N209 - Breast & Axilla
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
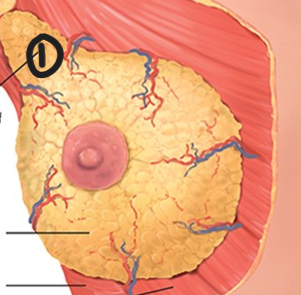
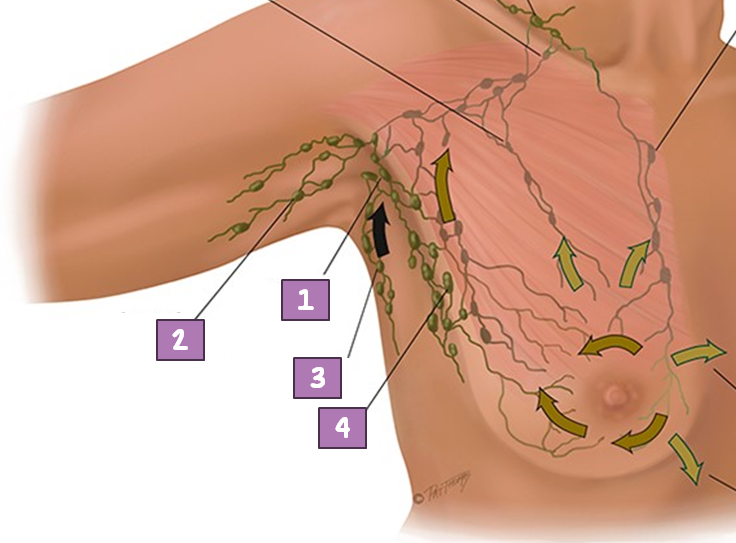
Tail of Spence
What is the superior lateral corner of breast tissue that projects up and laterally into the axilla?
Montgomery glands
What are the small elevated sebaceous glands located in the areola that secrete a protective lipid material during lactation?
Tail of Spence
Central Axillary Node
#1?
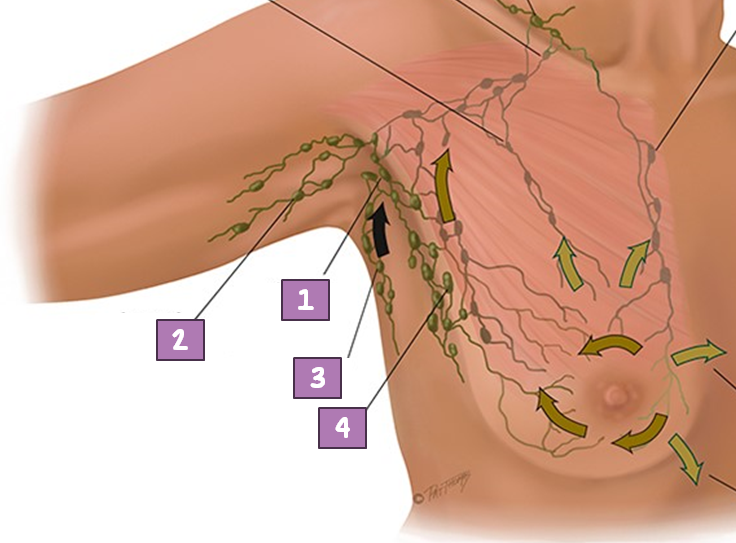
Pectoral (anterior)
#4?
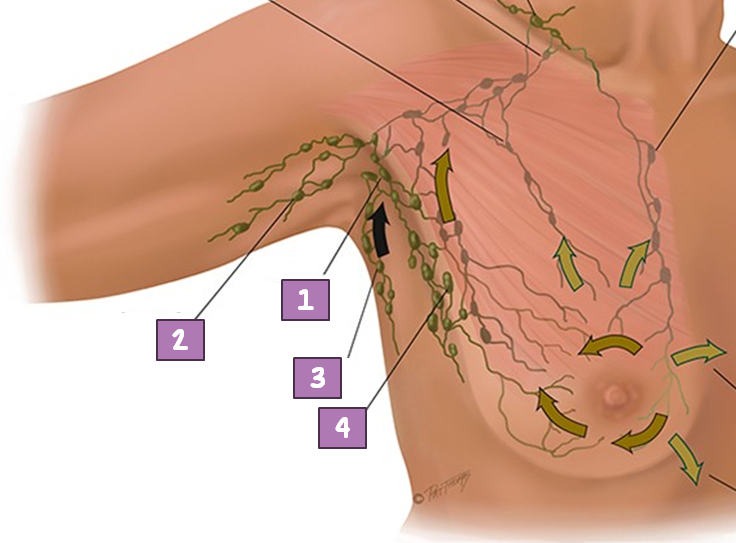
Subscapular (posterior)
#3?
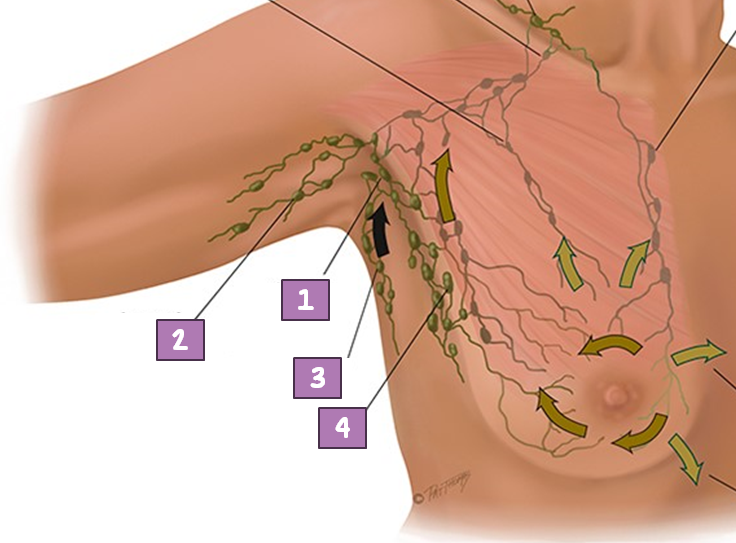
Lateral Axillary Node
#2?
Estrogen
Which hormone is responsible for changes in the breast?
“milk line”
Supernumerary nipple
What are the ventral epidermal ridges that curve down from the axillae to the groin bilaterally? What is a congenital variation that can persist here?
thelarche
= the beginning of breast development
menarche
= the beginning of menstruation
BRCA1 and BRCA2
A mutation in which genes indicates a higher risk for developing breast CA (70%)?
breast CA survival varies by the stage when it’s diagnosed (early detection = greater chance of survival)
Why is it important to have screenings and mammograms?
estrogen receptors & HER-2
What receptors are targeted to prevent the spread of breast CA?
@ age 40-44
@ age 45
When should annual screening mammography begin for at risk patients? Definitely?
later stage diagnosis
Why is there racial disparity in breast CA survival?
Less likely to get screened (CA develops to later stages b4 it is detected & the survival rate drops)
How does socioeconomic conditions affect breast CA survival? (e.g., poverty, lower education levels, lack of access to care, lack of health insurance)
alcohol drinking
postmenopausal hormone therapy & weight gain
Decreased physical activity
What are some lifestyle risk factors for developing breast cancer?
Breast cancer
What is the 2nd major cause of death from cancer in women?
99%
85%
early detection
5-year survival rate has increased to ____ today & _____ if the CA has spread regionally because of:
>1; there is a higher likelihood of occurrence of breast CA
A relative risk of what indicates a higher likelihood of breast cancer occurrence? What does this mean?
primary purpose = lactation
the breasts are integrated w a women’s self-concept (affects body image)
What is the primary purpose of the female breast? How does this differ from the pt.’s view?
fear, anxiety and panic; they will initially assume the worst
What might a women who has found a lump in her breast feel?
Risk increases w age across all ages until 80
How does age affect the risk for breast CA?
High waist-hip ratio
High fat diet
No breastfeeding and low number of births (1)
Regular alcohol intake
Radiation exposure
Never been pregnant or late age @ 1st pregnancy (>30)
Higher education and socioeconomic group
Taller height
Physical Inactivity
age
gender
personal Hx of breast CA
family Hx of breast CA\
increased exposure to the female hormone estrogen
What are risk factors for breast CA?
c)
Which of the following does NOT pose a higher risk for breast CA?
a) having first period before 11
b) entering menopause after age 55
c) Birth control
d) using estrogen replacement therapy for more than 5 years
mastalgia
What is pain in breast?
milk secretions from the breasts in a non-breastfeeding woman
What is galactorrhea?
using a short gown that is open at the back and lift it up to the shoulders during inspection.
What is an alternative draping method when examining the breasts?
supine
What position should the pt. be in when palpating the breast?
Breast Self-Examination (BSE)
What should be taught after breast examination?
Symmetry is size and shape (slight asymmetry is common)
What is a normal general appearance of the breasts?
Sudden asymmetry/ growth in the breasts
What is an abnormal general appearance of the breasts?
bulging, discoloration or edema
What abnormalities might be found in the lymphatic drainage areas?
smooth and of even color
(in pregnant women) fine blue vascular network visible
(after pregnancy) striae (aka: Strech marks)
What should you normally find when inspecting the skin over the breasts?
localized areas of redness, bulging or dimpling
skin lesions or focal vascular patterns
edema
What would be an abnormal finding when inspecting the skin over the breasts?
it is fixed (cannot be pulled out)
it is a recent change to the nipple
What indicates that a nipple inversion is a bad sign?
usually protrude (some are flat and some are inverted)
symmetric on the same plane on both sides
What should you normally find when inspecting the nipples?
nipple line
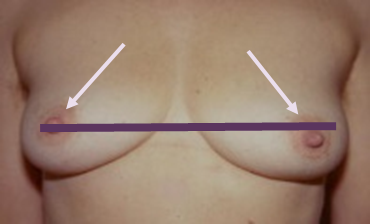
an extra nipple along the embryonic “milk line” (congenital)
What is a supernumerary nipple?
milk line
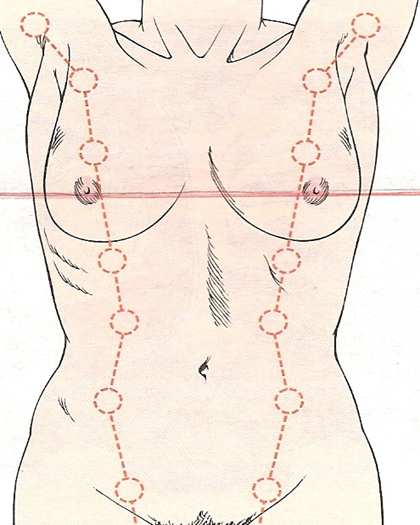
raise arms over their head
push into their hips
lean forward (if breasts are pendulous)
What 3 maneuvers should you have the pt do to screen for retractions?
changes in appearance (such as retractions, dimpling, or fixation)
uneven nipple line
What are abnormal findings when performing retraction screenings?
sitting
What position should the pt. be in to examine the axillae?
lift the arm and support it so that her muscles are loose and relaxed; use right hand to palpate left axillae
reach fingers high into axillae and move them firmly down in 4 directions
How would you palpate the axillae?
normal, all other nodes should be non palpable
Is it normal or abnormal to feel a small, soft, nontender, node in the central group?
you might feel something deeper that cant be felt with light palpations
Why should you alternate between light, medium and deep palpations?
3 fingers held together
using the flat part of the fingers
using rotary or circular movements
How should you palpate the breasts?
Supine with the arm over their head and pillow underneath side palpated
have a pt. w pendulous breasts rotate their hips to the opposite side
How should the pt. be positioned when palpating the breasts? What should you add if the breasts are pendulous?
vertical strip pattern
What is the preferred method for palpation patterns to detect breast masses?
vertical strip
start high in the axilla and move down and up medially to the sternal edge
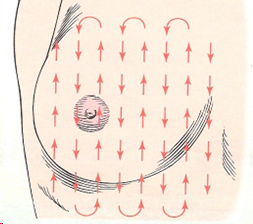
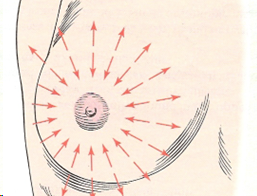
wedge (spokes)
palpating from the nipple to the posterior
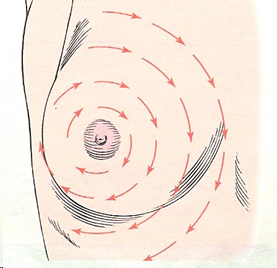
circular
palpating in concentric circles out to the periphery
fibrosis in the breast tissue, usually caused by growing neoplasms
What are retractions a sign of?
the position flattens the breast tissue & displaces it medially, making significant lumps more distinct
Why is it important for the pt. to be in the correct position to palpate the breasts?
In a woman with large, pendulous breasts
When would you use the bimanual technique to palpate the breasts?
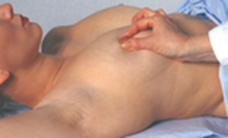
gently compress between the thumb and forefinger in all quadrants
color and consistency of discharge if any
How would you palpate the nipple & areola? What should you note?
physiological (benign)
___________ (________) discharge is usually bilateral.
pathological
____________ discharge is spontaneous, unilateral, has blood or is clear, serous, and is sometimes associated with a mass.
during pregnancy, lactation, and up to a year after weaning.
When would you expect galactorrhea to be present?
intact breast
Which breast is palpated first in a pt. post masectomy?
along the incision line
What is the most common site for reoccurrence of cancer in a post mastectomy patient?
no redness, swelling, or skin lesions noted
What is a normal finding in an incisional site of a post mastectomy pt.?
a flat disk of undeveloped breast tissue beneath the nipple
How would you describe the normal male breast?
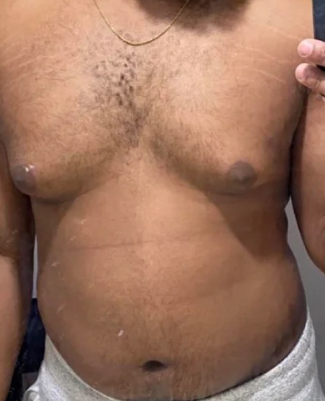
gynecomastia
what is a benign growth of breast tissue in males when estrogen levels are greater than testosterone that feels like a smooth, firm, movable disk?
occurs normally during puberty and is temporary
occurs in adult males with Cushing’s, adrenal disease, liver cirrhosis, hyperthyroidism, and multiple drugs (alcohol, steroids, cancer treatments)
Breast mass
Retractions
Edema
Axillary mass
Scaly nipple
Tender breast
What are the signs associated with more advanced breast cancer?
feels smooth, firm and elastic
tissue is softer and looser
What should a normal breast of a nulliparous woman feel upon palpation? How does this differ after pregnancy?
the woman has never been pregnant
What does it mean to be a nulliparous woman?
progesterone
Increased levels of which hormone in premenstrual women leads to breast engorgement?
inframammary ridge
yes
What is the firm transverse ridge of compressed tissue in the lower quadrants called? Is this a normal finding?
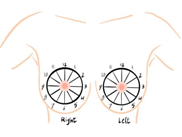
use the breast as a clock face
describe the distance from the nipple in cm using a ruler
e.g., “8:00, 2 cm from the nipple”
How would you assess the location of a breast mass?
judge in 3 dimensions (width x length x thickness)
e.g. “2 cm wide, 2 cm long, 1 cm thick”
How would you assess the size of a breast mass?
state whether the lump is round, oval, lobulated, or indistinct
How would you assess the shape of a breast mass?
state whether the lump is soft, hard or firm
How would you assess the consistency of a breast mass?
is the lump freely movable or is it fixed when you try to move it over the chest wall?
How would you assess the movability of a breast mass?
Is it displaced, retracted or inverted (& has it always been)?
How would you assess the nipple of a breast mass?
Is the lump solitary or multiple?
How would you assess the distinctness of a breast mass?
Is it erythematous (red, hot), thickened, vascular, dimpled or retracted?
How would you assess the skin over the lump of a breast mass?
Is the lump tender to palpation?
How would you assess the tenderness of a breast mass?
Are any regional lymph nodes palpable?
How would you assess the lymphadenopathy of a breast mass?
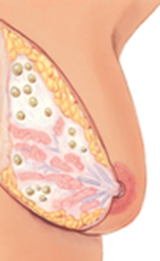
Age: 20-49 |
Occurrence: bilateral |
Location: UOQ |
Nipple discharge: No |
Pain or tenderness: yes |
#: multiple or single |
Shape: rounded |
Consistency: soft to firm or tense |
Mobility: Mobile |
Retractions: absent |
Borders: well defined |
Variations with menses: yes |
Benign (Fibrocystic) Breast Disease
Benign (Fibrocystic) Breast Disease
What is this an image of?
early development of the breasts with no other hormone-dependent signs (pubic hair, menses)
What is premature thelarche?
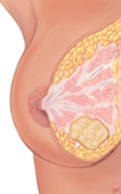
Age: 15-55 |
Occurrence: bilateral |
Location: no specific |
Nipple discharge: No |
Pain or tenderness: no |
#: single, sometimes multiple |
Shape: rounded or discoid |
Consistency: firm, rubbery |
Mobility: Mobile |
Retractions: absent |
Borders: well defined |
Variations with menses: no |
Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenoma
What is this an image of?
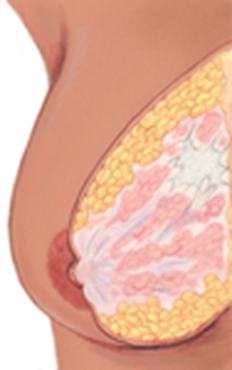
Age: 30-80 |
Occurrence: unilateral |
Location: 48% in UOQ |
Nipple discharge: bloody or clear if present |
Pain or tenderness: no |
#: single |
Shape: irregular or stellate |
Consistency: hard, stonelike |
Mobility: fixed |
Retractions: present |
Borders: poorly defined, irregular |
Variations with menses: no |
Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer
What is this an image of?
Mammary Duct Ectasia
What occurs when the milk ducts dialate, walls thicken, and the duct fills with fluid?
Produces sticky, purulent discharge that may be yellow-green or bloody
Intraductal Papilloma
What are discrete benign tumors that arise in papillary duct(s)?
Can have serous or serosanguineous discharge
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
What is a noninvasive cancer starting in the cells lining the milk ducts (precursor to invasive CA)?
Bloody, unilateral discharge
Paget’s Disease
What type of breast cancer involves the nipple & skin around it?
causes pain, burning sensation, tingling itching, scaling, crusty or hardened skin, lump in the breast and flattening of the nipple and nipple discharge
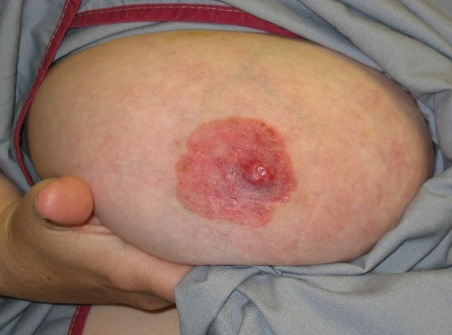
unilateral yellow or bloody discharge and dry, scaling crusts at the nipple
Spreads outward to the areola
How will an early lesion of Paget’s disease appear?
Male Breast CA
Presents as a painless, palpable mass (hard, irregular, nontender, fixed the area)
Spreads quicker bc of minimal breast tissue
5
Lack of screening and general awareness for male breast cancer is why men are diagnosed __ years later & @ later stages than women
nipple discharge
What is an early warning sign of male breast cancer?
enlarged and visible breasts (bc of maternal estrogen crossing the placenta)
“witch’s milk” secretion
What should you find in regards to the neonate’s breasts?
no, it is not significant and resolves within days or weeks
Is “witch’s milk” a concerning finding in neonates?
Symmetric, just lateral to midclavicular line, b/t 4th & 5th ribs
Nipple is flat, and areola is darker pigmented
What is the position of nipples on a prepubertal child?
Blue vascular pattern visible
Breasts & nipples increase in size (striae may develop)
Colostrum produced (precursor to breastmilk starting after 1st trimester)
What should you find in regard to the pregnant woman’s breasts?
Colostrum changes to milk production around the third postpartum day
Breast engorgement & nipple soreness can occur (treated w frequent nursing)
What should you find in regard to the lactating woman’s breasts?