Causes of Atrial Flutter
SNS stimulation r/t anxiety, caffeine/alcohol intake, thyrotoxicosis, CHD, MI, PE, and abnormal conduction syndromes.
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Commonly associated with aging.
Causes of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Heart disease, cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease, alcohol/caffeine/nicotine, hyperthyroidism, stress/anxiety, certain medications.
Causes of Idioventricular Rhythm
Heart block, electrolyte abnormalities, certain drugs, heart disease.
ECG of Atrial Flutter
Not provided in the notes.
ECG of Atrial Fibrillation
Not provided in the notes.
ECG of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Shows as a slurring/slow rise of QRS complex.
ECG of Idioventricular Rhythm
Not provided in the notes.
Premature Junctional Contractions
Occurs before the next expected beat of the underlying rhythm, originating in AV node tissue.
Causes of Premature Junctional Contractions
Excess caffeine/tobacco/alcohol intake, electrolyte imbalances, hypoxemia, HF, CAD, digitalis toxicity.
Asymptomatic Irregular Heartbeat Treatment
Continue to monitor.
Symptomatic Heartbeat Treatment
Avoid caffeine/tobacco/alcohol, avoid excess activity strain, BB, CBB, antiarrhythmics, catheter ablation if other treatments are unsuccessful.
Class 1 Sodium Channel Blockers
Slow electrical conduction by prevention of sodium entering cell.
Class 1 Sodium Channel Blockers Examples
Quinidine, Procainamide, Lidocaine.
Class II Beta Blockers
Reduces HR and Contractility.
Class II Beta Blockers Treatment
Tx of SVT rhythms: i.e. A fib and A flutter.
Class II Beta Blockers Examples
Metoprolol, Atenolol, Propranolol.
Class III Potassium Channel Blockers
Delays repolarization, prolong heart's electrical recovery.
Class III Potassium Channel Blockers Examples
Amiodarone, Sotalol.
Class IV Calcium Channel Blockers
Decreases SA automaticity, AV conduction and contractility.
Class IV Calcium Channel Blockers Effects
Slow heart rate, reduce contractions.
Class IV Calcium Channel Blockers Examples
Diltiazem, Verapamil, Flecainide.
Shock
A clinical syndrome characterized by decrease in blood flow resulting in inadequate oxygen.
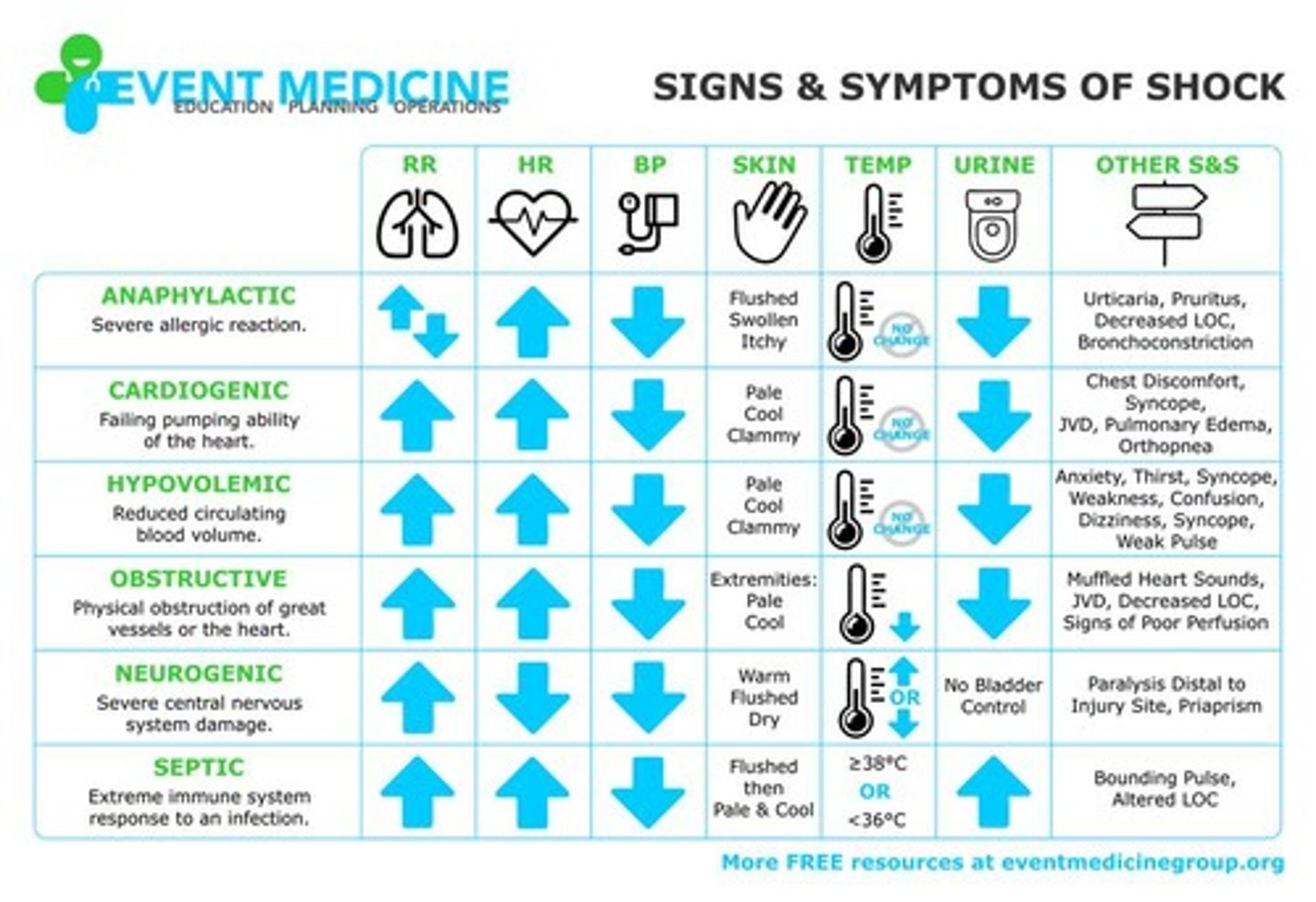
Signs and Symptoms of Shock
Pale, cool, clammy skin; rapid, shallow breathing; rapid, weak, or irregular heartbeat; anxiety, agitation, confusion; nausea or vomiting; low or no urine output; profuse sweating.
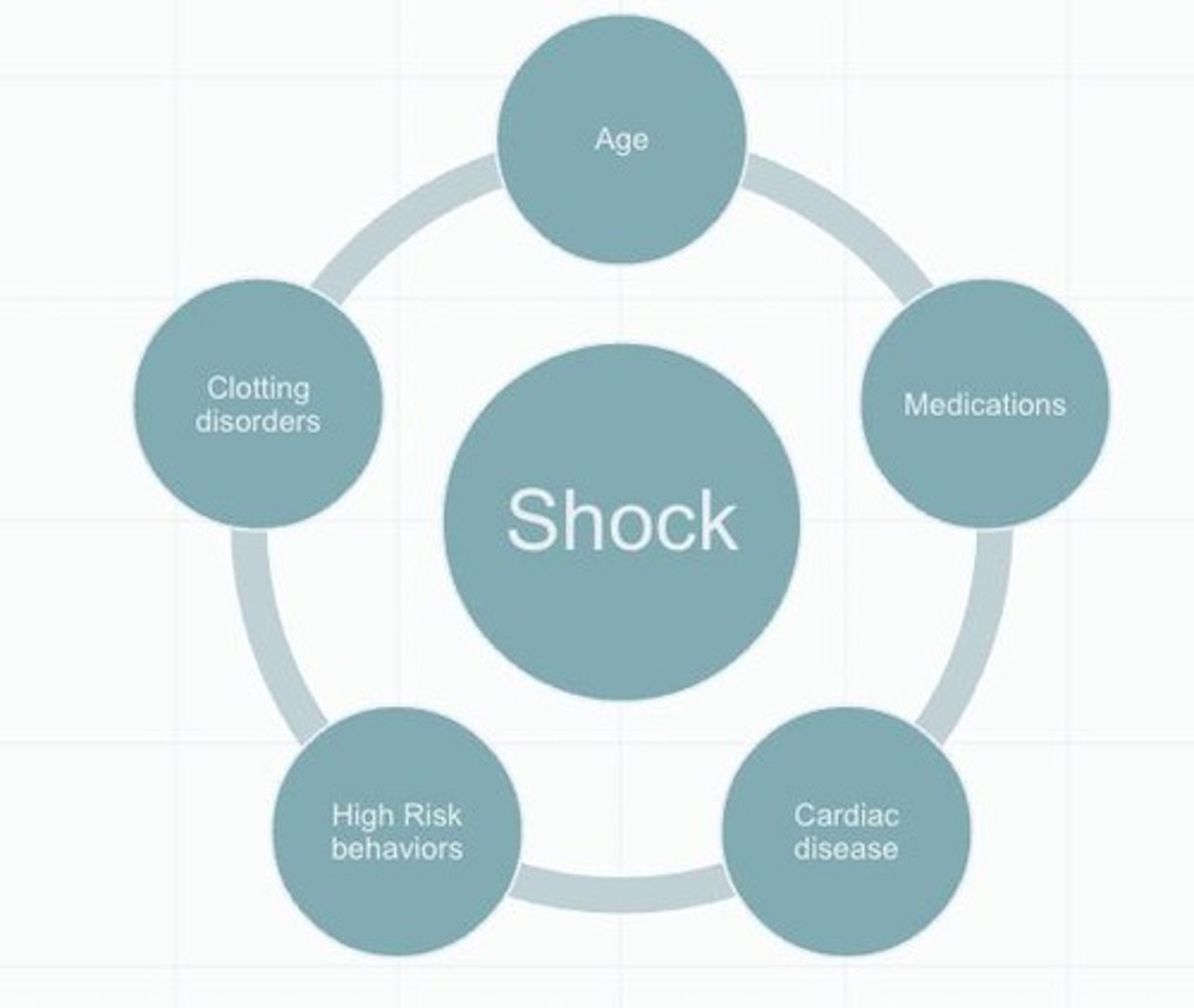
Causes/Risk Factors of Shock
Malnourished, immunosuppressed, clotting disorders, age, medications, cardiac diseases.
Hypovolemic Shock Nursing Assessment
Assessing fluid balance is essential. Strict I&Os, including wound drainage and perspiration.
Cardiogenic Shock Nursing Management
Maintain myocardial O2 supply, provide pain relief, rest and supplemental O2.
Neurogenic Shock Nursing Management
Maintain immobility, keep HOB 15-20 degrees.
Anaphylactic Shock Nursing Management
Preventative assessment of allergy history, noting allergies in chart and placing allergy wristband on patient.
Septic Shock Risk Factors
Patients who have invasive lines or procedures are at risk for infection and septic shock.
Septic Shock Prevention
Preventing HAIs is the responsibility of everyone who has contact with the patient; #1 thing to prevent infections is handwashing.
Nursing Diagnoses for Shock
Decreased cardiac output, ineffective tissue perfusion, anxiety.
Compensatory shock
Initial stage of shock where the body is still able to maintain adequate BP and tissue perfusion.
BP in compensatory shock
BP stays normal.
HR in compensatory shock
HR > 100 BPM.
Skin in compensatory shock
Skin cool.
Bowel sounds in compensatory shock
Bowel sounds hypoactive.
Urine output in compensatory shock
Urine output decreases.
Respiratory rate in compensatory shock
Resp rate increases slightly (> 22 breaths/min).
Mental status in compensatory shock
Confused/agitated mental status.
Respiratory alkalosis in compensatory shock
Respiratory alkalosis (from increased respirations).
Anxiety in compensatory shock
May display increase in anxiety.