A&P 2 Lab Practical 2 Studying (cont)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
More Respiratory, Digestive & Urogenital systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is another name for the GI tract
Alimentary canal
What what is chewed food in the mouth called?
Bolus
How does food travel down the esophagus to the stomach?
peristalisis
What are the two sphincters of the stomach?
The esophogeal and pyloric sphincters
What are the four regions of the stomach?
The cardiac region, the fundic region, the pyloric region, and the body.
What are the three regions of the small intestine?
The duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Where does most chemical breakdown of food happen?
duodenum
What is the sight of attachment for accessory organs?
the duodenum
What is bolus+mucus+gastric juices
chyme
Where does most abosrbtion of nutrients occur?
Judi says Duodenum, Amy says Jejunum.
What valve is at the end of the small intestine
ileocecal valve
What are the four main parts of the large intestine
the cecum, the colon (4 parts), the rectum and the anal canal (anus)
What accessory organ (formerly thought to have no function) comes off of the cecum
appendix
What are the four parts of the colon
ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid (s shaped)
What structures in the oral/buccal cavity aid in digestion
teeth and tongue (mechanical) and salivary glands (salivary amylase- chemical)
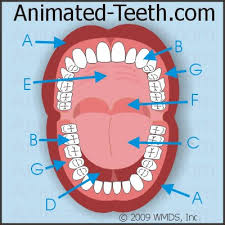
What is E, what is behind E?
E is the hard pallet, it is followed by the soft pallet.
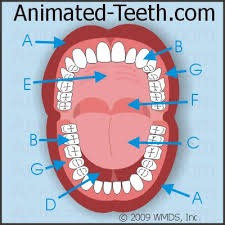
What is F
The uvula
What is the function of salivary amylase?
start the breakdown process of carbohydrates- breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter
control release of chyme from stomach into small intestine to allow time for digestion; protect small intestine from stomach acid
What is the function of rugae
Increase surface area of stomach
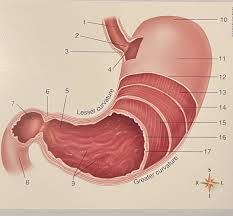
What is #2
Esophogeal sphincter
What is 10?
The fundic region/fundus
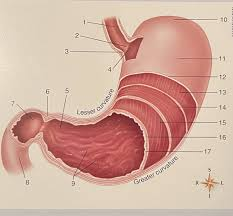
What is #11?
the body
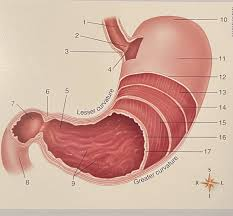
What is #4
The cardiac region
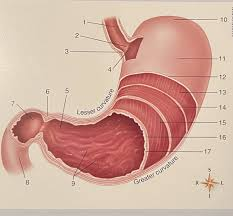
What is #5
The pyloric region/the plyorus
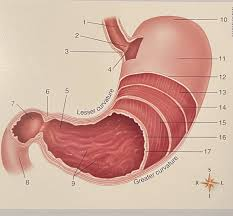
What is #9
Rugae
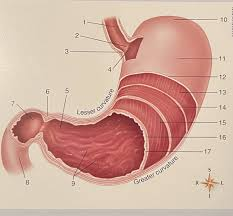
What are 13/14/15
The muscle layers
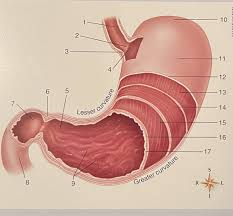
What is #7
The pyloric sphincter
What substance is in the gall bladder?
bile
Name the substance produced by the pancreas
insulin and glycogen
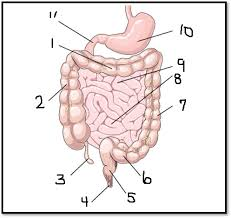
What is #9
The jejunum (small intestine)
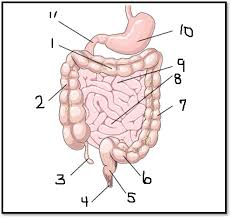
What is #8
The ileum (small intestine)
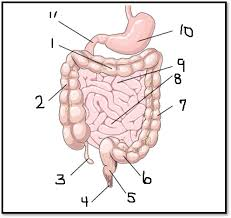
What is #3
The appendix (large intestine-ish)
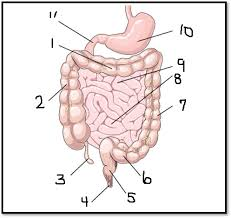
What is #2? What is inferior to #2
The accending colon, which is inferior to the cecum, the first part of the colon (large intestine)
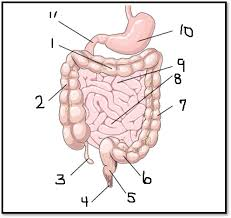
What is #1
The transverse colon (large intestine)
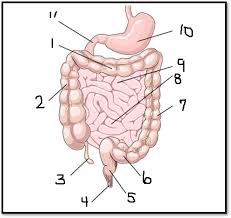
What is #7
The decending colon (large intestine)
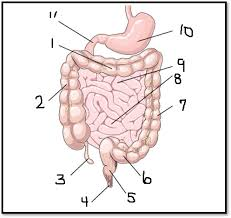
What is #5
The rectum (large intestine)
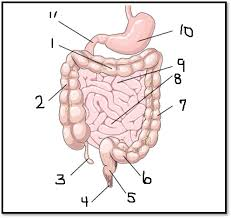
What is #4
The anus/anal canal (large intestine)
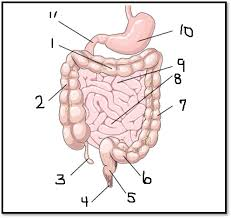
What is #6
sigmoid colon (large intestine)
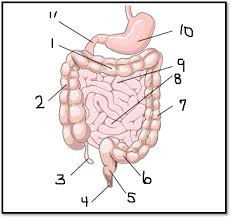
What is #11
The duodenum
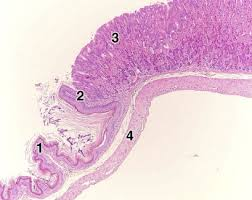
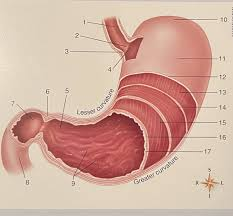
what is #4
the submucousa
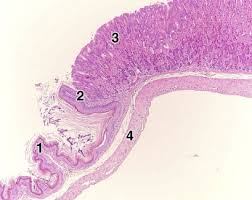
what is #3
gastric glands
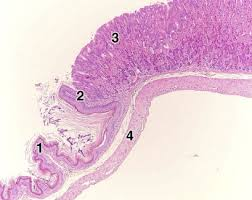
what are #2
gastric pits
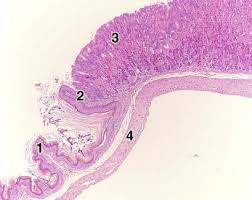
what is #1
the mucousa
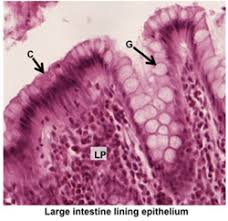
what is G
goblet cells
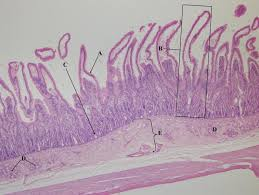
what is e
submucousa
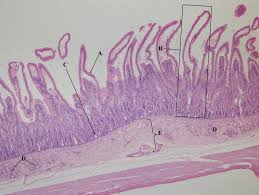
what is c
mucousa
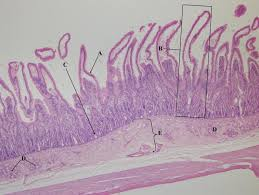
what is below d and e
muscularis
What is average (male) tidal volume
500mL
What is average (male) inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
3100mL
What is average (male) expiatory reserve volume (EVR)
1200mL
What is average (male) forced vital capacity (VC)
4800mL (TV+IRV+EVR)
What is average (male) residual volume (RV)
1200mL
What is average (male) total lung capacity (TLC)
6000mL (VC+RV/all combind)
what is tidal volume?
how much air you breath in/out in a normal breath.
what is IRV
a forced inhale, like if you were scared
what is EVR
forced exhale (ie “wind knocked out of you”)
what is vital capacity?
tidal volume, IRV, and ERV combind
what is residual volume
the amount of air that is always in your lungs (so they do not collapse, holds pressure)
what is total lung capacity
all other values combined, the entire amount of air your lungs can hold.