Polysaccharides and glycoconjugates
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Functions of Glycoconjugates and An Introduction to Antibiotics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
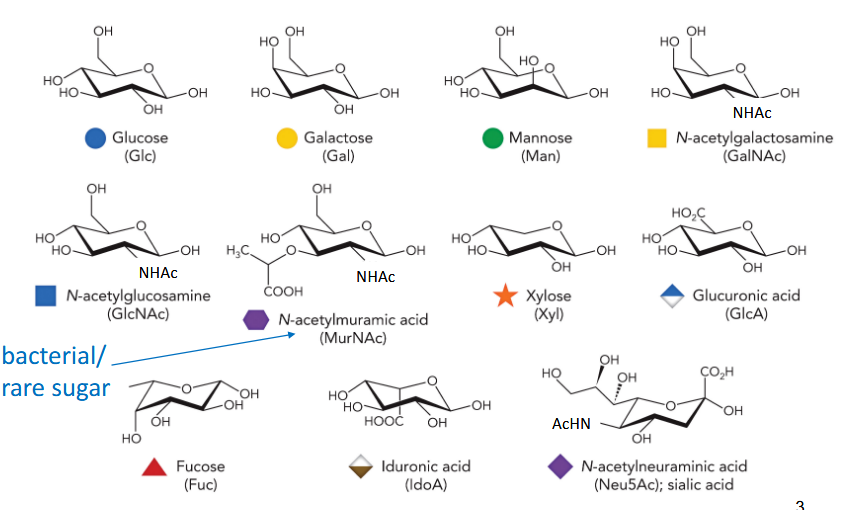
10 monosaccharides as building blocks for human fly and
glucose
galactose
mannose
N-acetylgalactosamine
N-acetylglucosamine
N-acetylmuramic acid
Xylose
glucuronic acid
fucose
iduronic acid
N-acetylneuraminic acid
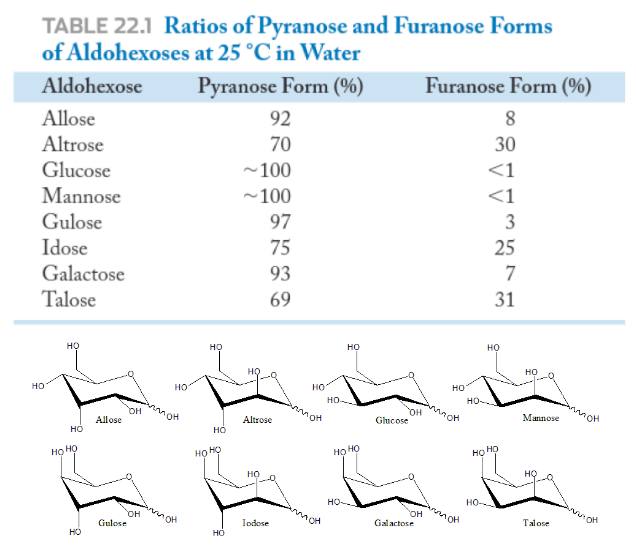
Are pyranoses or furanoses preferred?
Six Membered Rings Predominate
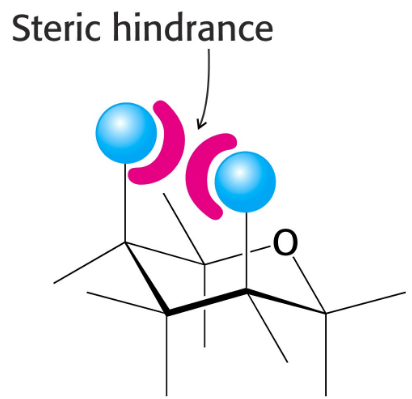
steric clashing
Will influence whether bulkier groups are “axial” or “equatorial” - prefer equatorial
anomers
depending of the side that hydroxyl attack comes from, makes two different rings
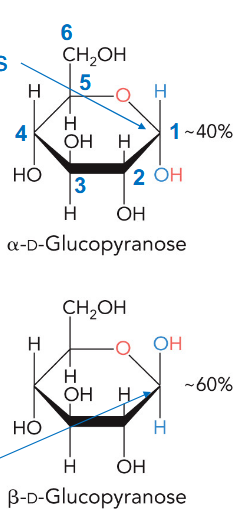
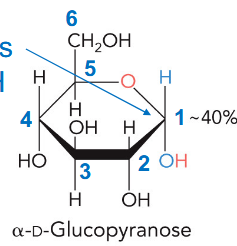
anomeric position
C1
alpha anomer
end group and hydroxyl opposite oxygen are trans (different sides)
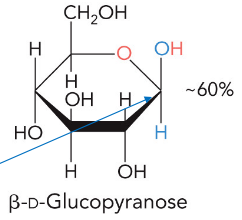
beta anomer
end group and hydroxyl opposite oxygen are cis (same sides)
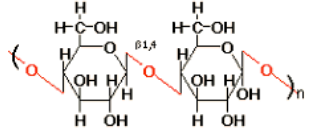
polysaccharides
glucose homopolymers
Cellulose. starch, glycogen
Disaccharide heteropolymers
chitin, keratan sulfate
cellulose
beta-1,4 linkages
not digested by humans (dietary fibre)
principal component of plant structure
most common biopolymer on Earth
starch
alpha-1,4 linkages
digested by humans w/ amylase
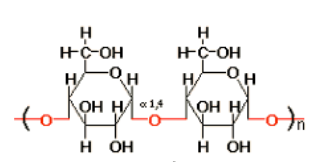
amylose
linear starch
amylopectin
branched starch
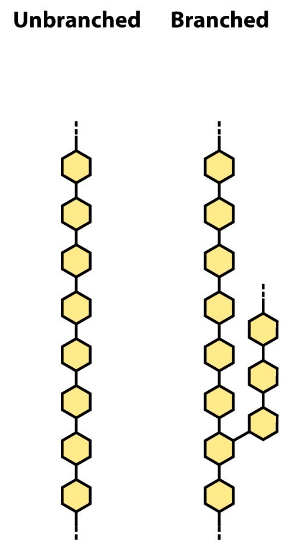
homopolysaccharides
same monosaccharide repeated; may be branched or unbranched
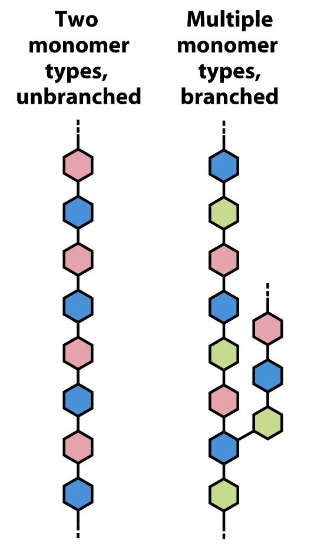
heteropolysaccharides
two or more monosaccharides; may be branched or unbranched
Overview of saccharide nomenclature
L-sugars, D-sugars
Triose/tetrose/pentose/hexose
Aldose/ketose
Furanose/pyranose
Epimers
Anomers: alpha-, beta-
Monosaccharide, disaccharide, oligosaccharide, polysaccharide
Reducing sugar/non-reducing sugar
Linear vs branched polysaccharides
Synthetic chemistry of oligosaccharides
No straightforward automated solid state synthesis strategy* has been developed for carbohydrates, similar to methods for nucleic acids or peptides, but there is progress by Seeberger and coworkers
Are glycans biosynthesized using template-directed synthesis?
1
glycoconjugates
glycoproteins
glycosyltransferases, mucin
proteoglycans
aggrecan, petidoglycan
glycolipids
blood antigens, mebrane anchors
glycoconjugates in cells
cell surfaces
mediate cellular interactions
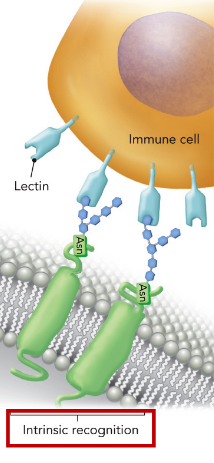
Lectins
glycan-binding proteins
Intrinsic binding
binding of glycans to lectins within the same host cell (intracellular) or between host cells (intercellular)
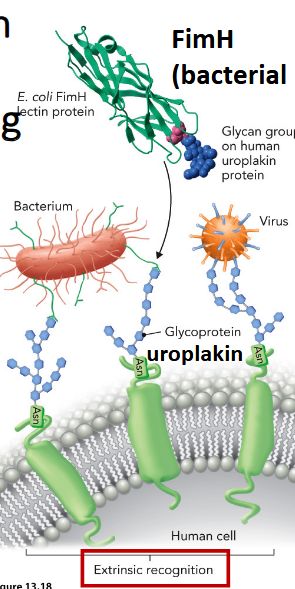
Extrinsic
binding between glycans/lectins on human and pathogen cells
ex. FimH - E.coli causes UTIs - binds mannose residues on the human glycoprotein uroplakin found on bladder cells & facilitates bacterial adhesion
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs)
affect human- bacterial interactions
Common GI bacteria can metabolize HMOs as an energy source
HMOs compete with bacterial glycans for human receptors
Some oligosaccharides might function as antivirals
Protein glycosylation
50% of all proteins are glycoslyated
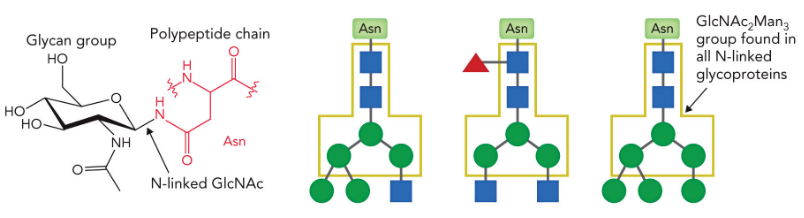
N-glycans are added to secreted and membrane-bound glycoproteins at Asn-X-Ser/Thr “sequons” (where X = any amino acid except Pro).
About 70% of eukaryotic proteins contain this sequon and ~70% of the sequons contain an N-glycan.
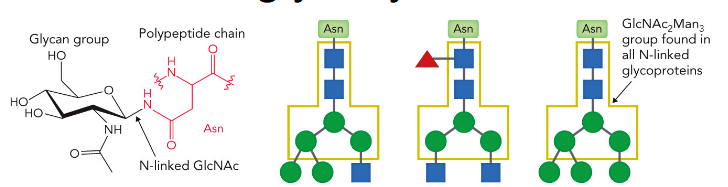
N-linked glycopoteins
2 N-acetylglucosamine + 3 mannose attached to Asn
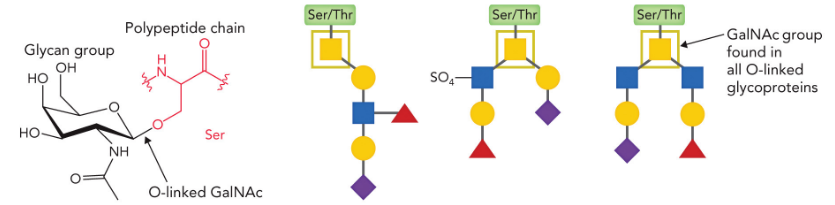
O-linked glycoproteins
N-acetylgalactosamine attached to Ser/Thr
N-glycan biosynthesis location
endoplasmic reticulum or ER make proteins (ribosomes on rough ER)
Golgi apparatus modifies them and are transported to surface for attachment/secretion
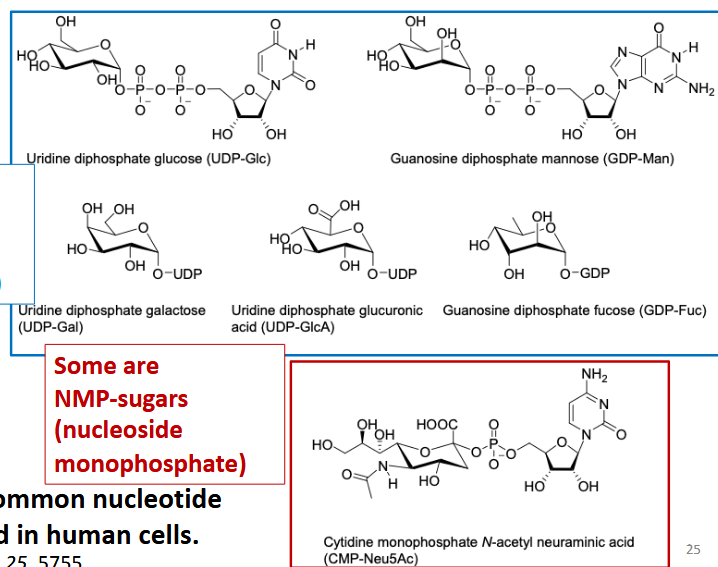
Nucleotide sugars
building blocks of glycans; usually NDP-sugars but may be NMP-sugars
Glycosyltransferases
enzymes that transfer sugars onto other molecules
ex. fucosyltransferase
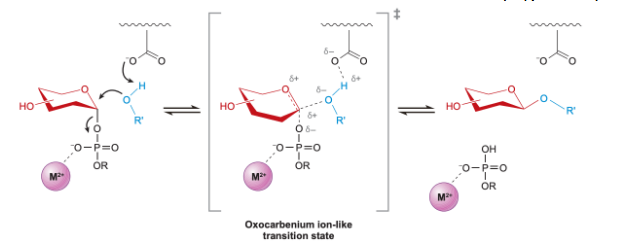
inverting Glycosylation
Sn2 like; opposite stereochem
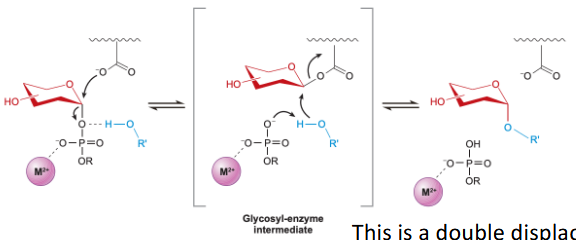
retaining Glycosylation
double displacement mechanism, same sterochem
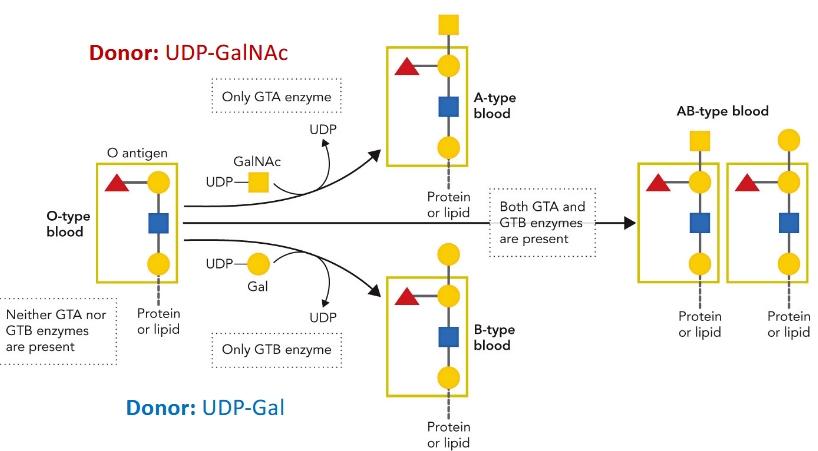
Blood groups
determined by glycosylation patterns and expression of GTs; each only differ by few amino acids but are indentifiably different; literally same evolutionary origin
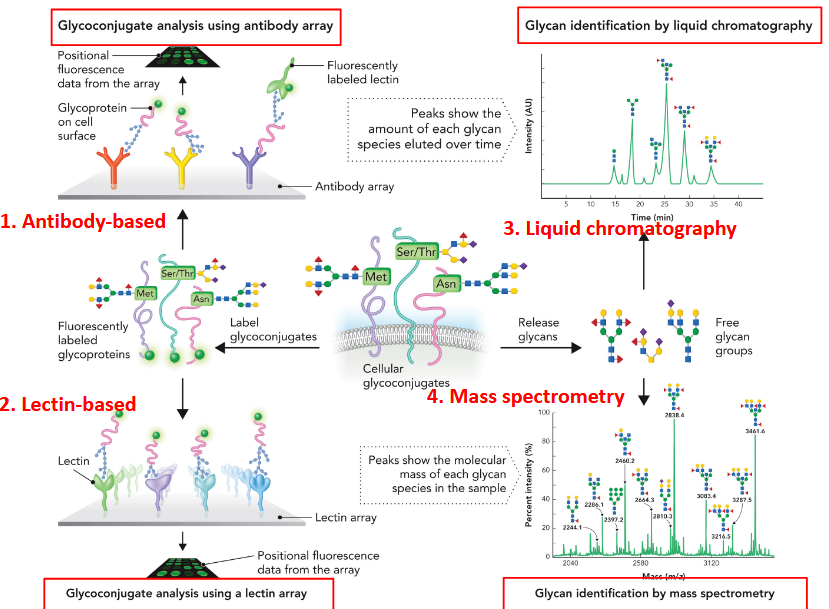
Techniques for “sequencing” glycoproteins
Antibody-based
Lectin-based
Liquid chromatography
Mass spectrometry
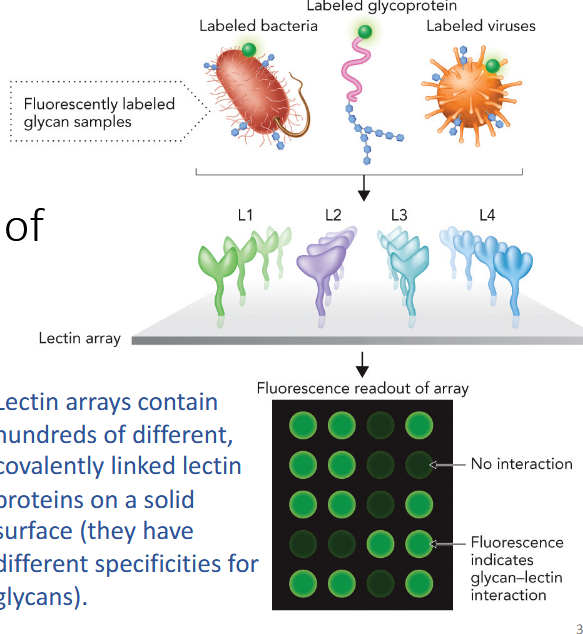
Lectin microarrays
rapid identification of glycan sequences; contain hundreds of different, covalently linked lectin proteins on a solid surface (different specificities for glycans).
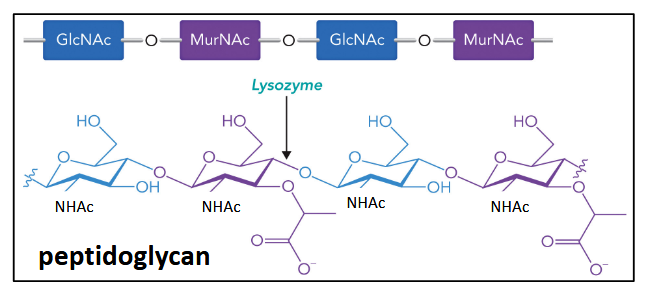
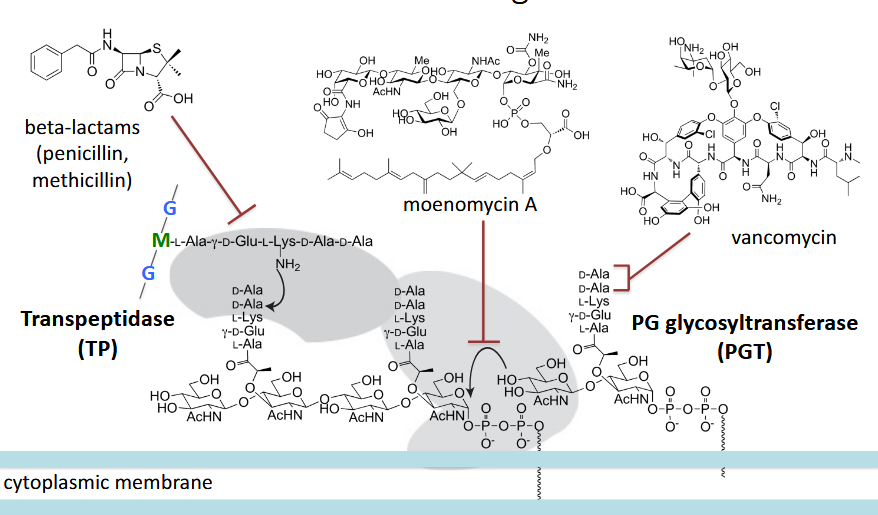
peptidoglycan
alternating GlcNAc-MurNAc polysaccharide component of bacterial cell walls; a type of proteoglycan; highly conserved structure
antibiotics
bacteriostatic - restrict growth and reproduction
batericidal - cause cell death
inhibit DNA/RNA (precursor) or protein or peptidoglycan synthesis
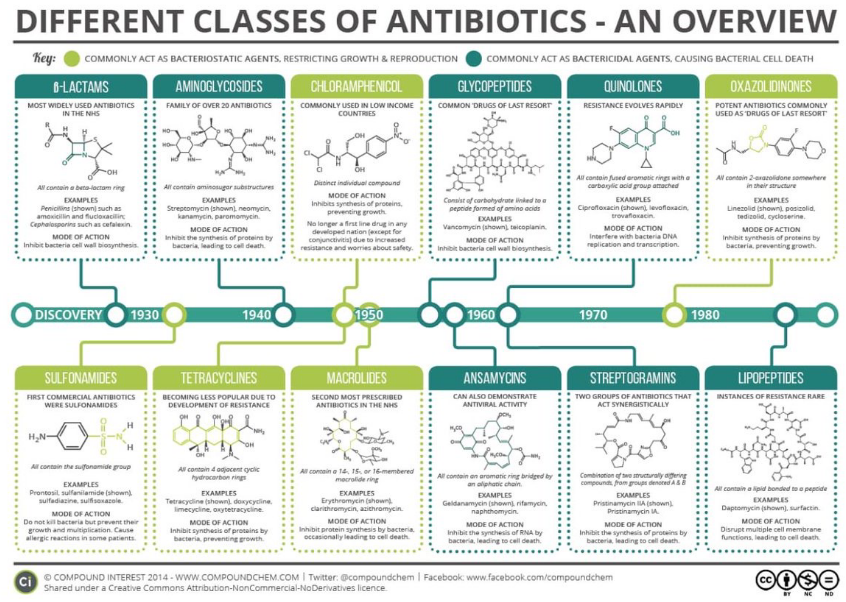
Gram-negative bacteria
outer membrane; thin peptidoglycan; no stain
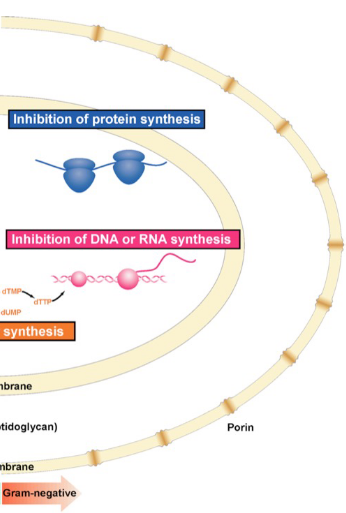
Gram-positive
only inner membrane; thick peptidoglycan; stain
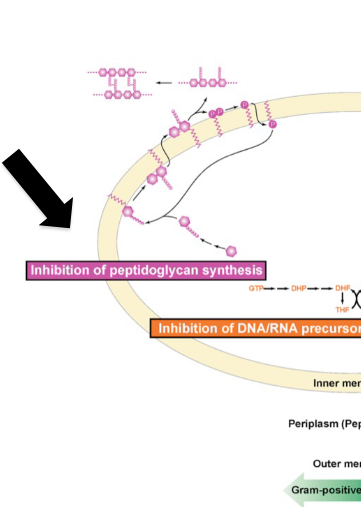
Peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis stages
lipid I
lipid II
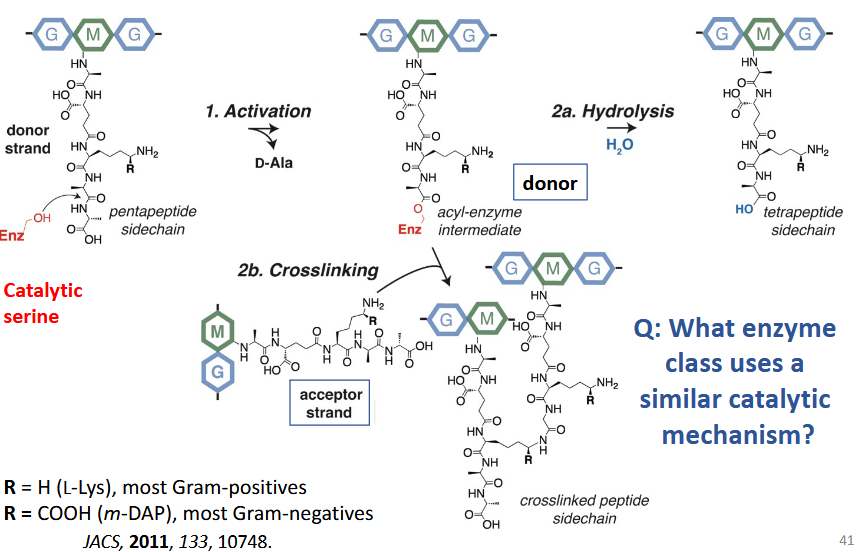
transpeptidation and glycosyltransfer
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)
major antibiotic targets; two major regions; A single bacterium has many that perform various functions
Transpeptidase reactions
acyl-enzyme intermediate
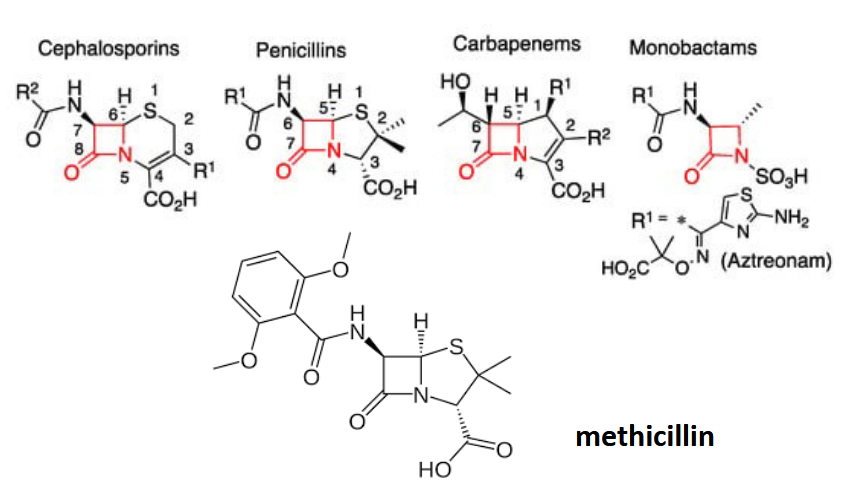
beta-lactams
most successful class of antibiotics; “suicide inhibitors’; square ring very reactive; substrate mimics (similar distances between backbone atoms in the terminal dipeptide and beta-lactams)