Plasma Proteins Enzymes As Diagnostic Tools
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Colloid osmotic pressure
pressure exerted by plasma proteins on permeable membranes in the body; synonym for oncotic pressure
Acute phase proteins
Proteins that have plasma concentrations that increase and decrease depending on inflammation
Where are most proteins synthesized
liver
Main anticoagulants
Heparin and EDTA
What do anticoagulants bind to
calcium, magnesium, iron
What type of protein are most plasma proteins
glycoproteins with the exception of albumin
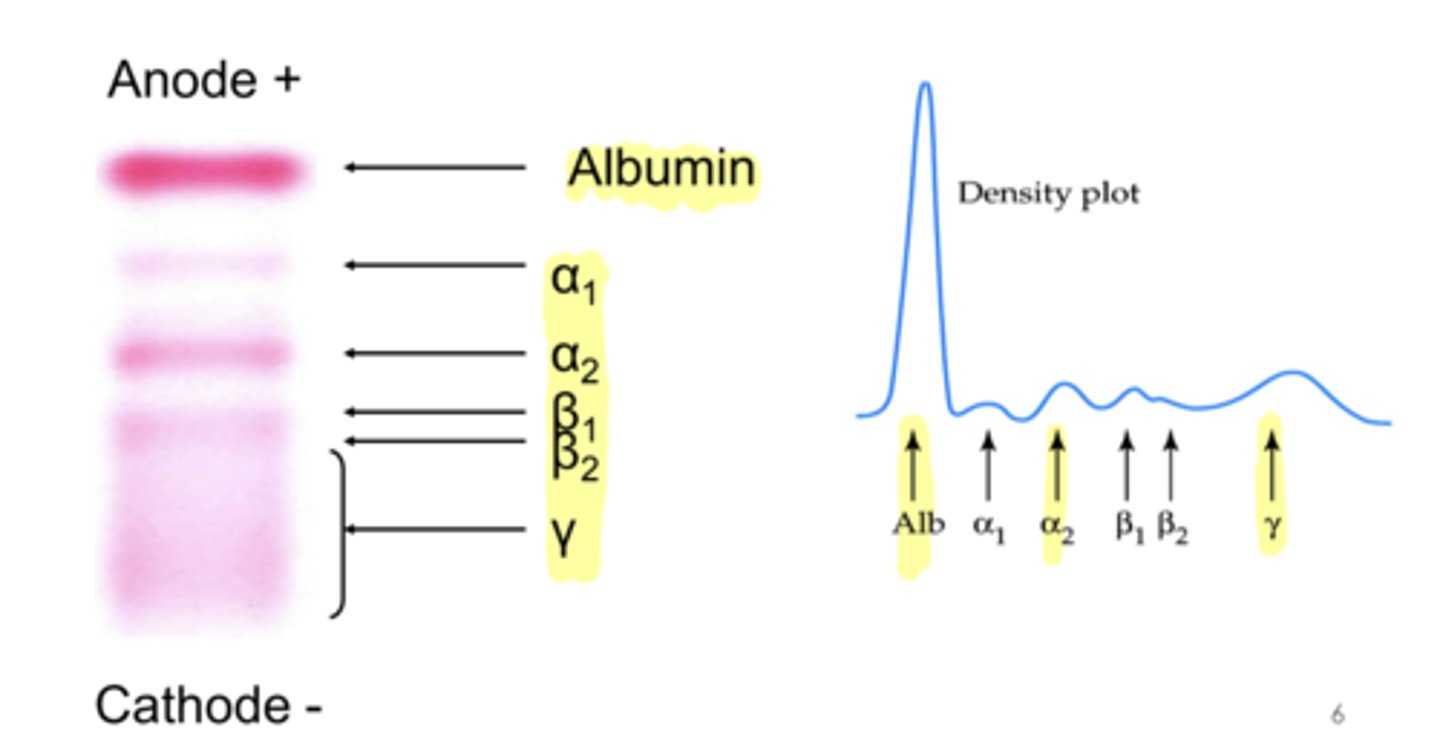
Plasma proteins on an electrophoresis description
Highest is albumin,
Second highest is gamma
then A2
function of albumin
maintain osmotic pressure, transport drugs and big molecules like TAGs
What does a lack of albumin do to the osmotic presure
it decreases it and causes H20 to leave the vessel and cause EDEMAS
hypoalbuminemia
low albumin levels in the blood leading to edema form increased capillary permeability
tied to renal disease
Hyperalbuminemia
an increased level of albumin in the blood causes dehydration and stasis
Alpha 1 antitrypsin
inhibits trypsin and elastase
What carries alpha 1 antitrypsin?
Alpha 1 globulin
Haptoglobin
Binds free hemoglobin after RBC lysis to be destroyed by spleen
Alpha 2 macroglobulin
thrombin inhibitor, and also carries cytokines and growthfacotrs, copper as well
Ceruplasmin
Copper carrying protein in the body, also controls ferroxidase activity
Thyroxine binding globulin
T3 T4 transporter
Alpha 2 antiplasmin
This enzyme inhibits plasmin activity:
plasmin
an enzyme that dissolves the fibrin of blood clots
Protein C
inactivates factors Va and VIIIa
Angiotensin
a peptide hormone that constricts blood vessels and regulates Bp
Ferroxidase
oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+ for transport on ferritin
Beta 2 microglobin
recognition of self vs nonself in the MHC complex
-regulates transferin
Plasminogen
inactive form of plasmin
Sex hormone binding globulin
A protein that binds with the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen
Immunoglobins
Activated B2 antibodies
B2 usually are antibodies IgA, IgM
B IgA function
regulates inflammation and cell mediated cytotoxicity, also degranulation
IgM Beta function
Signals phagocytosis w bacteria aka opsonization
10 binding sites Pantameric
Gamma globulin IgG
pathogen recognition, Phagocytosis, fetal placenta crossing
Retinol binding protein
the specific protein responsible for transporting retinol
thyroxine binding globulin
Majority of the thyroid hormones in blood are bound to this
Cortisol binding globulin
Also known as CBG or transcortin, this is the carrier protein for one molecule of cortisol in the blood. It helps to extend its half-life.
Pre albumin function
-Carrier protein for thyroid hormones T4 and T3
-Transport vitamin A
Low levels of alpha fetoprotein
May indicate fetal chromosome abnormalities such as Down's syndrome.
High levels of alpha fetoprotein
Indicate Neural tube defects
Low levels of ceruloplasmin
signify wilsons disease and kayser fleisher rings
wilsons disease
Disease of excess copper, which produces free radicals
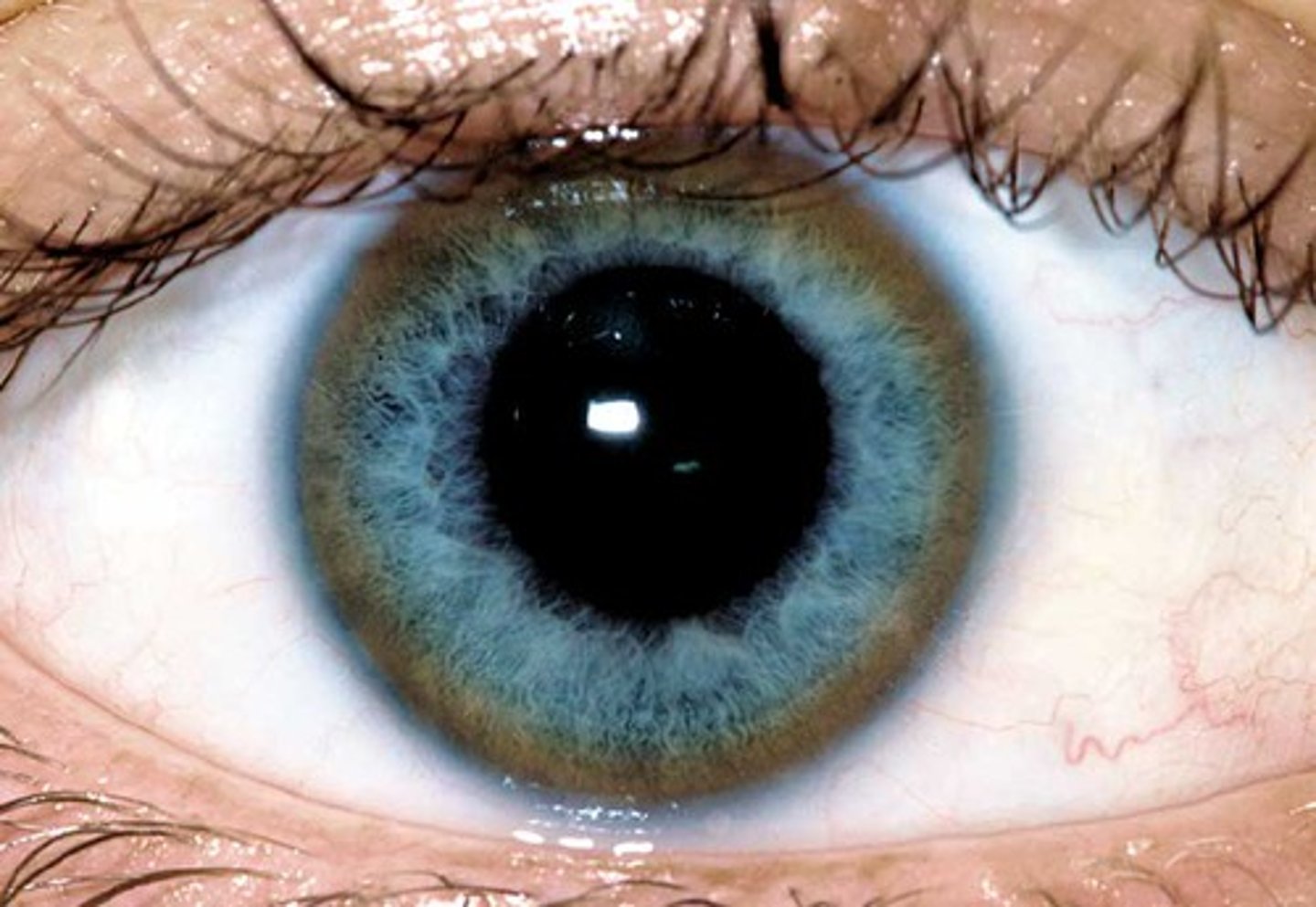
Kayser-Fleischer rings
golden-brown bands in the limbus of the cornea seen on slit lamp exam (due to copper deposition)
How to tell nephrotic syndrome?
increase B2 and A2 microglobulin
hemopexin
Binds free ferrous iron floating in system after RBC degredtation. tries to prevent ROS
C reactive protein
first line of defense in injury/inflamation bind to pneumococcal bacteria cell walls
What can cause increased red blood cell destruction
- Inheritied diseases (SCA, Spherocytosis)
-Spleen issues
-Cirrhosis
-Myelofibrosis
How to test for hemolytic anemia
Haptoglobin test - looks to see if heme is being destroyed faster than being replaced
function of alpha 1 antitrypsin
aids in cleaning out lungs
-Cometimes causes broncho constriction
- sometimes results in pulmonary emphysema
What is Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase
turns cholesterol to ester form. to make HDL. deficienct causes vision issues
what it Tissue derived enzymes
certain enzymes are found in specific tissue tyes, and the level of enzyme activity depends on tissue damage extent
butyrylcholinesterase
Metabolizes SUCCINYLCHOLINE, and cocaine
Alkaline phosphatase function
Removes phosphate groups from organic molecules; regulated by vitamin D
Acid phosphatase use
Identify T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia
Creatine kinase function
phosphorylate ATP as it leaves mitochondria
Gamma-Glutamyltransferase (GGT)
Elevated levels indicate early liver disorders found in bile ducts and liver
What raises GGT
liver damage via drinking, anticonvulsants, drugs
Amylase function
breaks down starches and sugars
When is amylase and lipase levels increased, how are they excreted?
During acute pancreatitis, and renal failure
- excreted through pee
Lipase fucntion
pancreatic enzyme necessary to digest fats
Acetylcholineesterase
-Breaks down acetylcholine in synaptic cleft
-Can be inhibited by ACE inhibitors
organophosphates
irreversible inhbitor of ACHE
Atropine function
Sympathetic stimulation as it is an anticholinergic
increased levels of BuCHE signal for
Nephrotic syndrome
Alanine transaminase (ALT) increases result in
High increase: Acute viral hepatitis
Moderate increase: Liver cirrhosis, Jaundice
Aspartate transaminse (AST)
take aspartate and oxoglutarate and make oxaloacetate and glutamate
found in liver and cardia and skele muscle
Where can you see increases of AST
Viral hepatitis, MI, Circulatory failure
What is the importance of AST/ALT ratio
ratio should be 0.8
-if over 2.0 - alcohol liver disease
-1.0 or less = possible non alcohol fatty liver
Alkaline and acid phosphatases main job it to?
facilitate membrane transport by droppping on phopho group and 5 or 10 PH
When should you see change in ALP levels?
Bile duct diseases and Bine diseases.
Pregnancy - Childhood
What is the biggest factor for Acid phosphatase?
Prostate tumor marker (PSA)
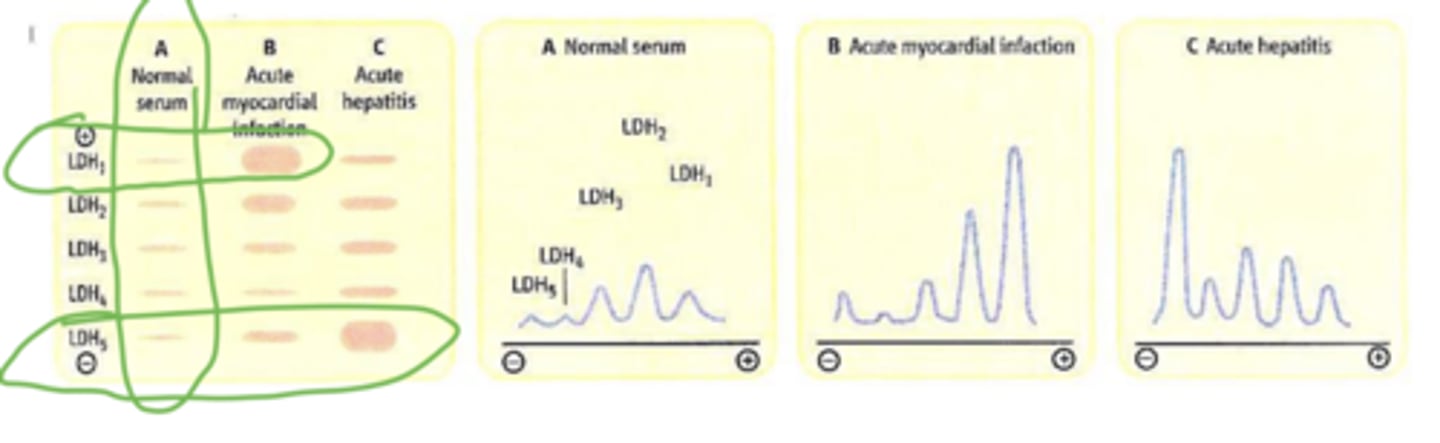
When is there an increase in LDH 1 and 2
during MI
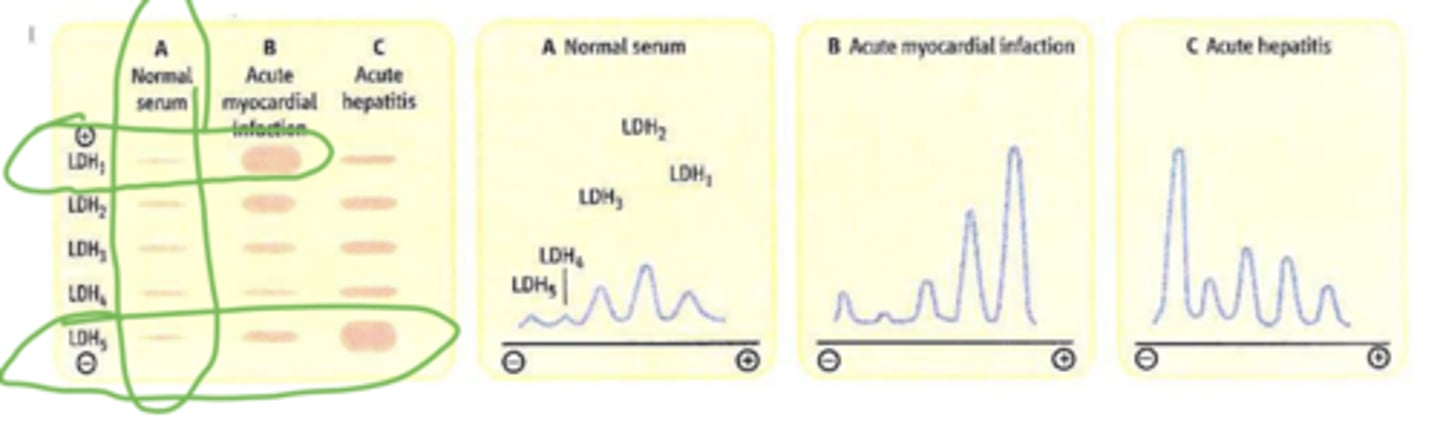
When is there an increase in LDH 5
During acute hepatitis
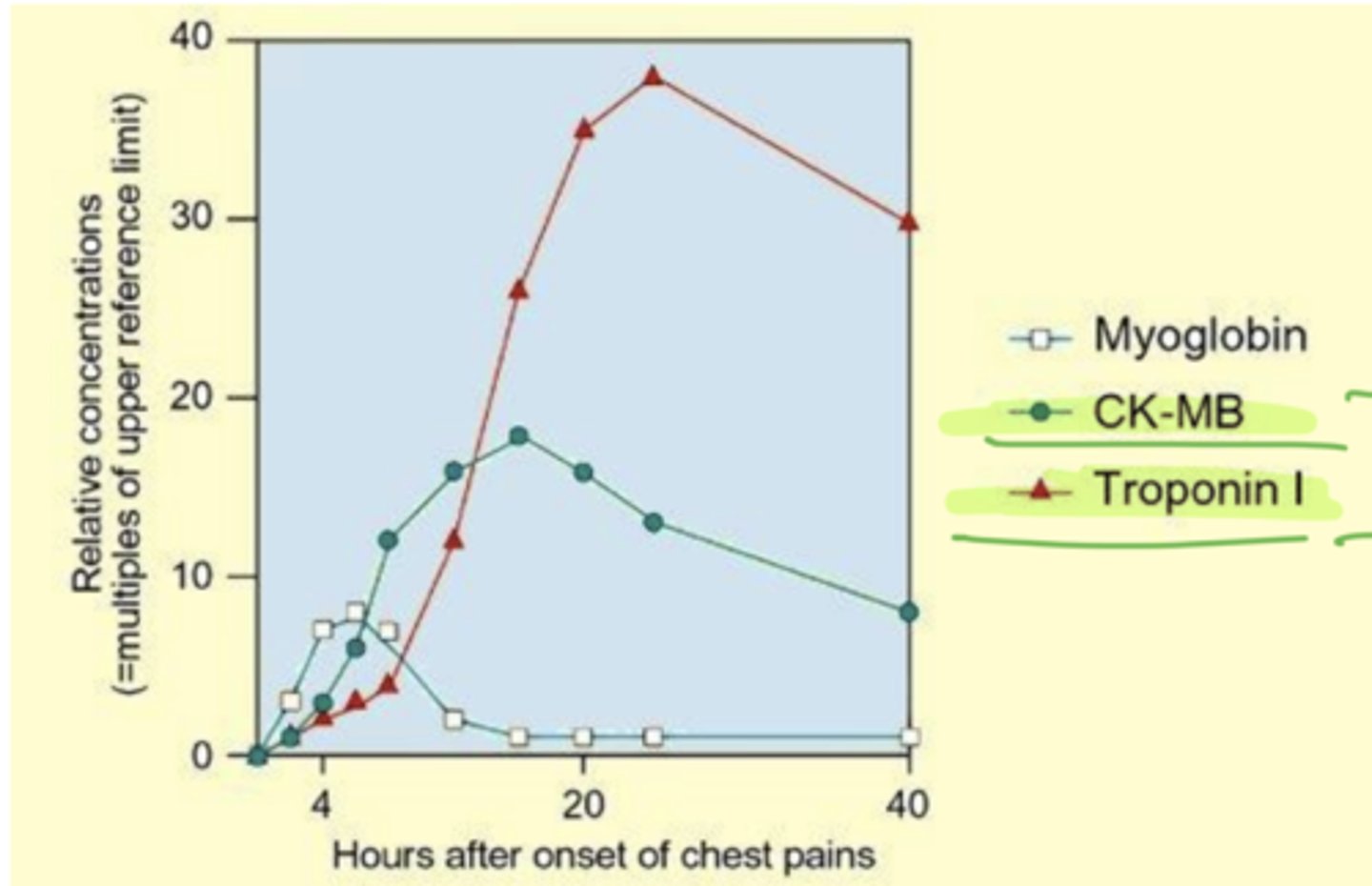
When does CK and Troponin spike
usually happens after chest pain troponin spikes higher than CK but it is good to know to watch out for MI
A 55-year old man reports to the physician complaining that his feet swell frequently. His history shows that he has been a heavy drinker for several years. His AST:ALT ratio is above 2 and his GGT is elevated. What is the most likely cause of the swelling?
increased LDH-5
Increased alpha 2 macroglobulin
Increase in gamma globulins
Decreased conjugation of bilirubin
Low plasma albumin
Low plasma albumin cause swelling due to water leaving blood vessels causing edemas
A chronic smoker is found to have lost elasticity of his lungs resulting in emphysema from overactivity of elastase. Which protein was most likely decreased in this patient?
Trypsinogen
Alpha-2 macroglobulin
Fibrinogen
Alpha-1 antitrypsin
Lipase
Alpha 1 antitrypsin!!!
causes emphysema and also removes elastin causing bronchoconstriction
A 42-year old woman is being treated for pneumococcal infection. Which protein would be useful to measure daily to determine whether she is recovering?
Albumin
C-Reactive protein
Protein C
alpha-2 macroglobulin
Gamma globulins
C reactive protein attaches to pneumonia to see if there is still inflammation you can use a test
- first line of inflammation and infection from bacteria prokaryotes